Effect of external carbon addition on pollutants removal from the tail water of a sewage treatment plant by biochar-based subsurface flow constructed wetland
-
摘要:
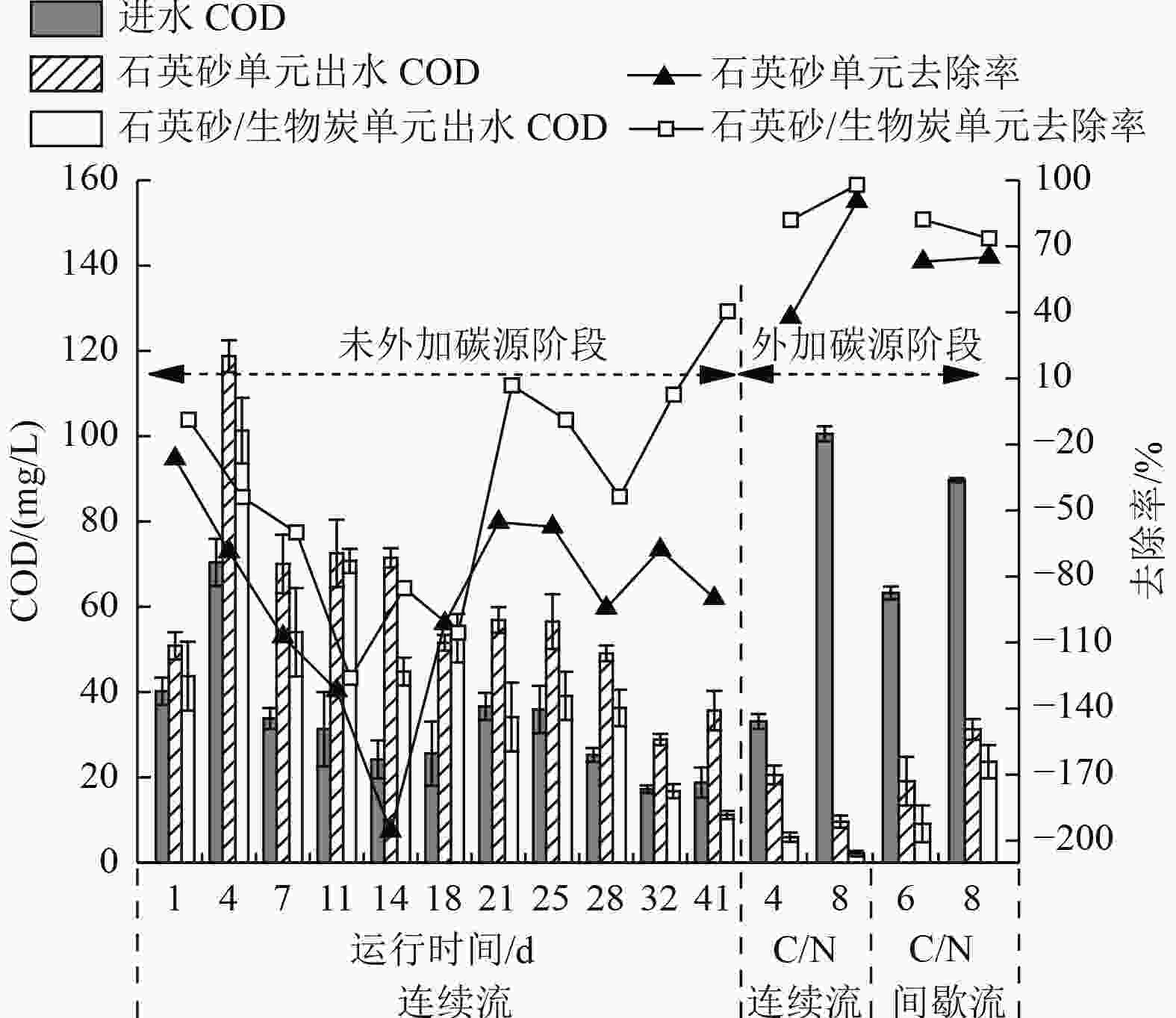
生物炭作为一种多功能生态环保材料,近年来被广泛应用于人工湿地污水处理中,其可为异养反硝化提供碳源,从而提高人工湿地的脱氮能力。通过室内构建石英砂/杏仁壳生物炭基质(体积比7∶3)人工湿地,同时以石英砂基质人工湿地为对照,运行后期通过外加碳源设计不同碳氮比(C/N),且分别采用连续流和间歇流的运行方式,探究外加碳源对生物炭基水平潜流人工湿地深度净化实际污水处理厂尾水效果的影响。结果表明:外加碳源前,人工湿地的化学需氧量(COD)去除率为负,总氮(TN)和硝氮(NO3 −-N)去除率在41 d内持续降低;而外加碳源后,石英砂单元和石英砂/生物炭单元的COD去除率分别增至37.88%~90.44%和73.60%~97.90%,TN和NO3 −-N去除率也明显提高。在外加碳源使进水C/N为8且间歇流运行时,石英砂/生物炭单元的TN和NO3 −-N去除率最高,分别达65.61%和74.20%。生物炭添加提高了湿地微生物生物量,同时创造了有利于反硝化作用发生的氧化还原环境,使石英砂/生物炭单元的COD、TN和NO3 −-N去除率分别提高了5.66%~130.35%、9.34%~54.03%和8.71%~63.04%。外加碳源与生物炭添加可作为一种有效手段强化实际污水处理厂尾水人工湿地系统的脱氮效能。
Abstract:As a kind of multifunctional eco-friendly material, biochar has been widely used in sewage treatment by constructed wetlands in recent years, which can provide carbon source for heterotrophic denitrification and enhance nitrogen removal capacity of constructed wetland. To explore the effect of external carbon addition on deep purification of the tail water of a sewage treatment plant by biochar-based horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland, two parallel indoor experimental units were set with quartz sand/almond shell biochar (volume ratio 7∶3) and quartz sand (the control) as the constructed wetland matrix, respectively. Moreover, in the later phase of operation, different C/N ratios were designed by external carbon addition and the operation modes of continuous flow and intermittent flow were adopted, respectively. Results showed that before external carbon addition, chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal rate of constructed wetland was negative, and total nitrogen (TN) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3 −-N) removal rates continued to decrease during 41 days. However, COD removal rates of quartz sand and quartz sand/almond shell biochar units increased to 37.88%-90.44% and 73.60%-97.90%, respectively, and TN and NO3 −-N removal rates also significantly increased after external carbon addition. The maximum removal rates of TN and NO3 −-N in quartz sand/biochar unit were 65.61% and 74.20%, respectively, as the influent C/N ratio was increased to 8 by external carbon addition and the intermittent flow mode was running. Biochar addition increased the microbial biomass of the constructed wetland, and created the appropriate redox environment facilitating denitrification. Therefore, the removal rates of COD, TN, and NO3 −-N of the wetland unit set with quartz sand/almond shell biochar increased by 5.66%-130.35%, 9.34%-54.03%, and 8.71%-63.04%, respectively, compared with the control. The external carbon addition and biochar application could be an effective measure to strengthen the denitrogenation efficiency of constructed wetland for tail water purification of sewage treatment plants.
-
表 1 试验用水水质
Table 1. Water quality of the influent water
mg/L COD TN浓度 NH4 +-N浓度 NO3 −-N浓度 NO2 −-N浓度 TP浓度 pH1) BOD5/
COD1)20~40 8.27~12.57 0.19~0.59 7.16~11.23 0.004~0.090 0.043~0.650 7.5~8.5 0.195~
0.2831)pH和BOD5/COD无量纲。 表 2 人工湿地运行C/N和运行方式
Table 2. C/N ratio and the operation pattern of the constructed wetland
试验阶段 运行
C/N外加碳源
类型运行
方式水样采
集位置水力停
留时间/d运行
天数/d第1~
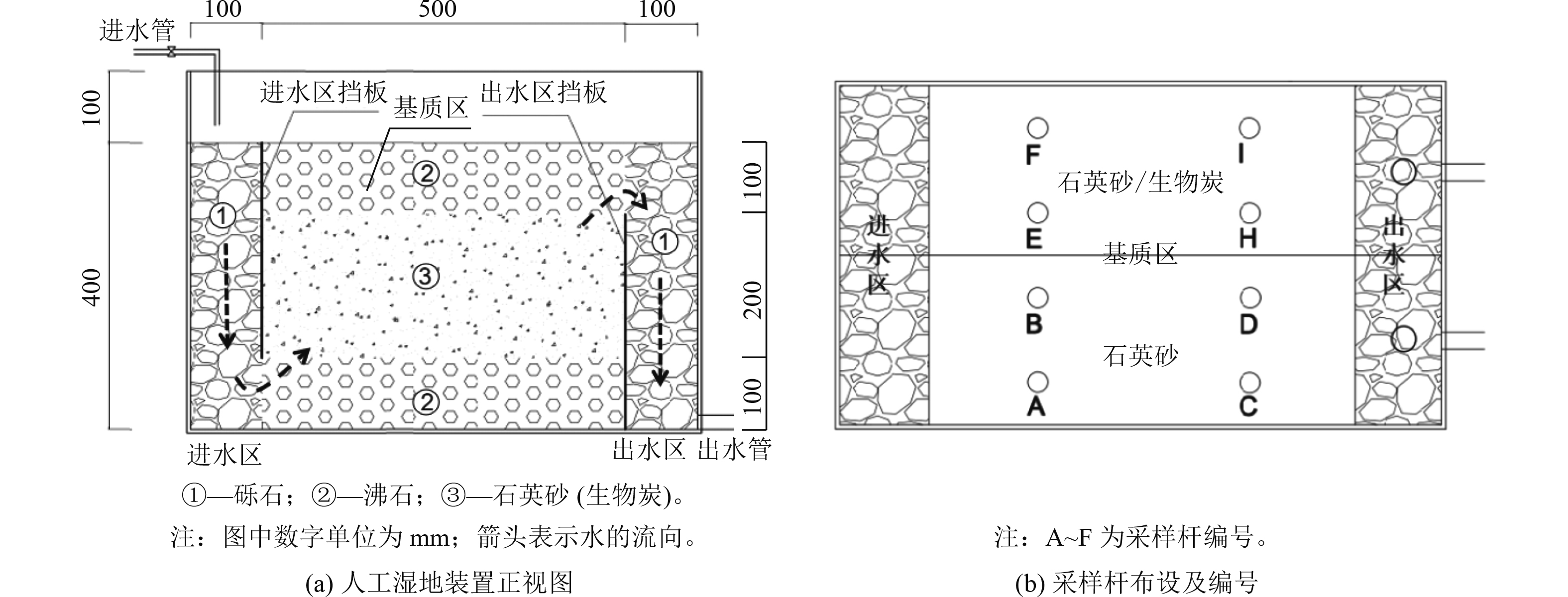
41天(未外加碳源)2~3(污水处理厂尾水) 无 连续流 出水区 2 41 第42~
71天(外加碳源)4 乙酸钠 连续流 出水区 2 6 8 乙酸钠 连续流 出水区 2 6 6 乙酸钠 间歇流 基质区 2 6 8 乙酸钠 间歇流 基质区 2 12 -
[1] 贾晓彤, 何小娟, 封吉猛, 等.菌藻共生系统净化污水处理厂尾水的条件探究与优化[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(4):1177-1184.JIA X T, HE X J, FENG J M, et al. Optimization of conditions for purification of wastewater treatment plant effluent by microalgae-bacteria symbiotic system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(4):1177-1184. [2] 王宇娜, 国晓春, 卢少勇, 等.人工湿地对低污染水中氮去除的研究进展: 效果、机制和影响因素[J]. 农业资源与环境学报,2021,38(5):722-734.WANG Y N, GUO X C, LU S Y, et al. Review of nitrogen removal in low-polluted water by constructed wetlands: performance, mechanism, and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment,2021,38(5):722-734. [3] EZZAT S M, MOUSTAFA M T. Treating wastewater under zero waste principle using wetland mesocosms[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2020,15(4):1-14. [4] 颜秉斐, 肖书虎, 廖纯刚, 等.潜流人工湿地长效运行脱氮研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(3):239-244. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.02.010YAN B F, XIAO S H, LIAO C G, et al. Research progress of long-term nitrogen removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(3):239-244. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.02.010 [5] ZHAO Y Q, JI B, LIU R B, et al. Constructed treatment wetland: glance of development and future perspectives[J]. Water Cycle,2020(1):104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.watcyc.2020.07.002 [6] 宋志文, 毕学军, 曹军.人工湿地及其在我国小城市污水处理中的应用[J]. 生态学杂志,2003,22(3):74-78.SONG Z W, BI X J, CAO J. Application of constructed wetlands in sewage treatment in small cities in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2003,22(3):74-78. [7] LIU X Y, HU S H, SUN R, et al. Dissolved oxygen disturbs nitrate transformation by modifying microbial community, co-occurrence networks, and functional genes during aerobic-anoxic transition[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,790:148245. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148245 [8] 邓朝仁, 梁银坤, 黄磊, 等.生物炭对潜流人工湿地污染物去除及N2O排放影响[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(6):2840-2846.DENG C R, LIANG Y K, HUANG L, et al. Influences of biochar on pollutant removal efficiencies and nitrous oxide emissions in a subsurface flow constructed wetland[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(6):2840-2846. [9] 王涛. 颗粒生物炭人工湿地对二级出水氮磷去除研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. [10] ZHENG F F, FANG J H, GUO F C, et al. Biochar based constructed wetland for secondary effluent treatment: waste resource utilization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,432:134377. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.134377 [11] 张梦媚, 何世颖, 唐婉莹, 等.TiO2/生物炭复合材料处理低浓度氨氮废水[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(9):1440-1447.ZHANG M M, HE S Y, TANG W Y, et al. Disposal of low concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater using TiO2/biochar composite[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(9):1440-1447. [12] WANG H X, WANG X Y, TENG H W, et al. Purification mechanism of city tail water by constructed wetland substrate with NaOH-modified corn straw biochar[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2022,238:113597. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113597 [13] JIA W, SUN X, GAO Y, et al. Fe-modified biochar enhances microbial nitrogen removal capability of constructed wetland[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,740:139534. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139534 [14] JIA W, YANG Y C, YANG L Y, et al. High-efficient nitrogen removal and its microbiological mechanism of a novel carbon self-sufficient constructed wetland[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,775:145901. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145901 [15] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [16] 管策, 郁达伟, 郑祥, 等.我国人工湿地在城市污水处理厂尾水脱氮除磷中的研究与应用进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2012,31(12):2309-2320.GUAN C, YU D W, ZHENG X, et al. Removing nitrogen and phosphoros of effluent from wastewater treatment plants by constructed wetlands in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2012,31(12):2309-2320. [17] 文浩舟. 反硝化滤池对农村生活污水的深度脱氮效能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2021. [18] 董国日, 柳建设, 周洪波, 等.铬离子对SBR工艺活性污泥毒性作用研究[J]. 环境工程学报,2010,4(4):847-851.DONG G R, LIU J S, ZHOU H B, et al. Study on toxicity of chromium ion to activated sludge in SBR process[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2010,4(4):847-851. [19] 王海燕, 赵远哲, 王文富, 等.人工湿地脱氮影响因素及强化措施研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(4):585-597.WANG H Y, ZHAO Y Z, WANG W F, et al. A review of influencing factors and enhanced measures for nitrogen removal of constructed wetlands[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(4):585-597. [20] 周新程, 彭明国, 陈晶, 等.低温低碳源下表面流人工湿地净化污水厂尾水[J]. 中国给水排水,2017,33(17):113-116.ZHOU X C, PENG M G, CHEN J, et al. Treatment of tail water of WWTP by surface flow constructed wetland under conditions of low temperature and low carbon source[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2017,33(17):113-116. [21] 吴代顺, 杨昕怡, 于雪, 等.碳氮比对硝化过程微生物代谢及功能基因的影响[J]. 中国给水排水,2021,37(7):20-26.WU D S, YANG X Y, YU X, et al. Effect of C/N ratio on microbial metabolism and related functional genes in biological nitrification process[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2021,37(7):20-26. [22] DONG J, WU Y, WANG C Y, et al. Three-dimensional electrodes enhance electricity generation and nitrogen removal of microbial fuel cells[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering,2020,43(12):2165-2174. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02402-9 [23] DENG C R, HUANG L, LIANG Y K, et al. Response of microbes to biochar strengthen nitrogen removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: microbial community structure and metabolite characteristics[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,694:133687. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133687 [24] WANG R G, ZHAO X, WANG T C, et al. Can we use mine waste as substrate in constructed wetlands to intensify nutrient removal: a critical assessment of key removal mechanisms and long-term environmental risks[J]. Water Research,2022,210:118009. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.118009 [25] 祝志超, 缪恒锋, 崔健, 等.组合人工湿地系统对污水处理厂二级出水的深度处理效果[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(12):2028-2036.ZHU Z C, MIAO H F, CUI J, et al. Advanced treatment performance of combined constructed wetland system on secondary effluent from wastewater treatment plant[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(12):2028-2036. [26] TANG S Y, LIAO Y H, XU Y C, et al. Microbial coupling mechanisms of nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: a review[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,314:123759. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123759 [27] LIANG Y K, WANG Q H, HUANG L, et al. Insight into the mechanisms of biochar addition on pollutant removal enhancement and nitrous oxide emission reduction in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: microbial community structure, functional genes and enzyme activity[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,307:123249. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123249 [28] DAI L C, LU Q, ZHOU H Q, et al. Tuning oxygenated functional groups on biochar for water pollution control: a critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,420:126547. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126547 [29] CHACÓN F J, CAYUELA M L, ROIG A, et al. Understanding, measuring and tuning the electrochemical properties of biochar for environmental applications[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology,2017,16(4):695-715. doi: 10.1007/s11157-017-9450-1 [30] 李怡冰, 李涵, 黄文轩, 等.生物炭的制备及其在强化电子传递和催化性能等方面的研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(5):1157-1167.LI Y B, LI H, HUANG W X, et al. Research progress on the biochar production and its applications in enhancing electron transport and catalysis performance[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(5):1157-1167. [31] 曾琳. 污泥基生物炭强化异养、自养、混养反硝化脱氮研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2022. [32] 殷芳芳, 王淑莹, 昂雪野, 等.碳源类型对低温条件下生物反硝化的影响[J]. 环境科学,2009,30(1):108-113.YIN F F, WANG S Y, ANG X Y, et al. Effects of carbon source types on denitrification performance at low temperature[J]. Environmental Science,2009,30(1):108-113. [33] 黄斯婷, 杨庆, 刘秀红, 等.不同碳源条件下污水处理反硝化过程亚硝态氮积累特性的研究进展[J]. 水处理技术,2015,41(7):21-25.HUANG S T, YANG Q, LIU X H, et al. Review on nitrite accumulation during the denitrification of wastewater treatment with different carbon sources[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2015,41(7):21-25. [34] 董晓莹, 彭党聪.不同碳氮比下污水反硝化过程中亚硝氮积累的特性研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2017,37(9):3349-3355.DONG X Y, PENG D C. Nitrite accumulation in denitrification with different C/N ratios[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(9):3349-3355. ◇ -





 下载:
下载: