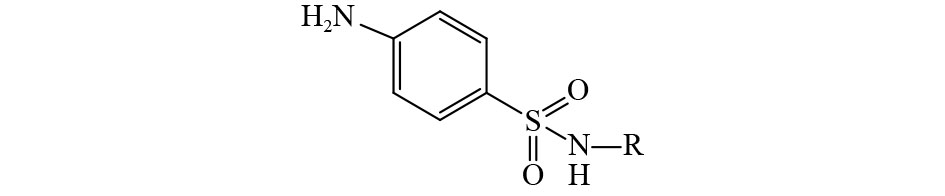
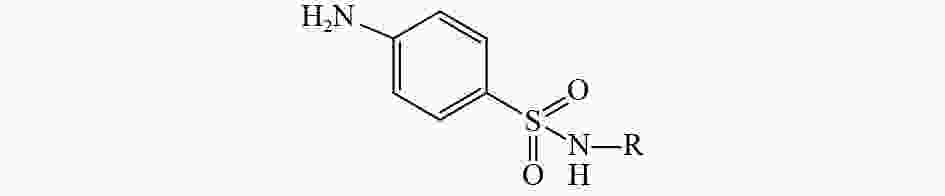
Research progress on aquatic environmental behavior and aquatic toxicity of sulfonamide drugs
-
摘要:
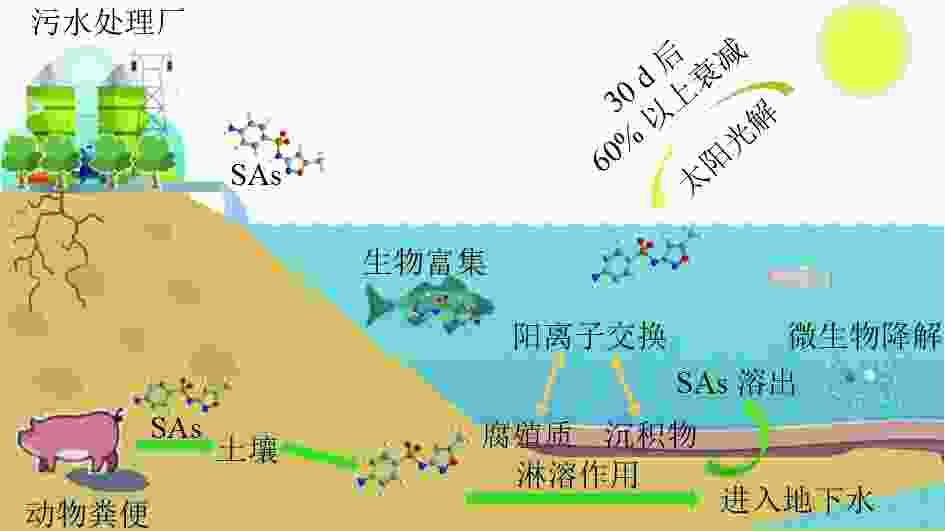
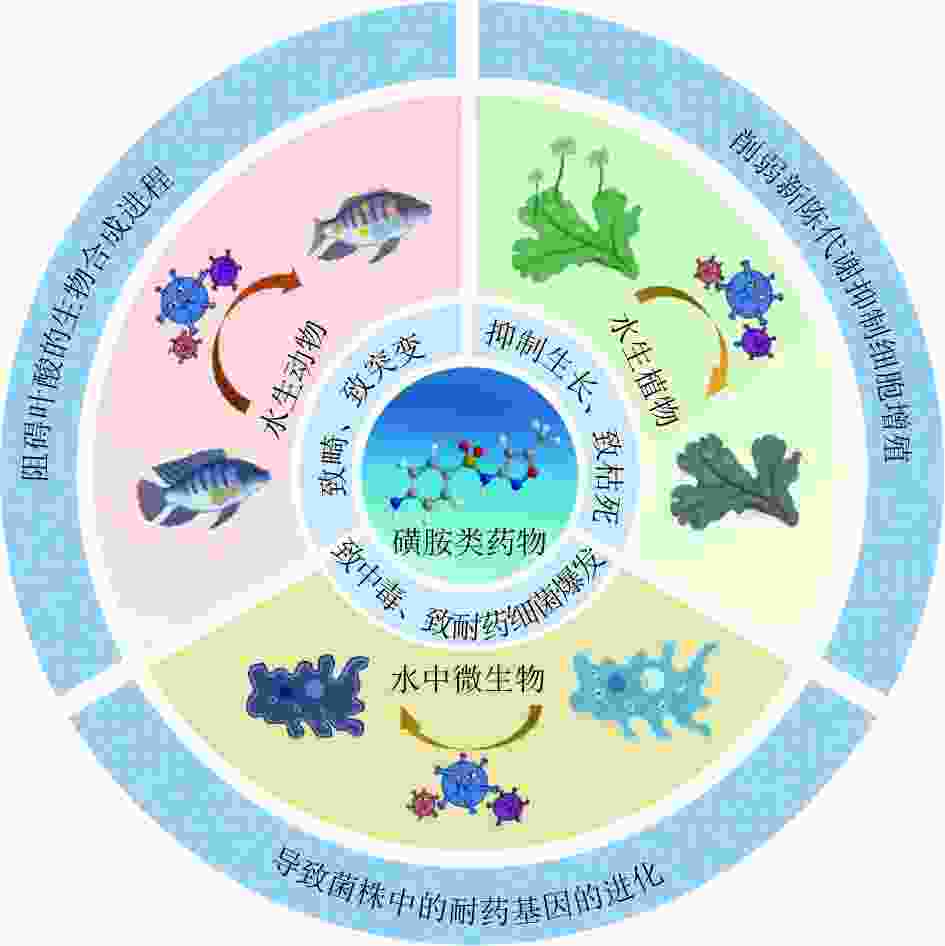
磺胺类药物(SAs)在水环境中普遍存在,大部分SAs以母体分子或代谢产物形式排放到环境中,地表水、地下水、海水甚至饮用水中都能检测到低浓度的SAs。因SAs排放量大、环境假性持久性强等特点,其对水生态环境和人类健康构成潜在风险。针对SAs在水环境中的归趋问题,总结了SAs在水环境中吸附、迁移、转化、降解、生物富集等典型行为规律,进一步分析SAs对水生植物、水生动物及水生微生物产生的毒性效应。结果表明:SAs在水环境中行为的研究多集中在环境介质表面的吸附特性与规律,而对SAs依赖水动力条件的迁移转化和生物富集规律研究较少;SAs在环境介质表面的吸附主要以阳离子交换和分子结合的形式发生,吸附质表面的电荷密度是决定吸附量的重要因素;SAs在水环境中广泛存在,虽然浓度水平较低,但对水生生物造成的负面影响会产生潜在的生态风险,主要表现为干预水生植物的生长发育过程,造成水生动物的特征性畸形,干扰水中微生物的群落结构与功能,最终会对整个水环境及其循环造成宏观的影响。未来应加强SAs在水环境中衰减过程的浓度和贡献率研究以及对水生生物毒性标准化测试,以期深入研究SAs生态毒理学、解决SAs污染问题。
-
关键词:
- 磺胺类药物(SAs) /
- 水环境行为 /
- 水生毒性 /
- 研究进展
Abstract:Sulfonamides (SAs) are commonly found in aquatic environment, and most of them are released into the environment in the form of parent molecules or metabolites. Low concentrations of SAs can be detected in surface water, groundwater, seawater, and even drinking water, and they pose potential risks to the aquatic eco-environment and human health due to their high emissions and strong pseudo persistence in the environment. Focusing on the fate of SAs in the aquatic environment, the typical behavioral patterns of SAs in adsorption, migration, transformation, degradation and bioconcentration in the aquatic environment were summarized. Moreover, an analysis was conducted on the toxic effects of SAs on aquatic plants, aquatic animals and aquatic microorganisms. The results showed that studies on the behavior of SAs in the aqueous environment had mostly focused on its adsorption characteristics and patterns on the surface of environmental media. However, there were fewer studies on the transport transformation and bioconcentration patterns of SAs under hydrodynamic conditions. Previous studies revealed that the adsorption of SAs on the surface of environmental media mainly occurred in the form of cation exchange and molecular binding, and the charge density of the adsorbent surface was an important factor determining the adsorption amount. SAs existed widely in the aquatic environment. Although the concentration level of SAs was low, the negative impact on aquatic organisms would produce potential ecological risks, mainly manifested as interfering with the growth and development process of aquatic plants, causing the characteristic deformities of aquatic animals, interfering with the community structure and function of aquatic microorganisms, and ultimately causing macro impacts on the entire water environment and its circulation. In the future, the study on the concentration and contribution rate of SAs attenuation process in water environment and the standardized toxicity test of aquatic organisms should be strengthened, so as to further study SAs ecotoxicology and solve SAs pollution problem.
-
表 1 10种抗生素的化学结构、衰减速率常数(k)、半衰期(t1/2)和相关系数(R2)
Table 1. Chemical structures, decay rate constants (k), half-lives (t1/2) and correlation coefficients of 10 antibiotics
抗生素 化学式 化学结构 k/d−1 t1/2/d R2 磺胺嘧啶[37] C10H10N4O2S 
0.032 21.7 0.984 磺胺二甲嘧啶[38] C12H14N4O2S 
0.040 17.3 0.975 磺胺甲噁唑[39] C10H11N3O3S 
0.034 20.4 0.984 磺胺二甲氧嘧啶[35] C12H14N4O4S 
0.038 18.2 0.960 磺胺甲嘧啶[31] C11H12N4O2S 
0.039 17.9 0.952 诺氟沙星[38] C16H18FN3O3 
0.123 5.64 0.979 恩诺沙星[39] C19H22FN3O3 
0.079 8.78 0.936 环丙沙星[39] C17H18FN3O3 
0.130 5.33 0.953 红霉素[40] C37H67NO13 
0.164 4.22 0.947 罗红霉素[40] C41H76N2O15 
0.251 2.76 0.958 表 2 长江流域和世界其他主要河流中SAs的分布情况
Table 2. Distribution of SAs in the Yangtze River Basin and other major rivers of the world
区域 采样点 采样点经纬度 介质 浓度/(ng/L) 国内 宜昌[50] 111°20′18″E,30°38′08″N 水体 48.8 岳阳[50] 113°08′19″E,29°26′48″N 水体 32.4 南京[51] 118°50'39"E,32°09'49"N 水体 16.2 武汉[52] 114°29′10″E,30°41′15″N 水体 24.3 九江[52] 116°00′24″E,29°44′47″N 水体 23.2 洞庭湖[53] 112°56'53"E,29°00'35"N 水体 62.91 鄱阳湖[54] 116°07'57"E,29°33'05"N 水体 63.4 巢湖[55] 117°28'04"E,31°34'57"N 水体 95.5 太湖[55] 120°23'59"E,31°27'05"N 水体 467.6 沉积物 48.61) 国外 韩国洛东江[56] 127°40'E,35°07'N 水体 136 美国伊利湖[57] 80°05'W,42°15'N 水体 242.25 西班牙埃布罗河[58] 0°51'47"E,40°43'12"N 水体 185 越南湄公河[59] 105°10'30"E,16°30'28"N 水体 162 1)单位为ng/g。 表 3 不同水环境中磺胺抗性基因的分布情况
Table 3. Distribution of sulfonamide resistance genes in different water environments
采样地点 介质 sul1丰度 sul2丰度 黄浦江[87] 水体 0.32×105~1.84×105 0.43×105~4.19×105 太湖[88] 水体 1.9×103~7.9×105 莱州湾[89] 水体 1.1×10−3~1.4×10−1 1.1×10−3~1.4×10−1 渤海湾[90] 水体 10−5~10−3 10−5~10−3 东海[91] 沉积物 8.05×107a 1.08×105~1.25×107 海河[92] 沉积物 7.8×109a 1.7×1011a 珠江[93] 水体 105b 105b 长江[94] 水体 2.5×10−2~7.0×10−1 8.6×10−4~4.7×10−2 注:a表示最大值;b表示平均值。水体中丰度单位为个/mL;沉积物丰度单位为个/g。 -
[1] GARCÍA-GALÁN M J, SILVIA DÍAZ-CRUZ M, BARCELÓ D, et al. Combining chemical analysis and ecotoxicity to determine environmental exposure and to assess risk from sulfonamides[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2009,28(6):804-819. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2009.04.006 [2] 敖蒙蒙, 魏健, 陈忠林, 等. 四环素类抗生素环境行为及其生态毒性研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):314-324. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200096AO M M, WEI J, CHEN Z L, et al. Research progress on environmental behaviors and ecotoxicity of tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):314-324. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200096 [3] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(11):6772-6782. [4] ZESSEL K, MOHRING S, HAMSCHER G, et al. Biocompatibility and antibacterial activity of photolytic products of sulfonamides[J]. Chemosphere,2014,100:167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.038 [5] ANJALI R, SHANTHAKUMAR S. Insights on the current status of occurrence and removal of antibiotics in wastewater by advanced oxidation processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,246:51-62. [6] 陈宇, 许亚南, 庞燕. 抗生素赋存、来源及风险评估研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):562-570. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200180CHEN Y, XU Y N, PANG Y. Advances in research on the occurrence, source and risk assessment of antibiotics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):562-570. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200180 [7] LI S, SHI W Z, LIU W, et al. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China’s major rivers and seas (2005-2016)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,615:906-917. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.328 [8] TIAN S H, ZHANG C, HUANG D L, et al. Recent progress in sustainable technologies for adsorptive and reactive removal of sulfonamides[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,389:123423. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123423 [9] 田永静, 武宇圣, 黄天寅, 等. 我国地表水和沉积物PPCPs赋存与交互迁移影响因素[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(2):585-596. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220418TIAN Y J, WU Y S, HUANG T Y, et al. Occurrence of PPCPs in surface water and sediment in China and influencing factors of interactive migration[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(2):585-596. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220418 [10] KÜMMERER K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment: a review. part I[J]. Chemosphere,2009,75(4):417-434. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086 [11] RICHTER M K, SANDER M, KRAUSS M, et al. Cation binding of antimicrobial sulfathiazole to leonardite humic acid[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2009,43(17):6632-6638. [12] KAHLE M, STAMM C. Sorption of the veterinary antimicrobial sulfathiazole to organic materials of different origin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(1):132-138. [13] KAHLE M, STAMM C. Time and pH-dependent sorption of the veterinary antimicrobial sulfathiazole to clay minerals and ferrihydrite[J]. Chemosphere,2007,68(7):1224-1231. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.061 [14] GAO J, PEDERSEN J A. Adsorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to clay minerals[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(24):9509-9516. [15] AVISAR D, PRIMOR O, GOZLAN I, et al. Sorption of sulfonamides and tetracyclines to montmorillonite clay[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2010, 209(1): 439-450. [16] THIELE-BRUHN S, SEIBICKE T, SCHULTEN H R, et al. Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2004,33(4):1331-1342. doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.1331 [17] KURWADKAR S T, ADAMS C D, MEYER M T, et al. Effects of sorbate speciation on sorption of selected sulfonamides in three loamy soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(4):1370-1376. doi: 10.1021/jf060612o [18] YANG W B, ZHENG F F, XUE X X, et al. Investigation into adsorption mechanisms of sulfonamides onto porous adsorbents[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2011,362(2):503-509. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.071 [19] BOREEN A L, ARNOLD W A, McNEILL K. Photochemical fate of sulfa drugs in the aquatic environment: sulfa drugs containing five-membered heterocyclic groups[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2004,38(14):3933-3940. [20] GE L K, ZHANG P, HALSALL C, et al. The importance of reactive oxygen species on the aqueous phototransformation of sulfonamide antibiotics: kinetics, pathways, and comparisons with direct photolysis[J]. Water Research,2019,149:243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.009 [21] JI L L, CHEN W, ZHENG S R, et al. Adsorption of sulfonamide antibiotics to multiwalled carbon nanotubes[J]. Langmuir:the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids,2009,25(19):11608-11613. doi: 10.1021/la9015838 [22] ZHANG D, PAN B, ZHANG H, et al. Contribution of different sulfamethoxazole species to their overall adsorption on functionalized carbon nanotubes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(10):3806-3811. [23] 何金华, 丘锦荣, 贺德春, 等. 磺胺类药物的环境行为及其控制技术研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学,2012,39(7):225-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.07.073HE J H, QIU J R, HE D C, et al. Environmental behavior and related control technologies of sulfonamides[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2012,39(7):225-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.07.073 [24] ZHAO F K, YANG L, CHEN L D, et al. Soil contamination with antibiotics in a typical peri-urban area in Eastern China: seasonal variation, risk assessment, and microbial responses[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2019,79:200-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.11.024 [25] KAY P, BLACKWELL P A, BOXALL A B A. A lysimeter experiment to investigate the leaching of veterinary antibiotics through a clay soil and comparison with field data[J]. Environmental Pollution,2005,134(2):333-341. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2004.07.021 [26] 金彩霞, 高若松, 吴春艳. 磺胺类药物在环境中的生态行为研究综述[J]. 浙江农业科学,2011,52(1):127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2011.01.047JIN C X, GAO R S, WU C Y. Review on ecological behavior of sulfonamide antibiotics in the environment[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2011,52(1):127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2011.01.047 [27] BOXALL A B A, JOHNSON P, SMITH E J, et al. Uptake of veterinary medicines from soils into plants[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2006,54(6):2288-2297. doi: 10.1021/jf053041t [28] 陈昦, 张劲强, 钟明, 等. 磺胺类药物在太湖地区典型水稻土上的吸附特征[J]. 中国环境科学,2008,28(4):309-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.04.005CHEN H, ZHANG J Q, ZHONG M, et al. Adsorption of sulfonamides on paddy soil of Taihu Lake regeion[J]. China Environmental Science,2008,28(4):309-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.04.005 [29] ZUO R, LIU X, ZHANG Q R, et al. Sulfonamide antibiotics in groundwater and their migration in the vadose zone: a case in a drinking water resource[J]. Ecological Engineering,2021,162:106175. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106175 [30] LI Z, SOBEK A, RADKE M. Flume experiments to investigate the environmental fate of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in streams[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(10):6009-6017. [31] BAENA-NOGUERAS R M, GONZÁLEZ-MAZO E, LARA-MARTÍN P A. Degradation kinetics of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface waters: photolysis vs biodegradation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,590/591:643-654. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.015 [32] CONDE-CID M, FERNÁNDEZ-CALVIÑO D, NÓVOA-MUÑOZ J C, et al. Biotic and abiotic dissipation of tetracyclines using simulated sunlight and in the dark[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,635:1520-1529. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.233 [33] LI Y, RASHID A, WANG H J, et al. Contribution of biotic and abiotic factors in the natural attenuation of sulfamethoxazole: a path analysis approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,633:1217-1226. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.232 [34] KAESEBERG T, ZHANG J, SCHUBERT S, et al. Abiotic, biotic and photolytic degradation affinity of 14 antibiotics and one metabolite–batch experiments and a model framework[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,241:339-350. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.074 [35] LIU X W, LV K, DENG C X, et al. Persistence and migration of tetracycline, sulfonamide, fluoroquinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in streams using a simulated hydrodynamic system[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,252:1532-1538. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.095 [36] BATCHU S R, PANDITI V R, O'SHEA K E, et al. Photodegradation of antibiotics under simulated solar radiation: implications for their environmental fate[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,470/471:299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.057 [37] 邓建朝, 丁军伟, 杨贤庆, 等. 磺胺甲噁唑和磺胺嘧啶在青石斑鱼组织中的分布及代谢规律[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(4):301-306. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201804045DENG J C, DING J W, YANG X Q, et al. Distribution and metabolism patterns of sulfamethoxazole and sulfadiazine in yellow grouper ( Epinephelus awoara) tissues[J]. Food Science,2018,39(4):301-306. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201804045 [38] WANG F, GAO J, ZHAI W J, et al. Effects of antibiotic norfloxacin on the degradation and enantioselectivity of the herbicides in aquatic environment[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,208:111717. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111717 [39] XU N, SUN W Y, ZHANG H, et al. Plasma and tissue kinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite, ciprofloxacin, in yellow catfish ( Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) after a single oral administration at different temperatures[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology,2023,266:109554. [40] YAN S W, DING N, YAO X N, et al. Effects of erythromycin and roxithromycin on river periphyton: structure, functions and metabolic pathways[J]. Chemosphere,2023,316:137793. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137793 [41] ARNOT J A, GOBAS F A. A review of bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) assessments for organic chemicals in aquatic organisms[J]. Environmental Reviews,2006,14(4):257-297. doi: 10.1139/a06-005 [42] ZHAO J L, LIU Y S, LIU W R, et al. Tissue-specific bioaccumulation of human and veterinary antibiotics in bile, plasma, liver and muscle tissues of wild fish from a highly urbanized region[J]. Environmental Pollution,2015,198:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.026 [43] ZHOU L J, WANG W X, LV Y J, et al. Tissue concentrations, trophic transfer and human risks of antibiotics in freshwater food web in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2020,197:110626. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110626 [44] HAN Q F, ZHAO S, ZHANG X R, et al. Distribution, combined pollution and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding the Yellow Sea, North China[J]. Environment International,2020,138:105551. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105551 [45] ZHANG R L, PEI J Y, ZHANG R J, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in mariculture farms, estuaries and the coast of the Beibu Gulf, China: bioconcentration and diet safety of seafood[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,154:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.006 [46] 许珊珊, 李学德, 花日茂, 等. 蔬菜中3种磺胺类药物残留污染调查[J]. 中国农学通报,2011,27(19):156-160.XU S S, LI X D, HUA R M, et al. Investigation of three suffonamides residues contamination in vegetables[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2011,27(19):156-160. [47] 朱峰, 苏丹, 安婧, 等. 磺胺类抗生素在土壤-植物系统中的迁移特征[J]. 生态学杂志,2017,36(5):1402-1407.ZHU F, SU D, AN J, et al. Transport processes of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil-plant system[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2017,36(5):1402-1407. [48] ZHU D, AN X L, CHEN Q L, et al. Antibiotics disturb the microbiome and increase the incidence of resistance genes in the gut of a common soil collembolan[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(5):3081-3090. [49] QIN L T, PANG X R, ZENG H H, et al. Ecological and human health risk of sulfonamides in surface water and groundwater of Huixian Karst wetland in Guilin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,708:134552. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134552 [50] 胡烨, 徐辉, 王殿常, 等. 长江重点江段枯水期药物及个人护理品(PPCPs)的空间分布特征及来源[J]. 环境科学学报,2022,42(2):164-173.HU Y, XU H, WANG D C, et al. Spatial distribution and source of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the dry season of the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2022,42(2):164-173. [51] 唐娜, 张圣虎, 陈玫宏, 等. 长江南京段表层水体中12种磺胺类抗生素的污染水平及风险评价[J]. 环境化学,2018,37(3):505-512. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017062705TANG N, ZHANG S H, CHEN M H, et al. Contamination level and risk assessment of 12 sulfonamides in surface water of Nanjing reach of the Yangtze River[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2018,37(3):505-512. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017062705 [52] WU C X, HUANG X L, WITTER J D, et al. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and associated environmental risks in the central and lower Yangtze River, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2014,106:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.029 [53] MA R X, WANG B, LU S Y, et al. Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Dongting Lake, China: occurrence, chiral profiling and environmental risk[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,557/558:268-275. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.053 [54] 苏超, 崔严. 长江流域淡水生态系统内分泌干扰物、药物和个人护理品的风险排序[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(11):4981-4988.SU C, CUI Y. Risk ranking of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products in the aquatic environment of the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(11):4981-4988. [55] LIU X H, LU S Y, GUO W, et al. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of lakes, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:1195-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.271 [56] KIM S D, CHO J, KIM I S, et al. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters[J]. Water Research,2007,41(5):1013-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.034 [57] SUBEDI B, CODRU N, DZIEWULSKI D M, et al. A pilot study on the assessment of trace organic contaminants including pharmaceuticals and personal care products from on-site wastewater treatment systems along Skaneateles Lake in New York State, USA[J]. Water Research,2015,72:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.049 [58] GARCÍA-GALÁN M J, DÍAZ-CRUZ M S, BARCELÓ D. Occurrence of sulfonamide residues along the Ebro River Basin: removal in wastewater treatment plants and environmental impact assessment[J]. Environment International,2011,37(2):462-473. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.011 [59] NGUYEN DANG GIANG C, SEBESVARI Z, RENAUD F, et al. Occurrence and dissipation of the antibiotics sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, trimethoprim, and enrofloxacin in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(7):e0131855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131855 [60] YANG C, SONG G, LIM W. A review of the toxicity in fish exposed to antibiotics[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology,2020,237:108840. [61] LIU L L, WU W, ZHANG J Y, et al. Progress of research on the toxicology of antibiotic pollution in aquatic organisms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(1):36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2018.01.006 [62] VILVERT E, CONTARDO-JARA V, ESTERHUIZEN-LONDT M, et al. The effect of oxytetracycline on physiological and enzymatic defense responses in aquatic plant species Egeria densa, Azolla caroliniana, and Taxiphyllum barbieri[J]. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry,2017,99(1):104-116. [63] 高礼, 石丽娟, 袁涛. 典型抗生素对羊角月牙藻的生长抑制及其联合毒性[J]. 环境与健康杂志,2013,30(6):475-478.GAO L, SHI L J, YUAN T. Growth inhibitive effect of typical antibiotics and their mixtures on Selenastrum capricornutum[J]. Journal of Environment and Health,2013,30(6):475-478. [64] 张晓晗, 万甜, 程文, 等. 喹诺酮类和磺胺类抗生素对绿藻生长的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2018,29(4):115-120.ZHANG X H, WAN T, CHENG W, et al. Effects of quinolones and sulfonamides on the growth of green algae[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2018,29(4):115-120. [65] SANDERSON H, BRAIN R A, JOHNSON D J, et al. Toxicity classification and evaluation of four pharmaceuticals classes: antibiotics, antineoplastics, cardiovascular, and sex hormones[J]. Toxicology,2004,203(1/2/3):27-40. [66] WAN J J, GUO P Y, PENG X F, et al. Effect of erythromycin exposure on the growth, antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Microcystis flos-aquae[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,283:778-786. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.10.026 [67] LUAN G D, LU X F. Tailoring cyanobacterial cell factory for improved industrial properties[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2018,36(2):430-442. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.01.005 [68] BIAŁK-BIELIŃSKA A, STOLTE S, ARNING J, et al. Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides[J]. Chemosphere,2011,85(6):928-933. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.058 [69] XIONG J Q, KIM S J, KURADE M B, et al. Combined effects of sulfamethazine and sulfamethoxazole on a freshwater microalga, Scenedesmus obliquus: toxicity, biodegradation, and metabolic fate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,370:138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.049 [70] SCHOLZ S, FISCHER S, GÜNDEL U, et al. The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment: applications beyond acute toxicity testing[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2008,15(5):394-404. doi: 10.1007/s11356-008-0018-z [71] van den BULCK K, HILL A, MESENS N, et al. Zebrafish developmental toxicity assay: a fishy solution to reproductive toxicity screening, or just a red herring[J]. Reproductive Toxicology,2011,32(2):213-219. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.06.119 [72] SIPES N S, PADILLA S, KNUDSEN T B. Zebrafish: as an integrative model for twenty-first century toxicity testing[J]. Birth Defects Research Part C, Embryo Today: Reviews, 2011, 93(3): 256-267. [73] LIN T, CHEN Y Q, CHEN W. Impact of toxicological properties of sulfonamides on the growth of zebrafish embryos in the water[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2013,36(3):1068-1076. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2013.09.009 [74] 刘丽丽, 吕鹏, 闫艳春. 磺胺二甲嘧啶对斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性作用[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准,2018,8(1):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1833.2018.01.005LIU L L, LÜ P, YAN Y C. Acute toxicities of sulfamethazine to zebrafish embryos[J]. Chinese Fishery Quality and Standards,2018,8(1):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1833.2018.01.005 [75] YAN Z Y, YANG Q L, JIANG W L, et al. Integrated toxic evaluation of sulfamethazine on zebrafish: including two lifespan stages (embryo-larval and adult) and three exposure periods (exposure, post-exposure and re-exposure)[J]. Chemosphere,2018,195:784-792. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.119 [76] XIONG J Q, KURADE M B, JEON B H. Can microalgae remove pharmaceutical contaminants from water[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,2018,36(1):30-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.09.003 [77] PROIA L, OSORIO V, SOLEY S, et al. Effects of pesticides and pharmaceuticals on biofilms in a highly impacted river[J]. Environmental Pollution,2013,178:220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.022 [78] HUANG D J, HOU J H, KUO T F, et al. Toxicity of the veterinary sulfonamide antibiotic sulfamonomethoxine to five aquatic organisms[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2014,38(3):874-880. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.09.006 [79] 刘洁雪, 梁萧, 覃礼堂, 等. 漓江流域桂林市区段有机磷农药和磺胺类抗生素的复合污染及其生态风险[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(1):60-69.LIU J X, LIANG X, QIN L T, et al. Combined pollution and ecological risk of organophosphorus pesticides and sulfonamides antibiotics in Guilin section of Lijiang River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(1):60-69. [80] GOMES I B, MAILLARD J Y, SIMÕES L C, et al. Emerging contaminants affect the microbiome of water systems: strategies for their mitigation[J]. NPJ Clean Water,2020,3:39. doi: 10.1038/s41545-020-00086-y [81] 胡劲召, 张璇, 王永强, 等. 磺胺甲噁唑胁迫下人工湿地植物与根际微生物的响应[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1474-1483. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210386HU J Z, ZHANG X, WANG Y Q, et al. Responses of plants and rhizosphere microorganisms in constructed wetlands under sulfamethoxazole stress[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1474-1483. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210386 [82] 张冰, 赵琳, 陈坦. 城市污水处理厂抗生素抗性基因研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(4):1384-1394. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220847ZHANG B, ZHAO L, CHEN T. Research progress of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(4):1384-1394. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220847 [83] ADESOJI A T, OGUNJOBI A A, OLATOYE I O. Characterization of integrons and sulfonamide resistance genes among bacteria from drinking water distribution systems in southwestern Nigeria[J]. Chemotherapy,2017,62(1):34-42. doi: 10.1159/000446150 [84] RODRIGUE D C, CAMERON D N, PUHR N D, et al. Comparison of plasmid profiles, phage types, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella enteritidis isolates in the United States[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,1992,30(4):854-857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.854-857.1992 [85] PRABHU D G, PANDIAN R S, VASAN P T. Pathogenicity, antibiotic susceptibility and genetic similarity of environmental and clinical isolates of Vibrio cholerae[J]. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology,2007,45(9):817-823. [86] 车琦, 王继华, 崔红, 等. 一株磺胺二甲嘧啶抗性菌的筛选及抗性机制研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(10):2405-2411.CHE Q, WANG J H, CUI H, et al. Screening and resistance mechanism of sulfamethazine-resistant strain[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(10):2405-2411. [87] JIANG L, HU X L, XU T, et al. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics in the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2013,458/459/460:267-272. [88] KRAIGHER B, KOSJEK T, HEATH E, et al. Influence of pharmaceutical residues on the structure of activated sludge bacterial communities in wastewater treatment bioreactors[J]. Water Research,2008,42(17):4578-4588. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.08.006 [89] LI Q W, NA G S, ZHANG L X, et al. Effects of corresponding and non-corresponding contaminants on the fate of sulfonamide and quinolone resistance genes in the Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,128:475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.051 [90] NIU Z G, ZHANG K, ZHANG Y. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the coastal area of the Bohai Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,107(1):245-250. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.03.064 [91] CHEN J Y, SU Z G, DAI T J, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of the East China Sea Bays[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2019,81:156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.01.016 [92] DANG B J, MAO D Q, XU Y, et al. Conjugative multi-resistant plasmids in Haihe River and their impacts on the abundance and spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Water Research,2017,111:81-91 [93] CHEN B W, LIANG X M, NIE X P, et al. The role of class Ⅰ integrons in the dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes in the Pearl River and Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,282:61-67 [94] YAN M T, XU C, HUANG Y M, et al. Tetracyclines, sulfonamides and quinolones and their corresponding resistance genes in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,631/632:840-848 [95] BEN MAAMAR S, HU J L, HARTMANN E M. Implications of indoor microbial ecology and evolution on antibiotic resistance[J]. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology,2020,30:1-15. [96] 敖蒙蒙, 魏健, 熊兆锟, 等. 典型 β-内酰胺类抗生素在臭氧氧化降解过程中毒性变化规律研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2023,43(5):206-215.AO M M, WEI J, XIONG Z K, et al. Study on the toxicity variation of typical β 3-Lactam antibiotics during ozonation degradation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2023,43(5):206-215. [97] LONG X, WANG D L, LIN Z F, et al. The mixture toxicity of environmental contaminants containing sulfonamides and other antibiotics in Escherichia coli: differences in both the special target proteins of individual chemicals and their effective combined concentration[J]. Chemosphere,2016,158:193-203. ◇ doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.048 -




 下载:
下载: