Typical elements distribution in water-based drilling cuttings from Hainan Province and their effects on groundwater after using as a pave in drilling site
-
摘要:
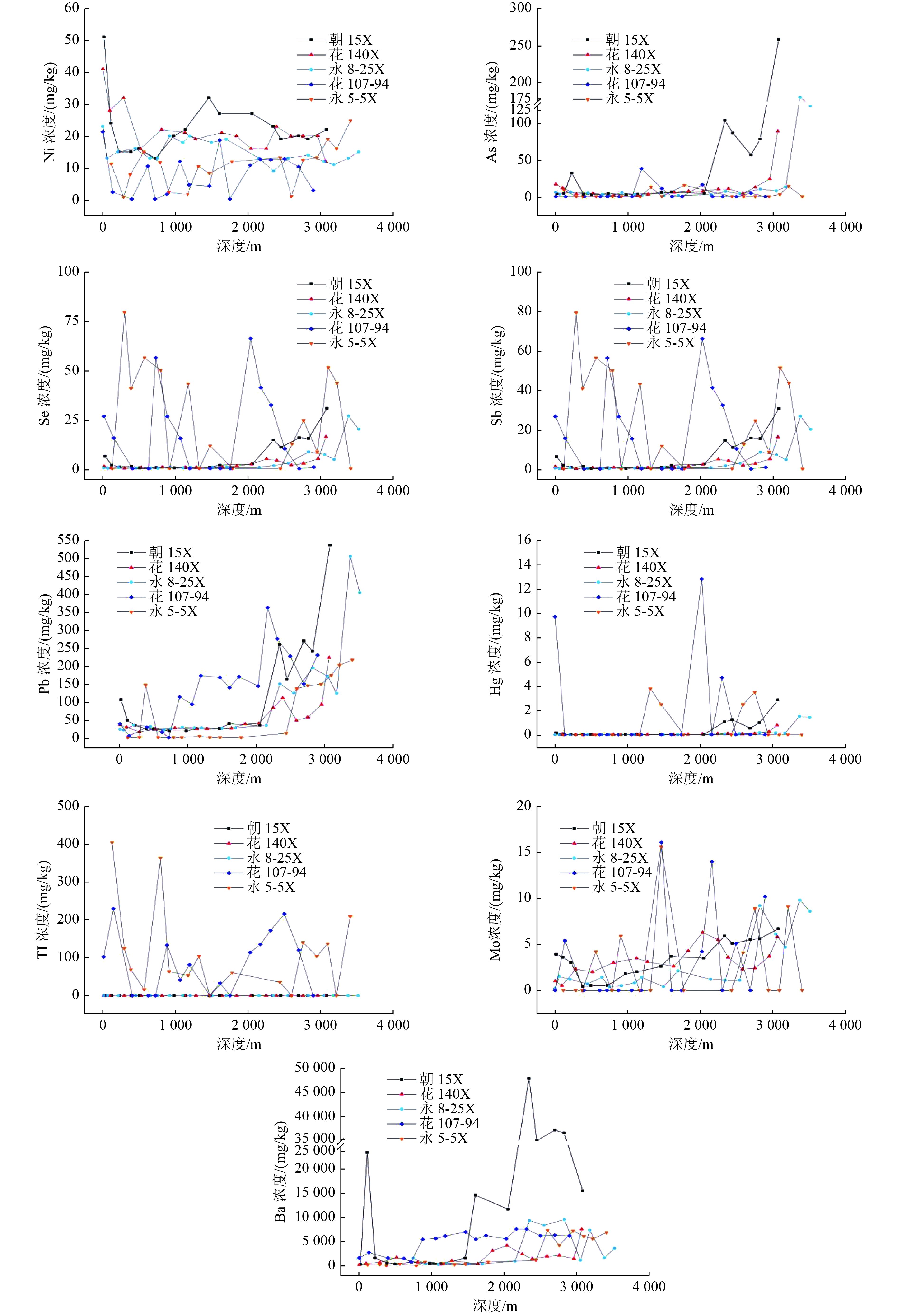
铺垫井场是水基钻屑再利用的重要路径。然而,不同区域水基钻屑中元素浓度存在差异,其再利用过程中环境影响仍未全面了解。调查海南5个典型油气田钻井平台的水基钻屑,分析典型元素的分布和浸出特征,评估铺垫井场后对地下水的环境影响。结果表明,海南水基钻屑中Ni、As、Se、Sb、Pb、Hg、Tl、Mo、Ba浓度均未超过GB 36600—2018《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》中规定的第二类用地的风险筛选值,除Tl外,其他元素浓度均与采样深度显著相关。浸出液中Pb、Tl、As浓度相对于GB/T 14848—2017《地下水质量标准》规定的Ⅲ类限值分别有36.5%、16.5%、16.5%的超标率,其中As浸出率最高,为35.7%。基于Texas模型的估算以及铺垫井场下方地下水的现场测定,所有检测项目浓度均未超过GB/T 14848—2017规定的Ⅲ类限值,表明水基钻屑铺垫井场是安全的。
Abstract:The use of water-based drilling cuttings as a pave in drilling site is an important way for the reuse of the waste. However, the environmental impact from the reuse has not been fully understood due to the variation in the contents of elements in water-based drill cuttings from different regions. The distribution and leaching characteristics of typical elements in the water-based drilling cuttings from the drilling platforms of five typical oil and gas fields in Hainan, China, were investigated. Further, the environmental impacts on groundwater from the reuse were assessed. The results indicated that the concentrations of Ni, As, Se, Sb, Pb, Hg, Tl, Mo and Ba in the investigated water-based drilling cuttings did not exceed the corresponding risk screening values for Class Ⅱ land specified in Soil environment quality: risk control standard for soil contamination of development land (GB 36600-2018); and the concentrations of all elements, excluding Tl, were related with the sampling depths significantly. Compared with the limits of Class Ⅲ set in Groundwater Quality Standard (GB/T 14848-2017), the exceedance rates of Pb, Tl and As in the leachate reached 36.5%, 16.5% and 16.5%, respectively. Among the investigated elements, arsenic had the highest leaching rate (35.7%). The results of risk estimation based on Texas model and on-site measurement of the groundwater below the pave in drilling site suggested that the use of water-based drill cuttings as a paved surface in drilling site was safe, with the concentrations of all tested items not exceeding the Class Ⅲ limit specified in GB/T 14848-2017.
-
表 1 水基钻屑消解液、浸出液及地下水样品中典型元素检出限
Table 1. Detection limit of typical elements in water-based drilling cuttings digestion solution, leaching solution and groundwater samples
mg/L 项目 水基钻屑元素总量
方法检出限水基钻屑浸出毒性及
地下水方法检出限Ni 2 6×10−5 As 0.01 3×10−4 Se 0.01 4×10−4 Sb 0.3 2×10−3 Pb 2 9×10−5 Hg 0.002 4×10−5 Tl 0.1 2×10−5 Mo 0.1 6×10−5 Ba 3.6 3×10−3 表 2 各钻井平台水基钻屑中典型元素浓度
Table 2. Concentrations of typical elements in water-based drilling cuttings from each drilling platform
mg/kg 项目 花107-94 永5-5X 朝15X 永8-25X 花140X 海南省土壤
背景值 [31]GB 36600—2018第二类
用地筛选值Ni 最小值 ND 7.00×10−1 13.1 12.4 9.20 14.4 900 最大值 18.7 24.8 51.2 41.2 23.1 中位值 10.3 11.7 21.0 20.0 14.3 As 最小值 ND ND 3.37 2.32 2.11 8.90 60 最大值 39.0 16.8 259 89.6 181 中位值 ND ND 6.16 8.51 6.29 Se 最小值 ND ND 5.00×10−3 8.00×10−2 6.00×10−2 2.88×10−1 — 最大值 69.3 114 2.23 4.50×10−1 4.50×10−1 中位值 22.1 15.2 8.00×10−2 1.95×10−1 1.60×10−1 Sb 最小值 ND ND 5.00×10−1 4.00×10−1 4.00×10−1 — 180 最大值 66.0 79.3 30.7 16.3 26.8 中位值 10.3 12.7 2.00 1.50 8.00×10−1 Pb 最小值 ND ND 19.0 16.0 21.0 36.0 800 最大值 361 216 533 222 503 中位值 141 3.80 36.5 36.5 31.0 Hg 最小值 ND ND 2.50×10−2 1.40×10−2 9.00×10−3 7.80×10−2 38 最大值 12.8 3.80 2.87 7.99×10−1 1.52 中位值 ND ND 4.30×10−2 3.80×10−2 2.40×10−2 注:ND表示未检出;—表示未检测该项目或标准中无此项指标。全文同。 表 3 不同地区水基钻屑中典型元素浓度
Table 3. Typical element content of water-based drilling cuttings in different regions
mg/kg 地区 Ni As Se Sb Pb Hg Tl Mo Ba 国内 涪陵区[3] 5.0~26.6 2.12~10.70 — — 0.63~10.9 0.15~0.63 — — — 西南某页岩气钻井平台[11] 19.4~22.6 3.9~5.7 — — 1.7~2.07 0.09~0.11 — — — 塔里木油田[17] 0.013~13.6 0.001 4~2.66 — — 0.016~22.2 0.000 05~0.054 — — — 大牛地气田[33] 102.14 58.33 0.157 90.32 66.6 5.17 0.049 — — 大港油田[34] 20 141 — — 35 3.11 — — — 榆林市与鄂尔多斯市[35] 9.58 — — — 19.27 0.02 — — — 国外 波兰[36] 24.0~70.1 ND~8.1 — — 28.1~250.0 ND~0.77 — — 8.6×103~8.14×104 北海油田[37] 36.0 11.8 — — 38.5 — — 1.10 3.20×104 沙特阿拉伯[38] 4~22 — — — 1~29 — — — — 意大利近海[39] — ND~0.66 ND — 0.19~0.43 — — — — 美国加州南部[40] 17~47 10~13 32~356 0.04~0.07 1.18×103~1.51×104 表 4 各钻井平台水基钻屑中典型元素的浸出浓度
Table 4. Leaching concentrations of typical elements in water-based drilling cuttings at each drilling platform
mg/L 项目 花107-94 永5-5X 朝15X 永8-25X 花140X GB/T 14848—2017 Ⅲ类限值 Ni 最小值 ND ND 1.90×10−3 1.16×10−3 1.13×10−3 2.00×10−2 最大值 7.14×10−1 3.24×10−2 7.16×10−3 2.16×10−2 4.12×10−2 中位值 ND ND 4.21×10−3 5.01×10−3 5.90×10−3 As 最小值 ND ND ND 5.00×10−4 4.00×10−4 1.00×10−2 最大值 4.24×10−1 6.18×10−1 3.70×10−3 2.61×10−2 3.05×10−2 中位值 ND ND 4.00×10−4 2.60×10−3 3.20×10−3 Se 最小值 ND ND ND ND ND 1.00×10−2 最大值 1.31×10−2 ND ND 2.30×10−3 1.60×10−3 中位值 ND ND ND ND ND 表 5 水基钻屑中典型元素的浸出率及超标率
Table 5. Leaching rate and excess rate of typical elements in water-based drilling cuttings
% 重金属 浸出率 超标率 Ni 2.93×10 −2~6.98 5.88 As 1.93×10 −3~35.7 16.5 Se 2.50×10 −1~20.0 0 Sb 6.50×10 −1~28.6 11.8 Pb 2.06×10 −4~13.2 36.5 Hg 1.40×10 −1~17.8 8.23 Tl 1.00×10 −1~4.20×10 −1 16.5 Mo 1.17~36.8 8.23 Ba 2.93×10 −2~6.98 9.41 表 6 不同地区水基钻屑中典型元素的浸出浓度
Table 6. Leaching concentrations of typical elements in water-based drilling cuttings in different regions
mg/L 地区 Ni As Se Sb Pb Hg Tl Mo Ba 国内 重庆市涪陵区[43] ND 0.016~0.033 ND — ND ND — — 4~7 四川南部某页岩气钻井平台[44] 5.3×10−4 9.7×10−3 ND — 6.7×10−3 3.7×10−4 — — 5.1×10−2 四川长宁区[45] — ND — — ND ND — — — 渤海某油气钻井平台[46] 4.2×10−3 9.93×10−3 7.5×10−4 — ND 1.6×10−4 — — 0.179 新疆油气田[47] 5×10−3~ 0.848 0.05~1.6 — — 0.025~3.43 5×10−6~5.23×10−2 — — 0.035~341 大牛地气田[33] 4.2×10−4~0.14 1.2×10−3~0.21 3.1×10−4~0.055 — 2.1×10−4~0.1 1.6×10−3~9.7×10−2 — — 9.8×10−3~1.7 国外 北海油田(mg/kg)[48] ND~0.5 ND ND ND ND ND ND~0.5 0.43~3.85 巴西[49] 0.24~0.93 — — — ND~0.88 — — — — 伊朗南部[50] — 6.5 ND — 310 — — 1.8 340 表 7 各井场Cwell计算结果
Table 7. Calculation results of Cwell values of each drilling site
mg/L 重金属 花107-94 永5-5X 朝15X 永8-25X 花140X GB/T 14848—2017 Ⅲ类限值 Ni 1.03×10−4 4.42×10−5 1.05 ×10−5 3.18×10−5 6.07×10−5 2.00×10−2 As 4.55×10−5 1.54×10−5 3.46 ×10−6 2.44×10−5 5.65×10−5 1.00×10−2 Se 9.76×10−5 4.88 ×10−5 1.95 ×10−6 2.24×10−5 1.56×10−5 1.00×10−2 Sb 1.42 ×10−4 5.28×10−6 1.58×10−5 2.11×10−6 1.58×10−6 5.00×10−3 Pb 5.56×10−4 5.09 ×10−4 3.10 ×10−6 2.22×10−4 4.47×10−4 1.00×10−2 Hg 1.36×10−5 2.27 ×10−5 1.00×10−8 4.00×10−8 8.00×10−8 1.00×10−3 Tl 8.1×10−6 3.89 ×10−5 4.1 ×10−7 7.00×10−8 1.20×10−7 1.00×10−4 Mo 1.17×10−4 1.17 ×10−4 4.93 ×10−5 3.69×10−5 2.16×10−4 7.00×10−2 Ba 8.8 ×10−4 1.28 ×10−2 1.36×10−3 9.99×10−4 3.55×10−3 7.00×10−1 表 8 试验井场地下水监测结果
Table 8. Groundwater monitoring results of the experimental drilling sites
mg/L 监测区域 Ni As Se Sb Pb Hg Tl Mo Ba 上游50 m 3.29×10−3 ND ND ND ND ND ND 1.44×10−2 ND 厂区内 6.82×10−3 ND ND ND 1.6×10−4 ND ND 3.58×10−3 0.24 下游50 m 4.06×10−3 ND ND ND ND ND ND 1.63×10−3 0.16 -
[1] 周奇, 姚光远, 包为磊, 等.油气田开采钻井岩屑分类利用处置 现状及环境管理[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,12(2):785-792. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220169ZHOU Q, YAO G Y, BAO W L, et al. Current utilization, disposal and environmental management on drilling cuttings from oil and gas field exploitation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,12(2):785-792. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20220169 [2] WANG C Q, XIONG D M. Leaching assessment of aerated concrete made of recycled shale gas drilling cuttings: particular pollutants, physical performance and environmental characterization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,282:125099. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125099 [3] 高昊辰, 张春, 张思兰, 等.中国西南地区页岩气田水基钻屑理化性状与污染物分析[J]. 土壤,2019,51(6):1168-1172.GAO H C, ZHANG C, ZHANG S L, et al. Analysis of physiochemical properties and pollutants of water-based drilling cuttings in shale gas field near southwest China[J]. Soils,2019,51(6):1168-1172. [4] 王茂仁.国内水基钻屑不落地技术应用现状与问题探讨[J]. 石油和化工设备,2015,18(9):95-99.WANG M R. Discussion on application status and problems of water-based drilling cuttings non-landing technology in China[J]. Petro & Chemical Equipment,2015,18(9):95-99. [5] 韩桂梅, 党春阁, 郭亚静, 等.天然气开采水基钻井固体废物污染特性及一体化处理技术效果: 以苏里格气田为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):967-974.HAN G M, DANG C G, GUO Y J, et al. Pollution characteristics and effect of integrated treatment technology of solid wastes from water-based drilling for natural gas exploitation: taking Sulige Gas Field as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):967-974. [6] 蒋孔杰, 张琛, 王骞, 等.海南省建筑业固废资源再利用研究[J]. 海峡科技与产业,2022,35(2):91-94.JIANG K J, ZHANG C, WANG Q, et al. Study on reuse of solid waste resources in construction industry in Hainan Province[J]. Technology and Industry Across the Straits,2022,35(2):91-94. [7] LIU Y C, YANG J, CHEN M Y, et al. Water-based drill cuttings, a shale gas extraction waste as supplementary cementitious material and optimization[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,346:128419. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128419 [8] YANG H, LIU Y L, BAI G L, et al. Solidification and utilization of water-based drill cuttings to prepare ceramsite proppant with low-density and high performance[J]. Petroleum Science,2022,19(5):2314-2325. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2022.06.006 [9] LIU D S, WANG C Q, MEI X D, et al. Environmental performance, mechanical and microstructure analysis of non-fired bricks containing water-based drilling cuttings of shale gas[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,183:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.107 [10] 石媛丽, 钱洪霞, 辛炜, 等.钻井固废资源化利用途径分析[J]. 油气田环境保护,2021,31(4):41-46.SHI Y L, QIAN H X, XIN W, et al. Discussion on utilization routes of drilling solid wastes[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields,2021,31(4):41-46. [11] WANG C Q, CHEN S, HUANG D M, et al. Pozzolanic activity and environmental risk assessment of water-based drilling cuttings of shale gas[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,348:128657. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128657 [12] 张晶, 杨玉飞, 杨金忠, 等.造粒飞灰沥青混凝土路面利用的地下水环境风险评估[J]. 环境污染与防治,2019,41(1):89-94.ZHANG J, YANG Y F, YANG J Z, et al. Environmental risk assessment of groundwater of granulated fly ash utilization on asphalt pavement[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2019,41(1):89-94. [13] 崔长颢, 李丽, 刘美佳, 等. 利用油基岩屑制备水泥路面基层的力学性能及重金属浸出特性研究[J/OL]. 环境科学研究. [2023-02-02]. https: //doi. org/10.13198/j. issn. 1001-6929.2023. 01.11.CUI C H, LI L, LIU M J, et al. Mechanical properties and heavy metal leaching characteristics of cement pavement base prepared from oil-based drilling cuttings[J/OL]. Research of Environmental Sciences. [2023-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2023.01.11. [14] 康得军, 张芳, 吕茳芏, 等.浸泡淋滤作用下煤矸石重金属元素的释放规律及特征研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2023,36(1):54-62.KANG D J, ZHANG F, LÜ J D, et al. Research on release law and characteristics of heavy metals in coal gangue under soaking and leaching[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2023,36(1):54-62. [15] 沈晓莉, 杨金忠, 徐天有, 等.典型地区油气田水基钻井岩屑污染特征研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2017,39(5):480-483.SHEN X L, YANG J Z, XU T Y, et al. Research on pollution characteristic of water-based drilling cuttings of typical oil-gas fields[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2017,39(5):480-483. [16] 吴娜, 聂志强, 李开环, 等.页岩气开采钻井固体废物的污染特性[J]. 中国环境科学,2019,39(3):1094-1100.WU N, NIE Z Q, LI K H, et al. Pollution characteristics of solid waste in shale gas mining drilling[J]. China Environmental Science,2019,39(3):1094-1100. [17] 杜春蕾. 油田钻井废弃泥浆中重金属分布特征与污染评价: 以中石油塔里木分公司塔北井区为例[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2015. [18] 孙强.论海南福山油田钻井中的几个复杂问题[J]. 石化技术,2017,24(1):93.SUN Q. Discussion on several complex drilling problems in Hainan Fushan oilfield[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology,2017,24(1):93. [19] 崔露, 曾思云, 谭晓峰, 等.福山油田钻井液处理剂检测评价综述[J]. 石油工业技术监督,2015,31(12):8-11.CUI L, ZENG S Y, TAN X F, et al. Detection and evaluation of drilling fluid additives in Fushan oilfield[J]. Technology Supervision in Petroleum Industry,2015,31(12):8-11. [20] 卢丽, 樊连杰, 裴丽欣, 等. 海南岛地下水资源状况及其环境地质问题[J/OL]. 中国地质. [2023-02-02]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1702.033.html.LU L, FAN L J, PEI L X, et al. Groundwater resources and environmental geologic problems in Hainan Island[J/OL]. Geology in China. [2023-02-02]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1702.033.html. [21] 樊连杰, 邹胜章, 卢丽, 等.海南岛琼北盆地孔隙承压水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 环境污染与防治,2022,44(9):1189-1195.FAN L J, ZOU S Z, LU L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water qualityevaluation of pore confined groundwater in Qiongbei Basin, Hainan Island[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2022,44(9):1189-1195. [22] 梁捷. 海南省典型作物系统中砖红壤的环境基准值及环境容量研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2020. [23] 杨爱萍, 王小燕, 肖细元, 等. 锌冶炼废渣重金属在地块土壤中的垂向迁移特征及归趋[J/OL]. 环境科学.[2023-02-24]. https: //doi. org/10.13227/j. hjkx. 202212083.YANG A P, WANG X Y, XIAO X Y, et al. Vertical migration characteristics and fate of heavy metals from zinc smelting slag in soil profile[J/OL]. Environmental Science. [2023-02-24]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202212083. [24] 吴胜安, 邢彩盈, 朱晶晶.海南岛气候特征分析[J]. 热带生物学报,2022,13(4):315-323.WU S A, XING C Y, ZHU J J. Analysis of climate characteristics in Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology,2022,13(4):315-323. [25] STRASSBERG G, MAIDMENT D, KATZ L. Dilution attenuation factors in susceptibility assessments: a GIS based method[R]. Texas: Center for Research in Water Resources, University of Texas at Austin, 2003 [26] 李开环. 涪陵地区页岩气开采固体废物污染特性及资源化环境风险研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2018. [27] 黄慧, 聂志强, 孟棒棒, 等.不同处理工艺页岩气钻井岩屑的污染特性[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(3):777-782.HUANG H, NIE Z Q, MENG B B, et al. Pollution characteristics of typical field shale gas drilling cuttings with different treatment processes[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(3):777-782. [28] 于劲磊, 向启贵, 蒋国斌, 等.深、浅层页岩气区块油基岩屑污染特征研究[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2021,50(4):124-129.YU J L, XIANG Q G, JIANG G B, et al. Research on pollution characteristics of oil-base cuttings from deep and shallow shale gas development[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas,2021,50(4):124-129. [29] 李福燕, 李许明.海口市农用地土壤硒含量与土壤理化性质的相关性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(14):42-47.LI F Y, LI X M. Soil selenium contents in relation to soil physicochemical properties in agricultural land of Haikou[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(14):42-47. [30] XIE Z, YANG J Z, HUANG Q F, et al. Occurrence of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in typical used mineral oil from China: implications for risk management[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(26):33065-33074. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09515-4 [31] 李佳桐. 琼北土壤高背景值区域重金属空间分布及健康风险评价[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2018. [32] 陈立荣, 胡攀峰, 唐攀, 等.川渝地区页岩气钻井固废分类资源化处置利用[J]. 油气田环境保护,2021,31(6):1-5.CHEN L R, HU P F, TANG P, et al. Soil waste classification, resource disposal and utilization of shale gas drilling in Sichuan-Chongqing areas[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields,2021,31(6):1-5. [33] 吕倩楠.大牛地气田水基钻井岩屑危险特性鉴别[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2018,47(5):112-116.LÜ Q N. Research on hazard identification of water-based drilling cuttings in Daniudi gas field[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas,2018,47(5):112-116. [34] 董庆梅, 王云鹏.大港油田免烧砖技术研究与应用[J]. 油气田环境保护,2019,29(3):16-18.DONG Q M, WANG Y P. The research and application of non-burnt brick technology in Dagang oilfield[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields,2019,29(3):16-18. [35] 范婧, 朱恒, 路心, 等.水基钻井废物泥浆池原位处理环境影响分析[J]. 油气田环境保护,2022,32(4):53-56.FAN J, ZHU H, LU X, et al. Environmental impact analysis of the mud pool in-situ treatment to the water-based drilling waste[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields,2022,32(4):53-56. [36] MIKOS-SZYMAŃSKA M, RUSEK P, BOROWIK K, et al. Characterization of drilling waste from shale gas exploration in Central and Eastern Poland[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(36):35990-36001. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2365-8 [37] AYATI B, MOLINEUX C, NEWPORT D, et al. Manufacture and performance of lightweight aggregate from waste drill cuttings[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,208:252-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.134 [38] NASIR U, SAEED M A, YOUSIF S M. Environmental impact assessment of heavy metals in surface disposed drilling waste[J]. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection,2021(9):227-238. [39] TERZAGHI C, BUFFAGNI M, CANTELLI D, et al. Physical-chemical and ecotoxicological evaluation of water based drilling fluids used in Italian off-shore[J]. Chemosphere,1998,37(14/15):2859-2871. [40] NJUGUNA J, SIDDIQUE S, BAKAH KWROFFIE L, et al. The fate of waste drilling fluids from oil & gas industry activities in the exploration and production operations[J]. Waste Management,2022,139:362-380. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.12.025 [41] 陈则良. 页岩气油基钻屑的污染特性和蒸汽浸洗研究[D]. 重庆: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院), 2018. [42] KUJAWSKA J, PAWŁOWSKA M, CEL W, et al. Potential influence of drill cuttings landfill on groundwater quality: comparison of leaching tests resultsand groundwater composition[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2016,57(3):1409-1419. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2015.1030117 [43] 王朝强. 页岩气钻井岩屑建材资源化利用中重金属污染预警、迁移及控制[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2019. [44] LIU W S, YUAN H, FAN Z Z, et al. Using water-based drilling cuttings from shale gas development to manufacture sintered bricks: a case study in the southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(23):29379-29393. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12847-4 [45] 刘宇程, 陈文博, 陈媛媛, 等.水泥窑协同处置掺加萃余钻屑对水泥熟料性能的影响[J]. 环境工程,2020,38(11):157-162.LIU Y C, CHEN W B, CHEN Y Y, et al. Effect of cement kiln co-processing extracted raffinate cuttings on performance of the cement clinker[J]. Environmental Engineering,2020,38(11):157-162. [46] 张忠亮, 陈俊生, 耿铁, 等.海上水基钻井岩屑制备硅酸盐水泥试验研究[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2022,51(1):92-97.ZHANG Z L, CHEN J S, GENG T, et al. Experimental study on preparation of cement clinker from offshore water-based drilling cuttings[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas,2022,51(1):92-97. [47] 高庆国, 章媛媛, 俞音, 等.新疆油气田钻井岩屑中特征污染物控制因子筛选研究[J]. 新疆环境保护,2019,41(2):1-5.GAO Q G, ZHANG Y Y, YU Y, et al. Control factor screening for specific pollutants in drilling cuttings from Xinjiang oil and gas fields[J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang,2019,41(2):1-5. [48] AYATI B. A novel use for oil-contaminated drill cuttings in the manufacture of lightweight aggregate[D]. London: University of East London, 2018. [49] SOARES A S F, da COSTA MARQUES M R, da CUNHA COSTA L. Physical-chemical characterization and leaching studies involving drill cuttings generated in oil and gas pre-salt drilling activities[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023,30(7):17899-17914. [50] GHASEMI S, GITIPOUR S, GHAZBAN F, et al. Treatment of petroleum drill cuttings using stabilization/solidification method by cement and modified clay mixes[J]. Iranian Journal of Health, Safety and Environment,2017,4(3):781-787. [51] Texas Commision on Environmental Quality. March 2017 PCL and suporting tables[EB/OL]. [2022-12-6]. https://www.tceq.texas.gov/remediation/trrp/trrppcls.html. -





 下载:
下载: