Study on the differences in the remediating effects of different formulations of bacterial agents on black and odorous water bodies and sediments
-
摘要:
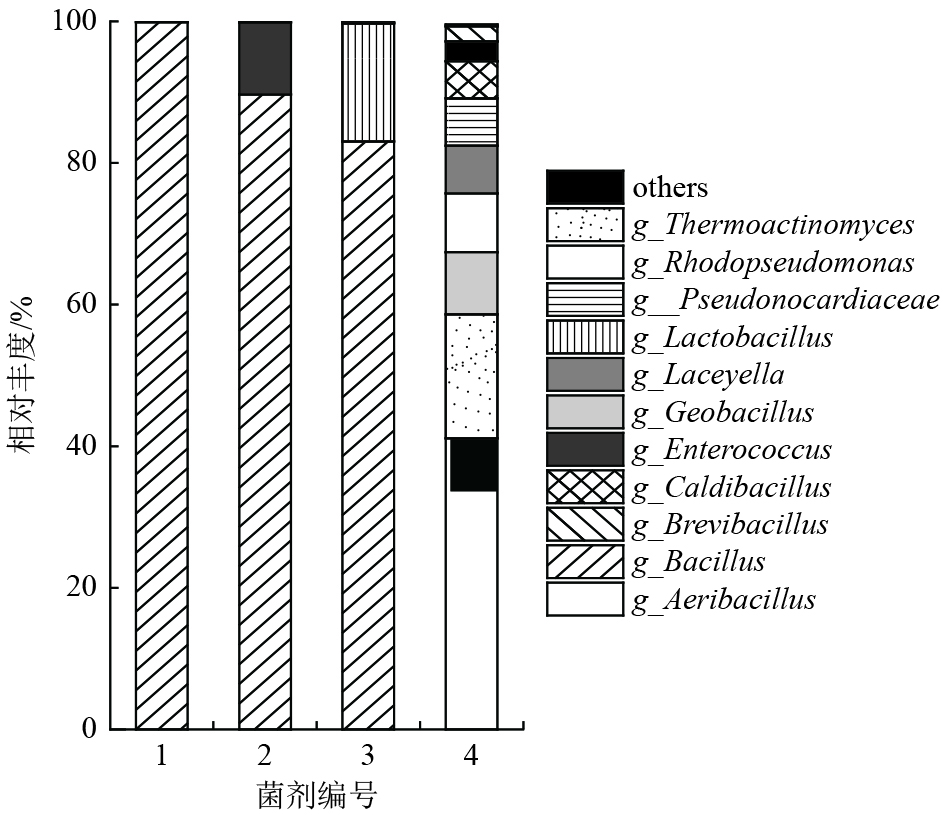
为探究不同菌剂对黑臭水体的修复效果,揭示研究过程中微生物群落变化规律,采用不同配方菌剂对黑臭水体进行修复,探讨不同菌剂对上覆水、底泥和微生物的影响。结果表明:投加菌剂组上覆水pH均略高于试验前;化学-复合微生物菌剂组上覆水DO浓度略低于空白组(6.95 mg/L),且上覆水NH4 +-N和TP去除率分别达到86.60%和66.07%,底泥酸可挥发性硫和有机质去除率分别达到79.20%和52.71%,去除效果均明显优于其他试验组;高通量测序表明,投加菌剂组底泥中硝化、反硝化细菌和有机质降解类细菌均具有较高相对丰度,且Vicinamibacterales下的某属在化学-复合微生物菌剂组中的相对丰度明显高于其他试验组(1.07%~2.18%)。研究显示化学-复合微生物菌剂对黑臭水体具有良好修复效果。
Abstract:In order to explore the remediation effect of different bacterial agents on black and odorous water bodies, and reveal the changing law of microbial communities during the research process, different formulations of bacterial agents were used to restore black and odorous water bodies, and the effects of different bacterial agents on overlying water, sediment and microorganisms were discussed. The results showed that the pH of the overlying water in the bacterial agent group was slightly higher than that before the experiment. DO concentration in the overlying water of the chemical-composite microbial agent group was slightly lower than that of the blank group (6.95 mg/L), and the removal rates of NH4 +-N and TP in the overlying water reached 86.60% and 66.07%, while the removal rates of volatile sulfur (AVS) and organic matter in the sediment reached 79.20% and 52.71%, respectively. The removal effects were significantly better than other experimental groups. High-throughput sequencing showed that nitrifying bacteria、denitrifying bacteria and organic matter degrading bacteria in the sediment of the microbial inoculum group had high relative abundance, and the relative abundance of a genus under Vicinamibacterales in the chemical-compound microbial inoculum group was significantly higher than that in other experimental groups (1.07%-2.18%). The results of this study indicate that the chemical composite microbial agent has a good remediation effect on black and odorous water bodies.
-
表 1 市售菌剂性质
Table 1. List of properties of commercially available microbial agents
分类 菌剂 组成 性状 用途 复合微生物菌剂 菌剂1 复合菌种、营养剂等 黄色固体粉末 用于轻污染水体,提高水体透明度,改善水色,
提升水体自净能力菌剂2 复合菌种、营养剂等 黄色固体粉末 用于黑臭、富营养化等污染严重水体治理,
提高水体自净能力化学-纯微生物菌剂 菌剂3 枯草芽孢杆菌、有机载体、
碳酸钙、蛋白质等黄色固体粉末,活菌数约
1130亿/g用于河道、市政、生活等污水的处理 菌剂4 光合细菌、沸石粉 黄色固体粉末,有效菌
含量约100 cfu/g用于调水净水,增加DO浓度 表 2 上覆水及底泥污染物指标
Table 2. Pollutant indicators of overlying water and sediment
项目 指标 数值 上覆水 pH 7.68~7.83 DO/(mg/L) 7.12~7.97 NH4 +-N/(mg/L) 1.35~1.81 CODCr/(mg/L) 43.33~69.44 TP/(mg/L) 0.51~0.59 底泥 AVS/(mg/kg) 553.59~554.87 有机质/(mg/kg) 9.40~9.53 表 3 试验组中投加的菌剂种类及数量
Table 3. Type and quantity of microbial agents added in the experimental group
试验组 投加菌剂 投加量/(g/L) 1 无 0 2 自制菌剂 2.30 3 菌剂1 0.10 4 菌剂2 0.10 5 菌剂3 0.20 6 菌剂4 0.50 -
[1] 汤茵琪, 常素云, 许伟, 等. 投菌法对天津护仓河底泥修复的试验研究[J]. 化学工程,2017,45(8):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.08.001TANG Y Q, CHANG S Y, XU W, et al. Evaluation of microbial inoculums addition on remediation of sediment in Hucang River[J]. Chemical Engineering,2017,45(8):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.08.001 [2] 唐伟, 张远, 王书平, 等. 微生物菌剂在水体修复中的应用进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(2):151-158. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2018.11.050TANG W, ZHANG Y, WANG S P, et al. Application progress of microbial agents in water remediation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(2):151-158. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2018.11.050 [3] SHENG Y Q, QU Y X, DING C F, et al. A combined application of different engineering and biological techniques to remediate a heavily polluted river[J]. Ecological Engineering,2013,57:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.04.004 [4] ZHANG X P, SHU M A, WANG Y B, et al. Effect of photosynthetic bacteria on water quality and microbiota in grass carp culture[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechonlogy,2014,30(9):2523-2531. [5] 田鹏飞, 孙宝盛, 李盈利, 等. 复合微生物修复受轻度污染河水的试验研究[J]. 中国给水排水,2011,27(19):57-59. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2011.19.018TIAN P F, SUN B S, LI Y L, et al. Experimental study on bioremediation of slightly polluted river water using compound microorganism[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2011,27(19):57-59. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2011.19.018 [6] 金位栋, 焦巨龙, 李剑屏, 等. 微生物菌剂强化A/O脱氮反应器运行效果及微生物群落变化[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):354-364. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200083JIN W D, JIAO J L, LI J P, et al. Operation effect and microbial community changes of A∕O denitrification reactor enhanced by microbial agents[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):354-364. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200083 [7] 杜聪, 冯胜, 张毅敏, 等. 微生物菌剂对黑臭水体水质改善及生物多样性修复效果研究[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(8):1-7. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201808001DU C, FENG S, ZHANG Y M, et al. Study on the improvement of water quality and biological diversity of black and odorous water by microbial inoculants[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(8):1-7. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201808001 [8] 袁芬. 过氧化钙原位修复黑臭底泥对上覆水体的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [9] 孙井梅, 刘晓朵, 汤茵琪, 等. 微生物-生物促生剂协同修复河道底泥: 促生剂投量对修复效果的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2019,39(1):351-357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.01.041SUN J M, LIU X D, TANG Y Q, et al. Microorganism and biostimulant collaboratively remediate river sediment: influence of biostimulant quantity on repair performance[J]. China Environmental Science,2019,39(1):351-357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.01.041 [10] 辛慧敏, 林建伟, 詹艳慧. 反硝化细菌、硝酸钙和锆改性沸石联用对底泥中氮磷迁移转化的影响及硝态氮释放风险评估[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(4):1847-1860. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008175XIN H M, LIN J W, ZHAN Y H. Effect of the combined use of denitrifying bacteria, calcium nitrate, and zirconium-modified zeolite on the mobilization of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments and evaluation of its nitrate-nitrogen releasing risk[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(4):1847-1860. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008175 [11] 吴越. 过氧化钙联合微生物菌剂治理黑臭水体的探究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021. [12] 唐露. 复合微生物原位修复黑臭河道底泥试验研究[D]. 西安: 西安工程大学, 2019. [13] 李宁, 吴琼, 罗欢, 等. 硝酸钙-微生物协同缓释颗粒原位修复污染底泥[J]. 环境科技,2022,35(6):6-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2022.06.002LI N, WU Q, LUO H, et al. In-situ remediation of contaminated sediment with calcium nitrate coupled microbial sustained-release granular[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2022,35(6):6-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2022.06.002 [14] 宁梓洁, 王鑫. 黑臭水体治理技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(8):26-29. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201808005NING X J, WANG X. Overview of the black-odorous waters treatment technologies[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(8):26-29. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201808005 [15] 许峥, 陈宇, 后志, 等. 不同纯生物菌剂对黑臭水体底泥的处理效果[J]. 中国给水排水,2021,37(1):102-108. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2021.01.017XU Z, CHEN Y, HOU Z, et al. Treatment efficiency of black and odorous water body sediment with different biological agents[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2021,37(1):102-108. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2021.01.017 [16] 唐玉兰, 董畅, 马悦, 等. 微生物菌剂在污染水体处理中的研究进展[J/OL]. 三峡生态环境监测: 1-15. [2023-07-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1214.X.20210521.1051.002.html.TANG Y L, DONG C, MA Y, et al. Treatment Research progress of microbial agents in the treatment of polluted water bodies[J/OL]. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges: 1-15. [2023-07-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1214.X.20210521.1051.002.html. [17] 陈重军, 潘钰伟, 谢嘉玮, 等. 河流污染底泥原位覆盖材料及其应用研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(1):100-109. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210107CHEN C J, PAN Y W, XIE J W, et al. Research progress of in situ covering materials for river polluted sediment and their applications[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(1):100-109. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210107 [18] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 200-285. [19] 胡彩莉, 马玉贞, 郭超, 等. 烧失量法测定土壤有机质含量的实验条件探究[J]. 地球与环境,2016,44(1):110-118. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2016.01.015HU C L, MA Y Z, GUO C, et al. Optimization of the experiment conditions for estimating organic matter content with loss-on-ignition method[J]. Earth and Environment,2016,44(1):110-118. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2016.01.015 [20] 徐桂茹. 沉积物中硫的形态分析及其应用[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2016. [21] 吴闪闪, 刘付文晓, 许志国, 等. 硝酸钙缓释颗粒原位修复黑臭底泥的作用机制及其应用[J]. 环境工程学报,2022,16(7):2198-2207. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202109158WU S S, LIU F W X, XU Z G, et al. Mechanism and application of in situ remediation of black and smelly sediment by calcium nitrate sustained-release particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2022,16(7):2198-2207. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202109158 [22] 王莉, 李亭亭, 刘萌硕, 等. 曝气联合菌剂对农村黑臭水体治理效果研究[J]. 工业水处理,2021,41(10):61-66. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2020-1265WANG L, LI T T, LIU M S, et al. Treatment effect of aeration combined with bacteriological agent on rural black and odorous water body[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,2021,41(10):61-66. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2020-1265 [23] 张华俊, 李森, 张莉, 等. 不同原位处理对黑臭底泥污染物抑制效果分析[J]. 环境工程,2019,37(6):37-41. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201906008ZHANG H J, LI S, ZHANG L, et al. Analysis on black-odor sediment pollutant inhibition effect of different in-situ treatment methods[J]. Environmental Engineering,2019,37(6):37-41. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201906008 [24] 莫华涛, 李海翔, 杨敏, 等. 基于硝酸盐缓释-功能微生物协同的污染底泥原位修复技术研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1451-1458. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.27MO H T, LI H X, YANG M, et al. In -situ remediation of contaminated sediment based on nitrate slow release-functional microbial compounding[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(6):1451-1458. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.27 [25] 刘珍珠, 樊振, 刘欢欢, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌的筛选及其与光合细菌复配对养殖水体的净化[J]. 江苏农业科学,2020,48(6):164-167. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.06.033LIU Z Z, FAN Z, LIU H H, et al. Screening of Bacillus subtilis and purification of aquaculture water by Bacillus subtilis and photosynthetic bacteria[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(6):164-167. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.06.033 [26] 杭小英, 叶雪平, 施伟达, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌制剂对罗氏沼虾养殖池塘水质的影响[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版),2008(2):197-200.HANG X Y, YE X P, SHI W D, et al. Effects of the biological preparation on the Shrimp (macrobrachium rosenbergii) Ponds' water quality[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science),2008(2):197-200. [27] 张给禄. 原位化学法对黑臭水体及底泥的修复研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021. [28] LIN L, LI Z, SONG X, et al. Preparation of chitosan/lanthanum hydroxide composite aerogel beads for higher phosphorus adsorption[J]. Materials Letters,2018,218:201-204. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.02.014 [29] YAMADA T M, SUEITT A P E, BERALDO D A S, et al. Calcium nitrate addition to control the internal load of phosphorus from sediments of a tropical eutrophic reservoir: Microcosm experiments[J]. Water Research,2012,46(19):6463-6475. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.018 [30] TANG Y, LI M, ZOU Y, et al. Mechanism of aerobic denitrifiers and calcium nitrate on urban river sediment remediation[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation,2018,126:119-130. [31] 刘晓朵, 孙井梅, 汤茵琪, 等. 促生剂投量对菌剂-促生剂协同修复沉积物的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2019,39(6):1825-1833. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0043LIU X D, SUN J M, TANG Y Q, et al. Effects of biostimulant dosage on the remediation of sediments in the collaborative repair of aerobic denitrifiers and biostimulant[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2019,39(6):1825-1833. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0043 [32] YAMADA T, SEKIGUCHI Y, IMACHI H, et al. Diversity, localization, and physiological properties of filamentous microbes belonging to Chloroflexi Subphylum I in mesophilic and thermophilic methanogenic sludge granules[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(11):7493-7503. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.7493-7503.2005 [33] LIU Q, LIU H C, ZHOU Y G, et al. Stenotrophobium rhamnosiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a glacier, proposal of Steroidobacteraceae fam. nov. in Nevskiales and emended description of the family Nevskiaceae[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 2019, 69(5): 1404-1410. [34] HUBER K J, GEPPERT A M, WANNER G, et al. The first representative of the globally widespread subdivision 6 Acidobacteria, Vicinamibacter silvestris gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from subtropical savannah soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 2016, 66(8): 2971-2979. [35] 曹洋, 孙鹤铭, 刘利, 等. 冬季衡水湖沉积物微生物群落结构特征及影响因素[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):154-163. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210652CAO Y, SUN H M, LIU L, et al. Microbial community structure characteristics and influencing factors in sediments of Hengshui Lake in winter[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):154-163. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210652 [36] FONSECA A, ESPINOZA C, NIELSEN L P, et al. Bacterial community of sediments under the Eastern Boundary Current System shows high microdiversity and a latitudinal spatial pattern[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,13:1016418. ⊕ doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1016418 -





 下载:
下载: