Effect of immobilized bacteria and algae on enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal in bioretention tank
-
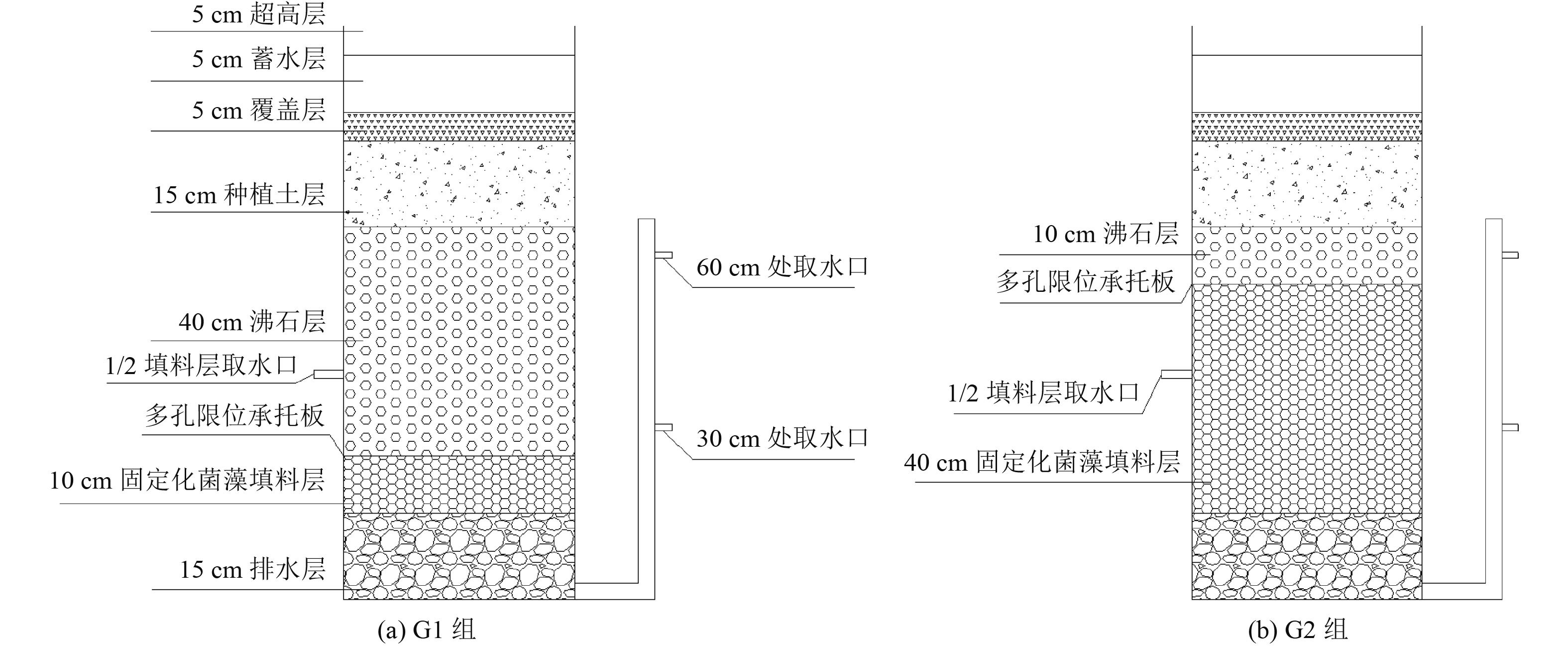
摘要:
针对传统生物滞留池对氮磷去除效果较差的问题,开展固定化菌藻填料淋洗试验和不同配比固定化菌藻填料的生物滞留池脱氮除磷效果研究。将固定化菌藻填料在去离子水中连续淋洗,研究营养物的释放特征,同时分别设置固定化菌藻填料占填料层的2/5(G1组)和占填料层的4/5(G2组),分析其在不同淹没高度(0、30、60 cm)和落干期下的脱氮除磷效果。结果表明:固定化菌藻填料在前8次淋洗中,未检测出总磷(TP)、总氮(TN),菌藻经过固定化后适合作为生物滞留池填料的改良剂;生物滞留池对氨氮(NH3-N)、TN的去除率随淹没高度的增加而提高,淹没高度为60 cm时,G1、G2组对NH3-N的平均去除率分别为68.25%和72.00%,对TN的平均去除率分别为64.20%和68.70%;淹没高度分别为0和60 cm时,G1、G2组对TP的去除率分别为79.50%和78.00%、70.05%和71.00%,而淹没高度为30 cm时,G2组对TP的去除率最高,达86.00%;落干期从2 d延长至8 d时,NH3-N和TN去除率分别从最高的69.38%和67.10%降至最低的55.13%和57.70%,对TP的去除率从最低的75.50%升至90.00%。固定化菌藻填料有效提高了生物滞留池脱氮除磷性能。
Abstract:In view of the poor nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency of the traditional bioretention tank, a study was carried out on the leaching test of immobilized bacteria algae packing, and the nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency of biological retention ponds with different proportions of immobilized bacteria algae packing. The characteristics of nutrient release were studied by continuous leaching of immobilized bacteria algae packing in deionized water. G1 group accounting for 2/5 of the filler layer and G2 group accounting for 4/5 of the filler layer were set up to study and analyze the nitrogen and phosphorus removal effects under different submergence heights (0, 30, 60 cm) and drying periods. The results showed that total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN) were not detected in the first 8 times leaching of immobilized bacteria algae packing, and immobilized bacteria algae packing was suitable as the improver of bioretention tank packing. With the increase of submergence height, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and TN by bioretention tank increased. At the submergence height 60 cm, the average removal rates of NH3-N in G1 and G2 groups were 68.25% and 72.00%, and the average removal rates of TN were 64.20% and 68.70%, respectively. At the submergence height 0 cm or 60 cm, the removal rates of TP in G1 and G2 groups were 79.50% and 78.00%, 70.05% and 71.00%, respectively. At the submergence height 30 cm, the removal rate of TP in G2 group was the highest, reaching 86.00%. When the drying period was extended from 2 days to 8 days, the removal rate of NH3-N and TN decreased from the highest of 69.38% and 67.10% to the lowest of 55.13% and 57.70%, respectively, while the removal rates of TP increased from the lowest of 75.50% to 90.00%. The test results showed that the immobilized bacteria and algae filler could effectively improve the nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance of bioretention tank.
-
-
[1] LI J K, LI N, LIU F, et al. Development and optimization of bioretention systems with modified fillers of corn straw biochar[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution,2021,232(9):383. [2] LIU C, LU J, LIU J Q, et al. Effects of lead (Pb) in stormwater runoff on the microbial characteristics and organics removal in bioretention systems[J]. Chemosphere,2020,253:126721. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126721 [3] HE Q M, LIN Z Z, DONG P, et al. Decontamination performance of a bioretention system using a simple sand-based filler proportioning method[J]. Environmental Technology,2022,43(5):709-717. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1803416 [4] JIANG C B, LI J K, LI H E, et al. Remediation and accumulation characteristics of dissolved pollutants for stormwater in improved bioretention basins[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,685:763-771. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.246 [5] YAN Q, DAVIS A P, JAMES B R. Enhanced organic phosphorus sorption from urban stormwater using modified bioretention media: batch studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering,2016,142(4):1-11. [6] 张哲源. 生物滞留池生物质炭填料对PAHs的去除效果研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2022. [7] 朋四海, 黄俊杰, 李田.过滤型生物滞留池径流污染控制效果研究[J]. 给水排水,2014,50(6):38-42.PENG S H, HUANG J J, LI T. Study on control effect of runoff pollution in filter biological retention pond[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering,2014,50(6):38-42. [8] 沈若非, 肖娴, 涂保华, 等.生物炭固定化复合菌群修复石油烃污染地下水[J]. 环境化学,2022,41(10):3435-3446.SHEN R F, XIAO X, TU B H, et al. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by biochar immobilized bacterial consortia[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022,41(10):3435-3446. [9] 刘双, 王思宇, 代云容.珠线型载漆酶电纺纤维膜对水中菲的净化性能和机理[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(4):389-396.LIU S, WANG S Y, DAI Y R. Purification performance and mechanism of phenanthrene in water by beads-in-string structural laccase-carrying electrospun fibrous membranes[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(4):389-396. [10] 余泽海, 胡云霜, 张晏菘, 等.聚乙烯醇/海藻酸钠/水性聚氨酯复合载体制备及固定化硝化菌降解氨氮废水的研究[J]. 水处理技术,2022,48(11):94-97.YU Z H, HU Y S, ZHANG Y S, et al. Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/waterborne polyurethane composite carrier and degradation of ammonia nitrogen wastewater by immobilization of nitrifying bacteria[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2022,48(11):94-97. [11] 尹超, 李莹, 张婷月, 等.好氧反硝化菌的固定化及其效能研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021(4):1-7.YIN C, LI Y, ZHANG T Y, et al. Immobilization and efficacy of an aerobic denitrifier[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science),2021(4):1-7. [12] 杨利伟, 张爽, 杨周, 等.径流中氮和磷在生物滞留池中的迁移及去除机理[J]. 中国给水排水,2019,35(9):133-138.YANG L W, ZHANG S, YANG Z, et al. Migration and removal mechanism of nitrogen and phosphorus of surface runoff in bioretention tank[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2019,35(9):133-138. [13] 卢少勇, 万正芬, 李锋民, 等.29种湿地填料对氨氮的吸附解吸性能比较[J]. 环境科学研究,2016,29(8):1187-1194.LU S Y, WAN Z F, LI F M, et al. Ammonia nitrogen adsorption and desorption characteristics of twenty-nine kinds of constructed wetland substrates[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2016,29(8):1187-1194. [14] GREBEL J E, MOHANTY S K, TORKELSON A A, et al. Engineered infiltration systems for urban stormwater reclamation[J]. Environmental Engineering Science,2013,30(8):437-454. doi: 10.1089/ees.2012.0312 [15] DAVIS A P, SHOKOUHIAN M, SHARMA H, et al. Laboratory study of biological retention for urban stormwater management[J]. Water Environment Research,2001,73(1):5-14. doi: 10.2175/106143001X138624 [16] 朱铭捷, 胡洪营, 何苗, 等.河道滞留塘系统对污染河水中氮磷的去除特性[J]. 生态环境,2006,15(1):11-14.ZHU M J, HU H Y, HE M, et al. NH3-N and TP removal performance of polluted river water with on-stream detention pond system[J]. Ecology and Environment,2006,15(1):11-14. [17] 冉阳. 改良生物滞留系统强化对氮磷的去除研究[D]. 株洲: 湖南工业大学, 2022. [18] 张瑞斌, 潘卓兮, 王乐阳, 等.固定化菌藻填料强化人工湿地脱氮除磷效果研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(1):91-96.ZHANG R B, PAN Z X, WANG L Y, et al. Effect of immobilized bacteria and algae filler on enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetland[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(1):91-96. [19] 王亚军, 耿冲冲, 许妍, 等.不同强化手段对生物滞留池脱氮除磷性能的影响[J]. 中国给水排水,2020,36(19):77-82.WANG Y J, GENG C C, XU Y, et al. Effect of different enhanced methods on efficiency of denitrification and phosphorus removal in bioretention cell[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2020,36(19):77-82. [20] 熊家晴, 何一帆, 白雪琛, 等.改良填料生物滞留池对雨水径流中磷的去除效果[J]. 环境工程学报,2019,13(9):2164-2172.XIONG J Q, HE Y F, BAI X C, et al. Removal effect of phosphorus in rain-runoff by the media-improved bioretention tank[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2019,13(9):2164-2172. [21] 方俊华, 张啸, 荆慧娟.磁化改性污泥基生物炭对水中磷的吸附[J]. 水处理技术,2021,47(12):37-41.FANG J H, ZHANG X, JING H J. Adsorption of phosphorus in water by magnetized modified sludge-based biochar[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2021,47(12):37-41. [22] 张鵾, 梁英, 马效芳, 等.混凝泥渣生物滞留池脱氮除磷性能的实验研究[J]. 环境工程,2016,34(增刊 1):326-331.ZHANG K, LIANG Y, MA X F, et al. Experimental research about denitrification and dephosphorization efficiency of WTR bioretention cells[J]. Environmental Engineering,2016,34(Suppl 1):326-331. [23] BALDWIN D S, MITCHELL A M. The effects of drying and re-flooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river-floodplain systems: a synthesis[J]. Regulated Rivers: Research & Management,2000,16(5):457-467. [24] 万哲希, 刘雨童, 李田.木屑强化生物滞留池对径流中营养物质的长期有效去除[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(2):215-221.WAN Z X, LIU Y T, LI T. Long-term and effective removal of nutrients in stormwater using a field-scale wood-chip bioretention system[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2019,47(2):215-221. [25] 戴云飞, 杨泽玉, 陈颖, 等.聚乙烯醇-海藻酸钠-活性炭固定化菌球处理二氯甲烷的研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(2):430-439.DAI Y F, YANG Z Y, CHEN Y, et al. Removel of DCM by microorganism cells immobilized into polyvinyl alcohol-alginate-activated carbon beads[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(2):430-439. [26] 袁敏, 刘晓冰, 唐美珍, 等.生物炭固定菌强化人工湿地对低温污水中氮素去除的模拟研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2018,34(5):463-468.YUAN M, LIU X B, TANG M Z, et al. Study on removal of nitrogen from low temperature sewage by Pseudomonas flava WD-3 immobilized biochar in constructed wetland[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2018,34(5):463-468. [27] 唐青青.蛋白核小球藻对单一及复合污染水中重金属的生物吸附研究[D].杭州:浙江工商大学,2015. -





 下载:
下载: