Phosphorus morphology characteristics and its response to climate change in Xingkai Lake
-
摘要:
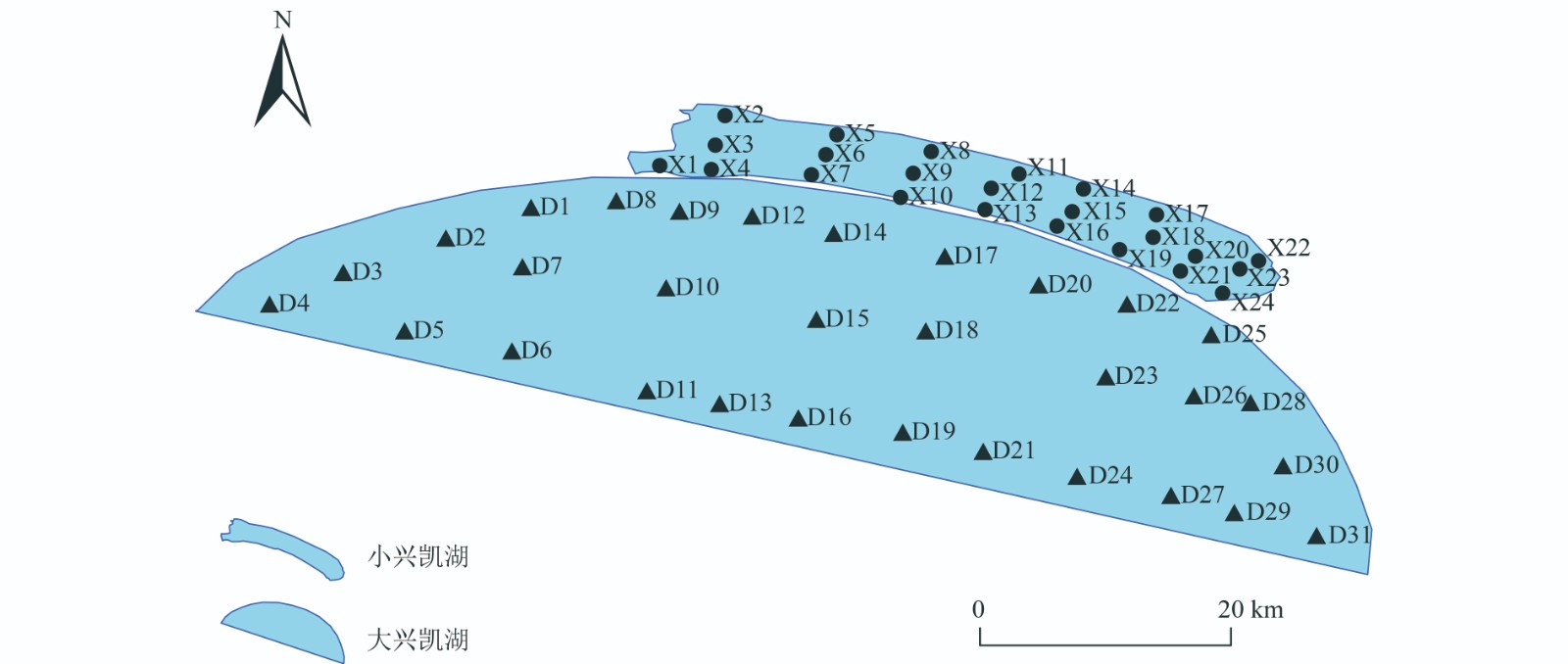
兴凯湖是亚洲东北部最大的淡水湖,水体总磷(TP)浓度超标是近年来兴凯湖水质下降的主要原因,气候可能对区域水质有重要的影响。以兴凯湖中国湖区为研究区域,通过分析兴凯湖水体磷素时空变化特征,探究其主要组成形态,明确区域内气候因子变化对兴凯湖水体TP浓度的影响。结果表明:1)2010—2021年,兴凯湖水体TP浓度整体呈先降后升的趋势,冰封期水质状况优于非冰封期,大兴凯湖TP浓度相较于小兴凯湖更高。2)2022年5月磷形态数据表明,大、小兴凯湖水体TP主要由颗粒态磷(PP)组成(占比为60%和76%),PP是大、小兴凯湖TP超标的主要形态;小兴凯湖的PP与溶解磷浓度表现为北部高于南部,大兴凯湖PP浓度总体表现为东部高于西部,溶解磷浓度则呈相反趋势。3)近年来兴凯湖流域的气温及降水量均呈上升趋势,小兴凯湖TP浓度与气温、降水量均呈显著正相关,气温与降水增加可能会导致更多的营养盐进入水体,造成水质下降;大兴凯湖TP浓度与气候变化无明显相关性,但小兴凯湖与大兴凯湖的TP浓度之间呈显著正相关,表明大兴凯湖受区域气候变化影响较小,但其水质状况与小兴凯湖有紧密的关联性。无论冰封期还是非冰封期,小兴凯湖水质均优于大兴凯湖,作为大兴凯湖的前置湖泊,小兴凯湖在净化上游流域面源污染方面起到了重要的作用。
Abstract:Xingkai Lake is the largest freshwater lake in northeast Asia, and its excessive concentration of total phosphorus (TP) is the main reason for the decline of water quality in Xingkai Lake in recent years. Climate change may have an important impact on regional water quality decline. Taking Chinese region of Xingkai Lake as the research area, by analyzing the temporal and spatial variation characteristics of phosphorus in the water body of Xingkai Lake, the main composition and morphology of phosphorus in the water body of Xingkai Lake were explored, and the change law of climate factors in the region and its influence on TP of the water body of Xingkai Lake were clarified. The results showed that: (1) From 2010 to 2021, the overall TP concentration change in Xingkai Lake showed a trend of first decreasing and then rising, and the water quality of Xingkai Lake in the freezing period was better than that in the non-freezing period, and TP concentration in Great Xingkai Lake was higher than that in Small Xingkai Lake. (2) The phosphorus morphology data in May 2022 showed that the TP of the water bodies in Great Xingkai Lake and Small Xingkai Lake was mainly composed of granular phosphorus (PP) (accounting for 60% and 76%, respectively), which was the main form of TP exceedance. Both the granular phosphorus and dissolved phosphorus in Small Xingkai Lake were higher in the north and lower in the south. For Great Xingkai Lake, the granular phosphorus was higher in the east than in the west, and the dissolved phosphorus showed the opposite trend. (3) In recent years, both temperature and rainfall had shown an upward trend in Xingkai Lake basin, and TP in Great Xingkai Lake had a significant positive correlation with temperature and rainfall, the increase in temperature and rainfall may lead to more nutrients entering the water body, resulting in a decrease in the quality of the water environment. There was no significant correlation between TP of Great Xingkai Lake and climate change, but there was a significant positive correlation between TP of Great Xingkai Lake and Small Xingkai Lake, indicating that Great Xingkai Lake was less affected by regional climate change, but its water quality condition was closely correlated with Small Xingkai Lake. The water quality of Small Xingkai Lake was better than that of Great Xingkai Lake no matter in the freezing or non-freezing period, and as the antecedent reservoir of Great Xingkai Lake, Small Xingkai Lake played an important role in purifying the surface source pollution in the upper watershed.
-
表 1 不同气候条件下兴凯湖水体TP浓度及超标率
Table 1. TP concentration and excess rate in Xingkai Lake under different climatic conditions
气候条件 出现
概率/%TP浓度/(mg/L) TP超标率/% 小兴
凯湖大兴
凯湖小兴
凯湖大兴
凯湖降水量
/
mm<25 35 0.07±0.04 0.08±0.04 50 63 25~50 17 0.07±0.02 0.08±0.02 69 81 ≥50 48 0.08±0.02 0.08±0.02 77 70 平均气温
/
℃<10 38 0.07±0.04 0.09±0.04 51 63 10~20 36 0.07±0.02 0.08±0.02 73 70 ≥20 26 0.08±0.02 0.08±0.02 79 79 平均风速/
(m/s)<2 25 0.08±0.02 0.09±0.02 83 87 2~3 63 0.07±0.04 0.08±0.04 66 66 >3 12 0.06±0.02 0.07±0.02 36 55 表 2 大兴凯湖水体不同磷形态浓度与其他水质指标的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis between phosphorus forms and other water quality factors in Great Xingkai Lake
指标 PP DIP DOP SS Chla pH DO EC 水深 PP 1 DIP −0.330 1 DOP −0.540** −0.155 1 SS 0.291 −0.141 0.205 1 Chla 0.241 −0.432* 0.125 0.175 1 pH −0.419* 0.169 0.127 −0.142 0.030 1 DO 0.169 0.122 −0.358* −0.116 −0.075 −0.394* 1 EC 0.341 −0.394* 0.276 0.517** 0.421* −0.283 −0.291 1 水深 −0.113 0.267 −0.197 −0.288 −0.134 −0.240 0.139 −0.259 1 注:*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。EC为电导率。 表 3 小兴凯湖水体不同磷形态浓度与其他水质指标的相关性
Table 3. Correlation between phosphorus forms and other water quality factors in Small Xingkai Lake
指标 PP DIP DOP SS Chla pH DO EC 水深 PP 1 DIP 0.479* 1 DOP −0.032 0.083 1 SS 0.110 0.151 0.196 1 Chla 0.680** 0.480* 0.404* 0.191 1 pH 0.149 −0.035 0.258 0.022 0.510* 1 DO −0.097 −0.134 −0.418* −0.043 −0.237 −0.128 1 EC 0.010 0.018 0.270 0.105 −0.031 −0.309 −0.326 1 水深 0.221 0.456* 0.039 0.403 0.329 0.368 0.200 −0.044 1 注:*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。EC为电导率。 表 4 兴凯湖流域气候因子与湖泊水体TP浓度相关性
Table 4. Correlation between climatic factors in Xingkai Lake area and TP in the lake body
因子 气温 降水量 最大风速 平均风速 温差 小兴凯
湖TP
浓度大兴凯
湖TP
浓度气温 1 降水量 0.734** 1 最大
风速−0.669** −0.458** 1 平均
风速−0.640** −0.382** −0.942** 1 温差 −0.067 −0.299** 0.398** 0.272* 1 小兴凯
湖TP浓度0.381** 0.330** −0.370** −0.412** −0.076 1 大兴凯
湖TP浓度0.030 0.084 −0.090 −0.045 −0.097 0.357** 1 注:*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。 -
[1] BAI J H, YE X F, JIA J, et al. Phosphorus sorption-desorption and effects of temperature, pH and salinity on phosphorus sorption in marsh soils from coastal wetlands with different flooding conditions[J]. Chemosphere,2017,188:677-688. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.117 [2] 唐富江, 刘伟, 王继隆, 等.兴凯湖与小兴凯湖鱼类组成及差异分析[J]. 水产学杂志,2011,24(3):40-47.TANG F J, LIU W, WANG J L, et al. Fish composition in Lake Xingkai (Khanka) and Lake mini-Xingkai[J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries,2011,24(3):40-47. [3] 于淑玲, 李秀军, 李晓宇, 等.小兴凯湖水质评价[J]. 湿地科学,2013,11(4):466-469.YU S L, LI X J, LI X Y, et al. Evaluation of water quality of Xiaoxingkai Lake[J]. Wetland Science,2013,11(4):466-469. [4] 郑恺原, 向小华.基于AHM-CRITIC赋权的小兴凯湖水质评价模型[J]. 节水灌溉,2020(9):79-83.ZHENG K Y, XIANG X H. Water quality evaluation model of Xiaoxingkai Lake based on AHM-CRITIC weighting[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2020(9):79-83. [5] 黑龙江省生态环境状况公报[R]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江省生态环境厅, 2012—2021. [6] 周楠楠, 王赢, 高顺峰, 等.两种不同根系特征沉水植物对沉积物剖面不同形态磷的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(6):2222-2228.ZHOU N N, WANG Y, GAO S F, et al. Effects of two submerged macrophytes with different root systems on different fractions of phosphorus in sediment profiles[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(6):2222-2228. [7] QIN B Q, ZHOU J, ELSER J J, et al. Water depth underpins the relative roles and fates of nitrogen and phosphorus in lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(6):3191-3198. [8] WORSFOLD P J, MONBET P, TAPPIN A D, et al. Characterisation and quantification of organic phosphorus and organic nitrogen components in aquatic systems: a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2008,624(1):37-58. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.06.016 [9] 吴金华, 盛芝露, 杜加强, 等.1956—2017年东北地区气温和降水的时空变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(3):340-347.WU J H, SHENG Z L, DU J Q, et al. Spatiotemporal change patterns of temperature and precipitation in northeast China from 1956 to 2017[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(3):340-347. [10] 金安琪, 张昂, 赵昕奕.气候变化情景下中国东部地区未来气候舒适度变化预测[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2019,55(5):887-898.JIN A Q, ZHANG A, ZHAO X Y. Estimation of climate comfort in Eastern China in the context of climate change[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2019,55(5):887-898. [11] 王锦旗, 宋玉芝, 薛艳.气候变化诱导水体富营养化研究进展[J]. 水资源保护,2022,38(4):145-155.WANG J Q, SONG Y Z, XUE Y. Research progress of water eutrophication induced by climate change[J]. Water Resources Protection,2022,38(4):145-155. [12] 安国英, 郭兆成, 叶佩.云南大理地区1989—2019年期间气候变化及对洱海水质的影响[J]. 现代地质,2022,36(2):406-417.AN G Y, GUO Z C, YE P. Climatic changes and impacts on water quality of Erhai Lake in Dali area, Yunnan Province over the period from 1989 to 2019[J]. Geoscience,2022,36(2):406-417. [13] 韩玉丽, 卜红梅.极端降水条件下白洋淀主淀区水化学特征及水质变化[J]. 湖泊科学,2022,34(6):1968-1979. doi: 10.18307/2022.0613HAN Y L, BU H M. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality variations in the main area of Lake Baiyangdian under extreme precipitation[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2022,34(6):1968-1979. doi: 10.18307/2022.0613 [14] 安睿, 康铁东, 于立峰.小兴凯湖湿地浮游生物功能群季节性变化研究[J]. 防护林科技,2018(2):16-19.AN R, KANG T D, YU L F. Seasonal changes of plankton functional groups in Xiaoxingkaihu wetland[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology,2018(2):16-19. [15] 冯尚柱, 黄庆阳, 王继丰, 等.兴凯湖国家级自然保护区种子植物属的区系分析[J]. 国土与自然资源研究,2020(4):86-87.FENG S Z, HUANG Q Y, WANG J F, et al. Floristic analysis of spermatophyte Genera in Xingkai Lake National Nature Reserve, China[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Study,2020(4):86-87. [16] 赵婷婷, 刘妍, 葛蕾, 等.兴凯湖湿地中国新记录硅藻[J]. 水生生物学报,2016,40(5):1087-1094.ZHAO T T, LIU Y, GE L, et al. Newly recorded diatom species from Xingkai Lake wetland, China[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2016,40(5):1087-1094. [17] 齐竟辰. 基于全成本法的兴凯湖灌区水价研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020. [18] 陈志辉, 秦超, 姚章村.井灌与渠灌典型区农业发展特点剖析: 以创业农场与兴凯湖农场为例[J]. 水利科技与经济,2011,17(10):74-76.CHEN Z H, QIN C, YAO Z C. Analysis of agricultural development characteristics in typical areas of well irrigation and canal irrigation: taking Chuangye farm and Xingkai Lake farm as examples[J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy,2011,17(10):74-76. [19] 孟凡淇. 兴凯湖农场农业产业化发展现状与对策研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018. [20] 李亮芳, 李春华, 叶春, 等.兴凯湖百余年营养演化历史及营养物基准[J]. 地球环境学报,2022,13(5):557-570.LI L F, LI C H, YE C, et al. Nutrient history in the past century and its baseline of Xingkai Lake[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2022,13(5):557-570. [21] 孙黛茜, 谢自建, 汪洋, 等. 兴凯湖沉积物营养盐分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(6):1976-1986.SUN D X, XIE Z J, WANG Y, et al.Distribution characteristics and source analysis of nutrients in sediments of Xingkai Lake[J].Journal of EnvironmentalEngineering Technology, 2023, 13(6): 1976-1986. [22] 中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所. 湖泊调查技术规程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. [23] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M].4版.北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [24] 张博, 郭云艳, 王书航, 等.呼伦湖水体磷的时空演变及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(4):824-830.ZHANG B, GUO Y Y, WANG S H, et al. Spatial-temporal changes of phosphorus and its influential factors in Lake Hulun[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(4):824-830. [25] 万美英, 刘宝玲, 蒋志伟.兴凯湖地区农业面源污染负荷分析[J]. 科技创新与应用,2013(20):5-6.WAN M Y, LIU B L, JIANG Z W. Analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution load in Xingkai Lake area[J]. Technology Innovation and Application,2013(20):5-6. [26] 朱广伟, 邹伟, 国超旋, 等.太湖水体磷浓度与赋存量长期变化(2005—2018年)及其对未来磷控制目标管理的启示[J]. 湖泊科学,2020,32(1):21-35. doi: 10.18307/2020.0103ZHU G W, ZOU W, GUO C X, et al. Long-term variations of phosphorus concentration and capacity in Lake Taihu, 2005-2018: implications for future phosphorus reduction target management[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2020,32(1):21-35. doi: 10.18307/2020.0103 [27] 余佑金, 方向京, 王圣瑞, 等.滇池水体不同形态磷负荷时空分布特征[J]. 湖泊科学,2017,29(1):59-68. doi: 10.18307/2017.0107YU Y J, FANG X J, WANG S R, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution patterns of loadings of different phosphorous forms in Lake Dianchi[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2017,29(1):59-68. doi: 10.18307/2017.0107 [28] 孙冬, 孙晓俊.兴凯湖水文特性[J]. 东北水利水电,2006,24(4):21.SUN D, SUN X J. Hydrological characteristics of Xingkai Lake[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China,2006,24(4):21. [29] CYR H, McCABE S K, NÜRNBERG G K. Phosphorus sorption experiments and the potential for internal phosphorus loading in littoral areas of a stratified lake[J]. Water Research,2009,43(6):1654-1666. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.050 [30] TAO Y Q, LU J. Occurrence of total phosphorus in surface sediments of Chinese Lakes and its driving factors and implications[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,580:124345. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124345 [31] 赵丽, 蔚静雯, 邢健宇, 等.南湖水体中悬浮物的时空分布特征及环境效应[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):905-911.ZHAO L, YU J W, XING J Y, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and environmental effects of suspended solids in Nanhu Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):905-911. [32] 柯长青, 蔡宇, 肖瑶.1979年—2019年兴凯湖湖冰物候变化的被动微波遥感监测[J]. 遥感学报,2022,26(1):201-210.KE C Q, CAI Y, XIAO Y. Monitoring ice phenology variations in Khanka Lake based on passive remote sensing data from 1979 to 2019[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2022,26(1):201-210. [33] SCHROTH A W, GILES C D, ISLES P D F, et al. Dynamic coupling of iron, manganese, and phosphorus behavior in water and sediment of shallow ice-covered eutrophic lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(16):9758-9767. [34] CHROST R J, SIUDA W, HALEMEJKO G Z. Longterm studies on alkaline phosphatase activity (APA) in a lake with fish-aquaculture in relation to lake eutrophication and phosphorus cycle[J]. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplementband,1984,70(1):1-32. [35] 李月. 不同磷酸盐浓度对虫黄藻生长、碱性磷酸酶活性以及基因表达影响的研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2021. [36] MALECKI L M, WHITE J R, REDDY K R. Nitrogen and phosphorus flux rates from sediment in the lower St. Johns River Estuary[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2004,33(4):1545-1555. doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.1545 [37] 蔡天祎, 叶春, 李春华, 等.太湖湖滨带水向辐射带水生植物多样性及生境因子分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):164-170.CAI T Y, YE C, LI C H, et al. Analysis on aquatic macrophyte diversity and environmental factors within the radiant belt toward lake of lake-terrestrial ecotone in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):164-170. [38] 王文怀. CaO2控制景观水体沉积物中氮磷释放的效果及作用机制研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2022. [39] BAXA M, MUSIL M, KUMMEL M, et al. Dissolved oxygen deficits in a shallow eutrophic aquatic ecosystem (fishpond) : sediment oxygen demand and water column respiration alternately drive the oxygen regime[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,766:142647. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142647 [40] 陈洪森, 叶春, 李春华, 等.入湖河口区水生植物群落衰亡分解释放营养盐过程模拟研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(2):220-228.CHEN H S, YE C, LI C H, et al. Simulation study on decomposition and release of nutrients from aquatic macrophyte communities in confluence area between lake and river[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(2):220-228. [41] 刘雪梅, 章光新.气候变化对湖泊蓝藻水华的影响研究综述[J]. 水科学进展,2022,33(2):316-326.LIU X M, ZHANG G X. A review of studies on the impact of climate change on cyanobacteria blooms in lakes[J]. Advances in Water Science,2022,33(2):316-326. [42] 徐升宝, 谷孝鸿, 蔡春芳, 等.溶氧·水温和水流对东太湖沉积物中氮·磷释放的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(9):5175-5177.XU S B, GU X H, CAI C F, et al. Effect on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediment of the East Taihu by dissolved oxygen, water temperature and currents[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(9):5175-5177. [43] 蔺星娜. 京津冀地区土壤风蚀扬尘起动传输特征及防治措施研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2021. [44] 陈洪森, 魏伟伟, 叶春, 等.大型水生植物混合腐解对入湖河口水质的影响及适宜生物量研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(3):589-598.CHEN H S, WEI W W, YE C, et al. Effects of mixed decomposition of macrophytes on water quality at lake-river confluence area and suitable macrophytes biomass after harvest[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(3):589-598. [45] JAMES R T, HAVENS K, ZHU G W, et al. Comparative analysis of nutrients, chlorophyll and transparency in two large shallow lakes (Lake Taihu, P. R. China and Lake Okeechobee, USA)[J]. Hydrobiologia,2009,627(1):211-231. doi: 10.1007/s10750-009-9729-5 [46] 任国玉, 姜彤, 李维京, 等.气候变化对中国水资源情势影响综合分析[J]. 水科学进展,2008,19(6):772-779.REN G Y, JIANG T, LI W J, et al. An integrated assessment of climate change impacts on China's water resources[J]. Advances in Water Science,2008,19(6):772-779. [47] 夏星辉, 吴琼, 牟新利.全球气候变化对地表水环境质量影响研究进展[J]. 水科学进展,2012,23(1):124-133.XIA X H, WU Q, MOU X L. Advances in impacts of climate change on surface water quality[J]. Advances in Water Science,2012,23(1):124-133. ◇ -





 下载:
下载: