FeS2 enhanced microbial fuel cell anode denitrification and electricity generation characteristics
-
摘要:
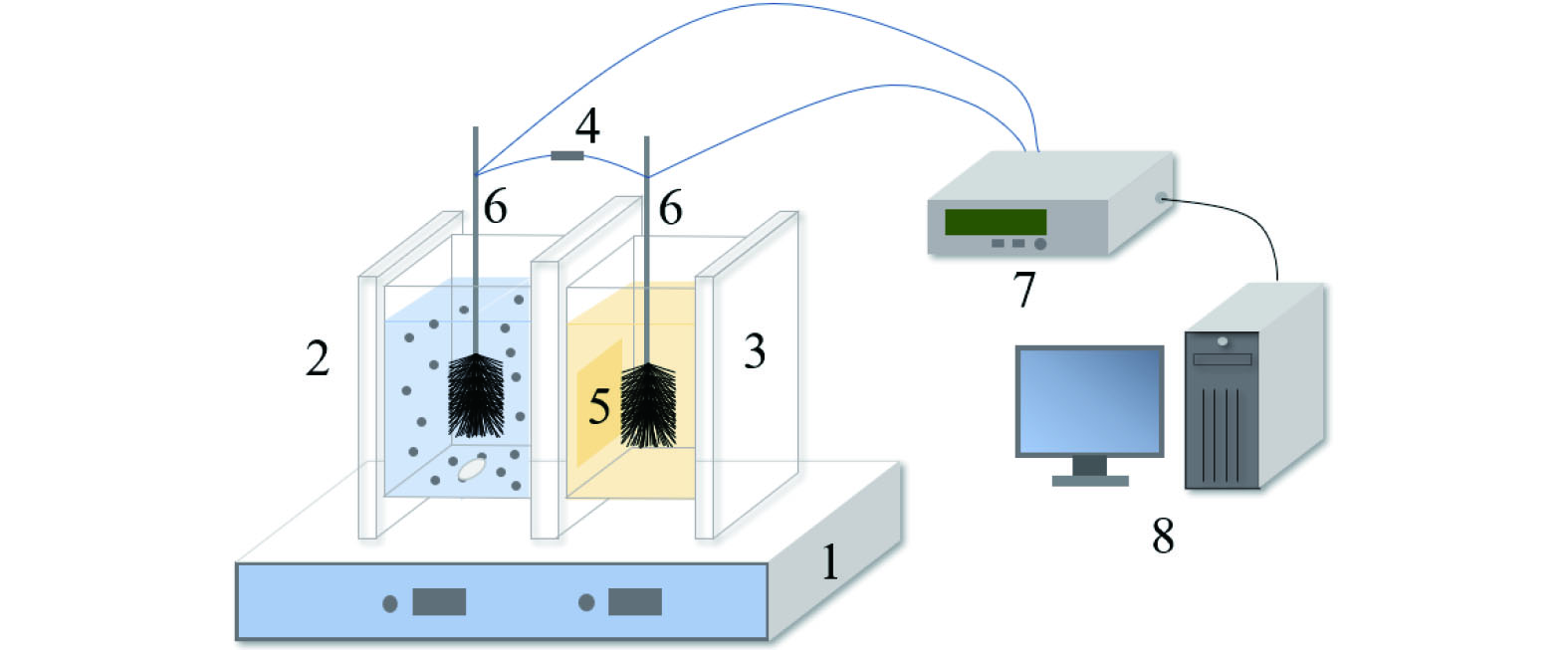
针对不同碳氮比(C/N)的含氮废水,将FeS2引入微生物燃料电池(MFC)阳极构建FeS2强化的微生物燃料电池(Pyr-MFC)体系,以不加FeS2的空白对照组(C-MFC)为对照,探究其对体系脱氮与产电的影响;采用高通量测序、X射线光电子能谱和扫描电子显微镜探究该体系中微生物丰度、硫和铁元素变化规律,解析FeS2强化体系低C/N下的脱氮机理。结果表明:1)Pyr-MFC的反硝化脱氮效率和产电功率密度均高于C-MFC,硝态氮去除率提高近15.7%,最高电压提高量可达0.274 V。2)C/N分别为4、3、2和1时Pyr-MFC对NO3-N的去除率为100%、97.8%、58.4%和49.7%,均高于C-MFC,表明FeS2有效降低体系对碳源的依赖。3)微生物群落检测结果表明,FeS2将产电微生物(Thauera、Thiobacillus和Geobacter)的物种丰度提高9.43%。4)物质转移分析结果表明,S−为反硝化过程提供电子,Fe2+作为电子穿梭体强化了电子传递,提高了体系的产电性能。
-
关键词:
- 微生物燃料电池(MFC) /
- FeS2 /
- 强化 /
- 反硝化脱氮 /
- 产电
Abstract:In recent years, the research on enhanced microbial fuel cell (MFC) treatment of nitrogen-containing wastewater has attracted extensive attention at home and abroad. FeS2 was introduced into MFC anode to construct a FeS2-enhanced microbial fuel cell (Pyr-MFC) system for wastewater with different carbon to nitrogen ratios (C/N). The blank control group without FeS2 (C-MFC) was used as a control to explore its effects on nitrogen removal and electro-generation. High throughput sequencing, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to investigate the changes of microbial abundance, sulfur and iron elements in the system, and the mechanism of nitrogen removal under low C/N in FeS2-enhanced system was obtained. The results showed: 1) The denitrification efficiency and power generation density of Pyr-MFC were higher than those of the control group, the nitrate nitrogen removal rate was increased by 15.7%, and the maximum voltage increase was as high as 0.274 V. 2) NO3 −-N removal rates of Pyr-MFC at different C/N ratios (4, 3, 2 and 1) were 100%, 97.8%, 58.4% and 49.7%, respectively, all higher than those of the control group, indicating that FeS2 could effectively reduce the dependence of the system on carbon sources. 3) The microbial community test results showed that FeS2 increased the species abundance of electrogenic microorganisms (Thauera, Thiobacillus and Geobacter) by about 9.43%. 4) The results of material transfer analysis showed that S− provided electrons for the denitrification process, and Fe2+ enhanced the electron transfer and improved the electro-generation performance of the system as an electron shuttle.
-
Key words:
- microbial fuel cell /
- FeS2 /
- enhance /
- denitrification and nitrogen removal /
- electricity production
-
表 1 微量元素溶液组成
Table 1. Composition of trace element solution
试剂名称 浓度/(g/L) CaCl2 1.00 MgCl2·6H2O 2.00 NaCl 0.20 FeCl2·4H2O 0.50 CoCl2·6H2O 0.10 MnCl2·4H2O 0.10 AlCl3·6H2O 0.05 (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O 0.30 H3BO3 0.10 NiCl2·6H2O 0.01 CuSO4·5H2O 0.10 ZnCl2 0.10 EDTA 0.50 -
[1] ZHANG Q G, HU J J, LEE D J. Microbial fuel cells as pollutant treatment units: research updates[J]. Bioresource Technology,2016,217:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.006 [2] 林莉莉, 鲁汭, 龙忆年, 等.MFC处理人工湿地生物堵塞物及同步产电研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1504-1513.LIN L L, LU R, LONG Y N, et al. MFC treating bio-clogging matter of constructed wetland and synchronous electricity generation[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(6):1504-1513. [3] 王琳, 李雪, 王丽.复合生物阴极型微生物燃料电池处理废水及同步产电性能[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(7):1098-1104.WANG L, LI X, WANG L. Performance of a hybrid biocathode microbial fuel cell for wastewater treatment and electricity generation[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(7):1098-1104. [4] 李朝明, 许丹, 黄铭意, 等.不同阳极设置对人工湿地-微生物燃料电池脱氮及产能的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):205-213.LI C M, XU D, HUANG M Y, et al. Effects of different anode settings on the performance of nitrogen removal and electrogenesis capacity in constructed wetland-microbial fuel cells[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):205-213. [5] ZHENG D C, GU W Z, ZHOU Q M, et al. Ammonia oxidation and denitrification in a bio-anode single-chambered microbial electrolysis cell[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,310:123466. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123466 [6] 李文英, 刘玉香, 任瑞鹏, 等.微生物燃料电池在水与废水脱氮方面的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2019,38(2):1097-1106.LI W Y, LIU Y X, REN R P, et al. Research progress on removal of nitrogen in water and wastewater by microbial fuel cell[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2019,38(2):1097-1106. [7] SHI S H, FAN X, HE X J, et al. Enhanced nitritation/denitritation and potential mechanism in an electrochemically assisted sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating sludge digester liquor with extremely low C/N ratios[J]. Bioresource Technology,2022,363:127936. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127936 [8] 郑力, 李志勇, 黄剑, 等.竹刨花-铁耦合体系对低碳氮比污水的脱氮性能[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):214-221.ZHENG L, LI Z Y, HUANG J, et al. Denitrification performance of bamboo shavings-iron coupled system for low C/N ratio wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):214-221. [9] ZHOU Q M, YANG N, ZHENG D C, et al. Electrode-dependent ammonium oxidation with different low C/N ratios in single-chambered microbial electrolysis cells[J]. Bioelectrochemistry,2021,142:107889. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.107889 [10] TONG S, ZHANG B G, FENG C P, et al. Characteristics of heterotrophic/biofilm-electrode autotrophic denitrification for nitrate removal from groundwater[J]. Bioresource Technology,2013,148:121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.146 [11] LIU H Y, CHEN N, FENG C P, et al. Impact of electro-stimulation on denitrifying bacterial growth and analysis of bacterial growth kinetics using a modified Gompertz model in a bio-electrochemical denitrification reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,232:344-353. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.064 [12] AI T, ZHAN H, ZOU L Z, et al. Potential applications of endogenous sulfide for enhanced denitrification of low C/N domestic wastewater in anodic mixotrophic denitrification microbial fuel cell: the mechanism of electrons transfer and microbial community[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,722:137830. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137830 [13] GE X Y, CAO X, SONG X S, et al. Bioenergy generation and simultaneous nitrate and phosphorus removal in a pyrite-based constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,296:122350. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122350 [14] WANG Y M, LIN Z Y, WANG Y, et al. Sulfur and iron cycles promoted nitrogen and phosphorus removal in electrochemically assisted vertical flow constructed wetland treating wastewater treatment plant effluent with high S/N ratio[J]. Water Research,2019,151:20-30. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.005 [15] WANG R W, YAN M, LI H D, et al. FeS2 nanoparticles decorated graphene as microbial-fuel-cell anode achieving high power density[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(22):1800618. doi: 10.1002/adma.201800618 [16] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [17] 周昱宏. 微生物燃料电池处理含氮废水的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [18] PANG Y M, WANG J L. Insight into the mechanism of chemoautotrophic denitrification using pyrite (FeS2) as electron donor[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,318:124105. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124105 [19] PU J Y, FENG C P, LIU Y, et al. Pyrite-based autotrophic denitrification for remediation of nitrate contaminated groundwater[J]. Bioresource Technology,2014,173:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.092 [20] Di CAPUA F, PIROZZI F, LENS P N L, et al. Electron donors for autotrophic denitrification[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,362:922-937. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.069 [21] JU W J, JHO E H, NAM K. Effect of initial pH, operating temperature, and dissolved oxygen concentrations on performance of pyrite-fuel cells in the presence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,360:512-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.034 [22] TORRENTÓ C, URMENETA J, OTERO N, et al. Enhanced denitrification in groundwater and sediments from a nitrate-contaminated aquifer after addition of pyrite[J]. Chemical Geology,2011,287(1/2):90-101. [23] 周娅, 买文宁, 代吉华, 等.硫代硫酸钠联合硫铁矿自养反硝化脱氮性能[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(5):2081-2086.ZHOU Y, MAI W N, DAI J H, et al. Study on autotrophic denitrification performance of sodium thiosulfate combined with pyrite system[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(5):2081-2086. [24] WU W Z, YANG L H, WANG J L. Denitrification using PBS as carbon source and biofilm support in a packed-bed bioreactor[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2013,20(1):333-339. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-0926-9 [25] WAGNER M, AMANN R, LEMMER H, et al. Probing activated sludge with oligonucleotides specific for proteobacteria: inadequacy of culture-dependent methods for describing microbial community structure[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1993,59(5):1520-1525. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1520-1525.1993 [26] 朱春燕. 基于氢自养反硝化的生物电化学系统脱氮性能研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. [27] 褚雨秋. 基于铁自养反硝化微生物的市政污水深度脱氮效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. [28] 谢作甫, 郑平, 张吉强, 等.产电微生物及其生理生化特性[J]. 科技通报,2013,29(7):56-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2013.03.008XIE Z F, ZHENG P, ZHANG J Q, et al. The electricigens and their physiological and biochemical characteristics[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology,2013,29(7):56-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2013.03.008 [29] SHEN Z Q, ZHOU Y X, WANG J L. Comparison of denitrification performance and microbial diversity using starch/polylactic acid blends and ethanol as electron donor for nitrate removal[J]. Bioresource Technology,2013,131:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.169 [30] 刘双, 赵剑强, 王莎, 等.硫自养与异养混合亚硝酸盐反硝化过程铵生成机制[J]. 环境工程学报,2019,13(6):1366-1373. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201810064LIU S, ZHAO J Q, WANG S, et al. Ammonia production mechanism in a simultaneous occurrence of sulfur autotrophic and heterotrophic mixed nitrite denitrification process[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2019,13(6):1366-1373. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201810064 [31] KŁODOWSKA I, RODZIEWICZ J, JANCZUKOWICZ W, et al. Effect of citric acid on the efficiency of the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus compounds during simultaneous heterotrophic-autotrophic denitrification (HAD) and electrocoagulation[J]. Ecological Engineering,2016,95:30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.076 [32] YANG Y, GERRITY S, COLLINS G, et al. Enrichment and characterization of autotrophic Thiobacillus denitrifiers from anaerobic sludge for nitrate removal[J]. Process Biochemistry,2018,68:165-170. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2018.02.017 [33] LEANG C, COPPI M V, LOVLEY D R. OmcB, a c-type polyheme cytochrome, involved in Fe(Ⅲ) reduction in Geobacter sulfurreducens[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2003,185(7):2096-2103. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.7.2096-2103.2003 [34] 陆圆. 反硝化滤池耦合电极生物膜反应器(DF-BER)深度脱氮试验研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. [35] DENG S H, LI D S, YANG X, et al. Biological denitrification process based on the Fe(0)-carbon micro-electrolysis for simultaneous ammonia and nitrate removal from low organic carbon water under a microaerobic condition[J]. Bioresource Technology,2016,219:677-686. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.08.014 [36] WANG R, YANG C, ZHANG M, et al. Chemoautotrophic denitrification based on ferrous iron oxidation: reactor performance and sludge characteristics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,313:693-701. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.052 [37] KASHEFI K, TOR J M, NEVIN K P, et al. Reductive precipitation of gold by dissimilatory Fe(Ⅲ)-reducing bacteria and Archaea[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2001,67(7):3275-3279. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.7.3275-3279.2001 [38] FLYNN T, O'LOUGHLIN E, MISHRA B, et al. Sulfur-mediated electron shuttling during bacterial iron reduction[J]. Science,2014,344:1039-1042. ⊗ doi: 10.1126/science.1252066 -





 下载:
下载: