Development, application and prospect of cyanobacteria blooms control technology in lakes and reservoirs
-
摘要:
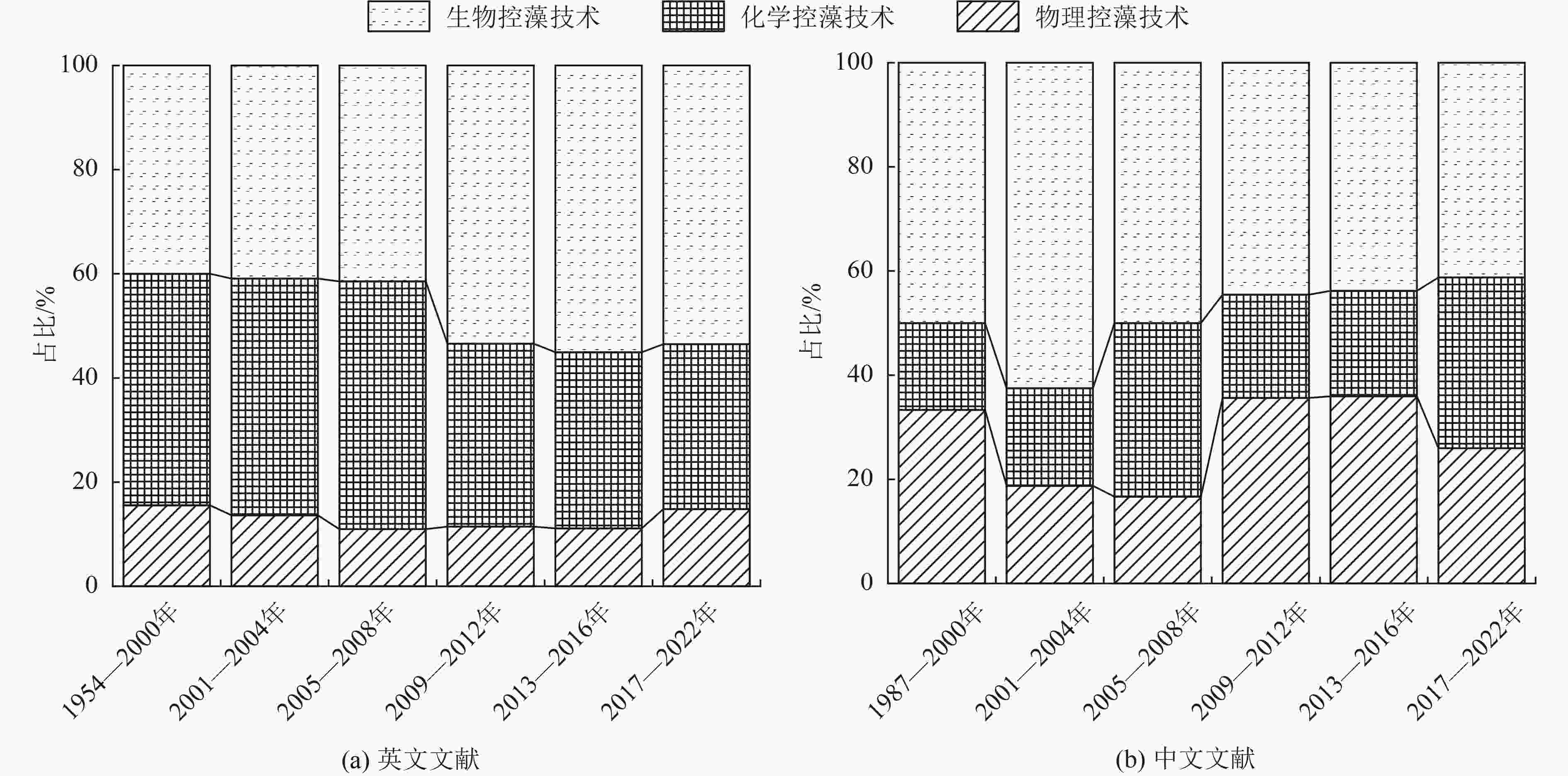
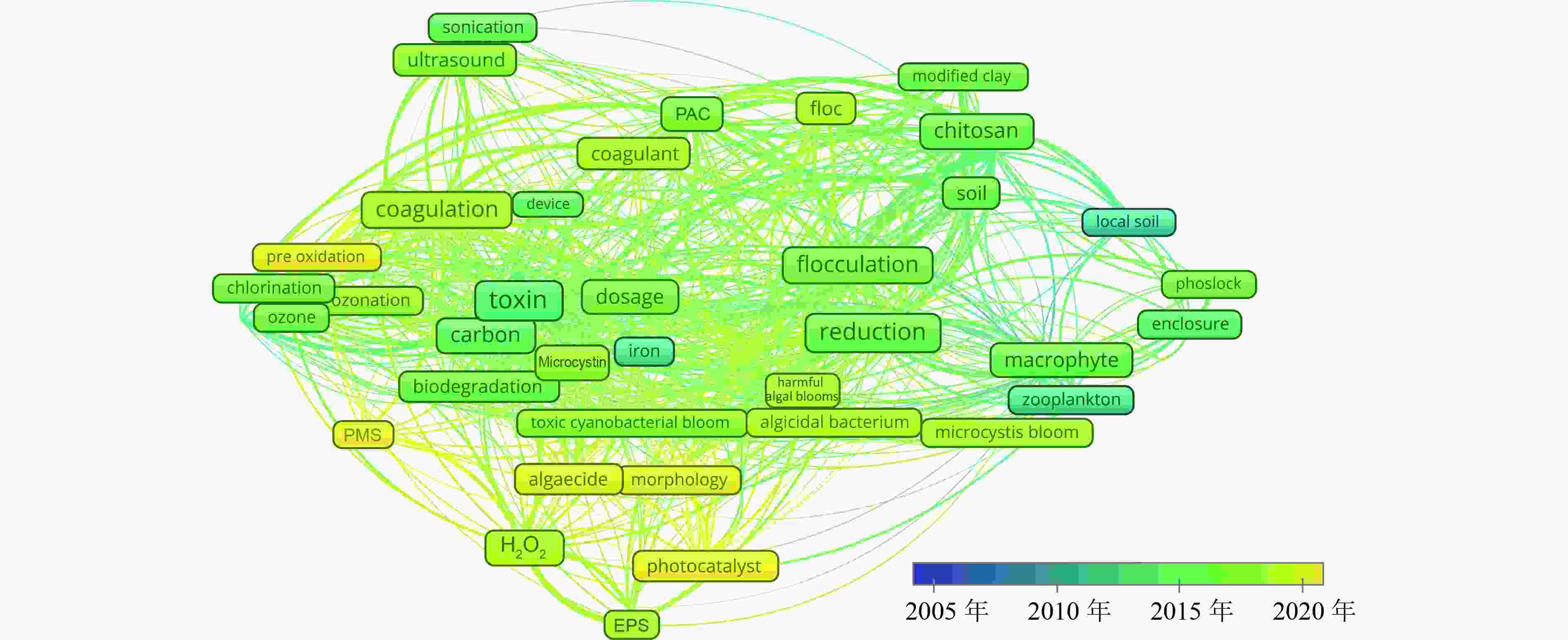
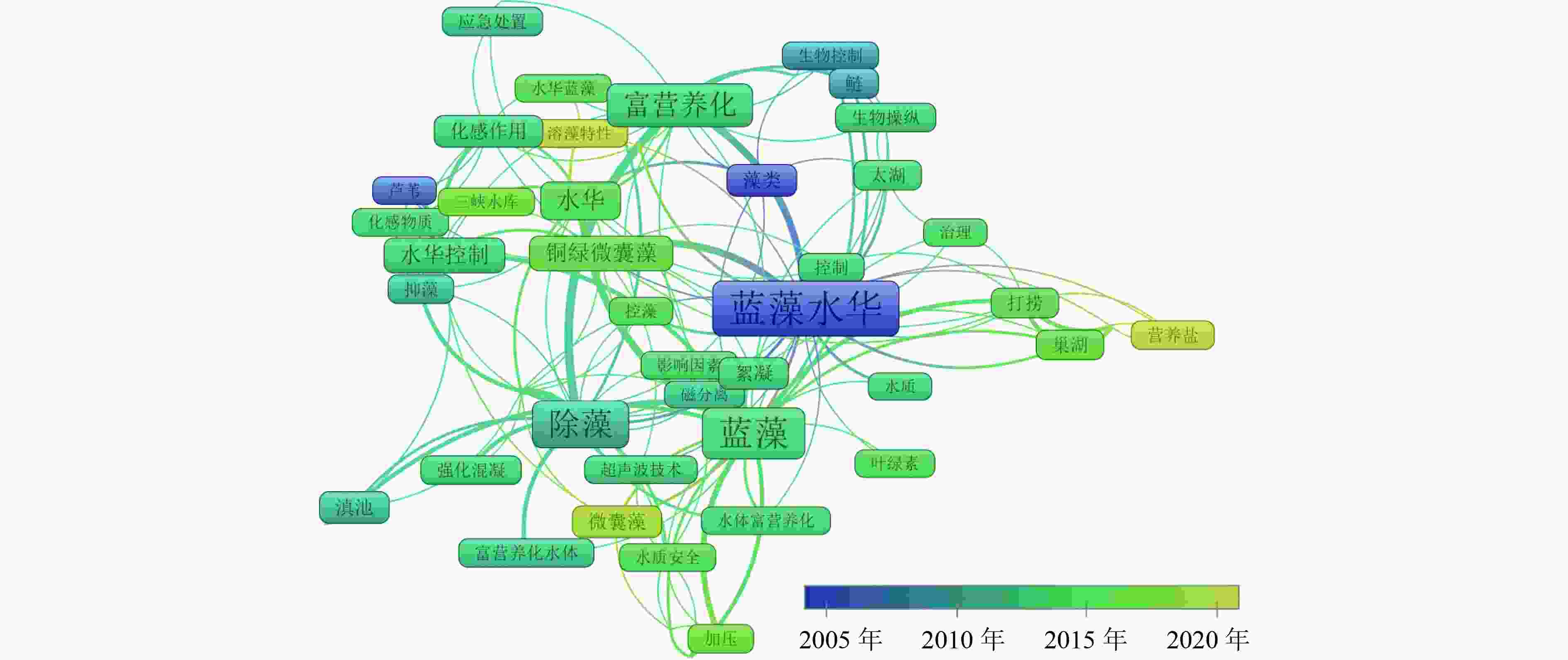
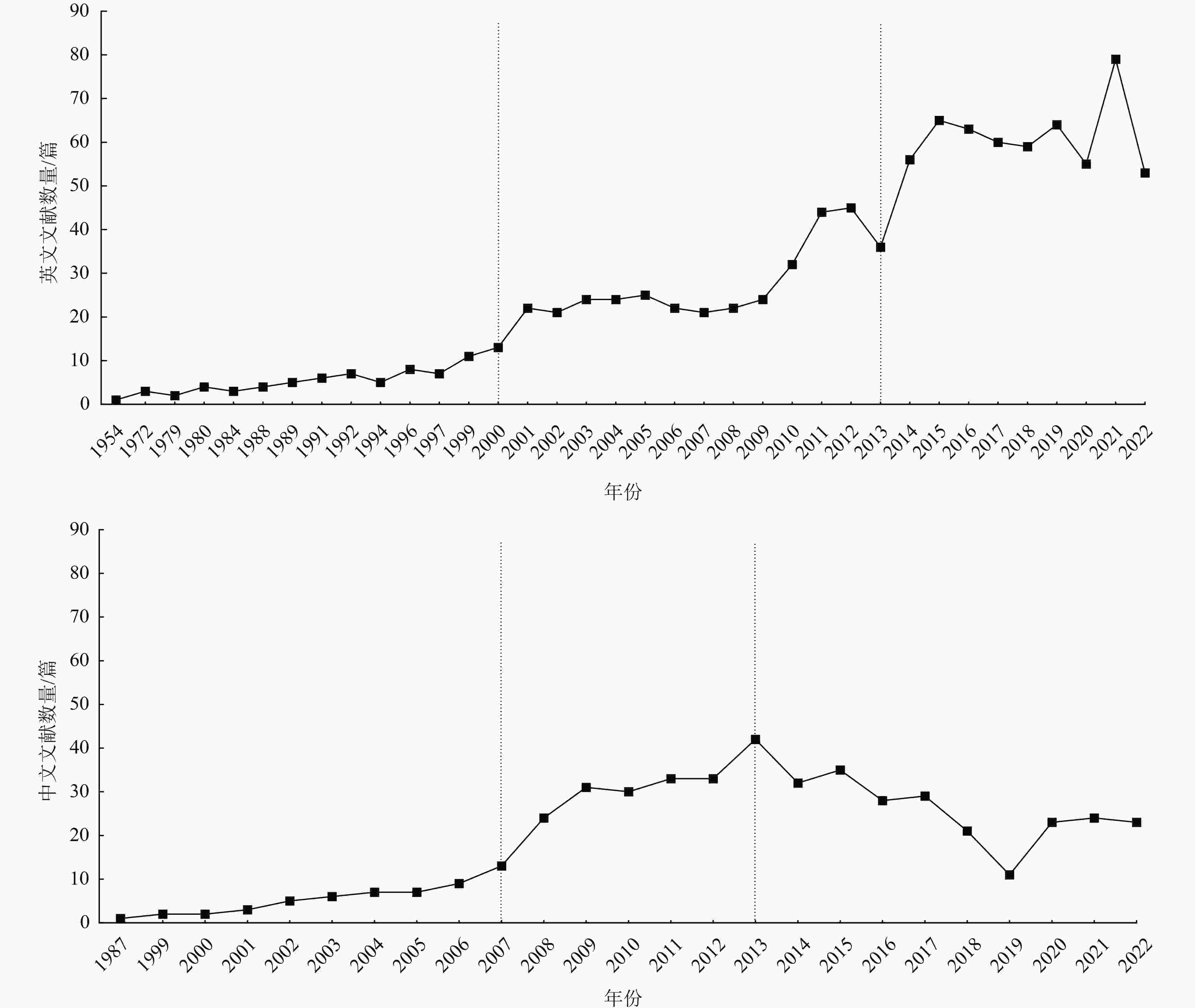
蓝藻水华暴发会引起供水系统堵塞、水体异味、水生生物死亡等一系列生态环境问题,严重时还将威胁饮用水安全,因此采取切实有效的蓝藻水华控制技术对蓝藻水华防控至关重要。通过文献调研系统梳理了国内外蓝藻水华控制技术发展历程,综述了典型蓝藻水华控制技术及其适用范围、应用情况及优缺点等。结果表明:蓝藻水华控制技术总体分为物理控藻技术、化学控藻技术和生物控藻技术。从技术文献关键词时间发展脉络看,2010年之前国外蓝藻水华控制技术关键词多集中在絮凝、混凝等化学控藻技术,2010年后向水生植物抑藻等生物控藻技术发展;我国蓝藻水华控制技术关键词2010年前主要集中在鲢鳙鱼控藻、水生植物抑藻等生物控藻技术,2010年后超声波、机械除藻等物理控藻技术和絮凝等化学控藻技术快速发展,2015年后物理控藻技术进一步发展。国外蓝藻水华控制技术于20世纪50年代起步于化学控藻技术,2000年后研发了超声波、光波等物理控藻技术,2010年后主要以生物控藻和化学控藻技术为主;国内蓝藻水华控制技术于20世纪80年代起步于针对小型水体的生物控藻技术,2000年后逐渐发展为针对大型湖库的机械除藻技术(物理控藻技术)。物理控藻、化学控藻技术的应急效果显著,但物理控藻技术存在成本高、长效性不足等缺点,化学控藻技术存在二次污染风险;而生物控藻技术存在见效慢、有外来物种入侵风险、生态系统被扰乱风险等生态安全问题,目前实际应用案例较少。未来应加快推进蓝藻水华控制技术优化筛选和示范应用,同时开展蓝藻水华控制技术与内外源污染控制、水生态修复等技术的集成应用,提高蓝藻水华控制效果。
Abstract:Cyanobacteria blooms will cause a series of ecological environment problems such as the water supply system blockage, water odor, aquatic death, etc., and even threaten the safety of drinking water. Therefore, effective control technology is very important for the prevention and control of cyanobacteria blooms. The development history of cyanobacteria blooms control technology at home and abroad was summarized through literature research, and application scope, application situation, advantages and disadvantages of typical cyanobacteria blooms control technology were reviewed. The algal bloom control technology can be divided into physical algal control technology, chemical algal control technology and biological algal control technology. From the perspective of the time development of key words in technical literature, before 2010, foreign cyanobacteria bloom control technology mainly focused on chemical algal control technology such as flocculation and coagulation, and after 2010, it developed to biological algal control technology such as aquatic plant algal suppression. Before 2010, China's cyanobacteria bloom control technologies mainly focused on biological algal control technologies such as silver carp bighthys algae control and aquatic plant algae suppression. After 2010, physical algal control technologies such as ultrasonic and mechanical algal removal and chemical algal control technologies such as flocculation developed rapidly. After 2015, physical algal control technology further developed. Foreign cyanobacteria bloom control technology started from chemical algal control technology in the 1950s, and developed physical algal control technology such as ultrasonic wave and light wave after 2000, and mainly biological algal control and chemical algal control technology after 2010. Domestic cyanobacteria bloom control technology started from biological algal control technology for small water bodies in the 1980s, and gradually developed into mechanical algal removal technology (physical algal control technology) for large lakes and reservoirs after 2000. Physical algal control technology and chemical algal control technology have significant emergency effects, but physical algal control technology has disadvantages such as high cost and insufficient long-term performance, and chemical algal control technology has secondary pollution risk. However, the biological algal control technology has some ecological security problems, such as slow effect, risk of invasion of alien species, and risk of disturbance of ecosystem, so there are few practical application cases. In the future, the optimization, screening and demonstration application of cyanobacteria bloom control technology should be accelerated, and the integrated application of cyanobacteria bloom control technology with internal and external pollution control and water ecological restoration technologies should be carried out to improve the effect of cyanobacteria bloom control.
-
表 1 典型蓝藻水华控制技术适用范围及优缺点
Table 1. Application range, advantages and shortages of typical cyanobacteria bloom control technology
技术分类 技术名称 适用范围 作用效果 国内应用情况 优点 缺点 物理控藻
技术超声波控藻技术 有藻华堆积趋势的小型湖泊或景观水体,Chla>50 μg/L[63] 适宜频率和强度可使60%以上藻类
沉降成功应用于银川市中山公园银湖[57]、上海曲阳公园景观湖[58]、深圳某水库围栏[59]、三峡库区澎溪河流域[61] 沉降效果好,应急速度较快 可能造成藻细胞破裂,藻毒素释放 物理控藻
技术水力控藻技术 曝气充氧技术 有水华发生的表层水体,Chla>100
μg/L [63]溶解氧浓度增加 多与其他技术组合使用[65] 快速增氧,防止黑臭 持续曝气可能会引起沉积物再悬浮和营养盐释放 扬水筒曝气抑藻
技术有藻类及温度垂直分层的深水(>10 m)水体,Chla<100 μg/L[44] 溶解氧浓度增加,藻类垂直分布格局被打破,Chla削减率在40%以上[44] 多应用于深水水库,如西安市黑河金盆水库[66] 无二次污染 受限于有藻类分层的水体,浅水湖泊一般不适用 密度流扩散抑藻
技术与外部水交换困难的闭锁性水域,温度有垂直分层的深水(>10 m)水体,Chla<80 μg/L[67] 藻类垂直分布格局被打破,表层Chla削减率为60%~80%[67],
无明显蓝藻堆积成功应用于日本东京某海域内湾[67],国内鲜见报道 利用水体自身密度差打破垂直热分层,能耗低、应用灵活 受限于有温度分层的水体 机械除藻技术 有明显水华堆积的近岸水域,Chla>500 μg/L 实现近岸堆积藻类的日聚日清,蓝藻去除率>70% 成功应用于太湖、巢湖、滇池等[48-49] 将蓝藻进行异位处理,有效减少水体藻量 处理量过小、处理效率不高 黏土絮凝技术 藻华暴发初期的小水体或局部水域,Chla<200 μg/L[63] 藻类在短时间内快速沉降 大多在实验阶段,在滇池围隔区域有应用[80] 天然无毒、使用方便、吸附效果明显 藻细胞暂时沉降,存在潜在生态风险 加压控藻技术 有水华堆积的近岸水域,Chla>200 μg/L 透明度快速提升,蓝藻沉降率>70% 应用于太湖、巢湖、滇池、星云湖等[48] 能耗低、效率高、运行成本低 蓝藻仍留在水体,存在潜在生态风险 化学控藻
技术化学杀藻剂 小型水体、景观
水体除藻效果明显,Chla削减率>90% 应用于滇池草海特定水域[111] 速度快、效果好 有二次污染风险 化学混凝/絮凝技术 小水体或局部水域,Chla>1500 μg/L[63],常与其他技术联用 蓝藻去除率>80%[63] 对藻类进行异位处理,未见直接作用于水体中藻类处理的报道[112] 沉降速度快,透明度提升效果好 一些有机高分子絮凝剂存在二次污染风险 生物控藻
技术微生物制剂 小型水体或试验水体,藻华暴发初期,Chla<200 μg/L 溶藻率>70%[87] 多处于实验阶段 见效快 微生物控制难度大,后续潜在的生态风险高 生物操纵技术 面积较小水体或试验水域,藻华暴发初期,Chla<50 μg/L 对藻类控制率>60% 成功应用于太湖、滇池特定水
域[37-38,104]安全、无二次污染风险 控制效果较慢,应急效果较差 水生植物抑藻技术 富营养化程度低、藻细胞密度较低的水体,藻密度低于
3 000万个/L[111]藻细胞密度减少率为25%~50%[107] 太湖、星云湖、滇池、武汉沙湖等[113] 效果好、费用低、材料易得、二次污染风险小 生长管理难度大,不确定性强 -
[1] 郑建军, 钟成华, 邓春光. 试论水华的定义[J]. 水资源保护,2006,22(5):45-47.ZHENG J J, ZHONG C H, DENG C G. Discussion on definition of algal bloom[J]. Water Resources Protection,2006,22(5):45-47. [2] QIN B Q, LI W, ZHU G W, et al. Cyanobacterial bloom management through integrated monitoring and forecasting in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu (China)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,287:356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.047 [3] REYNOLDS C S. Cyanobacterial water-blooms[J]. Advances in Botanical Research,1987,13:67-143. [4] SMAYDA T J. Harmful algal blooms: their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,1997,42(5):1137-1153. [5] LARSSON M E, AJANI P A, RUBIO A M, et al. Long-term perspective on the relationship between phytoplankton and nutrient concentrations in a southeastern Australian Estuary[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,114(1):227-238. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.011 [6] KENEFICK S L, HRUDEY S E, PREPAS E E, et al. Odorous substances and cyanobacterial toxins in prairie drinking water sources[J]. Water Science and Technology,1992,25(2):147-154. doi: 10.2166/wst.1992.0046 [7] KOTAK B G, KENEFICK S L, FRITZ D L, et al. Occurrence and toxicological evaluation of cyanobacterial toxins in Alberta lakes and farm dugouts[J]. Water Research,1993,27(3):495-506. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(93)90050-R [8] HO J C, MICHALAK A M, PAHLEVAN N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s[J]. Nature,2019,574(7780):667-670. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1648-7 [9] 朱喜, 朱云. 太湖蓝藻暴发治理存在的问题与治理思路[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):714-719.ZHU X, ZHU Y. Problems and countermeasures of controlling cyanobacteria bloom in Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):714-719. [10] 王菁晗, 何吕奇姝, 杨成, 等. 太湖、巢湖、滇池水华与相关气象、水质因子及其响应的比较(1981—2015年)[J]. 湖泊科学,2018,30(4):897-906. doi: 10.18307/2018.0403WANG J H, HE L, YANG C, et al. Comparison of algal bloom related meteorological and water quality factors and algal bloom conditions among Lakes Taihu, Chaohu, and Dianchi(1981-2015)[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2018,30(4):897-906. doi: 10.18307/2018.0403 [11] 国家环境保护总局. 国家环境科技发展“十五”计划纲要[J]. 环境保护,2001,29(8):3-9. [12] 关于印发《太湖水污染防治2002年度工作计划》的通知: 环办〔2002〕75号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/zj/bgt/200910/t20091022_173790.htm. [13] 关于印发巢湖流域水污染防治“十五”计划实施意见的函: 环办函〔2003〕307号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/zj/bgth/200910/t20091022_174072.htm. [14] 关于印发《滇池流域水污染防治“十五”计划》的通知: 环发〔2003〕84号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/zj/wj/200910/t20091022_172191.htm. [15] 国家环境保护总局. 湖库富营养化防治技术政策[J]. 环境保护,2004,32(8):18-22. [16] 谢平. 太湖蓝藻的历史发展与水华灾害: 为何2007年在贡湖水厂出现水污染事件: 30年能使太湖摆脱蓝藻威胁吗[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. [17] 关于印发《2008年全国环境监测工作计划》的通知: 环办〔2008〕8号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/zj/bgt/200910/t20091022_174048.htm. [18] 关于进一步加强饮用水水源安全保障工作的通知: 环办〔2009〕30号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/200910/t20091022_174787.htm. [19] 关于加强重点湖泊蓝藻水华防控工作的通知: 环办函〔2014〕796号[A/OL]. [2023-05-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgth/201407/t20140702_278137.htm. [20] FITZGERALD G P, SKOOG F. Control of blue-green algae blooms with 2, 3-dichloronaphthoquinone[J]. Sewage and Industrial Wastes, 1954, 26(9): 1136–1140. [21] Wetzel R G. Limnology[M]. 2nd Edition. New York: Mc Graw-Hill, Inc, 1994. [22] SHAPIRO J, LAMARRA V, LYNCH M. Biomanipulation: an ecosystem approach to lake restoration[J]. Proceedings of the Symposium on Water,1975,21(6):85-96. [23] SHAPIRO J. Biomanipulation: the next phase: making it stable[J]. Hydrobiologia,1990,200(1):13-27. [24] MURRAY-GULDE C L, HEATLEY J E, SCHWARTZMAN A L, et al. Algicidal effectiveness of clearigate, cutrine-plus, and copper sulfate and margins of safety associated with their use[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2002,43(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s00244-002-1135-1 [25] van HULLEBUSCH E, DELUCHAT V, CHAZAL P M, et al. Environmental impact of two successive chemical treatments in a small shallow eutrophied lake: part Ⅱ. case of copper sulfate[J]. Environmental Pollution,2002,120(3):627-634. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00191-4 [26] GARCı́A-VILLADA L, RICO M, ALTAMIRANO M, et al. Occurrence of copper resistant mutants in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: characterisation and future implications in the use of copper sulphate as algaecide[J]. Water Research,2004,38(8):2207-2213. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.01.036 [27] 郑少波, 杜鹤桂. 冷却水光磁协同处理技术[J]. 工业水处理,1998,18(1):9-11.ZHENG S B, DU H G. Researches on the technology of co treatment cooling water with photon and magnetic field[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,1998,18(1):9-11. [28] 陈贺林, 李芸, 储昭升, 等. 超声波控藻技术现状及研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(1):72-78.CHEN H L, LI Y, CHU Z S, et al. Present situation and research progress of ultrasonic algae control technology[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(1):72-78. [29] CONG H B, HUANG T L, CHAI B B, et al. A new mixing-oxygenating technology for water quality improvement of urban water source and its implication in a reservoir[J]. Renewable Energy,2009,34(9):2054-2060. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2009.02.007 [30] 方荣楠. 密度流扩散装置对闭锁海域的搅拌净化[J]. 渔业现代化,2000,27(1):42-43.FANG R N. Mixing and purification of closed sea area by density flow diffusion device[J]. Fishery Modernization,2000,27(1):42-43. [31] JUNGO E, VISSER P, STROOM J, et al. Artificial mixing to reduce growth of the blue-green alga Microcystis in Lake Nieuwe Meer, Amsterdam: an evaluation of 7 years of experience[J]. Water Science & Technology:Water Supply,2001,1:17-23. [32] 大内一之. 密度流拡散装置の研究開発[R]. 日本造船学会論文集, 1998: 183. [33] NEZBRYTSKA I, USENKO O, KONOVETS I, et al. Potential use of aquatic vascular plants to control cyanobacterial blooms: a review[J]. Water,2022,14(11):1727. doi: 10.3390/w14111727 [34] GHERNAOUT B, GHERNAOUT D, SAIBA A L. Algae and cyanotoxins removal by coagulation/flocculation: a review[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2010,20(1/2/3):133-143. [35] 谢平. 鲢、鳙与藻类水华控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. [36] XIE P, LIU J. Practical success of biomanipulation using filter-feeding fish to control cyanobacteria blooms: a synthesis of decades of research and application in a subtropical hypereutrophic lake[J]. The Scientific World Journal,2001,1:337-356. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2001.67 [37] 但文德, 王勇, 彭军, 等. 滇池内源污染生物治理(以鱼控藻)[R]. 昆明: 昆明市滇池管理局渔业行政执法处, 2015. [38] 李明锋. 太湖蓝藻治理推出“生物杀手”: 15万尾鲢鳙鱼游向内太湖[J]. 渔业致富指南,2001(19):17.LI M F. Blue-green algae control in Taihu Lake promotes “biological killer”: 150 000 silver carp and bighead carp swim to Taihu Lake[J]. Fishery Guide to Be Rich,2001(19):17. [39] 俞志明, 邹景忠, 马锡年, 等. 治理赤潮的化学方法[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1993,24(3):314-318.YU Z M, ZOU J Z, MA X N, et al. The chemical means of controlling red tides[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,1993,24(3):314-318. [40] YU Z M, ZOU J Z, MA X N. Application of clays to removal of red tide organisms: Ⅲ. the coagulation of kaolin on red tide organisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,1995,13(1):62-70. doi: 10.1007/BF02845350 [41] 兰智文, 赵鸣, 尹澄清. 藻类水华的化学控制研究[J]. 环境科学,1992,13(1):12-15.LAN Z W, ZHAO M, YIN C Q. Controlling algal overgrowth with chemical methods[J]. Environmental Science,1992,13(1):12-15. [42] 沈银武, 刘永定, 吴国樵, 等. 富营养湖泊滇池水华蓝藻的机械清除[J]. 水生生物学报,2004,28(2):131-136.SHEN Y W, LIU Y D, WU G Q, et al. Mechanical removal of heavy cyanobacterial bloom in the hyper-eutrophic Lake Dianchi[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2004,28(2):131-136. [43] 徐佳良, 杨栋, 陈嘉伟, 等. 适用船载的藻水高效分离技术研究[J]. 中国环保产业,2019(4):52-56.XU J L, YANG D, CHEN J W, et al. Study on high efficiency separation technology for algae water of shipborne[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry,2019(4):52-56. [44] 丛海兵, 黄廷林, 缪晶广, 等. 水体修复装置: 扬水曝气器的开发[J]. 中国给水排水,2005,21(3):41-45.CONG H B, HUANG T L, MIAO J G, et al. Development of rehabilitation device for water body: water lifting aerator[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2005,21(3):41-45. [45] 孙昕, 张梦丹, 黄廷林, 等. 扬水曝气器类型对分层水库藻类控制效果的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2014,27(12):1479-1485.SUN X, ZHANG M D, HUANG T L, et al. Comparison of water-lifting aerator type for algae inhibition in stratified reservoirs[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2014,27(12):1479-1485. [46] 付琨, 高云涛, 刘晓海. 超声波抑制滇池水华藻类生长的实验研究[J]. 化学与生物工程,2007,24(12):64-65.FU K, GAO Y T, LIU X H. Study on experiment of ultrasonic wave inhibiting the growth of water bloom algaes in Dianchi Lake[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2007,24(12):64-65. [47] 倪其军, 眭爱国, 杨栋. 蓝藻打捞船研发与应用[C]//第十三届中国国际船艇展暨高性能船学术报告会, 上海, 2008. [48] 湖泊生态系统功能修复及规模化推广应用成套技术[R]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2021. [49] 受损水体修复技术长清单(技术、工程、设备名片集)[R]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2021. [50] BROEKMAN S, POHLMANN O, BEARDWOOD E S, et al. Ultrasonic treatment for microbiological control of water systems[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2010,17(6):1041-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.11.011 [51] HAO H W, WU M S, CHEN Y F, et al. Cyanobacterial bloom control by ultrasonic irradiation at 20 kHz and 1.7 MHz[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A,2004,39(6):1435-1446. doi: 10.1081/ESE-120037844 [52] 储昭升, 庞燕, 郑朔芳, 等. 超声波控藻及对水生生态安全的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2008,28(7):1335-1339.CHU Z S, PANG Y, ZHENG S F, et al. Algal control by ultrasonic radiation and its risks to the aquatic environment[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2008,28(7):1335-1339. [53] FRENKEL V, KIMMEL E, IGER Y. Ultrasound-induced cavitation damage to external epithelia of fish skin[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology,1999,25(8):1295-1303. [54] HOLM E R, STAMPER D M, BRIZZOLARA R A, et al. Sonication of bacteria, phytoplankton and zooplankton: application to treatment of ballast water[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2008,56(6):1201-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.02.007 [55] 谭啸, 顾惠卉, 段志鹏, 等. 超声波控藻对氮磷释放及水质变化的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(4):1371-1376.TAN X, GU H H, DUAN Z P, et al. Effects of ultrasound on the released amount of nitrogen and phosphorus and changes of water quality during blooms control[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(4):1371-1376. [56] ZHOU Y C, HUANG H, WANG J, et al. Vaccination of the grouper, Epinephalus awoara, against vibriosis using the ultrasonic technique[J]. Aquaculture,2002,203(3/4):229-238. [57] 崔竣岭, 吴竹林. 超声波技术在防治人工湖水藻中的应用[J]. 宁夏农林科技,2009,50(2):41.CUI J L, WU Z L. Application of ultrasonic technology in controlling algae in artificial lake[J]. Journal of Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology,2009,50(2):41. [58] 丁永良, 卢守珍, 郭磊, 等. 超声波水域灭藻净水装置在上海曲阳公园景观湖的应用[J]. 上海水务,2006,22(4):15-18. [59] 闫莉. 超声共振技术在水库藻类抑制中的应用初探[J]. 人民珠江,2015,36(4):88-90.YAN L. Preliminary study on the application of ultrasonic resonance technology in algae inhibition in reservoirs[J]. Pearl River,2015,36(4):88-90. [60] RAJASEKHAR P, FAN L H, NGUYEN T, et al. A review of the use of sonication to control cyanobacterial blooms[J]. Water Research,2012,46(14):4319-4329. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.054 [61] 韩景明. 澎溪河水环境及超声波除(抑)藻技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011. [62] VISSER P M, IBELINGS B W, BORMANS M, et al. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: a review[J]. Aquatic Ecology,2016,50(3):423-441. doi: 10.1007/s10452-015-9537-0 [63] 史小丽, 杨瑾晟, 陈开宁, 等. 湖泊蓝藻水华防控方法综述[J]. 湖泊科学,2022,34(2):349-375. doi: 10.18307/2022.0201SHI X L, YANG J S, CHEN K N, et al. Review on the control and mitigation strategies of lake cyanobacterial blooms[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2022,34(2):349-375. doi: 10.18307/2022.0201 [64] 方荣楠. 间歇式空气扬水筒改善水质环境[J]. 渔业机械仪器,1989,16(6):39.FANG R N. Intermittent air pump improves water quality environment[J]. Fishery Modernization,1989,16(6):39. [65] 周真明, 黄廷林, 丛海兵. 扬水曝气/生物接触氧化工艺的除藻效果研究[J]. 中国给水排水,2007,23(15):13-16.ZHOU Z M, HUANG T L, CONG H B. Algae removal effect by combined process of water-lifting aeration and biological contact oxidation[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2007,23(15):13-16. [66] 马越, 黄廷林, 丛海兵, 等. 扬水曝气技术在河道型深水水库水质原位修复中的应用[J]. 给水排水,2012,48(4):7-13.MA Y, HUANG T L, CONG H B, et al. Application of the technology of water-lifting and aeration on water quality in situ restoration in a deep channel reservoir[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering,2012,48(4):7-13. [67] 密度流扩散装置技术资料[R]. 东京: 东京大学, 2005. [68] 倪其军, 眭爱国, 顾建民. 蓝藻水脱水处理方法: CN101648092A[P]. 2011-06-01. [69] 吴玉宝, 王启山, 王玉恒, 等. 混凝-气浮除藻工艺中各参数的优化[J]. 中国给水排水,2008,(3):95-99.WU Y B, WANG Q S, WANG Y H, et al.Optimization of parameters in coagulation/flotation process for algae removal[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2008,(3):95-99. [70] 张军, 杨铮, 李婷, 等. 藻水分离技术应用研究进展[J]. 环境科学导刊,2019,38(增刊2):97-99.ZHANG J, YANG Z, LI T, et al. Research progress on the application of the technology of separating algae from water[J]. Environmental Science Survey,2019,38(Suppl 2):97-99. [71] 史春琼, 黄光团, 周鼎, 等. 磁化处理对水中藻类的去除效果研究[J]. 净水技术,2009,28(6):54-57.SHI C Q, HUANG G T, ZHOU D, et al. Algae removal effect by magnetization[J]. Water Purification Technology,2009,28(6):54-57. [72] 胡明明, 胡云海, 孙阳, 等. 一种蓝藻深井处理设备: CN207645907U[P]. 2018-07-24. [73] 李敦海, 汪志聪, 秦红杰, 等. 蓝藻水华的拦截和陷阱捕获综合控藻技术研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2012,21(增刊2):45-50.LI D H, WANG Z C, QIN H J, et al. An integrated technology of bloom-barrier and bloom-trap for cyanobacterial bloom control[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2012,21(Suppl 2):45-50. [74] 柯凡, 李文朝, 潘继征, 等. 一种智能拦挡式围隔: CN108221891B[P]. 2023-08-18. [75] BELLOCQ B, RUIZ T, DELAPLACE G, et al. Screening efficiency and rolling effects of a rotating screen drum used to process wet soft agglomerates[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2017,195:235-246. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.09.023 [76] 肖邦定, 黄立新. 一种全自动船载除藻的方法及设备: CN105833596A[P]. 2019-03-26. [77] ANDERSON D M. Turning back the harmful red tide[J]. Nature,1997,388(6642):513-514. doi: 10.1038/41415 [78] 慕利梅, 王图锦, 曹琳, 等. 聚合氯化铝-镧改性膨润土的制备及除磷除藻研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(6):1450-1457.MU L M, WANG T J, CAO L, et al. Preparation of polyaluminum chloride-lanthanum modified bentonite and study on phosphorus and algae removal[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(6):1450-1457. [79] 蒋茜茜, 张小凤, 陈文清. 9种黏土对铜绿微囊藻的去除效果[J]. 中国给水排水,2018,34(7):56-59.JIANG Q Q, ZHANG X F, CHEN W Q. Effect of Microcystis aeruginosa removal by nine types of clay[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2018,34(7):56-59. [80] 孙珮石, 许晓毅, 毕晓伊, 等. 滇池水体除藻材料的除藻作用试验研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2004,4(6):3-6.SUN P S, XU X Y, BI X Y, et al. Experimental research on algae-removing effect of Dianchi Lake by algaecide material[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2004,4(6):3-6. [81] AKTAS T S, TAKEDA F, MARUO C, et al. Comparison of four kinds of coagulants for the removal of picophytoplankton[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2013,51(16/17/18):3547-3557. [82] 郭培章, 宋群. 中外水体富营养化治理案例研究[M]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2003. [83] 陆贻超, 王国祥, 李仁辉. 超声波和改性粘土集成技术在去除蓝藻水华上的应用[J]. 湖泊科学,2010,22(3):421-429.LU Y C, WANG G X, LI R H. Using the integrated technique of ultrasonic and modified-clay to remove algal blooms[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2010,22(3):421-429. [84] CHU Z S, JIN X C, YANG B, et al. Buoyancy regulation of Microcystis flos-aquae during phosphorus-limited and nitrogen-limited growth[J]. Journal of Plankton Research,2007,29(9):739-745. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbm054 [85] 曹泽磊, 陈旭清, 胡航宇, 等. 一种蓝藻打捞及加压控藻船: CN106638518B[P]. 2018-11-13. [86] 潘阳. 大型水体原位加压沉淀控制蓝藻生长机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. [87] 陈昕, 胡胜华, 陈晓飞, 等. 蓝藻水华应急处置方法与技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术,2023,46(5):108-116.CHEN X, HU S H, CHEN X F, et al. Progress on methods and technologies for the emergency treatment of cyanobacterial blooms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2023,46(5):108-116. [88] 郑婷婷, 牟霄, 张崇淼, 等. 电活化过硫酸盐去除铜绿微囊藻的效果及机理研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(1):98-107.ZHENG T T, MOU X, ZHANG C M, et al. Removal performance and mechanisms of Microcystis aeruginosa by electro-activated persulfate[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(1):98-107. [89] YANG Z, BULEY R P, FERNANDEZ-FIGUEROA E G, et al. Hydrogen peroxide treatment promotes chlorophytes over toxic cyanobacteria in a hyper-eutrophic aquaculture pond[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,240:590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.012 [90] MIAO H F, TAO W Y. The mechanisms of ozonation on cyanobacteria and its toxins removal[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2009,66(1):187-193. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2008.11.008 [91] 回东冰, 吴明松. 二氧化氯与PAC混凝剂同时投加对含藻水的处理效果[J]. 城镇供水,2022(5):30-34.HUI D B, WU M S. Effect of adding chlorine dioxide and PAC coagulant at the same time on algae-containing water treatment[J]. City and Town Water Supply,2022(5):30-34. [92] 王铮, 王珂, 夏萍. 二溴海因与次氯酸钠杀菌除藻效果对比研究[J]. 净水技术,2016,35(增刊1):39-41.WANG Z, WANG K, XIA P. Comparison of killing alga and bacteria by DBDMH and NaClO[J]. Water Purification Technology,2016,35(Suppl 1):39-41. [93] 赵小丽, 宋立荣, 张小明. 硫酸铜控藻对浮游植物群落的影响[J]. 水生生物学报,2009,33(4):596-602. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1035.2009.40596ZHAO X L, SONG L R, ZHANG X M. Effects of copper sulfate treatment on eutrophic urban lake phytoplankton communities[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2009,33(4):596-602. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1035.2009.40596 [94] 王寿兵, 徐紫然, 马小雪, 等. Cu2+对铜绿微囊藻生长及叶绿素荧光主要参数的影响研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2016,36(12):3759-3765.WANG S B, XU Z R, MA X X, et al. Effects of Cu2+ on the growth and main parameters of chlorophyll fluorescence of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. China Environmental Science,2016,36(12):3759-3765. [95] 柴仕淦, 贾钗, 李欣怡, 等. 季铵盐型Gemini表面活性剂去除铜绿微囊藻[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2016,6(1):8-15.CHAI S G, JIA C, LI X Y, et al. Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa by using quaternary ammonium salt of Gemini surfactant[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2016,6(1):8-15. [96] 王晓丽, 张永丽. 硫酸盐及其组合除藻的比较分析[J]. 资源开发与市场,2008,24(12):1060-1062.WANG X L, ZHANG Y L. Kraft and combinations algae removal of a comparative analysis[J]. Resource Development & Market,2008,24(12):1060-1062. [97] ZEMMOURI H, DROUICHE M, SAYEH A, et al. Coagulation flocculation test of keddara's water dam using chitosan and sulfate aluminium[J]. Procedia Engineering,2012,33:254-260. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.1202 [98] 张谦, 刘晓冬, 邓非凡. KMnO4预氧化强化混凝沉淀对太湖高藻水DON去除研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2018,8(5):527-532.ZHANG Q, LIU X D, DENG F F. Research on removal of Taihu Lake algal source DON by KMnO4 pre-oxidation and coagulation sedimentation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2018,8(5):527-532. [99] 陈春艳, 胡晗华, 王煜, 等. 氯化铁和聚丙烯酰胺絮凝剂WT652对三角褐指藻的絮凝作用[J]. 水生生物学报,2010,34(3):669-672.CHEN C Y, HU H H, WANG Y, et al. Flocculation of phaedactylum tricornutum induced by ferric chloride and polyacrylamide flocculant WT652[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2010,34(3):669-672. [100] 刘恩生. 生物操纵与非经典生物操纵的应用分析及对策探讨[J]. 湖泊科学,2010,22(3):307-314.LIU E S. Analysis on biomanipulation, non-traditional biomanipulation and discussion of the countermeasures of biomanipuiation application in waters[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2010,22(3):307-314. [101] SHAPIRO J, WRIGHT D I. Lake restoration by biomanipulation: round Lake, Minnesota, the first two years[J]. Freshwater Biology,1984,14:371-383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.1984.tb00161.x [102] 张喜勤, 徐锐贤, 许金玉, 等. 水溞净化富营养化湖水试验研究[J]. 水资源保护,1998,14(4):32-36.ZHANG X Q, XU R X, XU J Y, et al. Experimental study on purification of eutrophic lake water by water cress[J]. Water Resources Protection,1998,14(4):32-36. [103] 刘建康, 谢平. 用鲢鳙直接控制微囊藻水华的围隔试验和湖泊实践[J]. 生态科学,2003,22(3):193-198.LIU J K, XIE P. Direct control of microcystis bloom through the use of planktivorous carp-closure experiments and lake fishery practice[J]. Ecologic Science,2003,22(3):193-198. [104] 5亿尾鲢鳙鱼吃掉太湖658万吨蓝藻实现生态经济双赢[J]. 科学养鱼, 2018(8): 52.Million silver carp and bighead carp ate 6.58 million tons of cyanobacteria in Taihu Lake to achieve eco-economic win-win situation[J]. Scientific Fish Farming, 2018(8): 52. [105] 陈少莲, 刘肖芳, 胡传林, 等. 论鲢、鳙对微囊藻的消化利用[J]. 水生生物学报,1990,14(1):49-59.CHEN S L, LIU X F, HU C L, et al. On the digestion and utilization of microcystis by fingerlings of silver carp and bighead[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,1990,14(1):49-59. [106] 此里能布, 毛建忠, 黄少峰. 经典与非经典生物操纵理论及其应用[J]. 生态科学,2012,31(1):87-91.CI L, MAO J Z, HUANG S F. Theory and application of biomanipulation and non-traditional biomanipulation[J]. Ecological Science,2012,31(1):87-91. [107] BARRETT P R F, LITTLEJOHN J W, CURNOW J. Long-term algal control in a reservoir using barley straw[M]//CAFFREY J, BARRETT PRF, FERREIRA MT, et al. Biology, ecology and management of aquatic plants. Dordrecht: Springer, 1999: 309-313. [108] 王敏, 刘浩, 王江南, 等. 生物法治理蓝藻水华研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(1):92-99.WANG M, LIU H, WANG J N, et al. Research progress on the biological control of cyanobacterial blooms[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(1):92-99. [109] PROETZEL A E. Artificial floating islands: cities of the future[J]. Theses and Major Papers, 1983: 145. [110] 刘晶晶, 彭娟莹, 吴奇. 生态浮岛技术的研究现状及展望[J]. 湖南农业科学,2014(15):47-49.LIU J J, PENG J Y, WU Q. Research status and prospect of ecological floating island technology[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2014(15):47-49. [111] 和丽萍. 利用化学杀藻剂控制滇池蓝藻水华研究[J]. 云南环境科学,2001,20(2):43-44.HE L P. Control blue algal bloom by using algaecide[J]. Yunnan Environmental Science,2001,20(2):43-44. [112] 宁平, 朱易, 徐小军. 三氯化铁在滇池蓝藻爆发期除藻中的应用研究[J]. 农业环境保护,2001,20(5):348-350.NING P, ZHU Y, XU X J. Application of ferric chloride in removal of blue algae at algal eruptive period in Dianchi Lake[J]. Agro-Environmental Protection,2001,20(5):348-350. [113] 赵祥华, 田军. 人工浮岛技术在云南湖泊治理中的意义及技术研究[J]. 云南环境科学,2005(增刊1):130-132. ⊗ -




 下载:
下载: