Study on the composition and influencing factors of microbial community in ecological restoration rivers
-
摘要:
为明确生态修复类型河流的微生物群落结构、功能及其影响因素,以许昌市清潩河为例,采用高通量测序的方法研究生态修复措施对河流水体和沉积物微生物群落结构的影响,并在此基础上分析碳氮硫功能菌群在生态修复措施中的净化作用及水体病原菌分布状况。结果表明:在人类干扰较少的河段,近自然河岸带对陆源污染起着较好的拦截效果,生态滤坝设施的截留和复氧能力有助于河流对化学需氧量(COD)的去除;城区段河流受人类活动影响水质变化较大,生态修复措施净化效果不明显;城郊段人类干扰较少,河流自净能力提升,总磷(TP)、氨氮(NH4 +-N)等指标逐渐恢复原有水平。清潩河沉积物中微生物多样性和丰富度均高于水体,且变形菌门(Proteobacteria)是沉积物和水体中的优势物种。部分河段参与氮循环的蓝藻菌门(Cyanobacteria)相对丰度达到4.7%,说明清潩河仍存在富营养化河段。清潩河水体中相对丰度最高的致病菌群为不动杆菌(Acinetobacter),而沉积物中相对丰度最高的致病菌群为梭状芽孢杆菌属(Clostridium)、黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),其中拟杆菌门在城区段相对丰度最高。Spearman相关性分析表明,水体中微生物多样性与温度、pH、COD有显著相关性(P<0.05),城郊段沉积物中微生物群落结构的主要影响因子为NH4 +-N、总氮(TN)和TP。生态修复河流城区段微生物丰度和多样性较高,致病风险大;城郊段碳氮硫功能菌群丰度高,是物质循环的主要场所。
Abstract:In order to clarify the microbial community structure, function and influencing factors of ecological restoration rivers, the Qingyi River in Xuchang City was taken as an example, and high-throughput sequencing methods were used to study the influence of ecological restoration measures on the microbial community structure of river water and sediment, and then the purification effect of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur functional bacteria in ecological restoration measures and the distribution of waterborne pathogenic bacteria were analyzed. The results showed that: In the river sections with less human interference, the near-natural riverbank had a good interception effect on land-source pollution, and the interception and oxygenation capacity of ecological filter dams could help the river to remove chemical oxygen demand (COD). The water quality of the urban river section was greatly affected by human activities, and the purification effect of ecological restoration measures was not obvious. In the suburban river section, human interference was less, the river's self-purification capacity was improved, and the total phosphorus (TP) and ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +-N) indicators gradually returned to the original level. The microbial diversity and richness of the Qingyi River sediment were higher than that of the overlying water, and Proteobacteria was the dominant species in sediment and water. The relative abundance of Cyanobacteria, which participated in the nitrogen cycle, reached 4.7%, indicating that the Qingyi River still had eutrophic river sections. The most abundant pathogenic bacteria in the Qingyi River water was Acinetobacter, while the most abundant pathogenic bacteria in sediment were Clostridium, Flavobacterium and Bacteroidetes, among which Bacteroidetes was the most abundant in the urban section. Spearman correlation analysis showed that there was a significant correlation between microbial diversity in water and temperature (T), pH, COD (P<0.05). The main factors affecting the microbial community structure in the suburban sediment were NH4 +-N, total nitrogen (TN) and TP. The results showed that the abundance and diversity of microbes in the urban section of the ecologically restored river were high and the risk of pathogenicity was high; the abundance of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur functional bacteria in the suburban section was high, and it was the main place for material cycling.
-
Key words:
- Qingyi River /
- microorganism /
- diversity /
- community structure /
- environmental factors
-
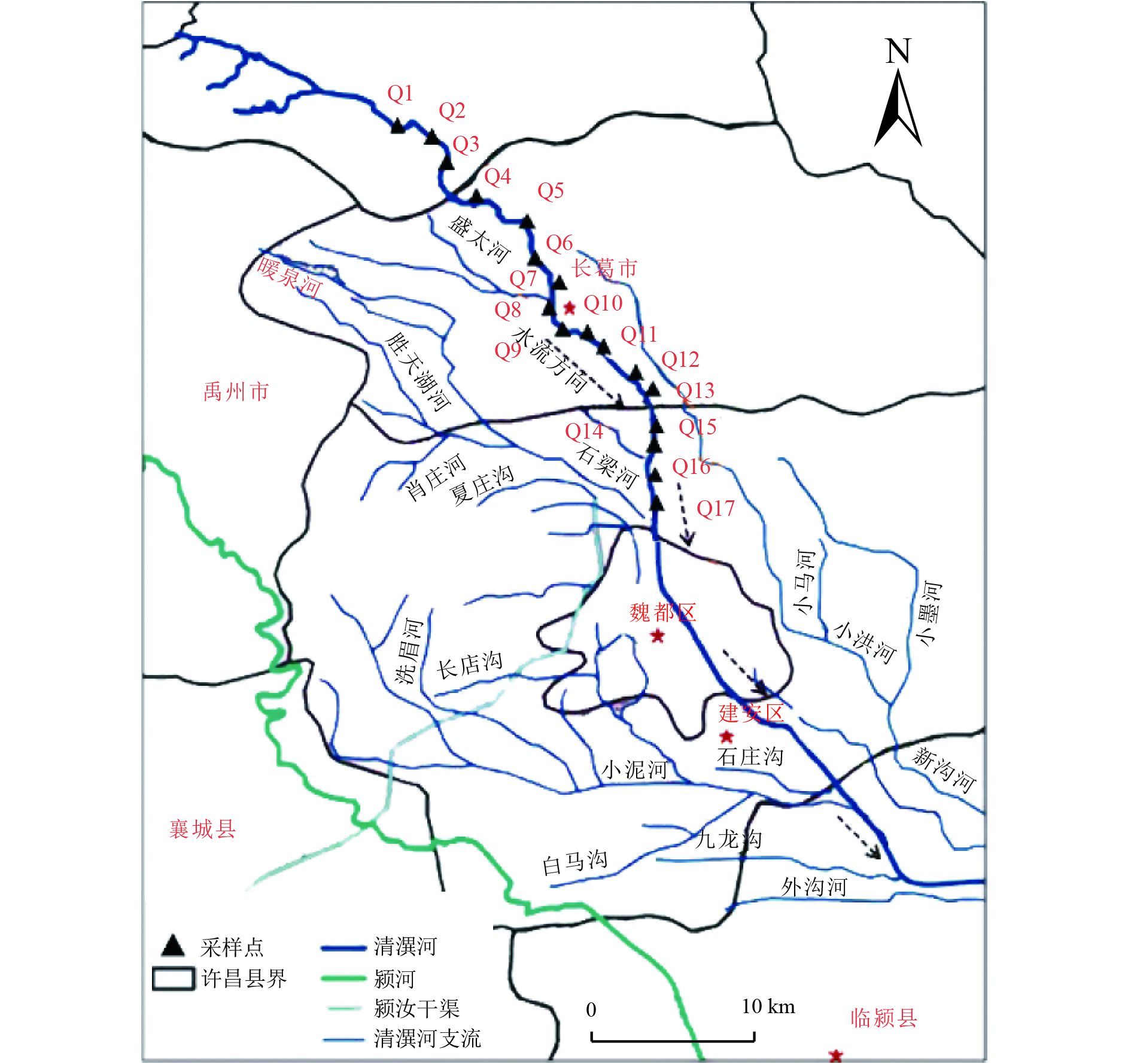
表 1 清潩河流域水体理化指标
Table 1. Physical and chemical indexes of water bodies in Qingyi River basin
采样点 pH 水温/℃ DO浓度/
(mg/L)COD/
(mg/L)NH4 +-N浓度/
(mg/L)NO3 −-N浓度/
(mg/L)NO2 −-N浓度/
(mg/L)TN浓度/
(mg/L)TP浓度/
(mg/L)Q1(增福庙水库) 8.66 27.3 9.29 2.50 0.013 0.41 0.005 6.98 0.020 Q2(高铁桥生态滤坝) 8.25 27.8 9.99 5.76 0.013 0.22 0.004 6.87 0.010 Q3(段黄庄观景台) 8.67 29.2 10.10 2.50 0.013 0.10 0.004 7.68 0.020 Q4(八一路生态滤坝) 9.37 29.6 12.06 22.40 0.013 0.10 0.004 7.84 0.030 Q5(长社路赵庄桥) 9.54 29.4 13.17 17.76 0.087 0.10 0.004 7.73 0.040 Q6(建设路生态浮岛) 10.01 30.2 13.53 33.76 0.390 0.10 0.016 8.80 0.070 Q7(建设路生态滤坝) 10.04 30.6 12.22 41.44 0.337 0.34 0.013 9.13 0.070 Q8(人民路生态浮岛) 10.08 30.5 11.98 30.40 0.275 0.10 0.002 3.07 0.050 Q9(英刘闸上游) 10.43 31.6 13.21 36.48 0.348 0.54 0.002 3.07 0.005 Q10(葛天大道生态滤坝) 8.45 34.0 7.67 61.12 0.337 0.27 0.008 11.54 0.230 Q11(杜村寺闸前后) 9.14 31.1 12.38 30.88 0.045 4.26 0.005 9.45 0.040 Q12(关庄闸上游) 9.08 31.0 13.13 19.68 0.045 5.81 0.005 10.63 0.005 Q13(关庄闸下游30 m) 7.62 28.9 4.45 19.92 0.108 6.36 0.007 11.27 0.050 Q14(关庄闸下游200 m) 7.68 28.0 5.07 12.40 0.076 6.06 0.007 10.84 0.040 Q15(关庄闸生态滤坝) 7.64 28.0 5.47 9.84 0.013 5.76 0.007 10.79 0.040 Q16(禄马桥下游500 m) 7.96 28.8 8.01 9.28 0.013 5.99 0.006 10.47 0.005 Q17(县道007) 8.03 28.6 7.99 2.50 0.076 5.18 0.005 10.14 0.050 表 2 水体和沉积物样品在97%水平下的丰富度和多样性指数
Table 2. Richness and diversity index of water and sediment samples at 97% level
采样点 水体 沉积物 Chao Shannon-Wninner Coverage Chao Shannon-Wninner Coverage Q1 1 332.6 5.10 0.99 Q2 1 386.8 6.99 0.99 Q6 3 935.6 9.06 0.99 Q7 5 202.2 9.66 0.99 Q10 5 156.3 9.85 0.99 Q11 5 919.3 10.4 0.99 Q12 5 762.3 10.5 0.99 Q14 1 526.0 6.39 0.99 5 844.3 10.1 0.99 Q16 2 530.4 5.13 0.99 Q17 1 741.7 5.38 0.99 5 754.2 9.73 0.99 -
[1] RIEMANN L, STEWARD G F, AZAM F. Dynamics of bacterial community composition and activity during a mesocosm diatom bloom[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2000,66(2):578-587. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.2.578-587.2000 [2] 董婧, 卢少奇, 伍娟丽, 等.基于微生物生物完整性指数的北京市城市河道生态系统健康评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1411-1419. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210368DONG J, LU S Q, WU J L, et al. Evaluation of urban river ecosystem health in Beijing based on the microbial index of biotic integrity[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(5):1411-1419. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210368 [3] JAMIESON R, GORDON R, JOY D, et al. Assessing microbial pollution of rural surface waters[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2004,70(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2004.05.006 [4] PERKINS T L, CLEMENTS K, BAAS J H, et al. Sediment composition influences spatial variation in the abundance of human pathogen indicator bacteria within an estuarine environment[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(11):e112951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112951 [5] 赵建国, 翟学正, 郭祥, 等.永定河怀来段冬季表层沉积物细菌群落特征及其主要影响因子[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(5):544-551. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.03.250ZHAO J G, ZHAI X Z, GUO X, et al. Bacterial community characteristics and key driving factors of surface sediments in Huailai section of Yongding River in winter[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(5):544-551. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.03.250 [6] MILLS H J, MARTINEZ R J, STORY S, et al. Identification of members of the metabolically active microbial populations associated with Beggiatoa species mat communities from Gulf of Mexico cold-seep sediments[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2004,70(9):5447-5458. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5447-5458.2004 [7] STALEY C, JOHNSON D, GOULD T J, et al. Frequencies of heavy metal resistance are associated with land cover type in the Upper Mississippi River[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,511:461-468. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.069 [8] 陈洪森, 叶春, 李春华, 等.入湖河口区水生植物群落衰亡分解释放营养盐过程模拟研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(2):220-228. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190108CHEN H S, YE C, LI C H, et al. Simulation study on decomposition and release of nutrients from aquatic macrophyte communities in confluence area between lake and river[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(2):220-228. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190108 [9] 魏佳明, 崔丽娟, 李伟, 等.表流湿地细菌群落结构特征[J]. 环境科学,2016,37(11):4357-4365. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201602108WEI J M, CUI L J, LI W, et al. Characteristics of bacterial communities in surface-flow constructed wetlands[J]. Environmental Science,2016,37(11):4357-4365. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201602108 [10] 刘峰, 冯民权, 王毅博.汾河入黄口夏季微生物群落结构分析[J]. 微生物学通报,2019,46(1):54-64. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.180252LIU F, FENG M Q, WANG Y B. Microbial community structure of estuary of the Fenhe River into the Yellow River in summer[J]. Microbiology China,2019,46(1):54-64. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.180252 [11] 白洁, 刘小沙, 侯瑞, 等.南海南部海域浮游细菌群落特征及影响因素研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2014,34(11):2950-2957.BAI J, LIU X S, HOU R, et al. Community structure and influencing factors of bacterioplankton in the southern South China Sea[J]. China Environmental Science,2014,34(11):2950-2957. [12] 王晓辉, 郭光霞, 郑瑞伦, 等.生物炭对设施退化土壤氮相关功能微生物群落丰度的影响[J]. 土壤学报,2013,50(3):624-631. doi: 10.11766/trxb201209180375WANG X H, GUO G X, ZHENG R L, et al. Effect of biochar on abundance of n-related functional microbial communities in degraded greenhouse soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2013,50(3):624-631. doi: 10.11766/trxb201209180375 [13] 高磊, 包卫洋, 张天文, 等.水体碳氮比对芽孢杆菌、乳酸菌与弧菌生长、拮抗作用及菌体碳氮比的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(1):34-40. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2013.01.005GAO L, BAO W Y, ZHANG T W, et al. Effect of water C∶N ratio on the growth, antagonism and C∶N ratio of Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria and Vibrio[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2013,43(1):34-40. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2013.01.005 [14] 李静, 陈芝兰, 李小卫.西藏湿地生态系统中氮循环微生物数量和多样性研究[J]. 西藏科技,2015(4):70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3403.2015.04.027LI J, CHEN Z L, LI X W. Study on the quantity and diversity of nitrogen cycling microorganisms in Tibet wetland ecosystem[J]. Tibet Science and Technology,2015(4):70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3403.2015.04.027 [15] GRANDLIC C J, GEIB I, PILON R, et al. Lead pollution in a large, prairie-pothole lake (Rush Lake, WI, USA): effects on abundance and community structure of indigenous sediment bacteria[J]. Environmental Pollution,2006,144(1):119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.029 [16] CHODAK M, GOŁĘBIEWSKI M, MORAWSKA-PŁOSKONKA J, et al. Diversity of microorganisms from forest soils differently polluted with heavy metals[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,2013,64:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.11.004 [17] 袁瑞强, 牛漾聃, 王鹏, 等.引黄对受水河段沉积物微生物群落的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2019,39(2):499-508. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0368YUAN R Q, NIU Y D, WANG P, et al. Effects of the Yellow River diversion on microbial communities in sediments of the receiving reach[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2019,39(2):499-508. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0368 [18] 刘幸春, 王洪杰, 王亚利, 等.府河水体及沉积物细菌群落结构分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态毒理学报,2021,16(5):120-135.LIU X C, WANG H J, WANG Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of bacteria community structure in water and sediments of Fuhe River[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2021,16(5):120-135. [19] 赵欣艳, 王海燕, 侯泽英, 等.洱海沙坪湾湖滨带不同植被带中细菌分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(5):705-711. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.01ZHAO X Y, WANG H Y, HOU Z Y, et al. Bacteria distribution characteristics of different vegetation belts along shapingwan riparian zone of Erhai Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(5):705-711. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.01 [20] 林海, 蔡怡清, 李冰, 等.北京市妫水河底泥微生物群落结构特征[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(20):7592-7601.LIN H, CAI Y Q, LI B, et al. Characteristics of microbial community structure in Guishui River sediment in Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(20):7592-7601. [21] 陈丽蓉. 北极深海沉积物中微生物的多样性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2012. [22] 奚万艳, 吴鑫, 叶文瑾, 等.太湖梅梁湾水域蓝藻水华前与水华末期细菌群落结构的变化[J]. 应用与环境生物学报,2007,13(1):97-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2007.01.022XI W Y, WU X, YE W J, et al. Changes in bacterial community structure during preceding and degraded period of cyanobacterial bloom in a bay of the Taihu Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology,2007,13(1):97-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2007.01.022 [23] KANALY R A, HARAYAMA S. Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2000,182(8):2059-2067. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2059-2067.2000 [24] 李垒, 孟庆义, 叶飞, 等.密云水库入库河流水体总细菌和反硝化菌群落组成与结构[J]. 水生态学杂志,2018,39(6):44-51. doi: 10.15928/j.1674-3075.2018.06.007LI L, MENG Q Y, YE F, et al. Microbial community structures of total bacteria and denitrifying bacteria in the tributaries of Miyun Reservoir[J]. Journal of Hydroecology,2018,39(6):44-51. ⊗ doi: 10.15928/j.1674-3075.2018.06.007 -





 下载:
下载: