Research progress of stable isotopes in source analysis of nitrate pollution in water
-
摘要:
准确识别水体中硝酸盐污染来源至关重要,目前稳定同位素已被广泛应用于水体硝酸盐污染源解析研究,但关于同位素分馏影响源解析结果准确性的研究仍不足。介绍了稳定同位素分析技术及其在水体硝酸盐污染源解析中的应用,通过对比氮转化中δ15N-NO3 −和δ18O-NO3 −的时空差异性,结合其他技术方法在硝酸盐污染源解析研究中的应用,提出目前稳定同位素技术在硝酸盐污染源解析中应用的局限性。结果表明,氮转化中同位素分馏对水体δ15N-NO3 −和δ18O-NO3 −的影响很大,使用符合环境特征的潜在来源δ15N-NO3 −和δ18O-NO3 −是保证稳定同位素模型解析结果准确性的关键。因此,深入研究水体中与氮转化相关的微生物信息将有助于进一步了解硝酸盐在迁移转化中的特征;土壤层或者地下水硝酸盐的输入应成为地表水体硝酸盐污染源解析的重点考察端元;结合机器学习发展出适应研究区域地理气候特征的稳定同位素模型是今后实现精准溯源的研究方向。
Abstract:Accurate identification of nitrate pollution sources in water bodies is crucial, and stable isotopes have been widely used in source analysis studies of nitrate pollution in water bodies. Still, there are few studies on the influence of isotope fractionation on the accuracy of source analysis results. The stable isotope analysis technology and its application in the analysis of nitrate pollution sources in water bodies were introduced, and by comparing the spatial and temporal variability of δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 − in nitrogen transformations and the application of other technical methods in the source analysis of nitrate pollution, the limitations of the current stable isotope techniques in the source analysis of nitrate pollution were presented. The results showed that isotopic fractionation in nitrogen transformation had a strong influence on δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 − in water, and the use of δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 − of potential sources that met environmental characteristics was the key to ensure the accuracy of stable isotope model analysis results. Therefore, an in-depth study of microbial information related to nitrogen transformation in water bodies would help to further understand the characteristics of nitrate in migration transformation; the input of nitrate from soil layer or groundwater should be the key investigation end source for nitrate pollution source analysis in surface water bodies; the development of stable isotope models adapted to the geoclimatic characteristics of the study area in combination with machine learning was the future research direction to achieve accurate source tracing.
-
Key words:
- stable isotope /
- nitrate pollution /
- source analysis /
- isotope fractionation
-
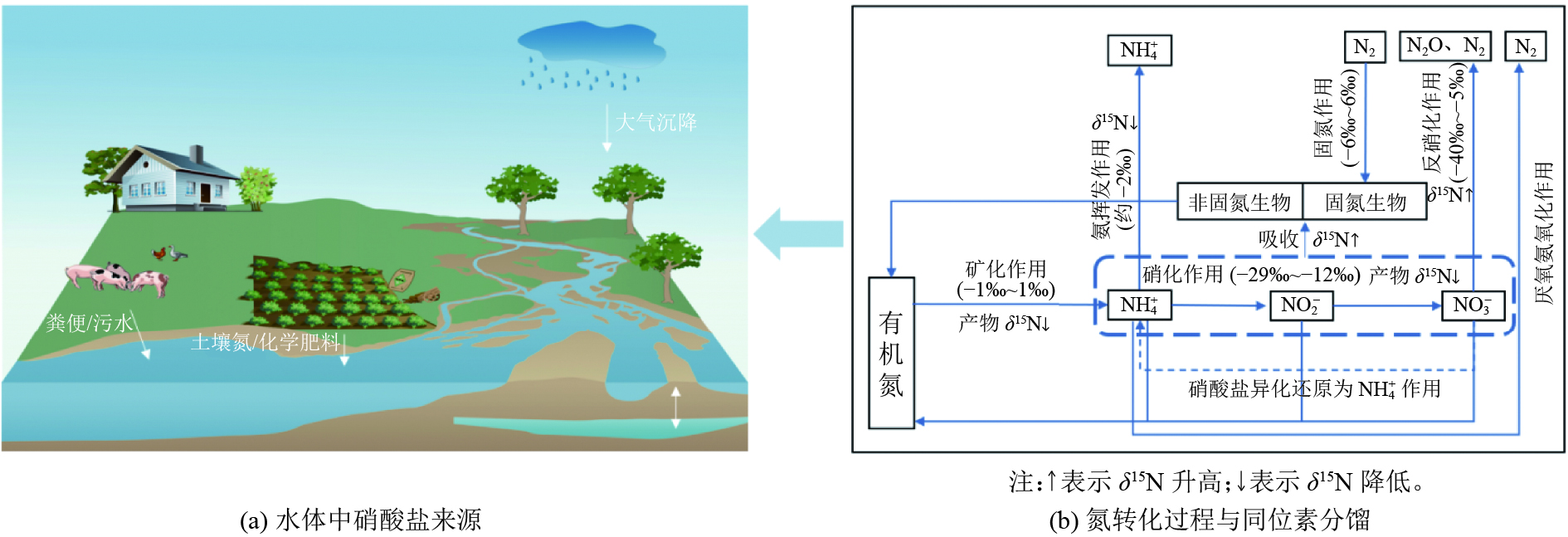
图 1 水体中硝酸盐来源及氮转化过程与同位素分馏
Figure 1. Nitrate source and nitrogen transformation mechanism and isotopic fractionation in water environment[28]
表 1 定性研究中不同硝酸盐来源δ15N-NO3 −和δ18O-NO3 −范围
Table 1. Range of δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 − values from different nitrate sources in qualitative research
表 2 各模型优缺点比较
Table 2. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of each model
表 3 定量研究中SIAR模型所使用的端元同位素组成
Table 3. Endmember isotope values used by SIAR models in quantitative studies
‰ 研究区域 硝酸盐来源 δ15N-NO3 − δ18O-NO3 − 均值 标准差 均值 标准差 国内 福建[86] 大气沉降 0.8 3.94 40.7 13.4 化学肥料 0.4 0.3 2.9 1.7 土壤氮 1.79 1.6 1.7 0.5 粪便和污水 14.3 1.9 6.7 2.5 河南[87] 大气沉降 3.2 2.4 44 9.1 化学肥料 0.9 2 3.02 0.55 土壤氮 5 1.5 3.02 0.55 粪便和污水 16.3 5.7 7 2.7
浙江杭州[13]大气沉降 0.6 1.5 57.2 6.9 化学肥料 −2.1 0.7 −4.1 2.7 土壤氮 3.8 1.8 −2.7 4.4 粪便和污水 17.4 3.9 6.1 1.6 山东胶州[47] 大气沉降 3.4 2.4 21.3 8.0 化学肥料 0.2 2.2 1.4 0.3 土壤氮 6.7 1.3 1.4 0.3 粪便和污水 12.5 2.5 2.5 2.2 安徽淮北[18] 大气沉降 −2.7 2.1 61.7 13.7 化学肥料 4.2 0.17 −5.7 1.7 土壤氮 4.4 2.13 3.7 0.29 粪便和污水 11.5 1.16 5.6 1.4 浙江[55] 大气沉降 2.3 1.4 60.8 15.0 化学肥料 0.04 1.87 4.08 0.33 土壤氮 4.52 2.67 4.08 0.33 粪便和污水 12.75 3.40 4.08 0.33 北京昌平[60] 大气沉降 4.23 4.34 54 13.2 化学肥料 0.4 0.3 2.92 1.69 土壤氮 1.79 1.56 1.7 0.5 粪便和污水 14.3 1.9 6.7 2.5 广西桂林[35] 大气沉降 3.1 1.5 56.7 17.8 化学肥料 −1.12 1.41 −5.7 1.7 土壤氮 5.7 2.0 1.24 3.13 粪便和污水 14.3 1.9 6.7 2.5 国外 北欧波罗的
海[88]大气沉降 0.3 1.4 76.7 6.8 氮的固定 −1.0 1.0 −0.7 2.9 土壤氮 1.3 1.4 1.5 0.9 农田径流 9.9 1.5 4.6 1.0 非洲加纳[89] 大气沉降 0.6 1.5 57.2 6.9 化学肥料 −2.1 0.7 −4.1 2.7 土壤氮 3.8 1.8 −2.7 4.4 粪便和污水 17.4 3.9 6.1 1.6 韩国[90] 大气沉降 −7.2 0.8 51.1 3.8 化学肥料 −2.6 0.7 11.2 6.1 土壤氮 4.1 0.3 9.6 0.1 污水 11.2 2.4 5.8 1.6 墨西
哥[91]大气沉降 0.89 2.12 57.59 12.47 土壤氮 3.98 1.95 2.51 1.41 污水 13.25 3.24 4.87 1.87 -
[1] GRUBER N, GALLOWAY J N. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle[J]. Nature,2008,451(7176):293-296. doi: 10.1038/nature06592 [2] XIA X H, ZHOU J S, YANG Z F. Nitrogen contamination in the Yellow River Basin of China[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2002,31(3):917-925. doi: 10.2134/jeq2002.9170 [3] XIA X H, YANG Z F, HUANG G H, et al. Nitrification in natural waters with high suspended-solid content: a study for the Yellow River[J]. Chemosphere,2004,57(8):1017-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.08.027 [4] XIA X H, LIU T, YANG Z F, et al. Enhanced nitrogen loss from rivers through coupled nitrification-denitrification caused by suspended sediment[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,579:47-59. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.181 [5] ZHANG Y, LI F D, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Tracing nitrate pollution sources and transformation in surface- and ground-waters using environmental isotopes[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,490:213-222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.004 [6] GREER F R, SHANNON M. Infant methemoglobinemia: the role of dietary nitrate in food and water[J]. Pediatrics,2005,116(3):784-786. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1497 [7] FEWTRELL L. Drinking-water nitrate, methemoglobinemia, and global burden of disease: a discussion[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives,2004,112(14):1371-1374. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7216 [8] van MAANEN J M, ALBERING H J, de KOK T M, et al. Does the risk of childhood diabetes mellitus require revision of the guideline values for nitrate in drinking water[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives,2000,108(5):457-461. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108457 [9] 沈志强, 周岳溪, 王建龙.利用淀粉/PCL共混物作为反硝化固体碳源和生物膜载体的研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2014,4(2):129-134. doi: 10.4103/0976-8580.141210SHEN Z Q, ZHOU Y X, WANG J L. Denitrification using starch/PCL blends as solid carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2014,4(2):129-134. doi: 10.4103/0976-8580.141210 [10] XUE D M, BOTTE J, de BAETS B, et al. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater[J]. Water Research,2009,43(5):1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048 [11] TAYEFEH M, SADEGHI S M, NOORHOSSEINI S A, et al. Environmental impact of rice production based on nitrogen fertilizer use[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(16):15885-15895. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1788-6 [12] CAMARGO J A, ALONSO Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: a global assessment[J]. Environment International,2006,32(6):831-849. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.002 [13] JIN Z F, ZHENG Q, ZHU C Y, et al. Contribution of nitrate sources in surface water in multiple land use areas by combining isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2018,93:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.03.014 [14] SCHLESINGER W. Biogeochemistry: an analysis of global change[J]. The Quarterly Review of Biology,1998,73(1):353-423. [15] HOLLOWAY J M, DAHLGREN R A, HANSEN B, et al. Contribution of bedrock nitrogen to high nitrate concentrations in stream water[J]. Nature,1998,395(6704):785-788. doi: 10.1038/27410 [16] 张金, 马金珠, 陈春武, 等.硝酸盐氮氧同位素在不同生态系统中的研究进展[J]. 干旱区地理,2015,38(2):312-319.ZHANG J, MA J Z, CHEN C W, et al. An overview on application of dual isotope compositions of nitrate in different ecosystems[J]. Arid Land Geography,2015,38(2):312-319. [17] TANG W Z, PEI Y S, ZHENG H, et al. Twenty years of China's water pollution control: experiences and challenges[J]. Chemosphere,2022,295:133875. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133875 [18] CHEN X, JIANG C L, ZHENG L G, et al. Identification of nitrate sources and transformations in basin using dual isotopes and hydrochemistry combined with a Bayesian mixing model: application in a typical mining city[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,267:115651. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115651 [19] KOHL D H, SHEARER G B, COMMONER B. Fertilizer nitrogen: contribution to nitrate in surface water in a corn belt watershed[J]. Science,1971,174(4016):1331-1334. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1331 [20] HU J, CHEN X, CHEN Y Y, et al. Nitrate sources and transformations in surface water of a mining area due to intensive mining activities: emphasis on effects on distinct subsidence waters[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,298:113451. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113451 [21] 王万洁, 侯兴旺, 刘稷燕, 等.传统稳定同位素技术在环境科学领域的应用及研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2021,40(12):3640-3650.WANG W J, HOU X W, LIU J Y, et al. Application and research progress of traditional stable isotope technology in environmental science[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2021,40(12):3640-3650. [22] IRRGEHER J, PROHASKA T. Application of non-traditional stable isotopes in analytical ecogeochemistry assessed by MC ICP-MS:a critical review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2016,408(2):369-385. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9025-3 [23] 冯冬霞, 廖海清, 杨芳, 等.中国土壤和湖泊沉积物中钚同位素分布特征和应用研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(6):1110-1120.FENG D X, LIAO H Q, YANG F, et al. Distribution characteristics and application of Pu isotopes in soils and lake sediments of China[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(6):1110-1120. [24] 杨蓉, 李垒.碳氮氧稳定同位素技术在水生态环境中的应用[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(1):191-201.YANG R, LI L. Applications of stable carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen isotope techniques in aquatic environment and ecology[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(1):191-201. [25] 杨延梅, 张田, 郑明霞, 等.基于水化学及当地稳定同位素的地下水硝酸盐污染空间分布特征及污染源解析[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(9):2164-2172.YANG Y M, ZHANG T, ZHENG M X, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution source analysis of nitrate pollution in groundwater based on hydrochemistry and local stable isotopes[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(9):2164-2172. [26] MICHALSKI G, KOLANOWSKI M, RIHA K M. Oxygen and nitrogen isotopic composition of nitrate in commercial fertilizers, nitric acid, and reagent salts[J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies,2015,51(3):382-391. doi: 10.1080/10256016.2015.1054821 [27] ZHANG Y, SHI P, SONG J X, et al. Application of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes for source and fate identification of nitrate pollution in surface water: a review[J]. Applied Sciences,2018,9(1):18. doi: 10.3390/app9010018 [28] ZHANG Y P, ZHOU A G, ZHOU J W, et al. Evaluating the sources and fate of nitrate in the alluvial aquifers in the Shijiazhuang rural and suburban area, China: hydrochemical and multi-isotopic approaches[J]. Water,2015,7(4):1515-1537. [29] YU Q B, WANG F, LI X Y, et al. Tracking nitrate sources in the Chaohu Lake, China, using the nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(20):19518-19529. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2178-9 [30] 孙文青, 陆光华, 薛晨旺, 等.基于稳定同位素技术识别河流硝酸盐污染源研究进展[J]. 四川环境,2019,38(3):193-198.SUN W Q, LU G H, XUE C W, et al. Research progress on identification of nitrate pollution sources in rivers by using stable isotope technique[J]. Sichuan Environment,2019,38(3):193-198. [31] RE V, KAMMOUN S, SACCHI E, et al. A critical assessment of widely used techniques for nitrate source apportionment in arid and semi-arid regions[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,775:145688. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145688 [32] 范丽俊, 赵峰华, 程晨.水体中氮稳定同位素的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报,2016,27(8):2699-2707.FAN L J, ZHAO F H, CHENG C. Research advances in stable nitrogen isotope in water bodies[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2016,27(8):2699-2707. [33] KENDALL C, CALDWELL E A. Fundamentals of isotope geochemistry[M]//Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1998: 51-86. [34] 李荣富, 罗跃辉, 曾洪玉, 等.稳定同位素技术在环境水体氮的生物地球化学循环研究中的应用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学),2016,52(1):16-26.LI R F, LUO Y H, ZENG H Y, et al. Review on applications of stable isotope techniques in studying biogeochemical cycle of nitrogen in environmental water[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences),2016,52(1):16-26. [35] ZHAO H J, XIAO Q, MIAO Y, et al. Sources and transformations of nitrate constrained by nitrate isotopes and Bayesian model in Karst surface water, Guilin, Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(17):21299-21310. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08612-8 [36] GUO J X, ZUO P, YANG L, et al. Quantitative identification of non-point sources of nitrate in urban channels based on dense in situ samplings and nitrate isotope composition[J]. Chemosphere,2021,263:128219. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128219 [37] HUANG X Y, ZHANG D, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Determining hydrogeological and anthropogenic controls on N pollution in groundwater beneath piedmont alluvial fans using multi-isotope data[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2021,229:106844. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106844 [38] JI X L, XIE R T, HAO Y, et al. Quantitative identification of nitrate pollution sources and uncertainty analysis based on dual isotope approach in an agricultural watershed[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,229:586-594. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.100 [39] KOU X Y, DING J J, LI Y Z, et al. Tracing nitrate sources in the groundwater of an intensive agricultural region[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2021,250:106826. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106826 [40] WONG W W, POTTAGE J, WARRY F Y, et al. Stable isotopes of nitrate reveal different nitrogen processing mechanisms in streams across a land use gradient during wet and dry periods[J]. Biogeosciences,2018,15(13):3953-3965. doi: 10.5194/bg-15-3953-2018 [41] YI Q T, CHEN Q W, HU L M, et al. Tracking nitrogen sources, transformation, and transport at a basin scale with complex plain river networks[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,51(10):5396-5403. [42] ZHANG Q Q, WANG H W, WANG L. Tracing nitrate pollution sources and transformations in the over-exploited groundwater region of North China using stable isotopes[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2018,218:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.06.001 [43] ZHANG Q Q, WANG H W. Assessment of sources and transformation of nitrate in the alluvial-pluvial fan region of North China using a multi-isotope approach[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2020,89:9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.09.021 [44] YANG P H, WANG Y Y, WU X Y, et al. Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in Karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:114835. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114835 [45] PANNO S V, HACKLEY K C, KELLY W R, et al. Isotopic evidence of nitrate sources and denitrification in the Mississippi River, Illinois[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2006,35(2):495-504. doi: 10.2134/jeq2005.0012 [46] YE H J, TANG C Y, CAO Y J. Sources and transformation mechanisms of inorganic nitrogen: evidence from multi-isotopes in a rural-urban river area[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,794:148615. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148615 [47] NESTLER A, BERGLUND M, ACCOE F, et al. Isotopes for improved management of nitrate pollution in aqueous resources: review of surface water field studies[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2011,18(4):519-533. doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0422-z [48] LI Y Q, YAN W J, WANG F, et al. Nitrogen pollution and sources in an aquatic system at an agricultural coastal area of Eastern China based on a dual-isotope approach[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(23):23807-23823. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05665-2 [49] YIN C, YANG H Q, WANG J F, et al. Combined use of stable nitrogen and oxygen isotopes to constrain the nitrate sources in a Karst Lake[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment,2020,303:107089. [50] 马宝强, 王潇, 汤超, 等.同位素技术在地下水研究中的主要应用[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(5):919-926.MA B Q, WANG X, TANG C, et al. Main applications of isotope technology in groundwater study[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(5):919-926. [51] SILVA S R, KENDALL C, WILKISON D H, et al. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2000,228(1/2):22-36. [52] 马文娟, 刘丹妮, 杨芳, 等.水环境中污染物同位素溯源的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(2):242-250.MA W J, LIU D N, YANG F, et al. Research progress in isotope methods for tracing contaminants in water environment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(2):242-250. [53] KENDALL C, ELLIOTT E M, WANKEL S D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems[M]//Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2008: 375-449. [54] YANG L P, HAN J P, XUE J L, et al. Nitrate source apportionment in a subtropical watershed using Bayesian model[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2013,463/464:340-347. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.021 [55] ZHANG M, ZHI Y Y, SHI J C, et al. Apportionment and uncertainty analysis of nitrate sources based on the dual isotope approach and a Bayesian isotope mixing model at the watershed scale[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,639:1175-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.239 [56] 徐璐, 蒋勇军, 段世辉, 等.基于双同位素(δ15N-NO3 −-δ18O-NO3 −)和IsoSource模型的岩溶槽谷区地下水硝酸盐来源的定量示踪[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(8):3637-3645.XU L, JIANG Y J, DUAN S H, et al. Quantification of nitrate sources to groundwater in Karst trough-valley areas based on dual stable isotopes of δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 − and the IsoSource model[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(8):3637-3645. [57] GUO Z F, YAN C Z, WANG Z S, et al. Quantitative identification of nitrate sources in a coastal peri-urban watershed using hydrogeochemical indicators and dual isotopes together with the statistical approaches[J]. Chemosphere,2020,243:125364. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125364 [58] ADEBOWALE T, SURAPANENI A, FAULKNER D, et al. Delineation of contaminant sources and denitrification using isotopes of nitrate near a wastewater treatment plant in peri-urban settings[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,651:2701-2711. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.146 [59] 张鑫, 张妍, 毕直磊, 等.中国地表水硝酸盐分布及其来源分析[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(4):1594-1606.ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, BI Z L, et al. Distribution and source analysis of nitrate in surface waters of China[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(4):1594-1606. [60] LIU J, SHEN Z Y, YAN T Z, et al. Source identification and impact of landscape pattern on riverine nitrogen pollution in a typical urbanized watershed, Beijing, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,628/629:1296-1307. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.161 [61] HUNDEY E J, RUSSELL S D, LONGSTAFFE F J, et al. Agriculture causes nitrate fertilization of remote alpine lakes[J]. Nature Communications,2016,7(1):1-9. [62] YUAN R Y, ZHENG T Y, ZHENG X L, et al. Identification of groundwater nitrate pollution sources in agricultural area using PCA and SIAR methods[J]. Episodes,2020,43(2):739-749. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2020/020047 [63] BU H M, MENG W, ZHANG Y. Nitrogen pollution and source identification in the Haicheng River Basin in Northeast China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2011,409(18):3394-3402. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.030 [64] REN L S, CHENG L R, ZHANG S R, et al. Quantifying nitrate pollution sources of the drinking water source area using a Bayesian isotope mixing model in the northeastern suburbs of Beijing, China[J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies,2021,57(4):350-367. doi: 10.1080/10256016.2021.1937149 [65] MUELLER C, KRIEG R, MERZ R, et al. Regional nitrogen dynamics in the TERENO Bode River Catchment, Germany, as constrained by stable isotope patterns[J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies,2016,52(1/2):61-74. [66] LIU T, WANG F, MICHALSKI G, et al. Using 15N, 17O, and 18O to determine nitrate sources in the Yellow River, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(23):13412-13421. [67] CHETELAT B, GAILLARDET J, FREYDIER R. Use of B isotopes as a tracer of anthropogenic emissions in the atmosphere of Paris, France[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2009,24(5):810-820. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.01.007 [68] WIDORY D, PETELET-GIRAUD E, NÉGREL P, et al. Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: a synthesis[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(2):539-548. [69] WIDORY D, KLOPPMANN W, CHERY L, et al. Nitrate in groundwater: an isotopic multi-tracer approach[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2004,72(1/2/3/4):165-188. [70] XUE D M, BAETS B D, van CLEEMPUT O, et al. Classification of nitrate polluting activities through clustering of isotope mixing model outputs[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2013,42(5):1486-1497. doi: 10.2134/jeq2012.0456 [71] BASSETT R L. A critical evaluation of the available measurements for the stable isotopes of boron[J]. Applied Geochemistry,1990,5(5/6):541-554. [72] FENECH C, ROCK L, NOLAN K, et al. The potential for a suite of isotope and chemical markers to differentiate sources of nitrate contamination: a review[J]. Water Research,2012,46(7):2023-2041. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.044 [73] FIELD K G, SAMADPOUR M. Fecal source tracking, the indicator paradigm, and managing water quality[J]. Water Research,2007,41(16):3517-3538. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.056 [74] 王会霞, 史浙明, 姜永海, 等.地下水污染识别与溯源指示因子研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(8):1886-1898.WANG H X, SHI Z M, JIANG Y H, et al. Research progress on indicator of groundwater pollution identification and traceability[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(8):1886-1898. [75] YANG Z, CHEN J F, LI H L, et al. Sources of nitrate in Xiangshan Bay (China), as identified using nitrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science,2018,207:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.02.019 [76] PARNELL A C, INGER R, BEARHOP S, et al. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation[J]. PLoS One,2010,5(3):e9672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009672 [77] PHILLIPS D L, GREGG J W. Uncertainty in source partitioning using stable isotopes[J]. Oecologia,2001,128(2):304. doi: 10.1007/s004420100723 [78] DUDGEON D, CHEUNG F K W, MANTEL S K. Foodweb structure in small streams: do we need different models for the tropics[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society,2010,29(2):395-412. doi: 10.1899/09-058.1 [79] MOORE J W, SEMMENS B X. Incorporating uncertainty and prior information into stable isotope mixing models[J]. Ecology Letters,2008,11(5):470-480. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01163.x [80] ELLISON A. Bayesian inference in ecology[J]. Ecology Letters,2004,7(6):509-520. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00603.x [81] YU L, ZHENG T Y, ZHENG X L, et al. Nitrate source apportionment in groundwater using Bayesian isotope mixing model based on nitrogen isotope fractionation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,718:137242. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137242 [82] LI C, LI S L, YUE F J, et al. Identification of sources and transformations of nitrate in the Xijiang River using nitrate isotopes and Bayesian model[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,646:801-810. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.345 [83] JIN Z F, CEN J R, HU Y M, et al. Quantifying nitrate sources in a large reservoir for drinking water by using stable isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(20):20364-20376. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05296-7 [84] 康萍萍, 许士国.基于同位素模型法的莱州湾东岸地下水硝酸盐污染源贡献率研究[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(11):155-162.KANG P P, XU S G. The study on contribution of nitrate source to groundwater in the east coast of Laizhou Bay based on isotope mixing model[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020,51(11):155-162. [85] LIU S S, WU F C, FENG W Y, et al. Using dual isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model to evaluate sources of nitrate of Tai Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(32):32631-32639. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3242-1 [86] HUANG Y L, HUANG J L, ERVINIA A, et al. Tracking riverine nitrate sources under changing land use pattern and hydrologic regime[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,152:110884. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.110884 [87] CAO S W, FEI Y H, TIAN X, et al. Determining the origin and fate of nitrate in the Nanyang Basin, Central China, using environmental isotopes and the Bayesian mixing model[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(35):48343-48361. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14083-2 [88] KORTH F, DEUTSCH B, FREY C, et al. Nitrate source identification in the Baltic Sea using its isotopic ratios in combination with a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Biogeosciences,2014,11(17):4913-4924. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-4913-2014 [89] GIBRILLA A, FIANKO J R, GANYAGLO S, et al. Nitrate contamination and source apportionment in surface and groundwater in Ghana using dual isotopes (15N and 18O-NO3) and a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2020,233:103658. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103658 [90] NAM T H, RYU H S, KANG T W, et al. Quantifying nitrogen source contribution ratios using stable isotope method: application of Bayesian mixing model[J]. Journal of Korean Society on Water Environment,2019,35(6):510-519. [91] TORRES-MARTÍNEZ J A, MORA A, KNAPPETT P S K, et al. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Water Research,2020,182:115962. ◇ doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115962 -





 下载:
下载: