Research on the application of EwE model in aquatic ecosystems and a case study of Changtan Reservoir
-
摘要:
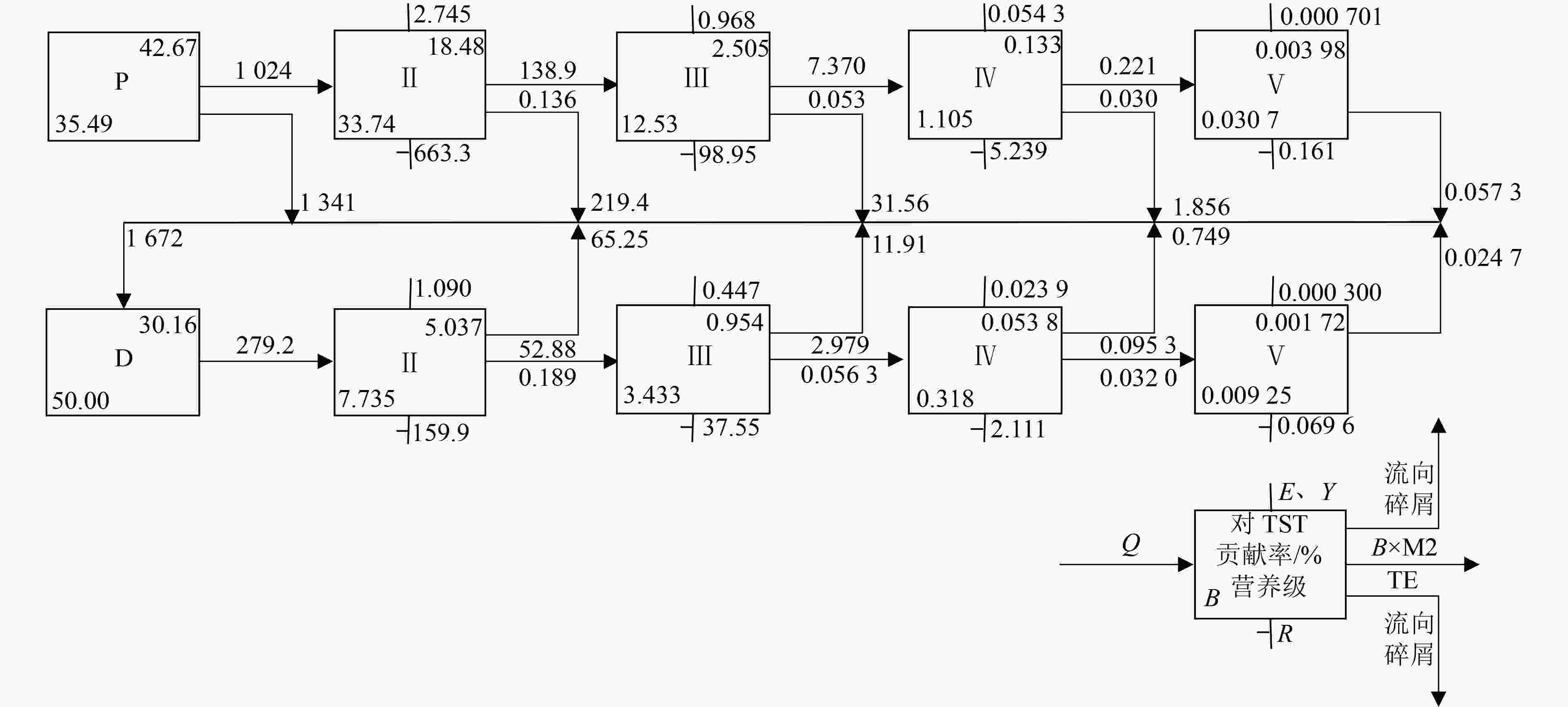
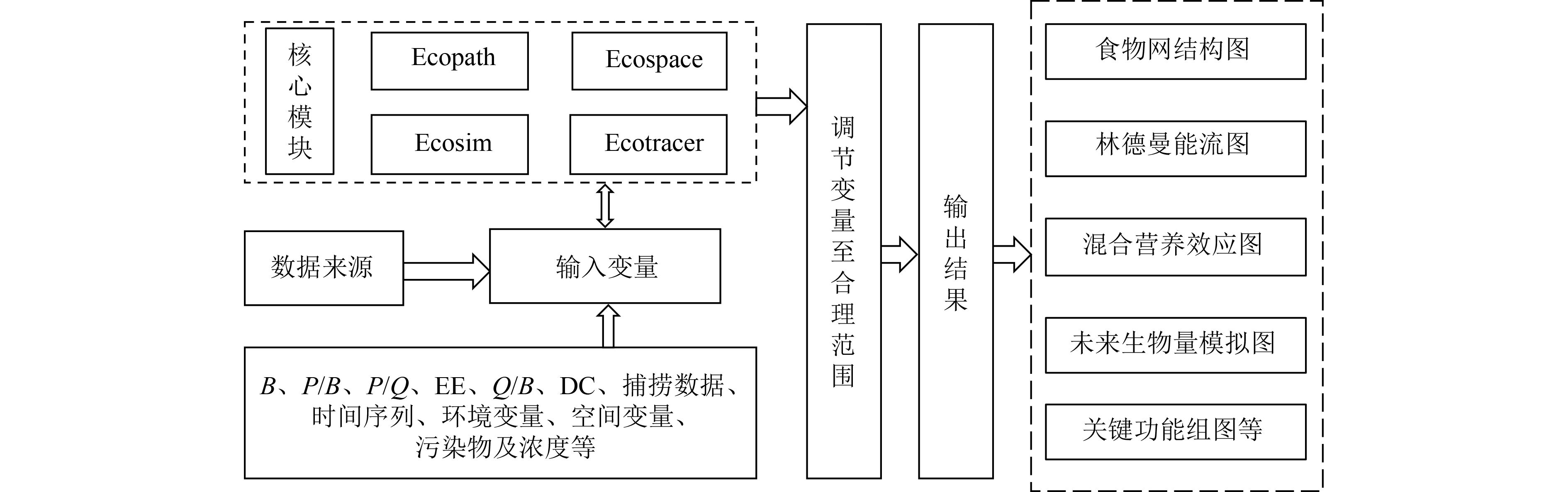
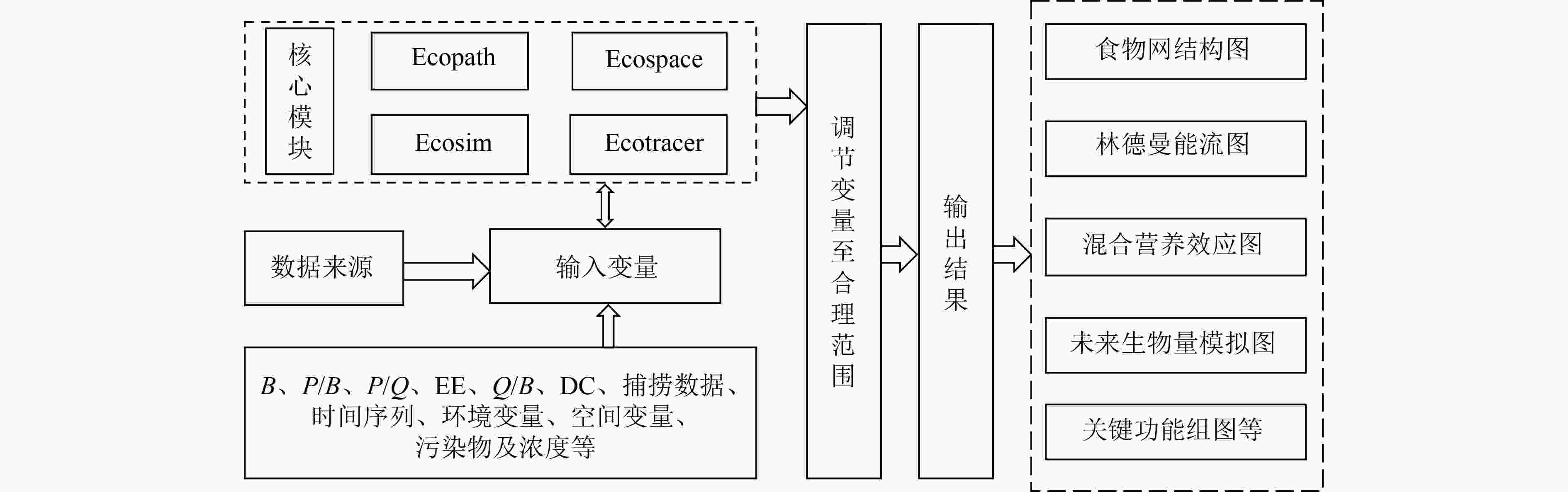
EwE(Ecopath with Ecosim)模型是一种用于定量研究水生态系统食物网结构和能量流动特征的模型。总结了EwE模型中Ecopath、Ecosim、Ecospace和Ecotracer模块的原理,综述了该模型在不同类型水生态系统中的应用研究进展,发现Ecopath可用来评估海洋和淡水生态系统的成熟度并确定关键种和生态容量,明确浮游植物生产量(P)对生态系统总通量(TST)的重要贡献;Ecosim用于在时间尺度上揭示关键种捕捞、港口建设等人类活动对生态系统结构和功能的影响机制;Ecospace可用来阐明海上平台建设、发电厂运行、火山爆发等外部因素影响下渔业经济和生态系统结构的空间差异性;Ecostracer可用来追踪同位素、重金属和新型污染物等物质在食物网中的迁移过程。采用Ecopath分析了长潭水库的营养结构和能量流动,结果表明,长潭水库营养级介于1.000~3.093,食物网结构简单,TPP/TR为2.445,是一个相对成熟的生态系统,能量传递效率较低。未来应加强气候变化和人类活动对水生态系统结构演替的影响研究,推进新污染物在食物网中富集特征研究,为水域生态系统健康状态评估和渔业经济发展政策的调整提供支撑。
Abstract:Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE) model is commonly used to quantitatively study the food web structure and energy flow characteristics in the aquatic ecosystem. The principles and progress of Ecopath, Ecosim, Ecospace, and Ecotracer modules of EwE model and its application in different types of aquatic ecosystems were summarized. The results indicated that Ecopath could be used to estimate the maturity of the ocean and freshwater ecosystems, to determine key species and ecological capacity, and to clarify the important contribution of phytoplankton production (P) to total system throughput (TST) in the aquatic ecosystem. Ecosim was used to reveal the impact mechanisms of human activities (e.g. keystone species catching, port construction) on ecosystem structure and function on a time scale. Ecospace was used to clarify spatial variability of fishing activity and ecosystem structure under external factor effects (e.g. offshore platform construction, power plant operation, and volcanic eruption). Ecotracer was used to trace the immigration progress of isotopes, heavy metal, new pollutant, and other matters in the food web. Combined with Ecopath, the nutrient structure and energy flow of Changtan Reservoir were analyzed. The results showed that the trophic level was in the range of 1.000-3.093, indicating a simple food web structure. The total primary production/total respiration (TPP/TR) value was 2.445, indicating Changtan Reservoir was a relatively mature ecosystem, and it had a low energy transfer efficiency. In the future, studies on the impacts of climate change and human activities on the structural succession of aquatic ecosystems, and the enrichment characteristics of new pollutants in the food web should be strengthened to provide a scientific basis for the assessment of aquatic ecosystem health and the adjustment of fishery economic development policies.
-
Key words:
- EwE model /
- aquatic ecosystems /
- climate change /
- new pollutants /
- Changtan Reservoir
-
表 1 Ecopath主要参数及参数来源
Table 1. Main parameters and their resources of Ecopath
主要参数 参数含义 获取来源 取值范围 生物量(B) 各功能组在某个时间段
内的平均生物量来自实测值或者调查资料 无 生产量/生物量(P/B) 各功能组在某个时间段内的生产力 P/B为捕捞死亡率(F)和自然死亡率(M)之和,其中F根据实际捕捞量进行计算,M根据Pauly[14]的经验公式进行计算。鱼类P/B根据fishbase等网站计算得到 无 消费量/生物量(Q/B) 各功能组在某个时间段内的
消费能力采用实测值或参考临近水域或通过日消费比值进行估计或使用fishbase等网站估计。其中鱼类Q/B可通过Palomares等[15]的经验公式估计,无脊椎动物Q/B使用P/Q来代替 无 生产量/消费量(P/Q) 各功能组生产量和消费量的比值 Ecopath根据P/B和Q/B来计算或参考相关研究的取值 通常为0.05~0.30,根据
体重变化调整生态营养效率(EE) 各功能组生产量被利用的效率 Ecopath根据B、P/B和Q/B计算或根据相关研究估计 0~1,其取值
通常接近1饮食结构(DC) 各功能组营养级数值的确定 采用胃含物分析法和稳定同位素法测定。鱼类DC可通过fishbase等网站获取,浮游生物和底栖动物DC参考其他研究 各功能组DC比例之和为1 表 2 Ecopath在中国的应用实例
Table 2. Application examples of Ecopath in China
水体名称 模型应用年份 系统总流量(TST)/〔t/(km2·a)〕 TPP/TR 浮游植物的(P/B)/a−1 系统连接指数(CI) 太湖[21] 1991—1995 13 386 3.85 185 0.21 太湖[22] 2008—2009 66 245 4.22 410 0.19 太湖[23] 2017—2018 7 388 2.55 410 0.21 太湖竺山湾[24] 2015 10 145 2.37 185 0.24 五里湖[25] 2009 9 132 1.34 262 0.28 淀山湖[26] 2008—2009 4 099 2.80 185 0.19 巢湖[27] 2007—2010 41 003 13.53 185 0.20 千岛湖[28] 2000 24 271 1.99 201 0.23 千岛湖[29] 2016 24 698 6.51 180 0.26 南海北部湾[30] 1997—1999 11 006 3.18 231 0.33 杭州湾[31] 2006 18 958 2.67 476 0.31 长江口[32] 2004 6 342 2.53 200 0.54 长江口[33] 2016—2017 1 329 1.25 119 0.35 长江口及毗邻水域[34] 2000—2006 1 959~6 554 1.82~5.29 180~200 0.41~0.45 象山港[35] 2011—2014 2 227~2 229 1.52 180 0.34 渤海[36] 1982—1992 3 316~5 362 8.40~9.75 380~398 渤海[37] 2014—2015 10 499 5.38 250 0.33 俚岛人工礁区[38] 2009 10 787 1.84 71 0.20 獐子岛人工鱼礁区[39] 2010—2012 28 691~40 486 2.05~2.29 105~132 0.20~0.23 獐子岛海域[40] 2017—2018 17 007-17 738 1.79~2.05 140 0.22 海州湾[41] 2013 9 335 1.33 107 0.42 庙岛[42] 1998 3 172 2.47 100 0.44 枸杞岛海藻场[43] 2004—2008 28 019 1.25 119 0.33 三沙湾[44] 2012 2 344 2.77 105 0.40 表 3 长潭水库Ecopath食物网模型的输入与输出参数
Table 3. Input and output parameters of Ecopath food web model of Changtan Reservoir
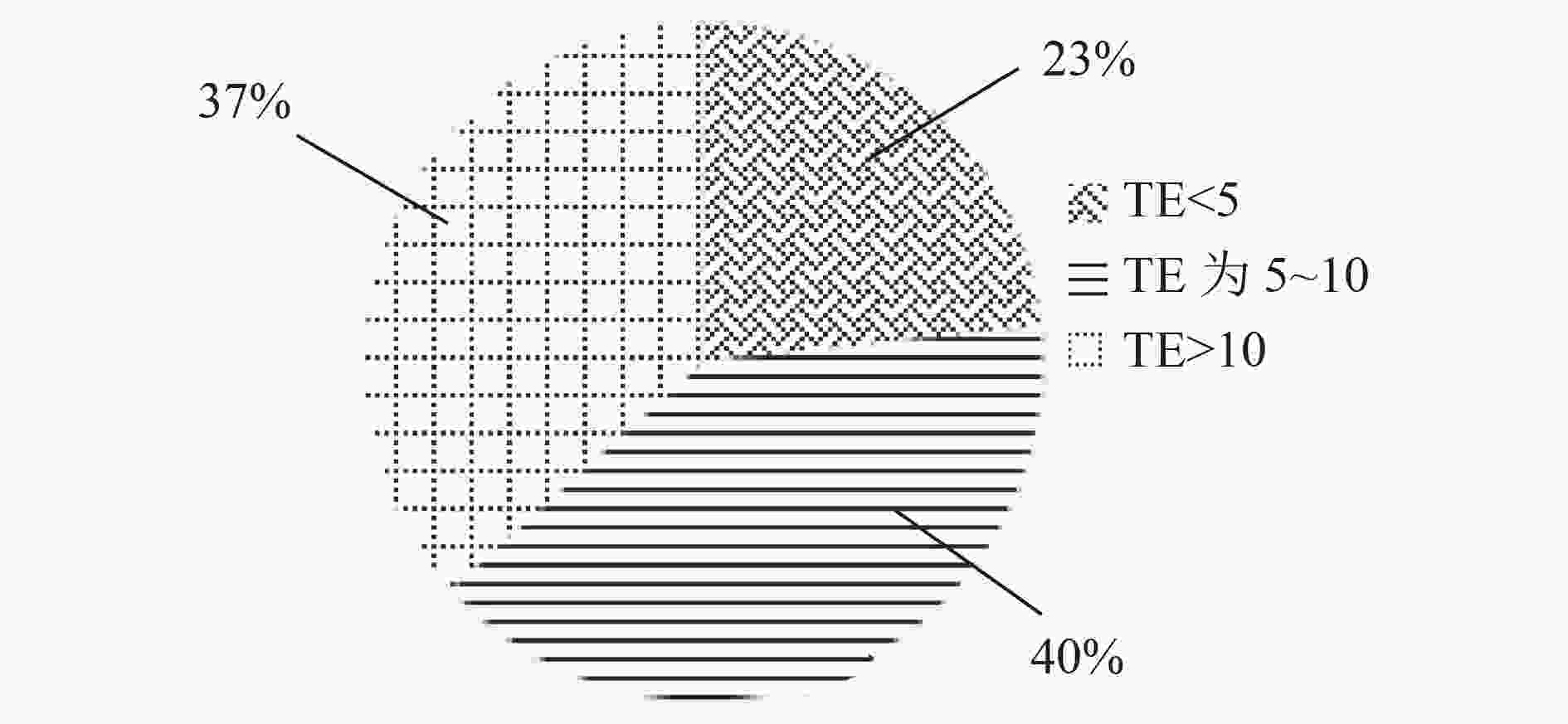
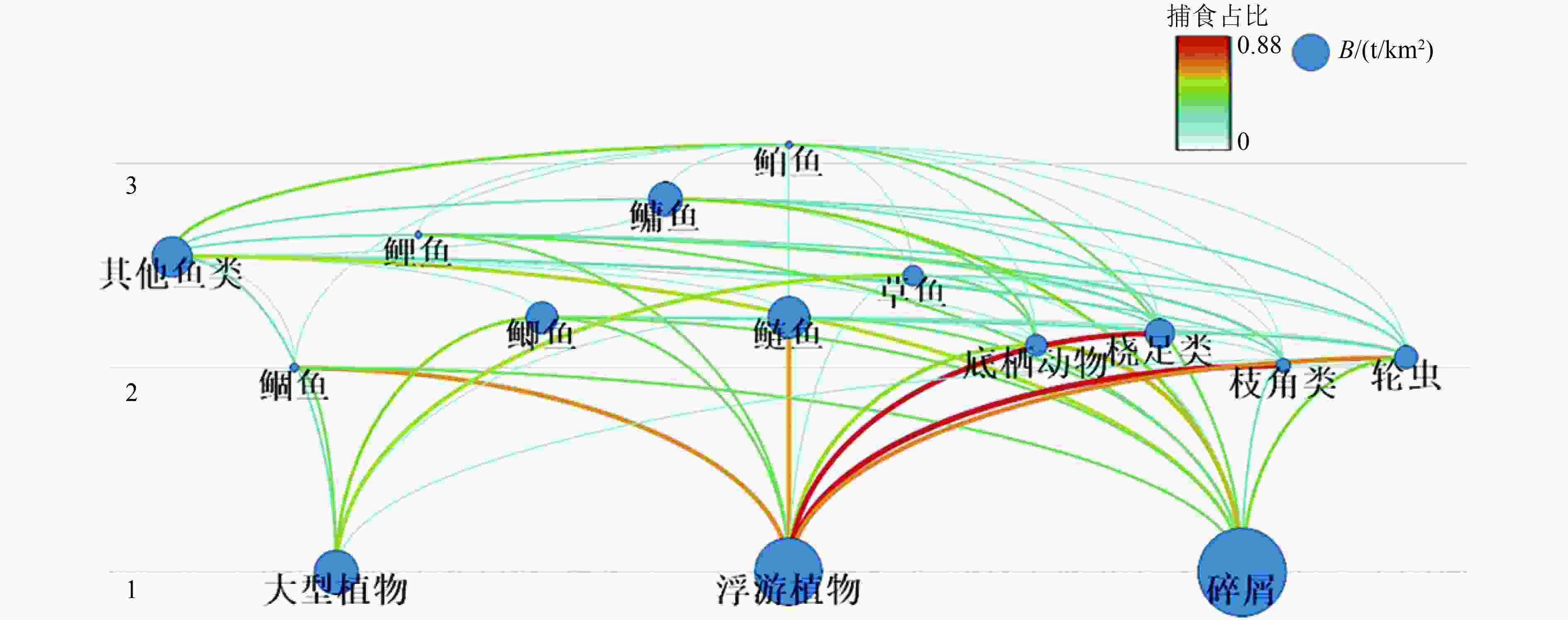
功能组 营养级 B/(t/km²) (P/B)/a−1 (Q/B)/a−1 EE (Q/P)/a−1 其他鱼类 2.547 9.021 1.200 13.000 0.500 0.092 鲌鱼 3.093 0.050 1.090 9.140 0.418 0.124 鲴鱼 2.000 0.351 2.011 16.270 0.950 0.124 鲤鱼 2.652 0.019 1.210 7.270 0.950 0.166 鲫鱼 2.247 5.931 1.150 8.370 0.950 0.137 鳙鱼 2.827 6.840 1.300 7.200 0.808 0.181 鲢鱼 2.248 9.290 1.500 8.450 0.800 0.178 草鱼 2.454 2.737 1.730 9.660 0.950 0.179 底栖动物 2.111 3.141 11.000 15.000 0.964 0.733 桡足类 2.170 5.270 6.000 100.000 0.935 0.060 枝角类 2.012 1.410 16.000 100.000 0.949 0.160 轮虫 2.050 3.350 40.000 150.000 0.950 0.267 大型植物 1.000 10.357 10.000 — 0.900 — 浮游植物 1.000 25.130 90.000 — 0.412 — 碎屑 1.000 50.000 — — 0.167 — 注:数据中加粗字体为模型输出值;—表示无须输入或输出,其余为输入值。 -
[1] PASQUAUD S, LOBRY J, ELIE P. Facing the necessity of describing estuarine ecosystems: a review of food web ecology study techniques[J]. Hydrobiologia,2007,588(1):159-172. doi: 10.1007/s10750-007-0660-3 [2] 车霏霏, 陈俊伊, 王书航, 等.南湖水系水-沉积物磷时空分布、影响因素及控制对策[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):928-935. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068CHE F F, CHEN J Y, WANG S H, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution, influencing factors and control strategies of phosphorus in water-sediment of Nanhu Lake water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):928-935. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068 [3] 王子为, 林佳宁, 张远, 等.鄱阳湖入湖河流氮磷水质控制限值研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(5):1163-1169.WANG Z W, LIN J N, ZHANG Y, et al. Water quality limits of nitrogen and phosphorus in the inflow rivers of Poyang Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(5):1163-1169. [4] 金相灿, 朱萱.我国主要湖泊和水库水体的营养特征及其变化[J]. 环境科学研究,1991,4(1):11-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.1991.01.003JIN X C, ZHU X. Tropic characteristics and changes of water bodies of the main lakes and reservoirs in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,1991,4(1):11-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.1991.01.003 [5] 徐从军, 隋昊志, 徐宾铎, 等.基于LIM-MCMC模型研究海州湾食物网能量流动特征[J]. 中国水产科学,2021,28(1):66-78.XU C J, SUI H Z, XU B D, et al. Energy flows in the Haizhou Bay food web based on the LIM-MCMC model[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,2021,28(1):66-78. [6] 胡文, 王济, 李春华, 等.浅水湖泊模型PCLake及其应用进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2019,35(6):681-688.HU W, WANG J, LI C H, et al. The application and review of shallow lake model: PCLake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2019,35(6):681-688. [7] HÅKANSON L. Consequences and correctives related to lake acidification, Liming and mercury in fish :a case-study for Lake Huljesjön, Sweden, using the LakeWeb-model[J]. Environmental Modeling & Assessment,2003,8(4):275-283. [8] JANSSEN A B G, de JAGER V C L, JANSE J H, et al. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: implications for Lake Taihu (China)[J]. Water Research,2017,119:276-287. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.045 [9] HEYMANS J J, COLL M, LINK J S, et al. Best practice in Ecopath with Ecosim food-web models for ecosystem-based management[J]. Ecological Modelling,2016,331:173-184. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.12.007 [10] POLOVINA J J. Model of a coral reef ecosystem[J]. Coral Reefs,1984,3(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/BF00306135 [11] CHRISTENSEN V, PAULY D. Ecopath Ⅱ: a software for balancing steady-state ecosystem models and calculating network characteristics[J]. Ecological Modelling,1992,61(3/4):169-185. [12] WALTERS C, CHRISTENSEN V, PAULY D. Structuring dynamic models of exploited ecosystems from trophic mass-balance assessments[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries,1997,7(2):139-172. doi: 10.1023/A:1018479526149 [13] CHRISTENSEN V,WALTERS C. Ecopath with Ecosim: methods, capabilities and limitations[J]. Ecological Modelling,2004,172(2):109-139. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2003.09.003 [14] PAULY D. On the interrelationships between natural mortality, growth parameters, and mean environmental temperature in 175 fish stocks[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science,1980,39(2):175-192. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/39.2.175 [15] PALOMARES M L D, PAULY D. Predicting food consumption of fish populations as functions of mortality, food type, morphometrics, temperature and salinity[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research,1998,49(5):447. doi: 10.1071/MF98015 [16] 仝龄.Ecopath: 一种生态系统能量平衡评估模式[J]. 海洋水产研究,1999,20(2):103-107.TONG L. Ecopath model: a mass-balance modeling for ecosystem estimation[J]. Marine Fisherries Reseach,1999,20(2):103-107. [17] PAPAPANAGIOTOU G, TSAGARAKIS K, KOUTSIDI M, et al. Using traits to build and explain an ecosystem model: Ecopath with Ecosim modelling of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science,2020,236:106614. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106614 [18] GEERS T M, PIKITCH E K, FRISK M G. An original model of the northern Gulf of Mexico using Ecopath with Ecosim and its implications for the effects of fishing on ecosystem structure and maturity[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2016,129:319-331. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.01.009 [19] WEBBER M, PERSAD G, HARRIS N, et al. An ecological assessment of Foul and Folly Bays, Morant wetlands area, Jamaica using Ecopath with Ecosim[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management,2015,105:127-137. [20] HOSSAIN M M, MATSUISHI T, ARHONDITSIS G. Elucidation of ecosystem attributes of an oligotrophic lake in Hokkaido, Japan, using Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE)[J]. Ecological Modelling,2010,221(13/14):1717-1730. [21] 宋兵. 太湖渔业和环境的生态系统模型研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2004. [22] 李云凯, 刘恩生, 王辉, 等.基于Ecopath模型的太湖生态系统结构与功能分析[J]. 应用生态学报,2014,25(7):2033-2040.LI Y K, LIU E S, WANG H, et al. Analysis on the ecosystem structure and function of Lake Taihu based on Ecopath model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2014,25(7):2033-2040. [23] 赵旭昊, 徐东坡, 任泷, 等.基于Ecopath模型的太湖鲢鳙生态容量评估[J]. 中国水产科学,2021,28(6):785-795.ZHAO X H, XU D P, REN L, et al. Assessment of the ecological carrying capacity of silver and bighead carp in the Taihu Lake based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,2021,28(6):785-795. [24] LI C H, XIAN Y, YE C, et al. Wetland ecosystem status and restoration using the Ecopath with Ecosim (EWE) model[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,658:305-314. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.128 [25] 黄孝锋. 五里湖生态系统ECOPATH模型的构建与评估[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. [26] 冯德祥, 陈亮, 李云凯, 等.基于营养通道模型的淀山湖生态系统结构与能量流动特征[J]. 中国水产科学,2011,18(4):867-876.FENG D X, CHEN L, LI Y K, et al. Structure and energy flow of Dianshan Lake ecosystem based on the Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,2011,18(4):867-876. [27] 刘恩生, 李云凯, 臧日伟, 等.基于Ecopath模型的巢湖生态系统结构与功能初步分析[J]. 水产学报,2014,38(3):417-425.LIU E S, LI Y K, ZANG R W, et al. A preliminary analysis of the ecosystem structure and functioning of Lake Chaohu based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2014,38(3):417-425. [28] 刘其根. 千岛湖保水渔业及其对湖泊生态系统的影响[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2005. [29] 于佳, 刘佳睿, 王利, 等.基于Ecopath模型的千岛湖生态系统结构和功能分析[J]. 水生生物学报,2021,45(2):308-317. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.128YU J, LIU J R, WANG L, et al. Analysis on the ecosystem structure and function of Lake Qiandao based on ecopath model[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2021,45(2):308-317. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.128 [30] 陈作志, 邱永松, 贾晓平.北部湾生态通道模型的构建[J]. 应用生态学报,2006,17(6):1107-1111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.06.030CHEN Z Z, QIU Y S, JIA X P. Mass-balance Ecopath model of beibu gulf ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2006,17(6):1107-1111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.06.030 [31] 徐姗楠, 陈作志, 何培民.杭州湾北岸大型围隔海域人工生态系统的能量流动和网络分析[J]. 生态学报,2008,28(5):2065-2072. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.05.021XU S N, CHEN Z Z, HE P M. Energy flux and network analysis for an artificial ecosystem of a large enclosed sea area in North Hangzhou Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(5):2065-2072. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.05.021 [32] 王远超, 梁翠, 线薇微, 等.基于生态通道模型的长江口及邻近海域生态系统能流动态分析[J]. 海洋科学,2018,42(5):54-67. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170816001WANG Y C, LIANG C, XIAN W W, et al. Ecopath based dynamic analyses of energy flows of Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Marine Sciences,2018,42(5):54-67. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170816001 [33] 徐超, 王思凯, 赵峰, 等.基于Ecopath模型的长江口生态系统营养结构和能量流动研究[J]. 海洋渔业,2018,40(3):309-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2018.03.006XU C, WANG S K, ZHAO F, et al. Trophic structure and energy flow of the Yangtze Estuary ecosystem based on the analysis with Ecopath model[J]. Marine Fisheries,2018,40(3):309-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2018.03.006 [34] 林群, 金显仕, 郭学武, 等.基于Ecopath模型的长江口及毗邻水域生态系统结构和能量流动研究[J]. 水生态学杂志,2009,30(2):28-36.LIN Q, JIN X S, GUO X W, et al. Study on the structure and energy flow of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters ecosystem based on ecopath model[J]. Journal of Hydroecology,2009,30(2):28-36. [35] 杨林林, 姜亚洲, 袁兴伟, 等.象山港典型增殖种类的生态容量评估[J]. 海洋渔业,2016,38(3):273-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2016.03.006YANG L L, JIANG Y Z, YUAN X W, et al. Ecological carrying capacity of typical enhancement species in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Marine Fisheries,2016,38(3):273-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2016.03.006 [36] 林群, 金显仕, 张波, 等.基于营养通道模型的渤海生态系统结构十年变化比较[J]. 生态学报,2009,29(7):3613-3620. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.07.020LIN Q, JIN X S, ZHANG B, et al. Comparative study on the changes of the Bohai Sea ecosystem structure based on Ecopath model between ten years[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(7):3613-3620. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.07.020 [37] 林群, 单秀娟, 王俊, 等.渤海中国对虾生态容量变化研究[J]. 渔业科学进展,2018,39(4):19-29.LIN Q, SHAN X J, WANG J, et al. Changes in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) carrying capacity of the Bohai Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences,2018,39(4):19-29. [38] 吴忠鑫, 张秀梅, 张磊, 等.基于Ecopath模型的荣成俚岛人工鱼礁区生态系统结构和功能评价[J]. 应用生态学报,2012,23(10):2878-2886.WU Z X, ZHANG X M, ZHANG L, et al. Structure and function of Lidao artificial reef ecosystem in Rongcheng of Shandong Province, East China: an evaluation based on Ecopath model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2012,23(10):2878-2886. [39] 许祯行. 基于Ecopath模型的獐子岛人工鱼礁区生态系统功能评价[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2015. [40] 张紫轩, 张继红, 吴文广, 等.獐子岛海域虾夷扇贝底播增殖生态容量评估[J]. 中国水产科学,2021,28(7):878-887.ZHANG Z X, ZHANG J H, WU W G, et al. Ecological carrying capacity assessment of bottom-culture Yesso scallops, Patinopecten yessoensis, in Zhangzi Island[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,2021,28(7):878-887. [41] 王腾, 张贺, 张虎, 等.基于营养通道模型的海州湾中国明对虾生态容纳量[J]. 中国水产科学,2016,23(4):965-975.WANG T, ZHANG H, ZHANG H, et al. Ecological carrying capacity of Chinese shrimp stock enhancement in Haizhou Bay of East China based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China,2016,23(4):965-975. [42] CUI P H, ZHU H J. Eosystem structure and energy flow analysis of the adjacent waters around Miaodao Islands based on Ecopath model[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2020,474(2):022027. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/474/2/022027 [43] 赵静, 章守宇, 许敏.枸杞海藻场生态系统能量流动模型初探[J]. 上海海洋大学学报,2010,19(1):98-104.ZHAO J, ZHANG S Y, XU M. The primary research of the energy flow in Gouqi kelp bed ecosystem[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University,2010,19(1):98-104. [44] 杨彬彬. 基于Ecopath模型的三沙湾能量流动分析及大黄鱼试验性增殖放流[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2017. [45] LINDEMAN R L. The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology,1991,53(1/2):167-191. [46] NATUGONZA V, AINSWORTH C, STURLUDÓTTIR E, et al. Simulating trade-offs between socio-economic and conservation objectives for Lake Victoria (East Africa) using multispecies, multifleet ecosystem models[J]. Fisheries Research,2020,229:105593. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105593 [47] MENGE B A, BERLOW E L, BLANCHETTE C A, et al. The keystone species concept: variation in interaction strength in a rocky intertidal habitat[J]. Ecological Monographs,1994,64(3):249-286. doi: 10.2307/2937163 [48] MONTERO L C, CHRISTENSEN V, CASTRO HERNÁNDEZ J J. Simulating trophic impacts of fishing scenarios on two oceanic islands using Ecopath with Ecosim[J]. Marine Environmental Research,2021,169:105341. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105341 [49] SZALAJ D, TORRES M A, VEIGA-MALTA T, et al. Food-web dynamics in the Portuguese continental shelf ecosystem between 1986 and 2017: unravelling drivers of sardine decline[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science,2021,251:107259. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2021.107259 [50] ANGELINI R, CONTENTE R F, ROSSI-WONGTSCHOWSKI C L D B, et al. Ecosystem modeling as a framework to convert a multi-disciplinary research approach into a useful model for the Araçá Bay (Brazil)[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management,2018,164:92-103. [51] PÜTS M, TAYLOR M, NÚÑEZ-RIBONI I, et al. Insights on integrating habitat preferences in process-oriented ecological models:a case study of the southern North Sea[J]. Ecological Modelling,2020,431:109189. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109189 [52] SERPETTI N, BENJAMINS S, BRAIN S, et al. Modeling small scale impacts of multi-purpose platforms: an ecosystem approach[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science,2021,8:694013. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.694013 [53] HALOUANI G, VILLANUEVA C M, RAOUX A, et al. A spatial food web model to investigate potential spillover effects of a fishery closure in an offshore wind farm[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2020,212:103434. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2020.103434 [54] MENDOZA J C, CLEMENTE S, HERNÁNDEZ J C. Modeling the role of marine protected areas on the recovery of shallow rocky reef ecosystem after a catastrophic submarine volcanic eruption[J]. Marine Environmental Research,2020,155:104877. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104877 [55] BOOTH S, WALTERS W J, STEENBEEK J, et al. An Ecopath with Ecosim model for the Pacific coast of eastern Japan: describing the marine environment and its fisheries prior to the Great East Japan earthquake[J]. Ecological Modelling,2020,428:109087. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109087 [56] 李道季.海洋微塑料污染状况及其应对措施建议[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(2):197-202.LI D J. Research advance and countermeasures on marine microplastic pollution[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(2):197-202. [57] 刘彬, 侯立安, 王媛, 等.我国海洋塑料垃圾和微塑料排放现状及对策[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(1):174-182.LIU B, HOU L, WANG Y, et al. Emission estimate and countermeasures of marine plastic debris and microplastics in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(1):174-182. [58] BOYER J, RUBALCAVA K, BOOTH S, et al. Proof-of-concept model for exploring the impacts of microplastics accumulation in the Maryland coastal bays ecosystem[J]. Ecological Modelling,2022,464:109849. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2021.109849 [59] SANDBERG J, KUMBLAD L, KAUTSKY U. Can ECOPATH with ECOSIM enhance models of radionuclide flows in food webs: an example for 14C in a coastal food web in the Baltic Sea[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity,2007,92(2):96-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.09.010 [60] FERRISS B E, ESSINGTON T E. Does trophic structure dictate mercury concentrations in top predators: a comparative analysis of pelagic food webs in the Pacific Ocean[J]. Ecological Modelling,2014,278:18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.01.029 [61] CRESSON P, BOUCHOUCHA M, MORAT F, et al. A multitracer approach to assess the spatial contamination pattern of Hake (Merluccius merluccius) in the French Mediterranean[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,532:184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.020 [62] McGILL L M, GERIG B S, CHALONER D T, et al. An ecosystem model for evaluating the effects of introduced Pacific salmon on contaminant burdens of stream-resident fish[J]. Ecological Modelling,2017,355:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.03.027 [63] TAFFI M, PAOLETTI N, LIÒ P, et al. Bioaccumulation modelling and sensitivity analysis for discovering key players in contaminated food webs: the case study of PCBs in the Adriatic Sea[J]. Ecological Modelling,2015,306:205-215. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.11.030 [64] LARSEN L H, SAGERUP K, RAMSVATN S. The mussel path:using the contaminant tracer, Ecotracer, in Ecopath to model the spread of pollutants in an Arctic marine food web[J]. Ecological Modelling,2016,331:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.10.011 [65] BENTLEY J W, SERPETTI N, FOX C, et al. Fishers' knowledge improves the accuracy of food web model predictions[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science,2019,76(4):897-912. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsz003 [66] 肖喆, 李文攀, 张靖天, 等.长潭水库生态问题诊断与对策研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(4):670-677. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200168XIAO Z, LI W P, ZHANG J T, et al. Diagnosis and countermeasures of eco-environmental problems in Changtan Reservoir[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(4):670-677. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200168 [67] CHRISTENSEN V, PAULY D. A guide to the Ecopath Ⅱ software system: version 2.1[M]. Manila: International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management, 1992: 1-67. [68] 刘其根, 王钰博, 陈立侨, 等.保水渔业对千岛湖食物网结构及其相互作用的影响[J]. 生态学报,2010,30(10):2774-2783.LIU Q G, WANG Y B, CHEN L Q, et al. Impacts of aquatic environment protection oriented fishery on the structure of food web in Lake Qiandaohu[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2010,30(10):2774-2783. ◇ -




 下载:
下载: