Study on micro-nanobubble control of membrane fouling in vacuum membrane distillation of high salt organic wastewater
-
摘要:
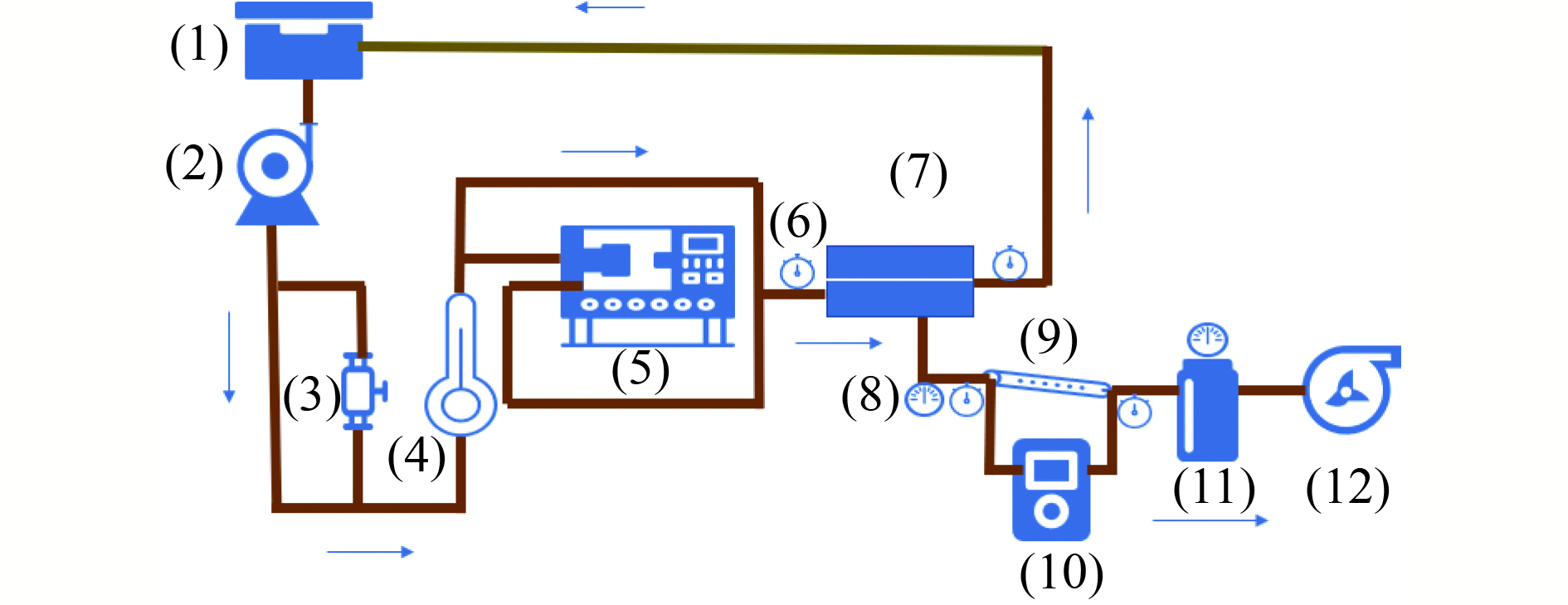
为探究真空膜蒸馏处理高盐废水过程中有机物和盐类对膜污染的贡献以及微纳米气泡对不同类型膜污染的控制作用,选取腐殖酸、牛血清蛋白、海藻酸钠为典型有机污染物代表,分别考察单一有机物、有机物与盐共存对膜污染的影响以及采用微纳米气泡曝气对上述情况产生的膜污染的控制作用。结果表明:3种有机物中,海藻酸钠造成的膜污染最严重,当海藻酸钠浓度为100 mg/L时,真空膜蒸馏系统运行7 h后,相对膜通量降至67.07%;腐殖酸与盐共存造成的复合污染最严重,当进料液腐殖酸浓度分别为10、50和100 mg/L时,系统运行7 h后,相对膜通量分别降至36.33%、33.15%和20.59%;3种有机物与盐共存时,造成的膜污染比单一有机物与盐共存时更严重;微纳米气泡可以有效控制有机物与盐共存时对真空膜蒸馏系统造成的复合污染。
Abstract:In order to explore the contribution of organics and salts to membrane fouling and the control effect of micro-nanobubbles on different types of membrane fouling in the treatment of high salt wastewater by vacuum membrane distillation, three typical organic pollutants, humic acid, bovine serum protein and sodium alginate, were selected to investigate the influence of single organic matter, the coexistence of organic matter and salt on membrane pollution and the control effect of micro-nanobubble aeration on membrane pollution. The results showed that the membrane pollution caused by sodium alginate was the most serious among the three organic compounds. When the sodium alginate concentration was 100 mg/L, the relative membrane flux decreased to 67.07% after 7 h of vacuum membrane distillation system operation. When the humic acid concentration of feed solution was 10, 50 and 100 mg/L, the relative membrane flux decreased to 36.33%, 33.15% and 20.59%, respectively, after 7 h of system operation. When three organic compounds coexisted with salt, the membrane pollution was worse than that when single organic compound coexisted with salt. Micro-nanobubbles could effectively control the compound pollution caused by organic-salt coexistence in vacuum membrane distillation system.
-
-
[1] ALKLAIBI A M, LIOR N. Membrane-distillation desalination: status and potential[J]. Desalination,2005,171(2):111-131. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.03.024 [2] BAGHEL R, UPADHYAYA S, SINGH K, et al. A review on membrane applications and transport mechanisms in vacuum membrane distillation[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering,2017,34(1):73-106. doi: 10.1515/revce-2016-0050 [3] ZHANG Y G, PENG Y L, JI S L, et al. Review of thermal efficiency and heat recycling in membrane distillation processes[J]. Desalination,2015,367:223-239. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2015.04.013 [4] DRIOLI E, ALI A, MACEDONIO F. Membrane distillation: recent developments and perspectives[J]. Desalination,2015,356:56-84. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.10.028 [5] NAIDU G, JEONG S, KIM S J, et al. Organic fouling behavior in direct contact membrane distillation[J]. Desalination,2014,347:230-239. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.05.045 [6] WANG P, CHUNG T S. Recent advances in membrane distillation processes: membrane development, configuration design and application exploring[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2015,474:39-56. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2014.09.016 [7] REZAEI M, WARSINGER D M, LIENHARD V J H, et al. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: mechanisms, reversal, and prevention[J]. Water Research,2018,139:329-352. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.058 [8] AGARWAL A, NG W J, LIU Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment[J]. Chemosphere,2011,84(9):1175-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.054 [9] KHUNTIA S, MAJUMDER S K, GHOSH P. Microbubble-aided water and wastewater purification: a review[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering,2012,28(4/5/6):191-221. [10] LOHSE D, ZHANG X H. Surface nanobubbles and nanodroplets[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics,2015,87(3):981-1035. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.87.981 [11] TEMESGEN T, BUI T T, HAN M, et al. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: a review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2017,246:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.06.011 [12] SUN Y J, XIE G Y, PENG Y L, et al. Stability theories of nanobubbles at solid-liquid interface: a review[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2016,495:176-186. [13] YASUI K, TUZIUTI T, KANEMATSU W. Mysteries of bulk nanobubbles (ultrafine bubbles): stability and radical formation[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2018,48:259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.05.038 [14] LEE E J, KIM Y H, KIM H S, et al. Influence of microbubble in physical cleaning of MF membrane process for wastewater reuse[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2015,22(11):8451-8459. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3928-y [15] WATABE T, MATSUYAMA K, TAKAHASHI T, et al. The effect of microbubbles on membrane fouling caused by different foulants[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2016,57(21):9558-9568. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2015.1031186 [16] DING Z W, LIU L Y, LIU Z, et al. The use of intermittent gas bubbling to control membrane fouling in concentrating TCM extract by membrane distillation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2011,372(1/2):172-181. [17] YE Y B, YU S L, HOU L A, et al. Microbubble aeration enhances performance of vacuum membrane distillation desalination by alleviating membrane scaling[J]. Water Research,2019,149:588-595. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.048 [18] CHEN G Z, YANG X, WANG R, et al. Performance enhancement and scaling control with gas bubbling in direct contact membrane distillation[J]. Desalination,2013,308:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2012.07.018 [19] CHEN G Z, YANG X, LU Y H, et al. Heat transfer intensification and scaling mitigation in bubbling-enhanced membrane distillation for brine concentration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2014,470:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2014.07.017 [20] CUI Z F, CHANG S, FANE A G. The use of gas bubbling to enhance membrane processes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2003,221(1/2):1-35. [21] JIANG L J, CHEN L, ZHU L. Fouling process of membrane distillation for seawater desalination: an especial focus on the thermal-effect and concentrating-effect during biofouling[J]. Desalination,2020,485:114457. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2020.114457 [22] 赵文, 夏圣骥, 彭浩轩.PTFE超滤膜对水中三种典型天然有机物的去除及其膜污染机制[J]. 净水技术,2018,37(10):33-38.ZHAO W, XIA S J, PENG H X. Removal of three typical natural organic matters in water by PTFE ultrafiltration membrane process and the mechanism of membrane fouling[J]. Water Purification Technology,2018,37(10):33-38. [23] 孟倩. 三种典型污染物对超滤膜的污染研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014. [24] TANG C Y, KWON Y N, LECKIE J O. Fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes by humic acid: effects of solution composition and hydrodynamic conditions[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2007,290(1/2):86-94. [25] JONES K L, O’MELIA C R. Protein and humic acid adsorption onto hydrophilic membrane surfaces: effects of pH and ionic strength[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2000,165(1):31-46. ⊗ doi: 10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00218-5 -





 下载:
下载: