Characterizing the composition of dissolved organic matter in groundwater at a polluted site and its indicating significance for natural attenuation
-
摘要:
溶解性有机质(DOM)影响着地下水中污染物的降解转化行为,其结构组成的变化可以反映外来污染物的迁移转化过程。以山东某污染场地地下水为研究对象,利用三维荧光光谱(EEM)、同步荧光光谱(SFS)和荧光区域体积积分法(FRI)分析研究区地下水DOM的组成及结构变化规律,并结合自然衰减能力评估方法——水文地球化学指标分析方法和微生物学分析方法探讨DOM光谱信息对地下水有机污染自然衰减效果的指示作用。结果表明:在地下水有机污染持续存在和长期的微生物作用下,地下水DOM中类腐殖质和类蛋白物质组分含量均增加,随着生物降解作用越来越强烈,DOM中类蛋白物质占比逐渐升高。基于FRI分区理论,提出可用特定荧光分区相对含量比〔P(Ⅰ+Ⅱ)/PⅤ〕,即类蛋白物质与类腐殖质物质的相对含量比,作为快速判断地下水有机污染自然衰减生物作用效果的代替表征指标,P(Ⅰ+Ⅱ)/PⅤ越大,表明自然衰减中的生物降解作用越强。
-
关键词:
- 地下水 /
- 溶解性有机质(DOM) /
- 荧光特征 /
- 自然衰减
Abstract:Dissolved organic matter (DOM) affects the degradation and transformation of pollutants in groundwater, and the changes of DOM structural composition can reflect the migration and transformation process of external pollutants. Taking groundwater from a polluted site in Shandong Province as the research object, three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy (EEM), synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy (SFS) and fluorescence region volume integral method (FRI) were used to analyze the composition and structure of the groundwater DOM. The role of DOM spectral information in indicating the natural attenuation effect of groundwater organic pollution was investigated in combination with the natural attenuation capacity assessment methods, i.e. hydrogeochemical index analysis method and microbiological analysis method. The results showed that the content of both humus-like and protein-like substances in groundwater increased under the persistence of organic pollution in groundwater and long-term microbial action, and the proportion of protein-like substances gradually increased with the increasingly strong biodegradation. Based on FRI region theory, a substitute characterization index was proposed to quickly assess the effect of the biodegradation in the natural attenuation of organic pollution in groundwater: the ratio of relative contents of specific fluorescence regions [P(Ⅰ +Ⅱ) /PⅤ], that was, the ratio of the relative content of protein-like substances to humus-like substances. The larger the value of P(Ⅰ+Ⅱ) /PⅤ was, the stronger the biodegradation in natural attenuation was.
-
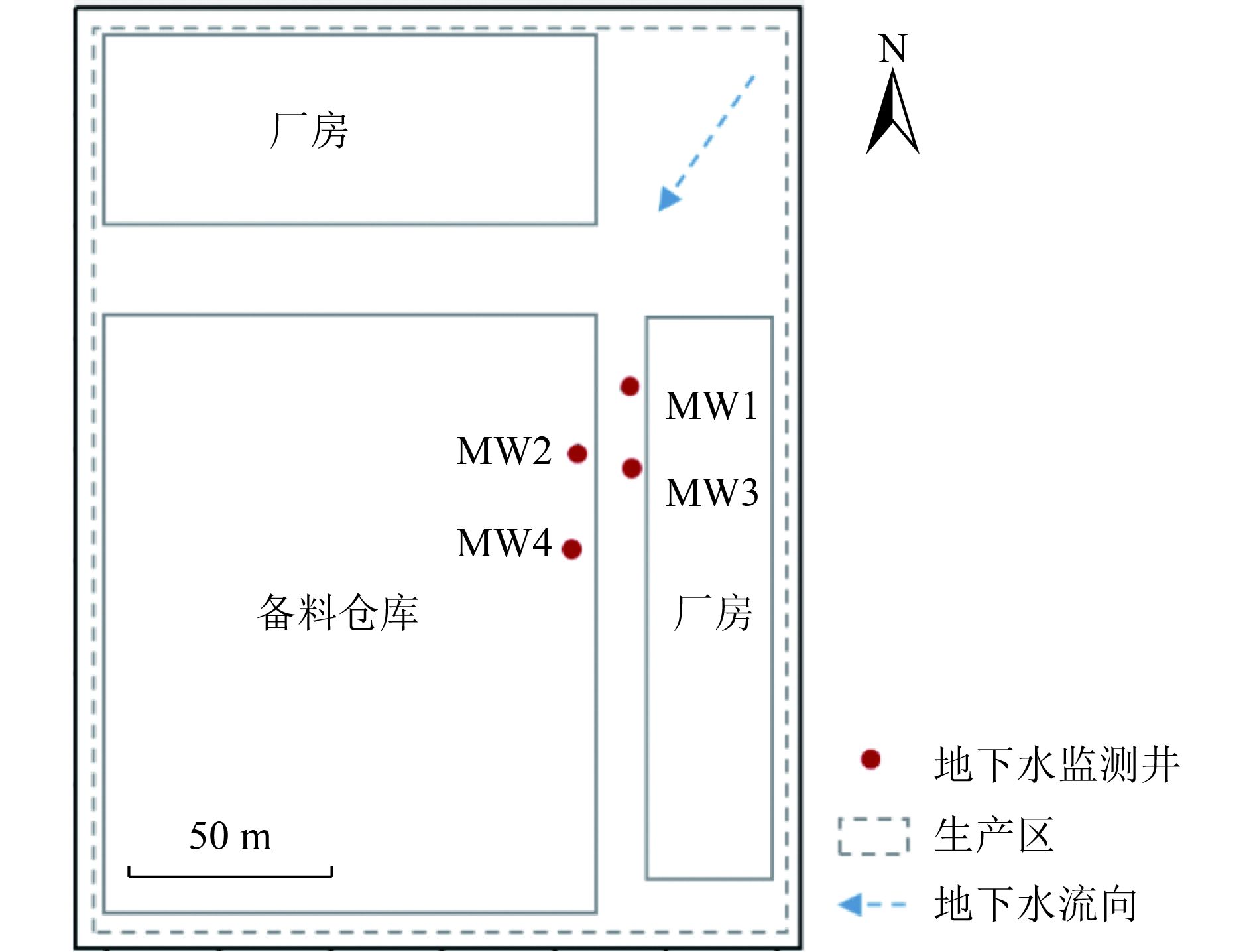
表 1 各监测井地下水常规水质指标及特征污染物指标
Table 1. Statistical information on the groundwater conventional quality indicators and characteristic pollutant indicators in various monitoring wells
监测井 井深/m pH TDS/
(mg/L)总硬度/ (mg/L,
以CaCO3计)耗氧量/
(mg/L)石油烃(C10~C40)
浓度/(mg/L)苯浓度
/
(μg/L)氯乙烯浓度
/
(μg/L)TOC
浓度/
(mg/L)MW1 12 6.65 2 450 502 10.1 0.87 9 180 3 100 36.23 MW2 12 6.81 2 320 917 22.1 0.19 242 1 130 10.83 MW3 12 6.68 3 060 1 850 26.2 0.20 462 2 030 7.71 MW4 12 6.97 1 680 1 100 18.8 0.13 803 3 050 4.38 表 2 已有研究中部分常见有机污染物及相关降解产物三维荧光光谱信息
Table 2. Three-dimensional fluorescence spectral information of some common organic pollutants and related products of degradation in previous researches
表 3 各监测井地下水的FI、BIX、HIX、β∶α指数描述统计
Table 3. Descriptive statistics of FI, BIX, HIX, (β∶α) of groundwater in various monitoring wells
监测井 FI BIX HIX β∶α MW1 1.82 1.18 1.14 1.08 MW2 1.80 1.17 2.87 1.07 MW3 1.82 1.22 3.30 1.10 MW4 1.84 1.14 3.43 1.04 表 4 地下水DOM三维荧光光谱区域积分结果
Table 4. Volume integration results of DOM in different regions of three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of groundwater
监测井 Фi/(105 a.u.·nm2) $\displaystyle\sum _{i=1}^{5}{\varPhi }_{i}$/(105 a.u.·nm2) Pi/% Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ MW1 12.9 16.6 10.2 12.5 21.7 73.9 17.44 22.42 13.78 16.94 29.43 MW2 2.3 4.8 5.7 4.2 13.8 30.8 7.39 15.62 18.68 13.56 44.74 MW3 0.2 1.5 3.1 5.6 18.5 28.9 0.58 5.33 10.74 19.47 63.87 MW4 0.2 1.3 2.3 3.2 11.2 18.2 1.13 6.91 12.88 17.54 61.54 表 5 各监测井地下水水化学指标
Table 5. Hydrochemistry indexes of groundwater in various monitoring wells
监测井 ORP/
mVDO浓度/
(mg/L)SO4 2−浓度/
(mg/L)NO3 −浓度/
(mg/L)1)(PⅠ+PⅡ)/
PⅤMW1 −52.6 3.01 191 0.9 1.35 MW2 −29.7 2.44 202 12.1 0.51 MW3 −26.0 1.54 166 10.7 0.09 MW4 −18.4 3.57 278 14.1 0.13 背景值 304 22.5 1) 以N计。 -
[1] MÜLLER J B, RAMOS D T, LAROSE C, et al. Combined iron and sulfate reduction biostimulation as a novel approach to enhance BTEX and PAH source-zone biodegradation in biodiesel blend-contaminated groundwater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,326:229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.005 [2] SPERFELD M, RAUSCHENBACH C, DIEKERT G, et al. Microbial community of a gasworks aquifer and identification of nitrate-reducing Azoarcus and Georgfuchsia as key players in BTEX degradation[J]. Water Research,2018,132:146-157. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.040 [3] 李元杰, 王森杰, 张敏, 等.土壤和地下水污染的监控自然衰减修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(3):1185-1193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.047LI Y J, WANG S J, ZHANG M, et al. Research progress of monitored natural attenuation remediation technology for soil and groundwater pollution[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(3):1185-1193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.047 [4] COZZARELLI I M, SCHREIBER M E, ERICKSON M L, et al. Arsenic cycling in hydrocarbon plumes: secondary effects of natural attenuation[J]. Ground Water,2016,54(1):35-45. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12316 [5] LIAO H H, YU K, DUAN Y H, et al. Profiling microbial communities in a watershed undergoing intensive anthropogenic activities[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,647:1137-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.103 [6] STENGER R, CLAGUE J C, MORGENSTERN U, et al. Vertical stratification of redox conditions, denitrification and recharge in shallow groundwater on a volcanic hillslope containing relict organic matter[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,639:1205-1219. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.122 [7] JIANG Y, LI R, YANG Y N, et al. Migration and evolution of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate-contaminated groundwater plume[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,2019,151:104463. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104463 [8] SARKAR D, FERGUSON M, DATTA R, et al. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated soils: comparison of biosolids addition, carbon supplementation, and monitored natural attenuation[J]. Environmental Pollution,2005,136(1):187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2004.09.025 [9] 刘东萍, 高红杰, 崔兵, 等.白塔堡河底泥DOM组成结构的荧光光谱与多元统计模型表征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):249-257. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200204LIU D P, GAO H J, CUI B, et al. Fluorescence spectra and multivariate statistical model characterization of DOM composition structure of Baitapu River sediment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):249-257. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200204 [10] HU Y, LU Y H, EDMONDS J, et al. Irrigation alters source-composition characteristics of groundwater dissolved organic matter in a large arid river basin, Northwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,767:144372. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144372 [11] 言宗骋, 高红杰, 郭旭晶, 等.蘑菇湖沉积物间隙水溶解性有机质紫外可见光谱研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):685-691. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.160YAN Z C, GAO H J, GUO X J, et al. Study on UV-vis spectra of dissolved organic matter from sediment interstitial water in Moguhu Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):685-691. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.160 [12] CONMY R N, COBLE P G, FARR J, et al. Submersible optical sensors exposed to chemically dispersed crude oil: wave tank simulations for improved oil spill monitoring[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(3):1803-1810. [13] PODGORSKI D C, ZITO P, McGUIRE J T, et al. Examining natural attenuation and acute toxicity of petroleum-derived dissolved organic matter with optical spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(11):6157-6166. [14] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2003,37(24):5701-5710. [15] 谢云峰, 曹云者, 柳晓娟, 等.地下水挥发性有机污染物自然衰减能力评价方法[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(2):104-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.02.018XIE Y F, CAO Y Z, LIU X J, et al. Assessment methods of volatile organic contaminants natural attenuation in contaminated aquifers[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(2):104-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.02.018 [16] 李英军, 何小松, 刘骏, 等.城市生活垃圾填埋初期有机质演化规律研究[J]. 环境工程学报,2012,6(1):297-301.LI Y J, HE X S, LIU J, et al. Study on organic matter evolution during the early few years of landfill of municipal solid wastes[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2012,6(1):297-301. [17] MA Y, LIU Z H, XI B D, et al. Molecular structure and evolution characteristics of dissolved organic matter in groundwater near landfill: implications of the identification of leachate leakage[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,787:147649. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147649 [18] BU L, WANG K, ZHAO Q L, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter during landfill leachate treatment by sequencing batch reactor, aeration corrosive cell-Fenton, and granular activated carbon in series[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,179(1/2/3):1096-1105. [19] 徐荣, 孙素琴, 陈君, 等.肉苁蓉种子成分及活力的红外光谱分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2009,29(1):97-101. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)01-0097-05XU R, SUN S Q, CHEN J, et al. Infrared spectroscopic study on the component and vigor analysis of Cistanche deserticola seeds[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2009,29(1):97-101. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)01-0097-05 [20] 谢理, 杨浩, 渠晓霞, 等.滇池优势挺水植物茭草和芦苇降解过程中DOM释放特征研究[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(9):3458-3466. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.09.003XIE L, YANG H, QU X X, et al. Dissolved organic matter release of Zizania caduciflora and Phragmites australis from Lake Dianchi[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(9):3458-3466. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.09.003 [21] 王碧, 席宏波, 周岳溪, 等.不同取代基对苯系物三维荧光光谱特征的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(12):3763-3770.WANG B, XI H B, ZHOU Y X, et al. Effects of different substituents on three dimensional fluorescence properties of BTEX[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2017,37(12):3763-3770. [22] 左兆陆, 赵南京, 孟德硕, 等.基于三维荧光光谱的土壤中石油类有机物分类识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(22):188-194.ZUO Z L, ZHAO N J, MENG D S, et al. Identification of petroleum organic matter in soil based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2019,56(22):188-194. [23] MENDOZA W G, RIEMER D D, ZIKA R G. Application of fluorescence and PARAFAC to assess vertical distribution of subsurface hydrocarbons and dispersant during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill[J]. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts,2013,15(5):1017-1030. [24] ZHOU Z Z, GUO L D. Evolution of the optical properties of seawater influenced by the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Environmental Research Letters,2012,7(2):025301. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/2/025301 [25] 王碧. 石化综合废水及其特征污染物的三维荧光光谱特性研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2017. [26] ZHOU Z Z, GUO L D, SHILLER A M, et al. Characterization of oil components from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico using fluorescence EEM and PARAFAC techniques[J]. Marine Chemistry,2013,148:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2012.10.003 [27] BIANCHI T S, OSBURN C, SHIELDS M R, et al. Deepwater Horizon oil in Gulf of Mexico waters after 2 years: transformation into the dissolved organic matter pool[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(16):9288-9297. [28] DVORSKI S E M, GONSIOR M, HERTKORN N, et al. Geochemistry of dissolved organic matter in a spatially highly resolved groundwater petroleum hydrocarbon plume cross-section[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(11):5536-5546. [29] 李丽, 檀文炳, 王国安, 等.腐殖质电子传递机制及其环境效应研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2016,35(2):254-266. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.02.2015071002LI L, TAN W B, WANG G A, et al. Electron transfer mechanisms of humic substances and their environmental implications: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2016,35(2):254-266. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.02.2015071002 [30] KROHN C, JIN J, WOOD J L, et al. Highly decomposed organic carbon mediates the assembly of soil communities with traits for the biodegradation of chlorinated pollutants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,404:124077. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124077 [31] van VAN der ZEE F P, CERVANTES F J. Impact and application of electron shuttles on the redox (bio)transformation of contaminants: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2009,27(3):256-277. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.01.004 [32] HE X S, XI B D, WEI Z M, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for characterizing composition and transformation of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachates[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,190(1/2/3):293-299. [33] COZZARELLI I M, BEKINS B A, BAEDECKER M J, et al. Progression of natural attenuation processes at a crude-oil spill site[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2001,53(3/4):369-385. [34] 宁卓, 郭彩娟, 蔡萍萍, 等.某石油污染含水层降解能力地球化学评估[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(11):4068-4074. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.010NING Z, GUO C J, CAI P P, et al. Geochemical evaluation of biodegradation capacity in a petroleum contaminated aquifer[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(11):4068-4074. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.010 [35] 蔡婧怡, 陈宗宇, 蔡五田, 等.某石化污染场地含水层自然降解BTEX能力评估[J]. 现代地质,2015,29(2):383-389.CAI J Y, CHEN Z Y, CAI W T, et al. The assessment of aquifer natural attenuation (BTEX) capacity in a petrochemical contaminated site[J]. Geoscience,2015,29(2):383-389. [36] 朱随洲, 储照波, 王志浩, 等. 淄博中心城区地下水时空分布特征及水资源评价[C]//2021中国水资源高效利用与节水技术论坛论文集. 阿拉善, 2021: 399-408. [37] 张明霞, 李安章, 陈猛, 等.异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌脱氮相关酶系及其编码基因的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展,2020,10(1):40-45.ZHANG M X, LI A Z, CHEN M, et al. Progress on nitrogen removal related enzymes and their coding genes in heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying bacteria[J]. Current Biotechnology,2020,10(1):40-45. [38] FONSECA B M, PAQUETE C M, NETO S E, et al. Mind the gap: cytochrome interactions reveal electron pathways across the periplasm of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. The Biochemical Journal,2013,449(1):101-108. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121467 [39] TAKAKI Y, SHIMAMURA S, NAKAGAWA S, et al. Bacterial lifestyle in a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney revealed by the genome sequence of the thermophilic bacterium Deferribacter desulfuricans SSM1[J]. DNA Research,2010,17(3):123-137. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsq005 [40] 曾湘, 邵宗泽.深海热液区微生物矿化过程的功能群和分子机制[J]. 微生物学通报,2017,44(4):890-901.ZENG X, SHAO Z Z. Microbial functional groups and molecular mechanisms for biomineralization in hydrothermal vents[J]. Microbiology China,2017,44(4):890-901. ⊗ -





 下载:
下载: