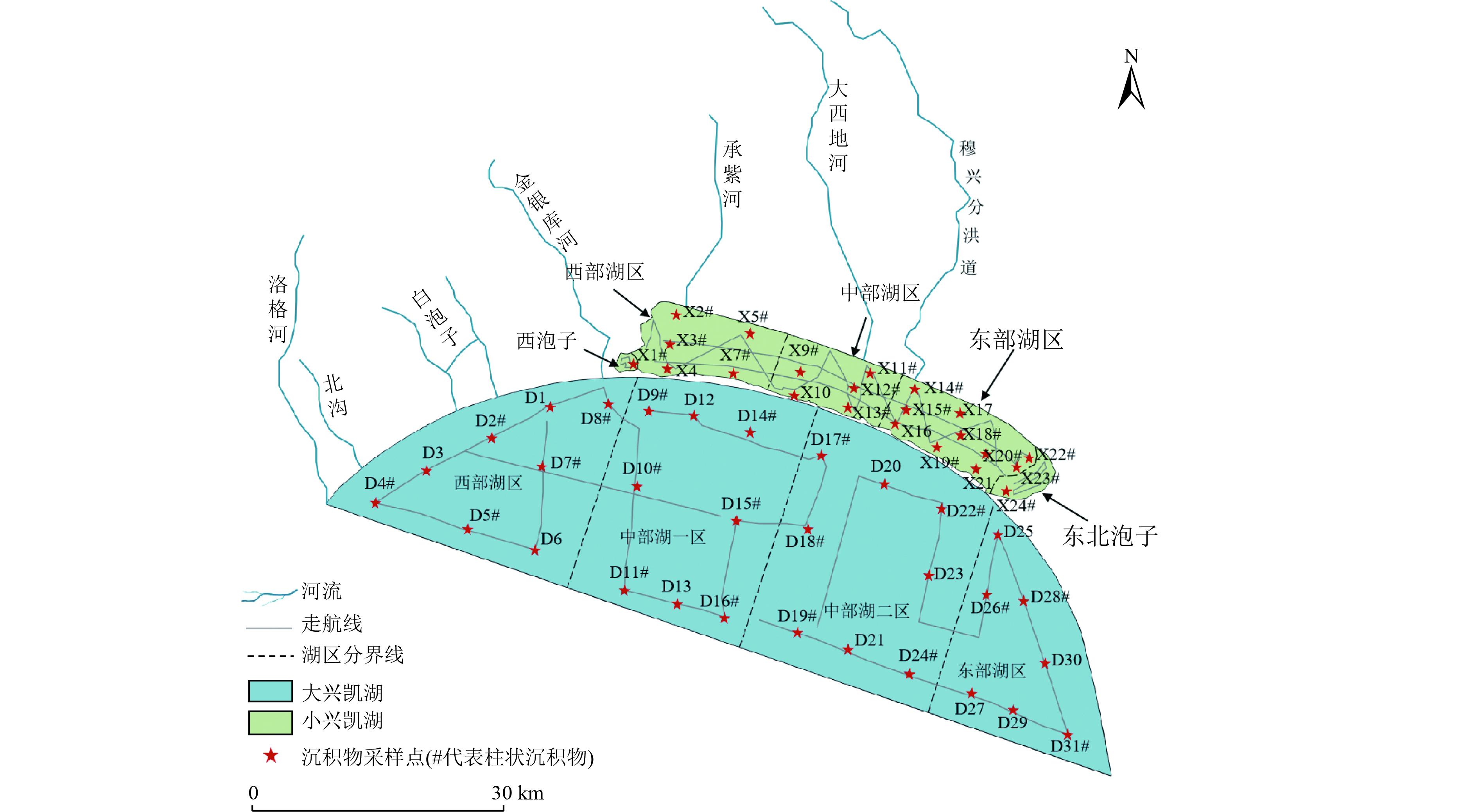
Distribution characteristics and source analysis of nutrients in sediments of Xingkai Lake
-
摘要:
兴凯湖是我国面积最大的跨境湖泊,其水质变化受到国际社会的共同关注。沉积物内源污染释放是影响水质的重要因素,研究沉积物营养盐的分布特征及来源,可为兴凯湖水环境治理提供重要依据。以兴凯湖中国湖区为研究对象,通过沉积物营养盐及蓄积量调查,阐明沉积物中总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)和有机质(OM)的分布特征及埋藏通量,采用有机污染指数法和沉积物碳氮比(C/N)、碳磷比(C/P)特征分析其污染程度及来源。结果表明:与国内其他湖泊相比,兴凯湖沉积物TP浓度处于较低水平,但小兴凯湖沉积物TN、OM浓度处于较高水平;水生植被覆盖度高的小兴凯湖西泡子和东北泡子及沉积物淤积严重的大兴凯湖西部湖区和中部湖一区营养盐浓度较高;兴凯湖OM来源同时受水生植物和陆源物质输入的影响,且小兴凯湖受陆源输入影响更大,OM与TN具有同源性,与TP不具有同源性;兴凯湖沉积物整体属轻度污染,其中小兴凯湖沉积物有机污染较大兴凯湖严重。研究显示,小兴凯湖作为大兴凯湖的前置湖泊,削减了输入大兴凯湖的污染物,但其较高的沉积物营养盐浓度可能会对大兴凯湖产生潜在影响,因此,应重视小兴凯湖沉积物引起的污染。
Abstract:Xingkai Lake is the largest international cross-border lake in China. The water quality of Xingkai Lake has attracted international attention. The release of sediment internal pollution is an important factor affecting water quality. Studying the distribution characteristics and sources of sediment nutrients can provide important support for the water environment management of Xingkai Lake. Small Xingkai Lake and Great Xingkai Lake in China were investigated. Firstly, the distribution characteristics and burial fluxes of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and organic matter (OM) in the sediments were clarified through the investigation of sediment nutrients and accumulation of sediment. Subsequently, the organic pollution index method was used to evaluate the sediment pollution level of Xingkai Lake. Additionally, nutrient sources were analyzed based on C/N and C/P values. The results showed that compared with other lakes in China, the average concentration of TP in the sediment of Xingkai Lake was at a low level, while the average concentrations of TN and OM in the sediment of Small Xingkai Lake were at a high level. The nutrient concentration was higher in the west and northeast of Small Xingkai Lake with high coverage of aquatic plants, and in the west and middle of Great Xingkai Lake with serious sediment deposition. The OM in the sediments was influenced by both aquatic plants and terrestrial inputs, and Small Xingkai Lake was more affected by terrestrial inputs. Pearson correlation analysis showed that OM and TN were homologous and not homologous with TP. The organic pollution evaluation results presented that Xingkai Lake was in light pollution, while the organic pollution in Small Xingkai Lake was more serious than that in Great Xingkai Lake. In conclusion, Small Xingkai Lake, as the front lake of Great Xingkai Lake, reduced the pollutants imported into Great Xingkai Lake. However, its high sediment nutrient concentrations may have a potential impact on Great Xingkai Lake. Therefore, attention should be paid to the sediment pollution of Small Xingkai Lake.
-
Key words:
- Xingkai Lake /
- sediment /
- nutrient /
- burial flux /
- pollution evaluation /
- source analysis
-
表 1 兴凯湖沉积物蓄积量和TN、TP、OM埋藏通量
Table 1. Sediment accumulation and burial fluxes of TN, TP and OM in Xingkai Lake
湖区 含水率
/%干密度
/(g/cm3)沉积物
平均厚度/m沉积物
蓄积量
/t埋藏通量
/(t/a)TN TP OM 西部湖区 31.29 1.26 0.20 1.06×107 159.48 18.94 3240.14 中部湖区 34.50 1.15 0.19 6.85×106 87.24 6.13 2065.76 小兴凯湖 东部湖区 36.09 1.06 0.17 6.92×106 118.16 18.26 2244.65 西泡子 56.87 0.48 0.13 3.23×104 2.23 0.60 29.89 东北泡子 37.57 1.07 0.15 1.08×106 18.99 1.23 536.17 大兴凯湖 西部湖区 37.07 0.97 0.41 6.01×107 182.86 55.61 2263.54 中部湖一区 28.87 1.25 0.29 8.01×107 301.27 143.80 4700.04 中部湖二区 30.18 1.06 0.25 6.04×107 207.75 116.45 3400.87 东部湖区 27.63 1.14 0.25 3.82×107 108.71 75.46 1521.81 表 2 兴凯湖表层沉积物中营养盐指标相关性分析
Table 2. Pearson correlation coefficients of nutrients in surface sediments of Xingkai Lake
指标 小兴凯湖 大兴凯湖 OM TN TP OM TN TP OM 1.000 1.000 TN 0.759** 1.000 0.521** 1.000 TP 0.403 0.759** 1.000 0.056 0.058 1.000 注:**表示P <0.01。 表 3 我国不同湖泊表层沉积物营养盐浓度、C/N和C/P对比
Table 3. Comparison of nutrient concentration, C/N and C/P in surface sediments of different lakes in China
湖泊 TN浓度/
(mg/kg)TP浓度/
(mg/kg)OM浓度/
(g/kg)C/N C/P 乌梁素海[42] 1960 560 38.5 12.70 73.93 衡水湖[43] 1 850 1020 160.72 60.2 233.1 太湖[44] 859.66 560.47 12.76 8.32 鄱阳湖[45] 1 340 460 15.9 洞庭湖[46] 1 046 368.85 22.86 13.22 洪泽湖[47] 1 020 580 13.64 7.86 呼伦湖[48] 1 600 800 27.58 10.2 青海湖[49] 1 740 590 32.07 巢湖[50] 918.01 684.40 22.01 6.37 小兴凯湖(本研究) 1 587.43 212.38 32.18 12.51 232.55 大兴凯湖(本研究) 519.24 246.55 7.51 8.72 19.25 -
[1] 范成新, 刘敏, 王圣瑞, 等.近20年来我国沉积物环境与污染控制研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2021,36(4):346-374.FAN C X, LIU M, WANG S R, et al. Research progress and prospect of sediment environment and pollution control in China in recent 20 years[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2021,36(4):346-374. [2] LIU C, SHAO S G, SHEN Q S, et al. Effects of riverine suspended particulate matter on the post-dredging increase in internal phosphorus loading across the sediment-water interface[J]. Environmental Pollution,2016,211:165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.045 [3] 马金玉, 王文才, 罗千里, 等.黄大湖沉积物营养盐分布及来源解析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(4):678-685.MA J Y, WANG W C, LUO Q L, et al. Distribution and source analysis of nutrients in sediments of Huangda Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(4):678-685. [4] 2021年黑龙江省生态环境状况公报[A/OL]. [2022-10-20]. http://www.hljdep.gov.cn/u/cms/stmh/202206/021135275hfw.pdf. [5] 刘伟, 周斌, 王丕波, 等.沉积物再悬浮氮磷释放的机制与影响因素[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(4):1311-1318.LIU W, ZHOU B, WANG P B, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus release via sediment re-suspension[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(4):1311-1318. [6] 安睿, 王凤友, 于洪贤, 等.小兴凯湖浮游植物功能群特征及其影响因子[J]. 环境科学研究,2016,29(7):985-994.AN R, WANG F Y, YU H X, et al. Characteristics and physical factors of phytoplankton functional groups in small Xingkai Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2016,29(7):985-994. [7] 郑恺原, 向小华.基于AHM-CRITIC赋权的小兴凯湖水质评价模型[J]. 节水灌溉,2020(9):79-83.ZHENG K Y, XIANG X H. Water quality evaluation model of Xiaoxingkai Lake based on AHM-CRITIC weighting[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2020(9):79-83. [8] 于淑玲, 李秀军, 陈国双, 等.小兴凯湖富营养化和沼泽化程度分析[J]. 湿地科学,2016,14(2):271-275.YU S L, LI X J, CHEN G S, et al. Analysis of eutrophication and terrestrialization of Xiaoxingkai Lake[J]. Wetland Science,2016,14(2):271-275. [9] 中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所. 湖泊调查技术规程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. [10] 环境保护部. 土壤质量 全氮的测定 凯氏法: HJ 717—2014[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2015. [11] 王圣瑞. 湖泊沉积物-水界面过程-基本理论与常用测定方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. [12] 陈殿波, 卢建伟.低温外热重铬酸钾氧化: 比色法测定脱水污泥有机碳[J]. 云南化工,2012,39(1):39-42.CHEN D B, LU J W. Low-temperature external-heat potassium dichromate oxidation-photo-colorimetric method for determination of organic carbon in dewatering sludge[J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology,2012,39(1):39-42. [13] 夏伟, 陈秋菊, 唐红渠, 等.浅地层剖面探测技术在山地型水库生态研究中的应用[J]. 生态科学,2013,32(3):276-281.XIA W, CHEN Q J, TANG H Q, et al. Application of shallow-strata profiling technique to sediment survey in canyon-type reservoirs[J]. Ecological Science,2013,32(3):276-281. [14] 杨国明, 朱俊江, 赵冬冬, 等.浅地层剖面探测技术及应用[J]. 海洋科学,2021,45(6):147-162.YANG G M, ZHU J J, ZHAO D D, et al. Development and application of sub-bottom profiler technologies[J]. Marine Sciences,2021,45(6):147-162. [15] WUNDERLICH J, WENDT G, MÜLLER S. High-resolution echo-sounding and detection of embedded archaeological objects with nonlinear sub-bottom profilers[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches,2005,26(2):123-133. [16] 沈吉, 袁和忠, 刘恩峰, 等.太湖表层沉积物的空间分布与层序特征分析[J]. 科学通报,2010,55(36):3516-3524. doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-36-3516SHEN J, YUAN H Z, LIU E F, et al. Spatial distribution and sequence characteristics of surface sediments in Taihu Lake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(36):3516-3524. doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-36-3516 [17] 李春华, 叶春, 魏伟伟. 镜泊湖生态环境调查与污染分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. [18] 罗千里, 胡艳芳, 马金玉, 等.疏浚对练江峡山大溪流域沉积物营养盐的影响分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(6):1985-1994.LUO Q L, HU Y F, MA J Y, et al. Effects of dredging on nutrients in sediments in Xiashan Daxi Basin of Lianjiang River[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(6):1985-1994. [19] YU N X, QIN Y, HAO F, et al. Using seismic surveys to investigate sediment distribution and to estimate burial fluxes of OC, N, and P in a canyon reservoir[J]. Acta Geochimica,2019,38(6):785-795. doi: 10.1007/s11631-019-00353-x [20] YU K K, ZHANG Y Q, HE X H, et al. Characteristics and environmental significance of organic carbon in sediments from Taihu Lake, China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2022,138:108796. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108796 [21] 李亮芳, 李春华, 叶春, 等.兴凯湖百余年营养演化历史及营养物基准[J]. 地球环境学报,2022,13(5):557-570.LI L F, LI C H, YE C, et al. Nutrient history in the past century and its baseline of Xingkai Lake[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2022,13(5):557-570. [22] 曹洋, 孙鹤铭, 刘利, 等.冬季衡水湖沉积物微生物群落结构特征及影响因素[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):154-163.CAO Y, SUN H M, LIU L, et al. Microbial community structure characteristics and influencing factors in sediments of Hengshui Lake in winter[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):154-163. [23] 兴凯湖流域生态环境调查报告[R]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2022. [24] 李乾岗, 田颖, 刘玲, 等.水体中沉积物氮和磷的释放机制及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 湿地科学,2022,20(1):94-103.LI Q G, TIAN Y, LIU L, et al. Research progress on release mechanisms of nitrogen and phosphorus of sediments in water bodies and their influencing factors[J]. Wetland Science,2022,20(1):94-103. [25] 王洪伟,王少明,张敏,等.春季潘家口水库沉积物-水界面氮磷赋存特征及迁移通量 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021,41(9):4284-4293.
WANG H W, WANG S M, ZHANG M, et al. Occurrence characteristics and transport fluxes of nitrogen and phosphorus at sediment-water interface of Panjiakou Reservoir in spring [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021,41(9):4284-4293.[26] 贾雪莹, 田志杰, 张冬杰, 等.小兴凯湖表层沉积物的理化特征和磷吸附效率研究[J]. 湿地科学,2021,19(5):577-584.JIA X Y, TIAN Z J, ZHANG D J, et al. Physical and chemical characteristic and phosphorus adsorption efficiency of surface sediment in Xiaoxingkai Lake[J]. Wetland Science,2021,19(5):577-584. [27] 何桐, 杨文丰, 谢健, 等.大亚湾柱状沉积物中C、N、P的分布特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋环境科学,2015,34(4):524-529.HE T, YANG W F, XIE J, et al. Distribution characteristics and environmental significance of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in core sediments of Daya Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2015,34(4):524-529. [28] 甘树, 卢少勇, 秦普丰, 等.太湖西岸湖滨带沉积物氮磷有机质分布及评价[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(9):3064-3069.GAN S, LU S Y, QIN P F, et al. Spatial distribution and evaluation of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments from western lakeside belt of Lake Taihu[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(9):3064-3069. [29] 邱祖凯, 胡小贞, 姚程, 等.山美水库沉积物氮磷和有机质污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学,2016,37(4):1389-1396.QIU Z K, HU X Z, YAO C, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in sediments of Shanmei Reservoir in Fujian, China[J]. Environmental Science,2016,37(4):1389-1396. [30] 苗慧, 沈峥, 蒋豫, 等.巢湖表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的分布及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报,2017,26(12):2120-2125.MIAO H, SHEN Z, JIANG Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2017,26(12):2120-2125. [31] 向速林, 吴涛哲, 龚聪远, 等.鄱阳湖沉积物与水界面氮的迁移特征及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报,2021,30(4):781-786.XIANG S L, WU T Z, GONG C Y, et al. Transportation features and pollution evaluation of nitrogen at the sediment-water interface of Poyang Lake[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2021,30(4):781-786. [32] 方家琪, 祁闯, 张新厚, 等.太湖竺山湾沉积物碳氮磷分布特征与污染评价[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(12):5367-5374.FANG J Q, QI C, ZHANG X H, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in sediments of Zhushan Bay at Taihu Lake[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(12):5367-5374. [33] 郭云艳, 周光鑫, 王雅雯, 等.南湖水系表层沉积物有机质的赋存特征、来源及生物有效性[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):936-943.GUO Y Y, ZHOU G X, WANG Y W, et al. Occurrence characteristics, sources and bioavailability of organic matter in surface sediments of Nanhu Lake water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):936-943. [34] MEYERS P A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter[J]. Chemical Geology,1994,114(3/4):289-302. [35] 王小雷, 杨浩, 顾祝军, 等.抚仙湖沉积物中营养盐和粒度垂向分布及相关性研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2014,4(5):353-360.WANG X L, YANG H, GU Z J, et al. Vertical distribution and correlation of nutrients and grain sizes in sediment cores of Lake Fuxian[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2014,4(5):353-360. [36] 李昶. 不同水库淤积形态对总有机碳、总氮埋藏通量的影响[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018. [37] SOBEK S, DURISCH-KAISER E, ZURBRÜGG R, et al. Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2009,54(6):2243-2254. doi: 10.4319/lo.2009.54.6.2243 [38] 杨洪, 易朝路, 谢平, 等.武汉东湖沉积物碳氮磷垂向分布研究[J]. 地球化学,2004,33(5):507-514.YANG H, YI C L, XIE P, et al. Vertical distribution of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of sediments at Stations Ⅰ and Ⅱ in Lake Donghu, Wuhan[J]. Geochimica,2004,33(5):507-514. [39] TANG F, HUANG T, FAN R, et al. Temporal variation in sediment C, N, and P stoichiometry in a plateau lake during sediment burial[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2020,20(3):1706-1718. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02501-5 [40] WU H P, HAO B B, CAI Y P, et al. Effects of submerged vegetation on sediment nitrogen-cycling bacterial communities in Honghu Lake (China)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,755:142541. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142541 [41] 贾雪莹, 田志杰, 张冬杰, 等.富铁农田退水对小兴凯湖沉积物磷吸附释放影响[J]. 生态学杂志,2022,41(6):1128-1134.JIA X Y, TIAN Z J, ZHANG D J, et al. Effect of iron-rich farmland drainage on phosphorus adsorption and release in sediments of Xiaoxingkai Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2022,41(6):1128-1134. [42] 张晓晶. 乌梁素海沉积物污染特征及营养盐释放规律试验研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2010. [43] 张嘉雯, 魏健, 刘利, 等.衡水湖沉积物营养盐形态分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(12):5389-5399.ZHANG J W, WEI J, LIU L, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nutrients in Hengshui Lake sediments[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(12):5389-5399. [44] 袁和忠, 沈吉, 刘恩峰, 等.太湖水体及表层沉积物磷空间分布特征及差异性分析[J]. 环境科学,2010,31(4):954-960.YUAN H Z, SHEN J, LIU E F, et al. Space distribution characteristics and diversity analysis of phosphorus from overlying water and surface sediments in Taihu Lake[J]. Environmental Science,2010,31(4):954-960. [45] 王圣瑞, 倪栋, 焦立新, 等.鄱阳湖表层沉积物有机质和营养盐分布特征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2012,2(1):23-28.WANG S R, NI D, JIAO L X, et al. Space-time variety of organic matter and nutrient in surface sediments from Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2012,2(1):23-28. [46] 刘俊, 田学达, 王琳杰, 等.洞庭湖表层沉积物营养盐空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):701-706.LIU J, TIAN X D, WANG L J, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of surface sediment nutrients in Lake Dongting[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):701-706. [47] 余辉, 张文斌, 卢少勇, 等.洪泽湖表层底质营养盐的形态分布特征与评价[J]. 环境科学,2010,31(4):961-968.YU H, ZHANG W B, LU S Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of surface sediments nutrients in Lake Hongze and their pollution status evaluation[J]. Environmental Science,2010,31(4):961-968. [48] 李卫平, 李畅游, 贾克力, 等.内蒙古呼伦湖沉积物营养元素分布及环境污染评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2010,29(2):339-343. [49] 陈学民, 朱阳春, 伏小勇, 等.青海湖表层沉积物营养元素分布特征及相关性分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2012,31(2):395-401.CHEN X M, ZHU Y C, FU X Y, et al. Investigation of eutrophic elements distribution and their correlation in Qinhai Lake surface sediments[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2012,31(2):395-401. [50] 李强, 霍守亮, 王晓伟, 等.巢湖及其入湖河流表层沉积物营养盐和粒度的分布及其关系研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(2):147-155.LI Q, HUO S L, WANG X W, et al. Distribution and correlation of nutrients and particle size in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu and its inflow rivers[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(2):147-155. ◇ -




 下载:
下载: