Study on zoning of ecological protection and restoration based on ecological assessment: taking Qinghai Lake Basin as an example
-
摘要:
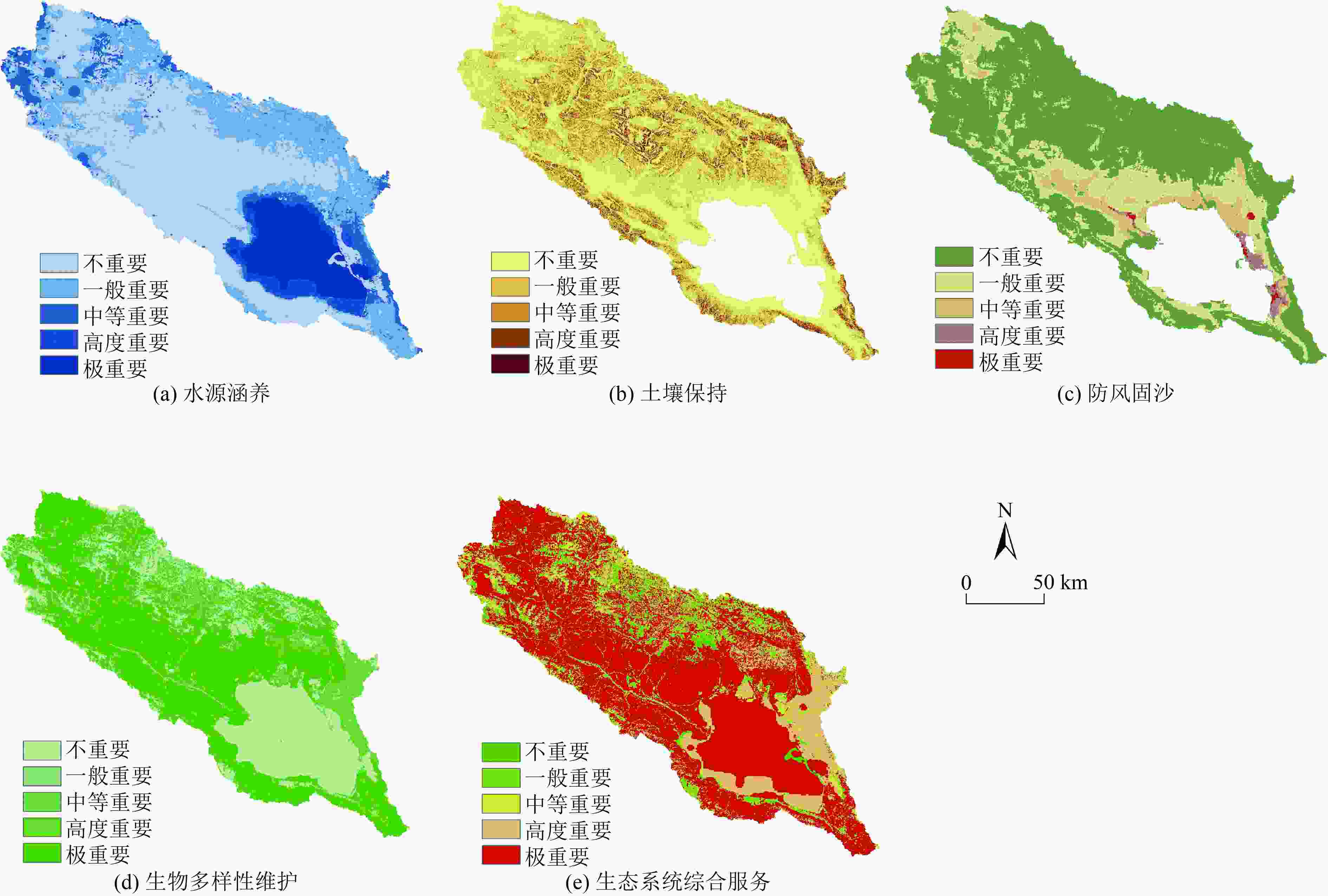
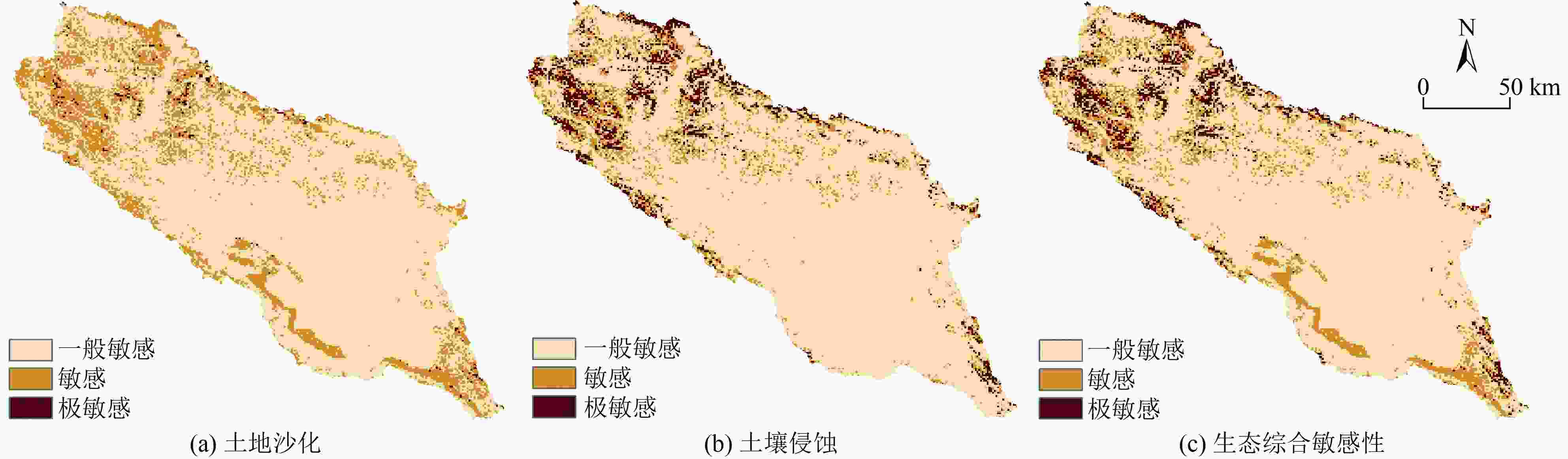
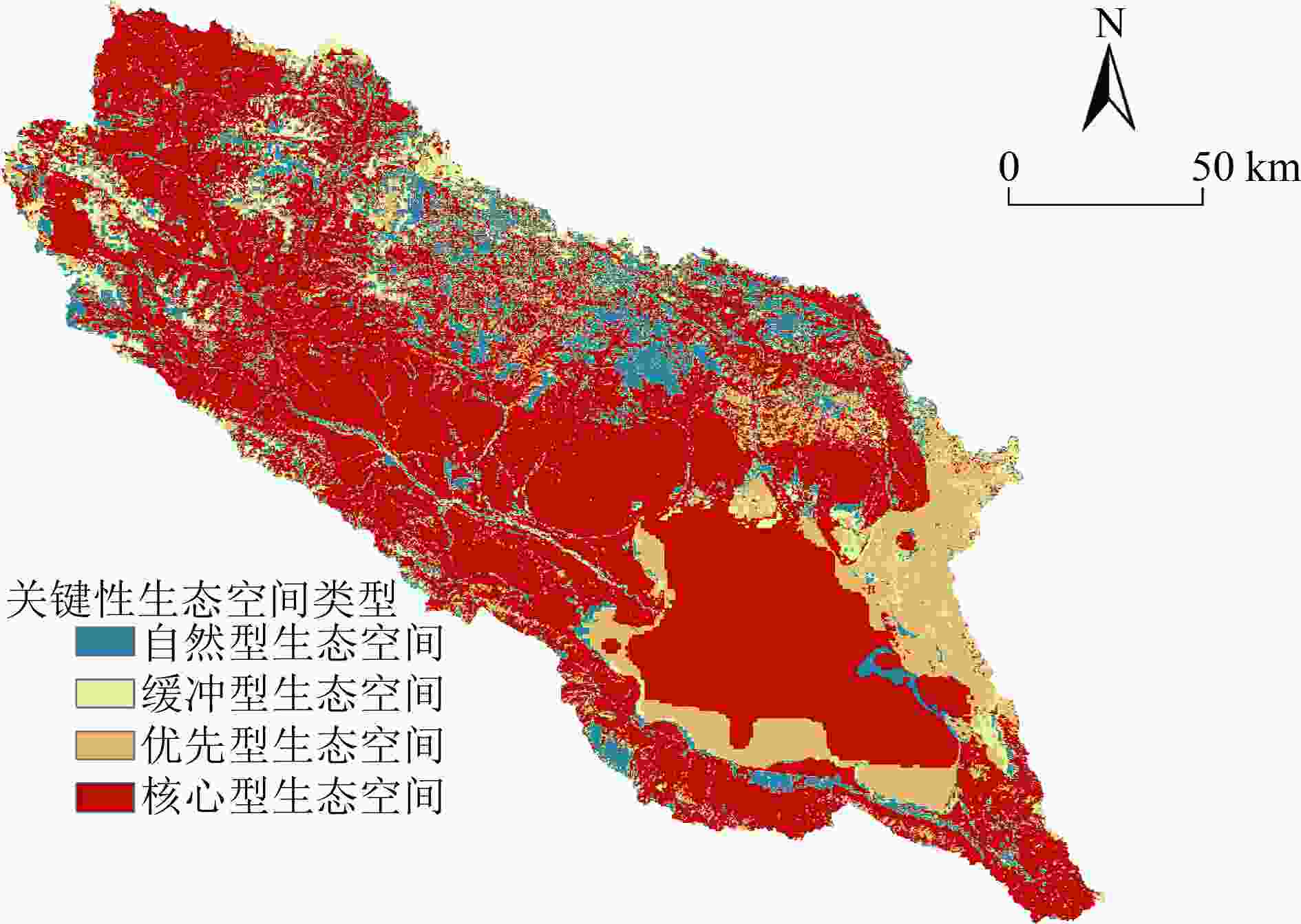
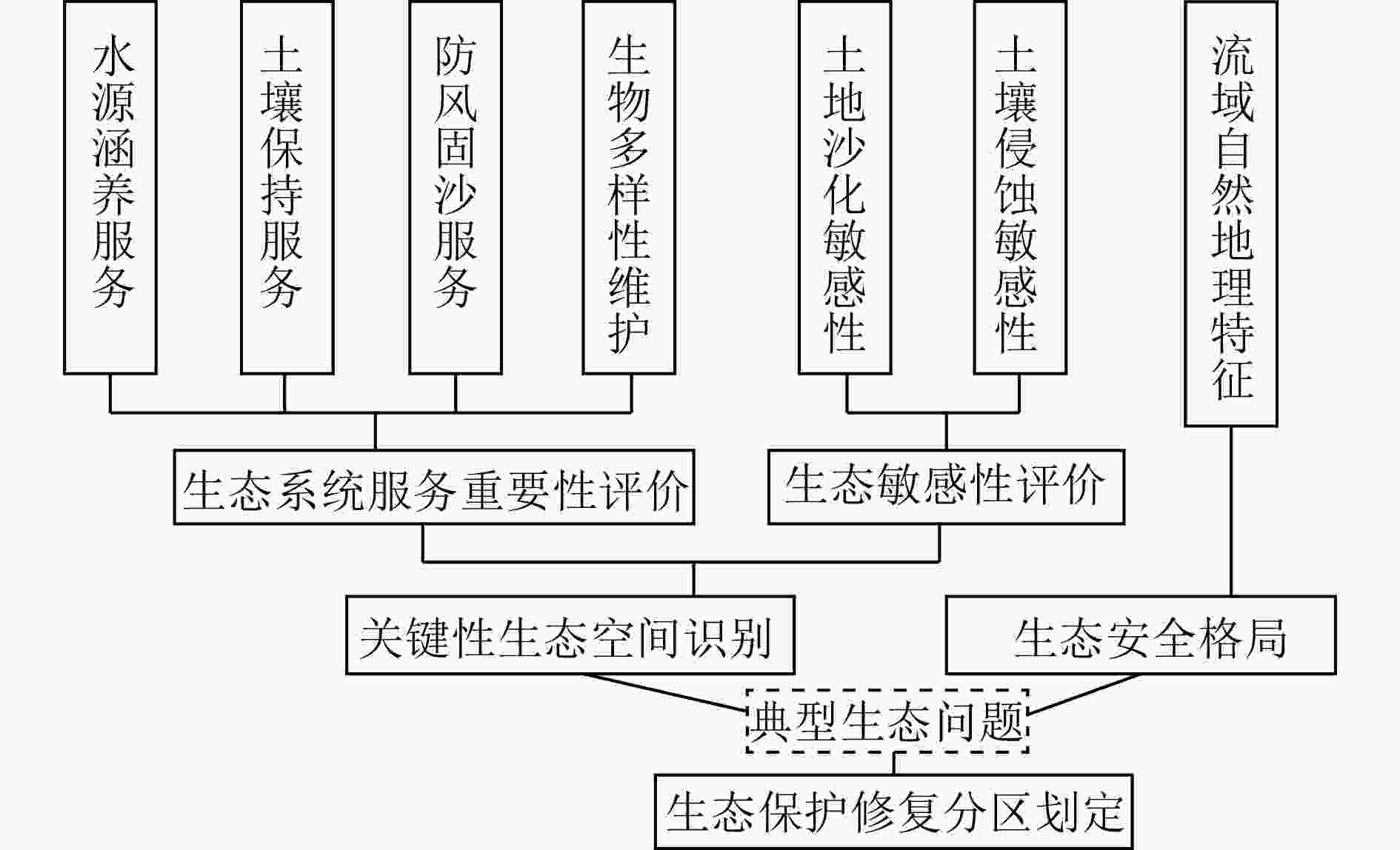
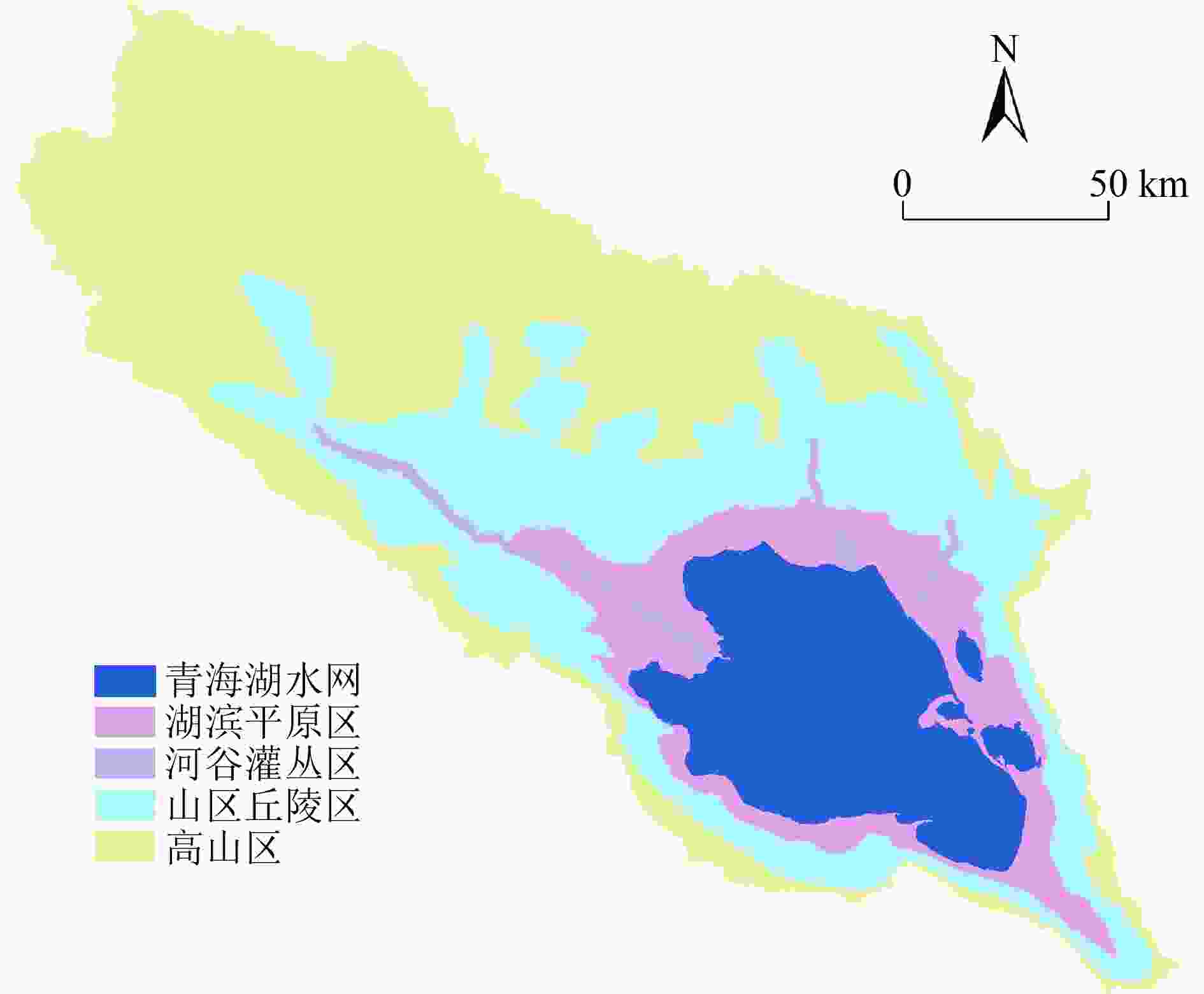
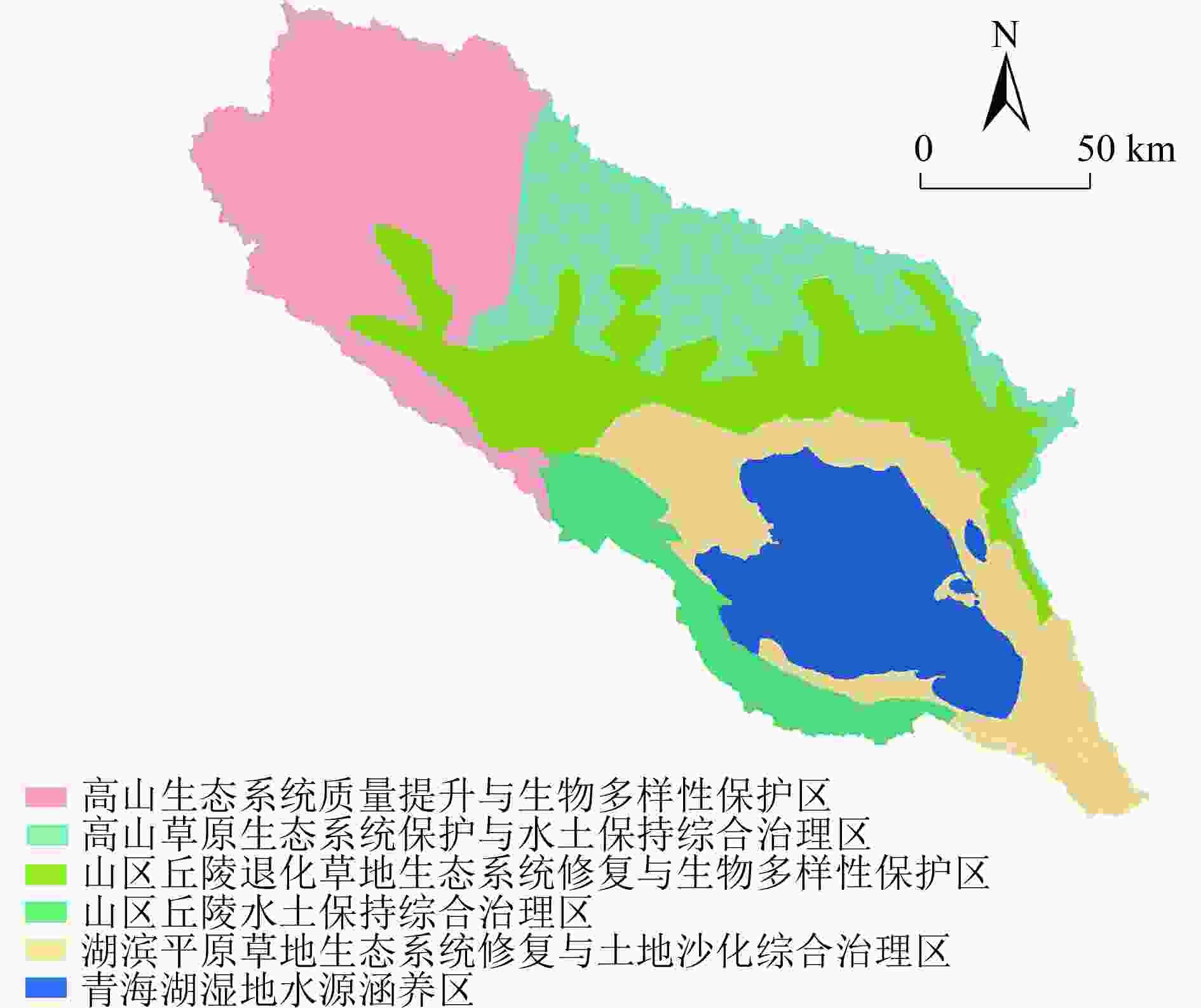
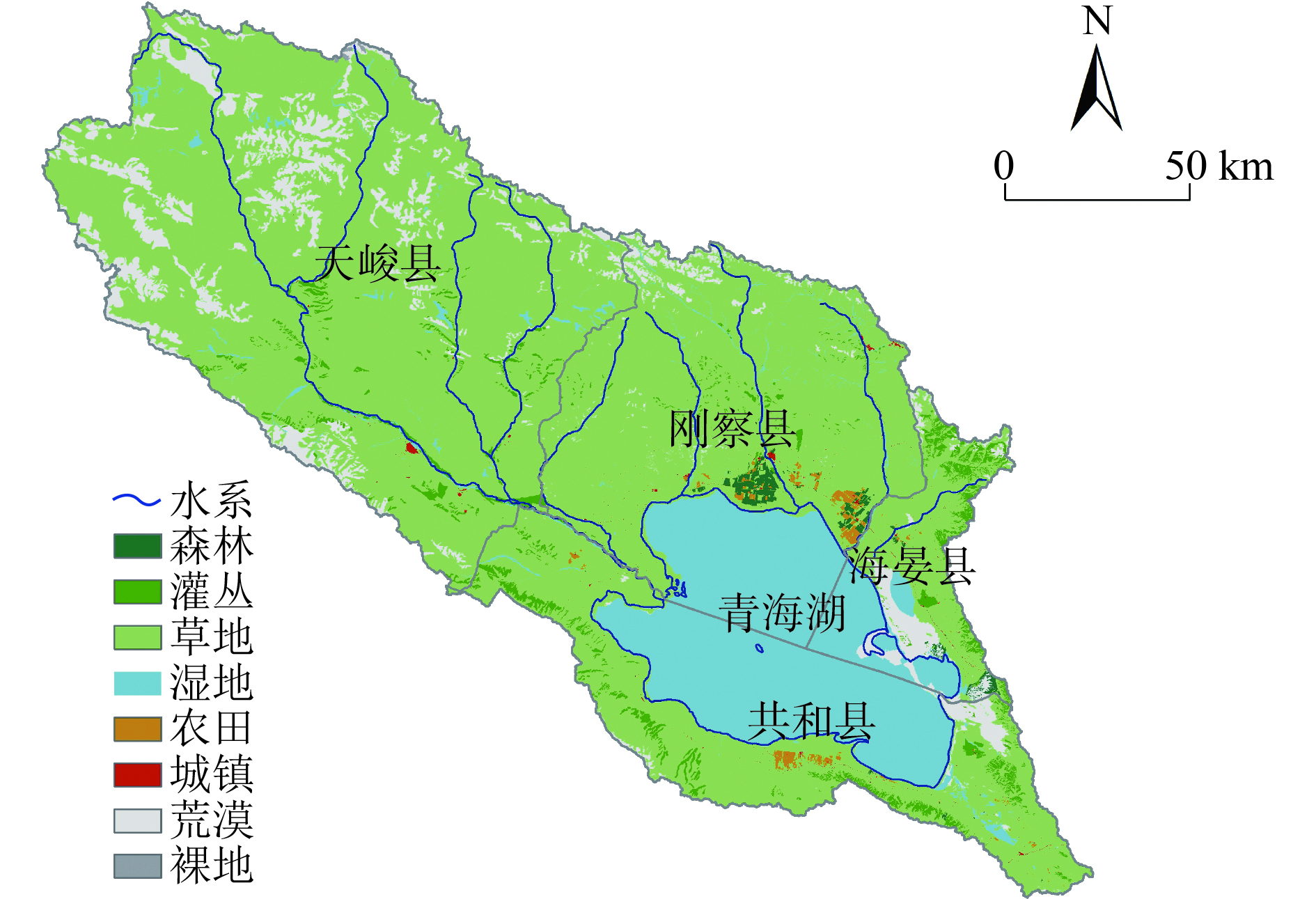
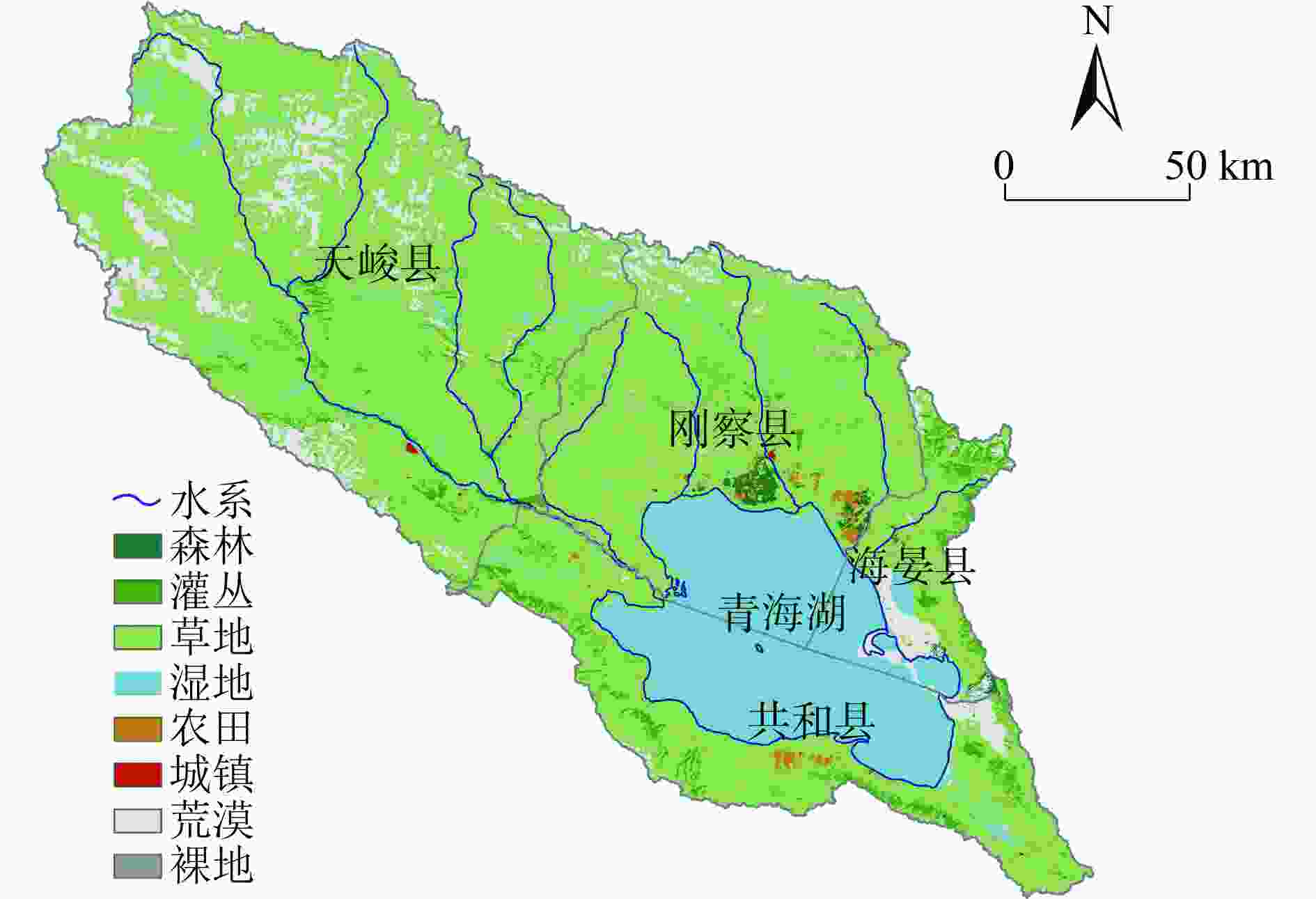
针对我国生态脆弱区生态保护修复问题,以青海湖流域为例,在生态系统服务重要性和生态敏感性基础上识别关键性生态空间,同时结合流域生态安全格局及典型生态问题,划定生态保护修复分区,并提出不同分区的修复策略。结果表明:青海湖流域内生态系统服务极重要区占流域总面积的63.2%,生态极敏感区占流域总面积的6.55%;青海湖流域的核心型生态空间面积为18 746.72 km2,优先型生态空间面积为5 324.26 km2,其共同构成的关键性生态空间占流域总面积的81.15%;根据流域上中下游、地形等实际自然地理特征,提出构建青海湖流域“一网四区”的生态安全格局,结合生态安全格局和关键性生态空间及典型生态问题,将青海湖流域划定为6个生态保护修复分区,并有针对性地提出生物多样性保护、构筑湿地生态系统网络和水土保持等工程措施。
Abstract:In view of the ecological protection and restoration in China's ecologically vulnerable areas, taking Qinghai Lake Basin as an example, key ecological spaces were identified by evaluating the importance of ecosystem services and ecological sensitivity. At the same time, ecological protection and restoration zones were delimited based on the ecological security pattern and typical ecological problems of the basin, and the restoration strategies for different zones were proposed. The results showed that: 1) The area of extremely important ecosystem services in the basin accounted for about 63.2% of the total basin area, and the area of extremely sensitive ecological zones accounted for 6.55% of the total basin area. 2) The area of core ecological space in Qinghai Lake Basin was 18 746.72 km2 and the area of priority ecological space was 5 324.26 km2, which together constituted the critical ecological space area accounting for 81.15% of the total area of the basin. 3) According to the natural geographic features of the upper, middle and lower reaches of the basin and the topography, the ecological security pattern of the basin was constructed as "one network and four zones". Based on the ecological security pattern, key ecological space and typical ecological problems, Qinghai Lake Basin was divided into six ecological protection and restoration sub-zones, and engineering measures such as biodiversity protection, construction of wetland ecosystem network and soil and water conservation were put forward.
-
表 1 青海湖流域不同生态系统服务类型评价等级面积及占比
Table 1. Area and percentage of valuation classes of different ecosystem service types in Qinghai Lake Basin
生态系统服务类型 极重要 高度重要 中等重要 一般重要 不重要 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 水源涵养 3 430.22 11.56 1 394.67 4.70 1 980.25 6.68 8 030.71 27.08 14 825.15 49.98 土壤保持 463.58 1.56 1 404.90 4.74 2 918.47 9.84 5 547.41 18.70 14 685.80 49.51 防风固沙 80.87 0.27 328.48 1.11 1 601.95 5.40 6 088.37 20.53 16 920.49 57.04 生物多样性维护 15 080.50 50.84 3 765.15 12.69 1 531.94 5.17 1 265.96 4.27 8 017.45 27.03 生态系统综合服务 18 745.67 63.20 5 167.56 17.42 2157.69 7.28 2 453.61 8.27 1 136.47 3.83 表 2 青海湖流域不同生态敏感性评价等级面积及占比
Table 2. Area and percentage of different ecological sensitivity evaluation classes in Qinghai Lake Basin
生态敏感性
类型极敏感 敏感 一般敏感 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 土地沙化 237.00 0.80 5 861.81 19.76 23 562.19 79.44 土壤侵蚀 1 923.82 6.49 3 142.12 10.59 24 595.06 82.92 综合敏感性 1 939.81 6.55 4 159.00 14.02 23 562.19 79.43 表 3 青海湖流域生态空间划定结果
Table 3. Delimitation results of ecological space in Qinghai Lake Basin
-
[1] HU T, PENG J, LIU Y X, et al. Evidence of green space sparing to ecosystem service improvement in urban regions: a case study of China's Ecological Red Line policy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,251:119678. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119678 [2] LIU Y, ZHAO W W, LIU Y X, et al. Global rainfall erosivity changes between 1980 and 2017 based on an erosivity model using daily precipitation data[J]. CATENA,2020,194:104768. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104768 [3] LI Q, ZHOU Y, YI S Q. An integrated approach to constructing ecological security patterns and identifying ecological restoration and protection areas: a case study of Jingmen, China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2022,137:108723. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108723 [4] TAO Q, GAO G H, XI H H, et al. An integrated evaluation framework for multiscale ecological protection and restoration based on multi-scenario trade-offs of ecosystem services: case study of Nanjing City, China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2022,140:108962. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108962 [5] 中共中央文献研究室. 习近平关于社会主义生态文明建设论述摘编[M]. 北京: 中央文献出版社, 2017: 47-56. [6] 中共中央宣传部,中共中央党史和文献研究院,中国外文出版发行事业局. 习近平谈治国理政: 第3卷[M]. 北京: 外文出版社, 2020: 359-369. [7] 蔡海生, 陈艺, 查东平, 等. 基于主导功能的国土空间生态修复分区的原理与方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(15):261-270. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.15.032CAI H S, CHEN Y, ZHA D P, et al. Principle and method for ecological restoration zoning of territorial space based on the dominant function[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(15):261-270. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.15.032 [8] WANG L, MAO X F, SONG X H, et al. How rising water levels altered ecosystem provisioning services of the area around Qinghai Lake from 2000 to 2020: an InVEST-RF-GTWR combined method[J]. Land,2022,11(9):1570. doi: 10.3390/land11091570 [9] 卢慧, 陈克龙, 曹生奎, 等. 青海湖流域生态系统服务功能与价值评估[J]. 生态经济,2011,27(11):145-147.LU H, CHEN K L, CAO S K, et al. Ecosystem services and its value evaluation of Qinghai Lake watershed[J]. Ecological Economy,2011,27(11):145-147. [10] 蒋红波, 覃盟琳, 王政强, 等. 基于生态系统服务簇评价的长沙市生态修复优先区识别[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(4):1325-1333. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220983JIANG H B, QIN M L, WANG Z Q, et al. Identification of priority areas for ecological restoration based on evaluation of ecosystem service bundles: taking Changsha City as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(4):1325-1333. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220983 [11] 欧阳志云, 王效科, 苗鸿. 中国生态环境敏感性及其区域差异规律研究[J]. 生态学报,2000,20(1):9-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.01.002OUYANG Z Y, WANG X K, MIAO H. China's eco-environmental sensitivity and its spatial heterogeneity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2000,20(1):9-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.01.002 [12] 田浩, 刘琳, 张正勇, 等. 天山北坡经济带关键性生态空间评价[J]. 生态学报,2021,41(1):401-414.TIAN H, LIU L, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Evaluation on the critical ecological space of the economic belt of Tianshan northslope[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(1):401-414. [13] 孔令桥, 郑华, 欧阳志云. 基于生态系统服务视角的山水林田湖草生态保护与修复: 以洞庭湖流域为例[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(23):8903-8910.KONG L Q, ZHENG H, OUYANG Z Y. Ecological protection and restoration of forest, wetland, grassland and cropland based on the perspective of ecosystem services: a case study in Dongting Lake Watershed[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(23):8903-8910. [14] ZHANG T, CAO G C, CAO S K, et al. Dynamic assessment of the value of vegetation carbon fixation and oxygen release services in Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(2):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2016.12.005 [15] CAO S K, CAO G C, HAN G Z, et al. Comparison of evapotranspiration between two alpine type wetland ecosystems in Qinghai Lake basin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology,2020,20(2):215-229. [16] 环境保护部, 国家发展和改革委员会. 生态保护红线划定指南: 环办生态〔2017〕48号[A/OL]. [2023-05-16]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/5c6fe57751e2524de518964bcf84b9d529ea2c4f.html?_wkts_=1698911823830. [17] 方臣, 匡华, 贾琦琪, 等. 基于生态系统服务重要性和生态敏感性的武汉市生态安全格局评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1446-1454. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210335FANG C, KUANG H, JIA Q Q, et al. Evaluation of ecological security pattern in Wuhan City based on the importance of ecosystem services and ecological sensitivity[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1446-1454. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210335 [18] REDHEAD J W, STRATFORD C, SHARPS K, et al. Empirical validation of the InVEST water yield ecosystem service model at a national scale[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,569/570:1418-1426. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.227 [19] 李杰, 贾坤, 张宁, 等. 基于遥感与生态服务模型的青岛市生态保护重要性评价[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2021,36(6):1329-1338.LI J, JIA K, ZHANG N, et al. Evaluation of ecological protection importance in Qingdao based on remote sensing and ecological service model[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2021,36(6):1329-1338. [20] 孙丽慧, 刘浩, 汪丁, 等. 基于生态系统服务与生态环境敏感性评价的生态安全格局构建研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(11):2508-2517.SUN L H, LIU H, WANG D, et al. Research on ecological security pattern construction based on the evaluation of ecosystem services and eco-environmental sensitivity[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(11):2508-2517. [21] 李恒凯, 李淑芳, 郑春燕, 等. 基于生态系统服务功能的东江流域关键性生态空间识别[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(3):257-266. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.03.030LI H K, LI S F, ZHENG C Y, et al. Identification of the critical ecological spaces in the Dongjiang River Basin based on ecosystem service function[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(3):257-266. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.03.030 [22] 袁骞骞. 基于多源遥感数据的青海湖流域生态环境变化研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2017. [23] 陈兴芳. 基于USLE模型的青海湖流域土壤侵蚀现状评价[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2012. [24] 赵明月, 赵文武, 靳婷, 等. 青海湖流域土地沙漠化敏感性评价[J]. 中国农学通报,2012,28(32):237-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.32.041ZHAO M Y, ZHAO W W, JIN T, et al. Land desertification sensitivity evaluation in Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(32):237-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.32.041 [25] 赵明月, 赵文武, 安艺明, 等. 青海湖流域土壤侵蚀敏感性评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2012,10(2):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2012.02.003ZHAO M Y, ZHAO W W, AN Y M, et al. Sensitivity evaluation of soil erosion in Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,10(2):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2012.02.003 [26] 习近平. 论坚持人与自然和谐共生[M]. 北京: 中央文献出版社, 2022: 193-199. [27] 张明. 基于遥感数据的青海湖流域土地沙漠化评价研究[J]. 国土与自然资源研究,2016(3):35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2016.03.010ZHANG M. Indicator system and assessment of land desertification in Qinghai-Lake area based on remote sensing[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Study,2016(3):35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2016.03.010 [28] 张明, 欧阳琰. 基于遥感数据的青海湖流域生物多样性评价研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展,2017,42(2):148-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2017.02.046ZHANG M, OUYANG Y. Indicator system and assessment of biodiversity in Qinghai Lake Area based on remote sensing[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development,2017,42(2):148-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2017.02.046 [29] ROUGET M, COWLING R M, PRESSEY R L, et al. Identifying spatial components of ecological and evolutionary processes for regional conservation planning in the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa[J]. Diversity and Distributions,2003,9(3):191-210. ◇ doi: 10.1046/j.1472-4642.2003.00025.x -




 下载:
下载: