Assessment of the contribution of factors affecting ozone pollution in Tianjin based on meteorological composite index
-
摘要:
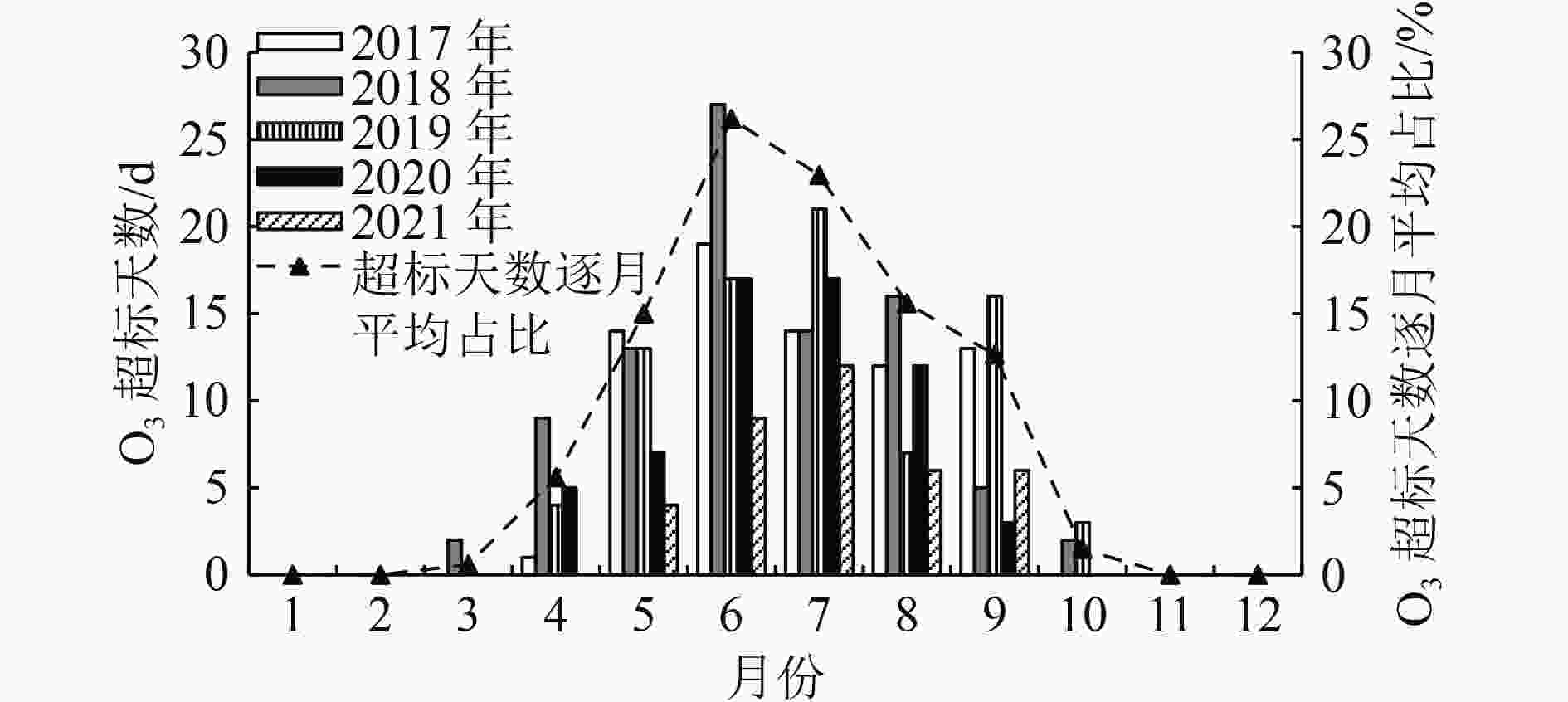
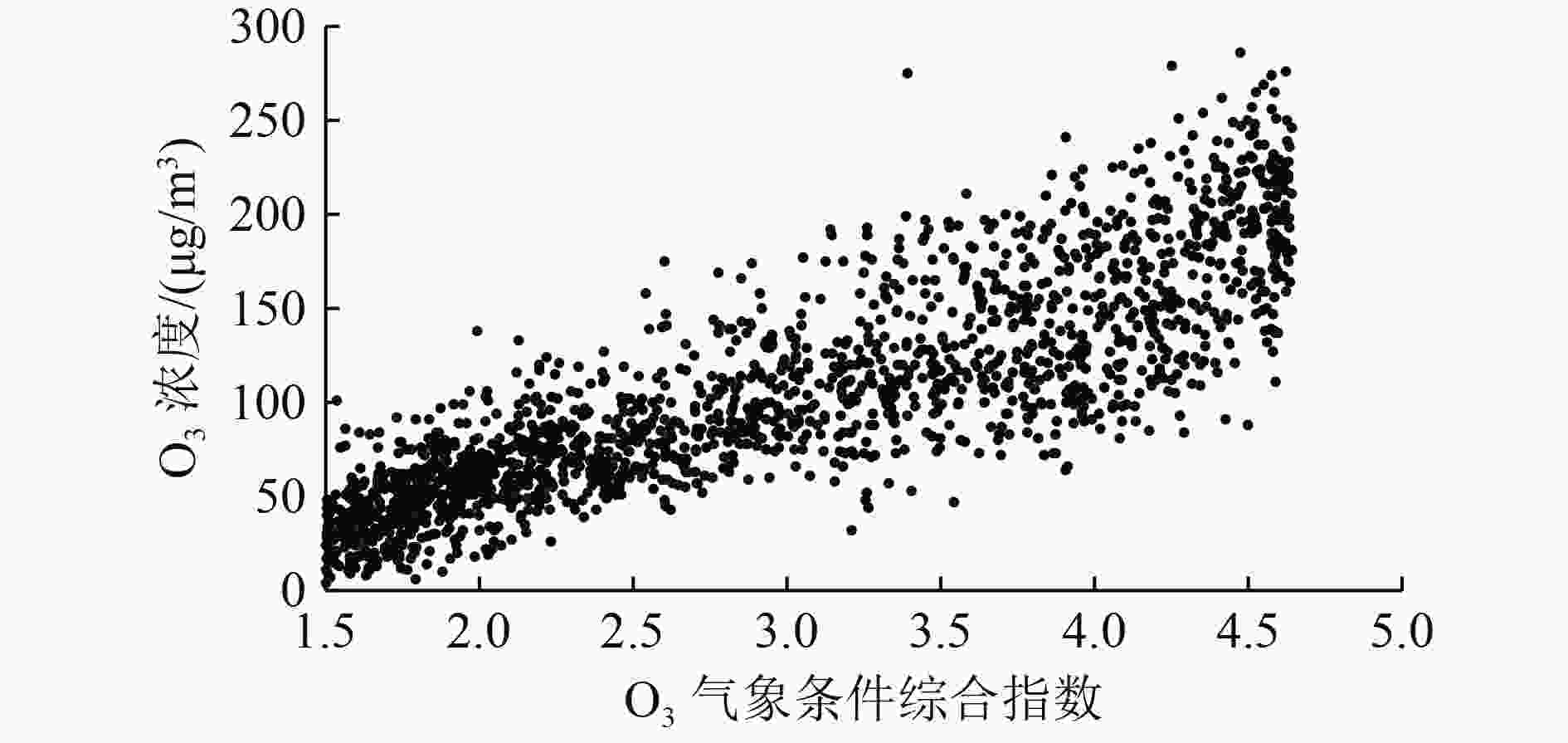
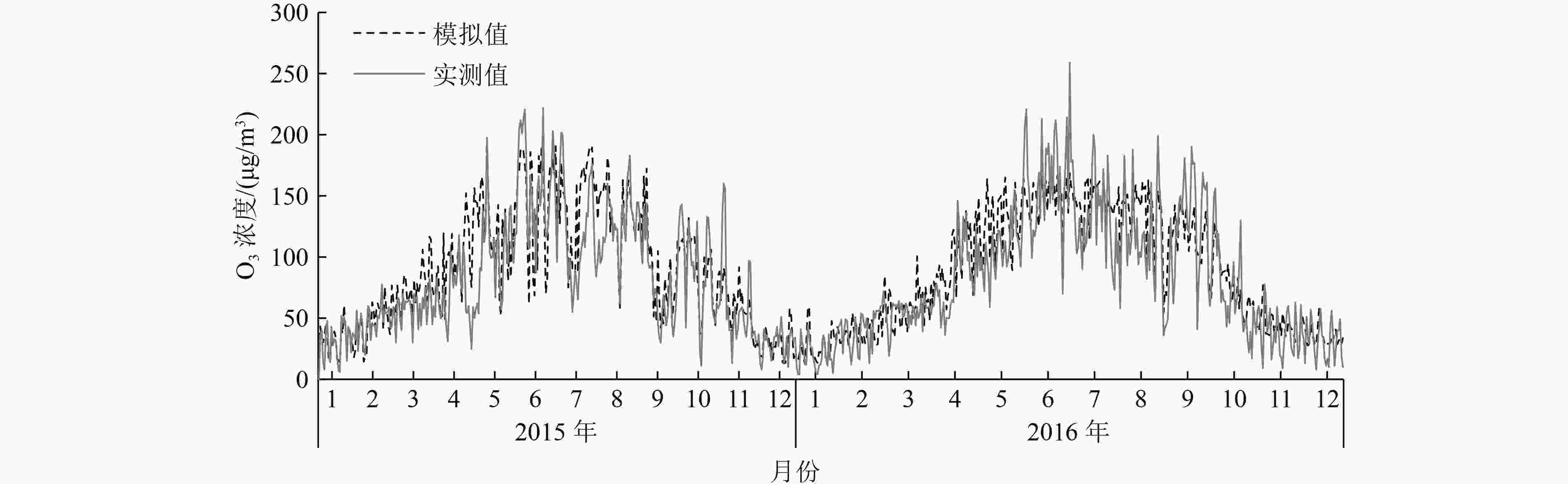
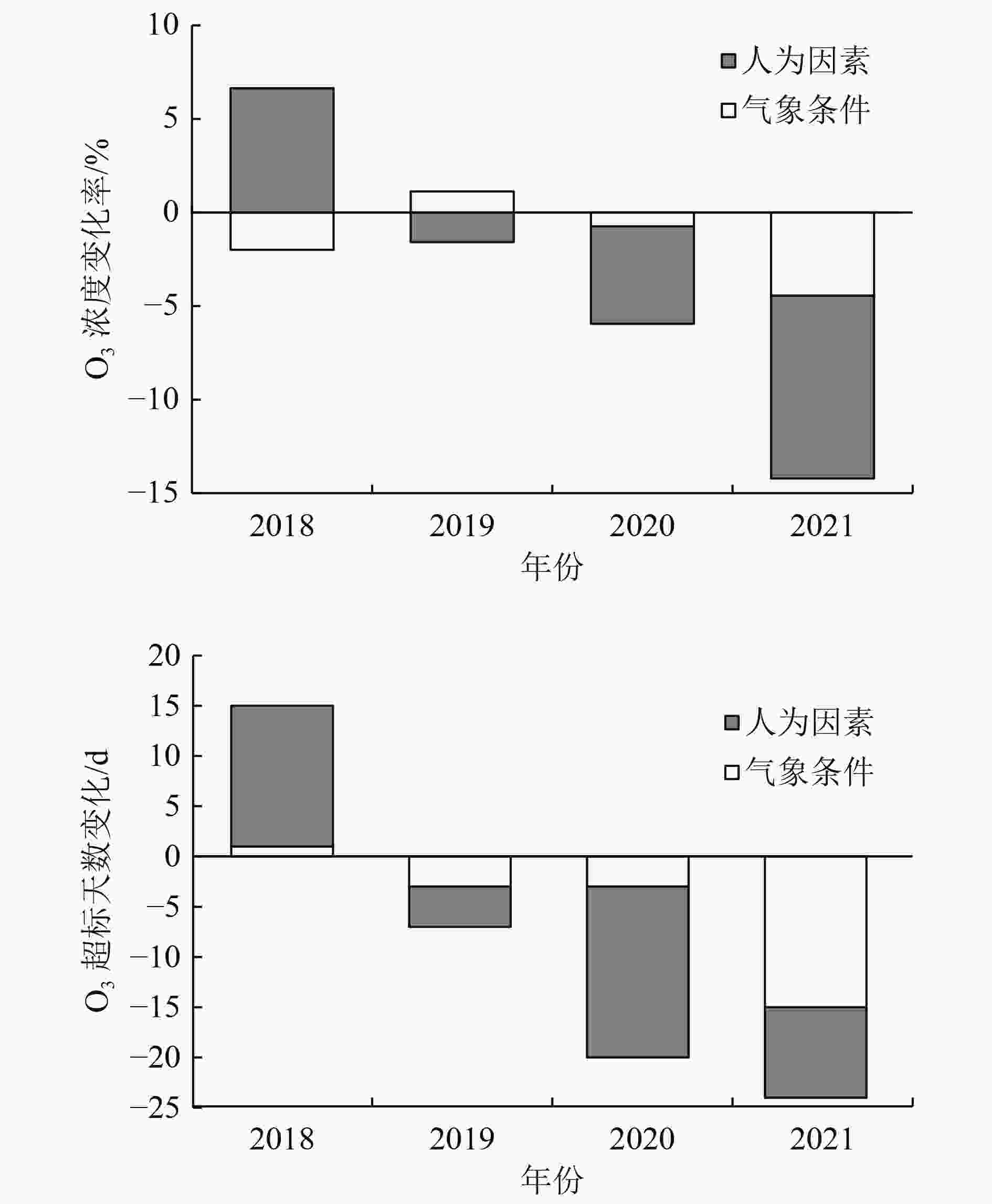
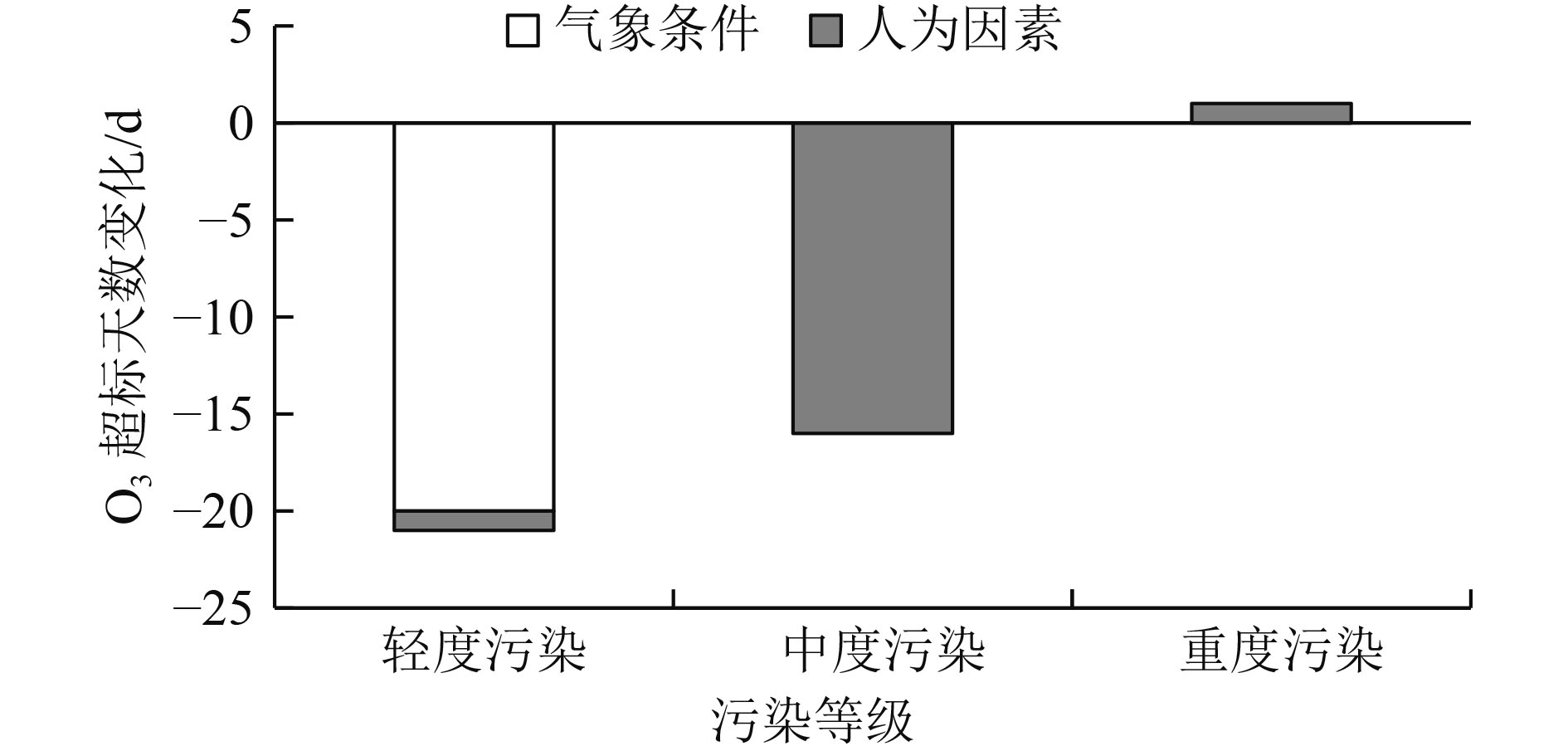
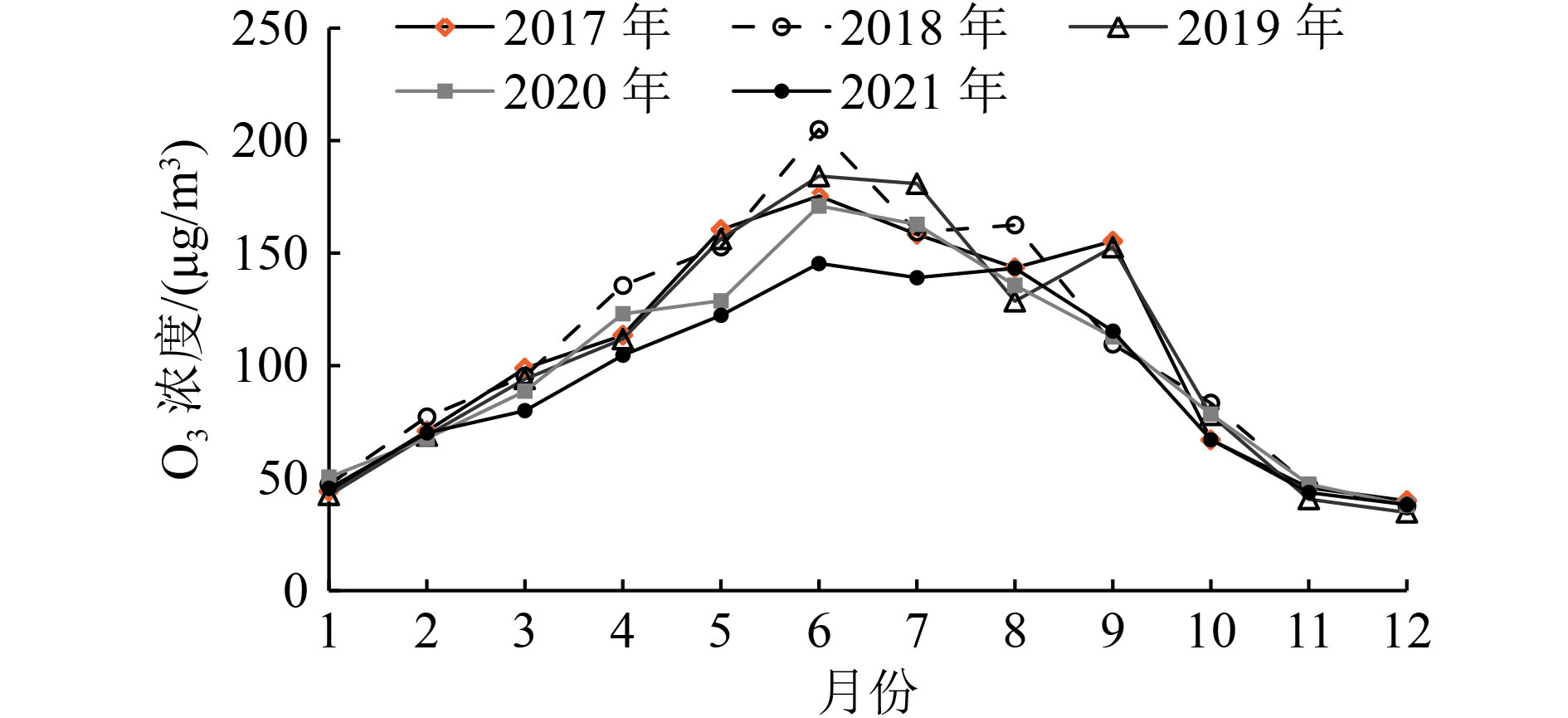
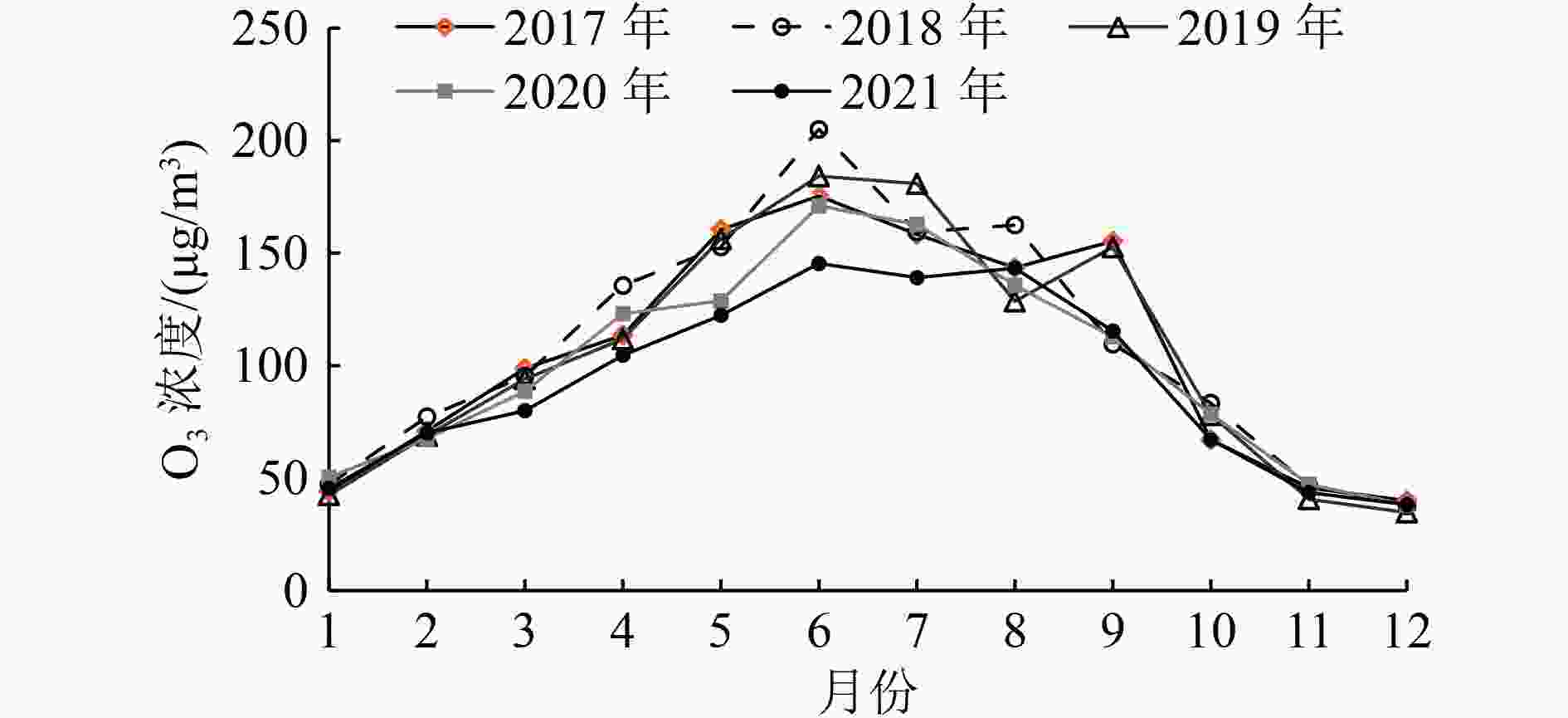
利用2017—2021年天津市近地面O3日最大8 h滑动平均浓度(O3_8 h)浓度和同时期气象数据,基于统计学方法构建天津市本地化O3气象条件综合指数,并据此评估气象和人为影响因素对O3浓度和超标天数的贡献情况。研究表明:基于日最高气温、海平面气压、平均风速、相对湿度、边界层厚度、短波辐射通量可以较好地建立O3气象条件综合指数,与实况O3浓度相关系数可以达到0.86(P<0.01),高于任何单一气象要素对O3浓度的影响;基于该指数评估,2017—2021年天津市O3浓度呈先升后降趋势,2021年较2017年下降15.9%,其中人为因素贡献了O3浓度下降的10.0%,气象因素贡献了5.9%。O3超标天数变化与浓度变化趋势一致,且超标天数中以轻度污染为主。2018年轻度污染占比高是导致该年O3超标天数最高的主要原因;2021较2017年天津市O3超标天数减少了36 d,其中气象条件导致的超标天数减少20 d,人为因素导致的超标天数减少16 d。对导致不同污染等级超标天数变化的影响要素分析显示,气象条件是导致O3轻度污染天数减少的主要因素,而人为管控措施的贡献主要体现在中度污染天数的减少。
Abstract:By using the near-ground ozone concentrations and simultaneous meteorological data in Tianjin from 2017 to 2021, a localized ozone meteorological composite index was constructed based on statistical methods, and the contributions of meteorological and anthropogenic factors to changes in ozone concentration and exceedance days were assessed. The results showed that the ozone meteorological composite index could be well established based on the daily maximum temperature, sea level pressure, average wind speed, relative humidity, boundary layer thickness and short-wave radiation flux, and the correlation coefficient with the actual ozone concentration could reach 0.86 (P<0.01), which was higher than any single meteorological factor. Based on the evaluation of this index, the ozone concentration in Tianjin showed an increasing trend at first and then a decreasing trend from 2017 to 2021, with a decrease of 15.9% in 2021 compared to 2017. Anthropogenic factors played a dominant role in the concentration change, contributing 10.0%, while meteorological factors contributed 5.9%. The change in the number of exceedance days in the five years was consistent with the trend of concentration change, and mild pollution was the main type of exceedance days. The high proportion of mild pollution in 2018 was the main reason for the highest number of ozone exceedance days in that year. The number of ozone exceedance days in Tianjin decreased by 36 days from 2017 to 2021, with meteorological conditions contributing to a decrease of 20 days and anthropogenic factors contributing to a decrease of 16 days. The analysis of the factors affecting changes in the number of exceedance days at different pollution levels showed that meteorological conditions were the main factor leading to a decrease in mild pollution days, while the contribution of anthropogenic control measures was mainly reflected in the reduction of moderate pollution weather.
-
Key words:
- meteorological composite index /
- ozone /
- meteorological factors /
- anthropogenic factors /
- Tianjin
-
表 1 2017—2021年天津市O3等级占比
Table 1. Annual ozone quality rating ratio in Tianjin in 2017-2021
% 年份 优 良 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 2017 51.23 28.77 15.07 4.93 0.00 2018 53.70 22.19 17.81 5.75 0.55 2019 54.52 23.29 14.52 7.12 0.55 2020 59.56 23.77 13.93 2.46 0.27 2021 59.45 30.41 9.32 0.55 0.27 表 2 O3浓度与气象要素的相关性
Table 2. Correlation between ozone concentration and meteorological factors
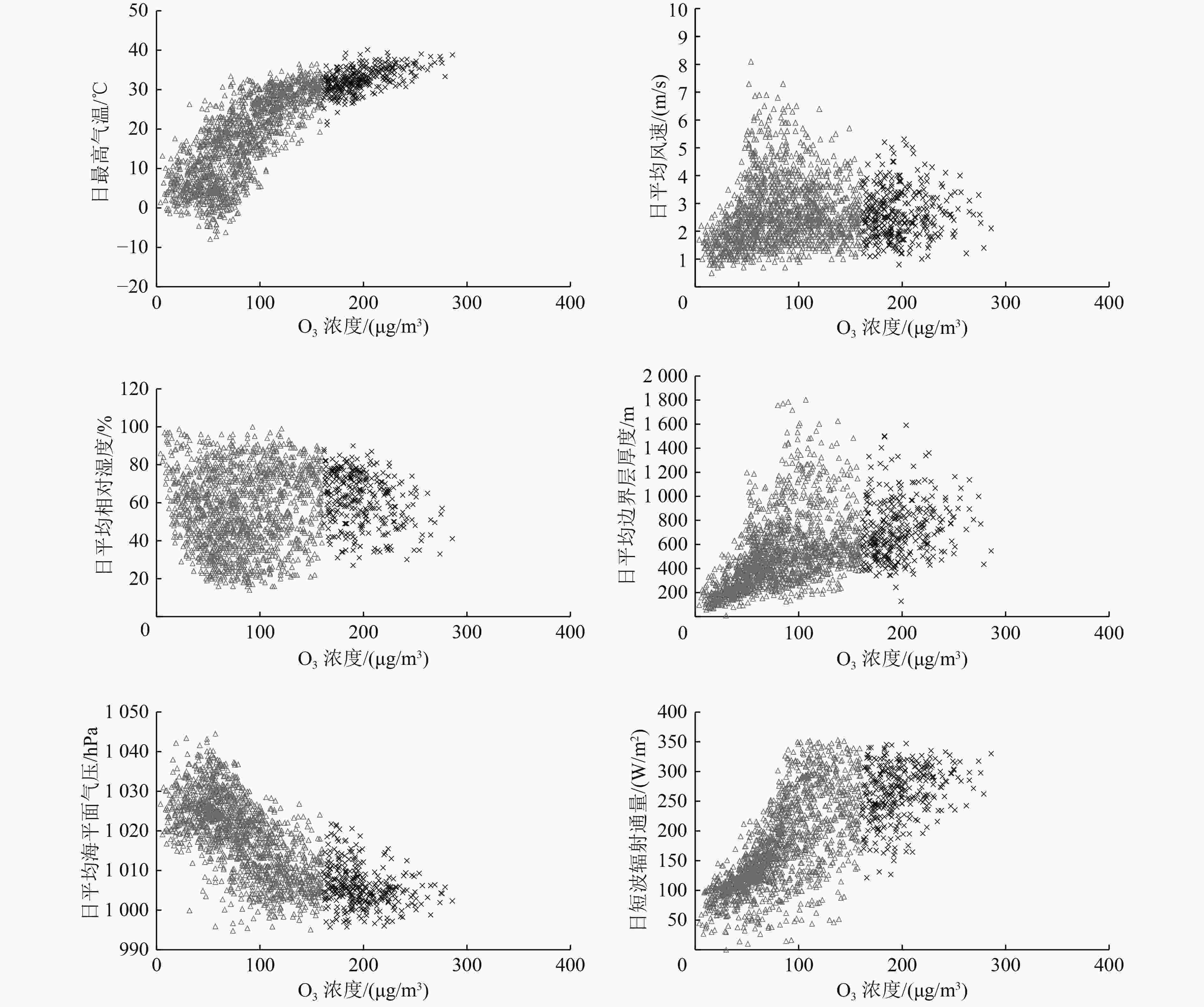
日平均相对湿度 日最高气温 日平均风速 日平均海平面气压 日平均边界层厚度 日短波辐射通量 0.10 0.82** 0.11 −0.72** 0.47** 0.71** 注:**表示在0.01水平上相关性显著。 表 3 天津市O3气象条件综合指数初步权重系数
Table 3. Preliminary weight coefficient of the ozone meteorological composite index in Tianjin
区间 日平均相对湿度 日最高气温 日平均风速 日平均海平面气压 日平均边界层厚度 日短波辐射通量 范围/% 权重系数 范围/℃ 权重系数 范围/(m/s) 权重系数 范围/hPa 权重系数 范围/m 权重系数 范围/(W/m2) 权重系数 1 <34 0.808 <5.0 0.462 <1.5 0.787 <1 004.2 1.598 <254.2 0.475 <102.5 0.456 2 34~41 0.923 5.0~8.5 0.499 1.5~1.8 0.852 1 004.2~1 006.6 1.598 254.2~327.4 0.6 102.5~118.0 0.483 3 41~46 0.937 8.5~13.3 0.543 1.8~2 0.959 1 006.6~1 009.4 1.385 327.4~391.6 0.753 118.0~133.9 0.623 4 46~52 1.026 13.3~17.2 0.716 2~2.2 0.97 1 009.4~1 013.1 1.247 391.6~448.1 0.908 133.9~157.2 0.712 5 52~58 0.991 17.2~21.0 0.82 2.2~2.4 1.069 1 013.1~1 017.0 1.013 448.1~503.3 1.029 157.2~181.4 0.907 6 58~64 0.958 21.0~25.1 0.983 2.4~2.6 1.073 1 017.0~1 019.9 0.811 503.3~562.2 1.107 181.4~208.6 1.05 7 64~69 1.181 25.1~28.0 1.207 2.6~2.9 1.075 1 019.9~1 022.6 0.712 562.2~633.2 1.179 208.6~236.9 1.219 8 69~74 1.116 28.0~30.3 1.355 2.9~3.3 1.149 1 022.6~1 025.1 0.631 633.2~724.2 1.21 208.6~262.7 1.425 9 74~79 1.102 30.3~32 1.529 3.3~3.8 1.106 1 025.1~1 028.4 0.531 724.2~874.1 1.385 262.7~290.5 1.477 10 ≥79 0.993 ≥32 1.798 ≥3.8 0.999 ≥1 028.4 0.518 ≥874.1 1.318 ≥290.5 1.585 -
[1] LIU Y M, WANG T. Worsening urban ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2017: part 2. the effects of emission changes and implications for multi-pollutant control[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2020,20(11):6323-6337. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-6323-2020 [2] ZHENG D Y, HUANG X J, GUO Y H. Spatiotemporal variation of ozone pollution and health effects in China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(38):57808-57822. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19935-z [3] 王玫, 郑有飞, 柳艳菊, 等. 京津冀臭氧变化特征及与气象要素的关系[J]. 中国环境科学,2019,39(7):2689-2698.WANG M, ZHENG Y F, LIU Y J, et al. Characteristics of ozone and its relationship with meteorological factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. China Environmental Science,2019,39(7):2689-2698. [4] MAO J, WANG L L, LU C H, et al. Meteorological mechanism for a large-scale persistent severe ozone pollution event over Eastern China in 2017[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2020,92:187-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.02.019 [5] 张莹, 许建敏, 汪瑶, 等. 京津冀地区2015—2020年臭氧持续污染事件特征、气象影响及潜在源区分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2023,43(6):2714-2721.ZHANG Y, XU J M, WANG Y, et al. Characteristics, meteorological impacts and potential sources of persistent ozone pollution events in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region during 2015-2020[J]. China Environmental Science,2023,43(6):2714-2721. [6] LIU T, WANG C L, WANG Y Y, et al. Impacts of model resolution on predictions of air quality and associated health exposure in Nanjing, China[J]. Chemosphere,2020,249:126515. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126515 [7] ARNOLD S R, LOMBARDOZZI D, LAMARQUE J F, et al. Simulated global climate response to tropospheric ozone-induced changes in plant transpiration[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(23):13070-13079. doi: 10.1029/2018GL079938 [8] 徐静馨, 郑有飞, 王圣, 等. O3胁迫下冬小麦总初级生产力的损耗模拟[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(10):4725-4732.XU J X, ZHENG Y F, WANG S, et al. Simulated ozone damage on gross primary productivity (GPP) in a winter wheat field[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(10):4725-4732. [9] 宁一,孙洁亚,薛志钢, 等. 受焦化影响的下风向城区臭氧污染特征及潜在源区分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):710-717.NING Y, SUN J Y, XUE Z G, et al. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and potential sources of ozone pollution in downwind urban areas affected by coking[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):710-717. [10] 王芃, 朱盛强, 张梦媛, 等. 大气氧化性及其对二次污染物形成的贡献[J]. 科学通报,2022,67(18):2069-2078.WANG P, ZHU S Q, ZHANG M Y, et al. Atmospheric oxidation capacity and its contribution to secondary pollutants formation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2022,67(18):2069-2078. [11] 唐孝炎, 张远航, 邵敏. 大气环境化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 272-273. [12] 赵龙一, 郭佳华, 张宇航, 等. 2015—2019年南阳市臭氧污染特征及气象因素影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):718-725. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210205ZHAO L Y, GUO J H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and meteorological parameters in Nanyang City from 2015 to 2019[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):718-725. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210205 [13] LIAO H, CHANG W Y, YANG Y. Climatic effects of air pollutants over China: a review[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2015,32(1):115-139. doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-0013-x [14] 吴丽萍, 李梦辉, 张向炎, 等. 淄博市2016-2019年近地面大气臭氧时空分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(5):1044-1052.WU L P, LI M H, ZHANG X Y, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics of ground ozone in Zibo City from 2016 to 2019[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(5):1044-1052. [15] 黄俊, 廖碧婷, 吴兑, 等. 广州近地面臭氧浓度特征及气象影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报,2018,38(1):23-31.HUANG J, LIAO B T, WU D, et al. Guangzhou ground level ozone concentration characteristics and associated meteorological factors[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2018,38(1):23-31. [16] 卓俊玲,朱珊娴,隆重, 等. 基于卫星数据识别臭氧生成高值区的方法及其应用[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(6):2039-2048.ZHUO J L, ZHU S X, LONG Z, et al. A satellite-based method and application for identifying high ozone production area[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(2):2039-2048. [17] HE J J, GONG S L, YU Y, et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014-2015 in major Chinese Cities[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,223:484-496. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.050 [18] LI K, JACOB D J, SHEN L, et al. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: anthropogenic and meteorological influences[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2020,20(19):11423-11433. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-11423-2020 [19] 黄俊, 廖碧婷, 王春林, 等. 广州逐时臭氧污染气象条件指数研究及应用[J]. 环境科学学报,2023,43(1):63-75.HUANG J, LIAO B T, WANG C L, et al. Meteorological condition index (MCI) for hourly ozone pollution in Guangzhou: development and application[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2023,43(1):63-75. [20] 杨欣, 杨元琴, 李红, 等. 基于气象条件指数的我国重点区域PM2.5和臭氧复合污染气象影响评估[J/OL]. 环境科学. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202212101.YANG X, YANG Y Q, LI H, et al. Meteorological impact assessment of PM2.5 and O3 complex pollution in key regions of China based on meteorological conditions index[J/OL]. Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202212101. [21] 叶深, 王鹏, 折远洋, 等. 2015—2020年中国三大城市群臭氧浓度时空变化特征及影响因子[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(4):1444-1453.YE S, WANG P, SHE Y Y, et al. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and influencing factors of ozone in three major urban agglomerations in China from 2015 to 2020[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(4):1444-1453. [22] CHEN L, GUO B, HUANG J S, et al. Assessing air-quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region: the method and mixed tales of PM2.5 and O3[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2018,193:290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.08.047 [23] 潘巧英, 李婷苑, 陈靖扬, 等. 基于GRAPES模式佛山市臭氧污染气象指数的构建和预报[J]. 环境科学学报,2023,43(1):140-151.PAN Q Y, LI T Y, CHEN J Y, et al. Construction and prediction of ozone weather index in Foshan based on GRAPES model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2023,43(1):140-151. [24] 蔡子颖, 姚青, 韩素芹, 等. 21世纪以来天津细颗粒物气象扩散能力趋势分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(6):2040-2046.CAI Z Y, YAO Q, HAN S Q, et al. The trends of fine particulate meteorological diffusivity in Tianjin form 21th[J]. China Environmental Science,2017,37(6):2040-2046. [25] 李源, 陆彦彬, 白宇, 等. 基于天津臭氧污染特点的气象条件与天气分型研究[J]. 中国环境监测,2022,38(5):56-64.LI Y, LU Y B, BAI Y, et al. Study of meteorological conditions and weather types based on ozone pollution characteristics in Tianjin[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China,2022,38(5):56-64. [26] 姜华, 常宏咪. 我国臭氧污染形势分析及成因初探[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(7):1576-1582.JIANG H, CHANG H M. Analysis of China's ozone pollution situation, preliminary investigation of causes and prevention and control recommendations[J]. Research of Environmental Science,2021,34(7):1576-1582. [27] 李娜, 周涛, 刘小雪, 等. 廊坊市臭氧污染特征及其与气象因素的关系[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):217-225.LI N, ZHOU T, LIU X X, et al. Characteristics of ozone pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in Langfang City[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):217-225. [28] 全澍, 刘淼晗, 陈博轩, 等. 河南省近地表O3污染特征及其与气象因素之间的关系[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(12):2666-2676.QUAN S, LIU M H, CHEN B X, et al. Characteristics of near-surface O3 pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in Henan Province[J]. Research of Environmental Science,2022,35(12):2666-2676. [29] 赵伟, 高博, 刘明, 等. 气象因素对香港地区臭氧污染的影响[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(1):55-66.ZHAO W, GAO B, LIU M, et al. Impact of meteorological factors on the ozone pollution in Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(1):55-66. [30] 丁愫, 陈报章, 王瑾, 等. 基于决策树的统计预报模型在臭氧浓度时空分布预测中的应用研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2018,38(8):3229-3242.DING S, CHEN B Z, WANG J, et al. An applied research of decision-tree based statistical model in forecasting the spatial-temporal distribution of O3[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2018,38(8):3229-3242. [31] 余晓艳. 河南平原PM2.5和O3数据的评估和修正方法研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2022. [32] 王帅, 冯亚平, 崔建升, 等. 石家庄市臭氧污染的时空演变格局和潜在源区[J]. 环境科学学报,2020,40(9):3081-3092.WANG S, FENG Y P, CUI J S, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution patterns and potential source areas of ozone pollution in Shijiazhuang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2020,40(9):3081-3092. [33] 唐颖潇, 姚青, 蔡子颖, 等. 基于过程分析的京津冀区域典型城市臭氧成因[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(6):2917-2927.TANG Y X, YAO Q, CAI Z Y, et al. Exploring formation of ozone in typical cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using process analysis[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(6):2917-2927. □ -




 下载:
下载: