Analysis of the characteristics of water eco-environment and comprehensive countermeasure for typical cities in the Yangtze River Basin
-
摘要:
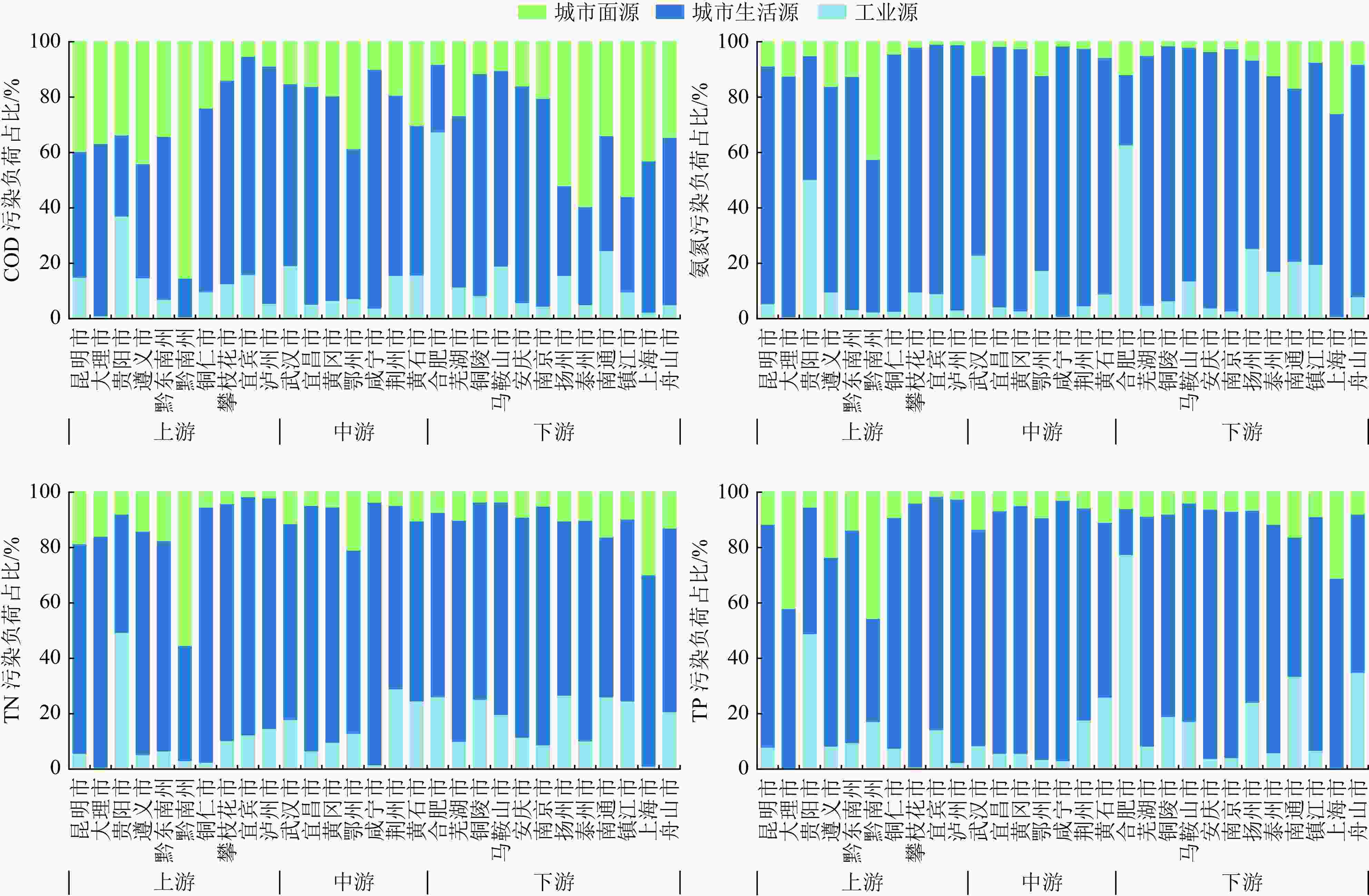
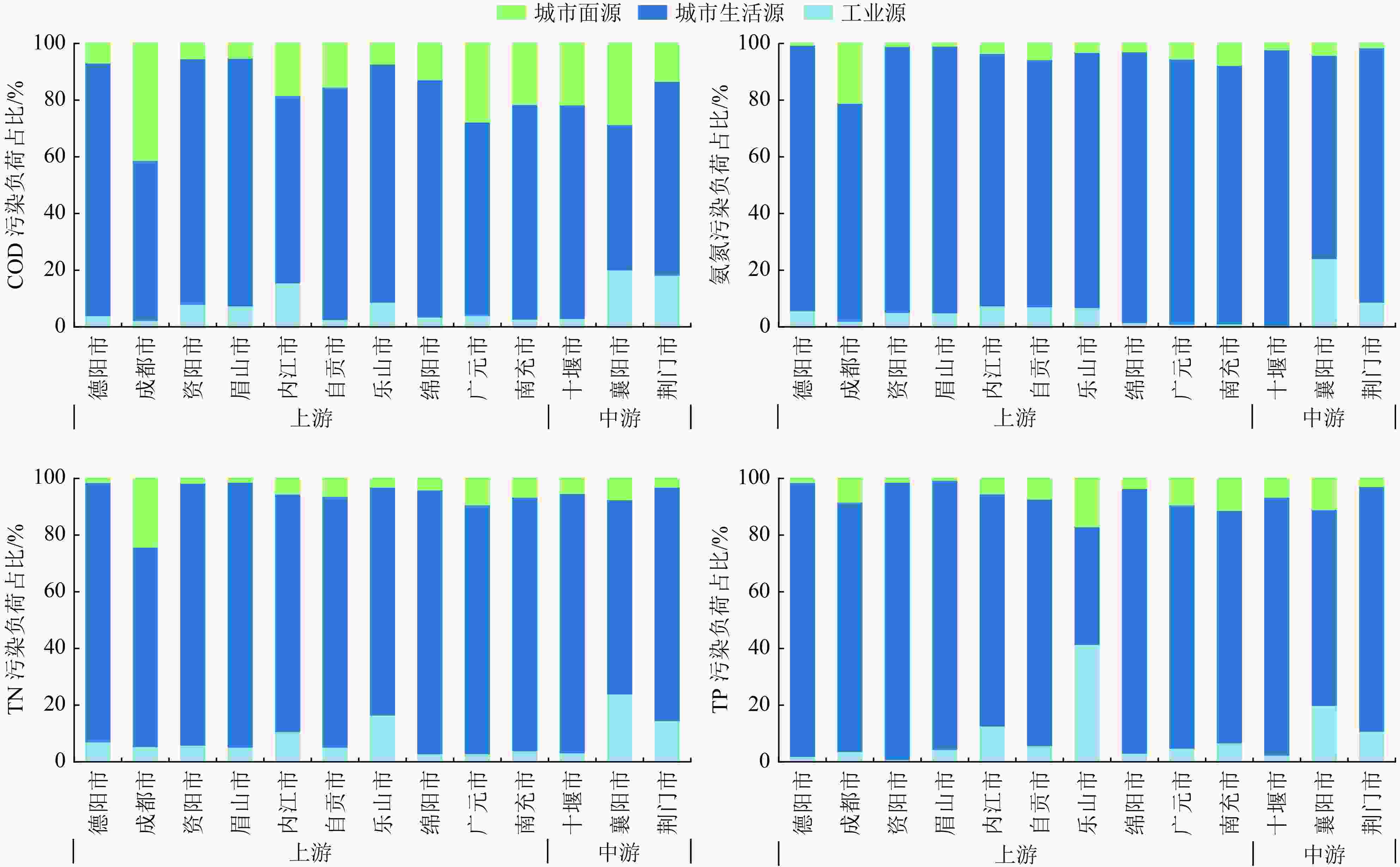
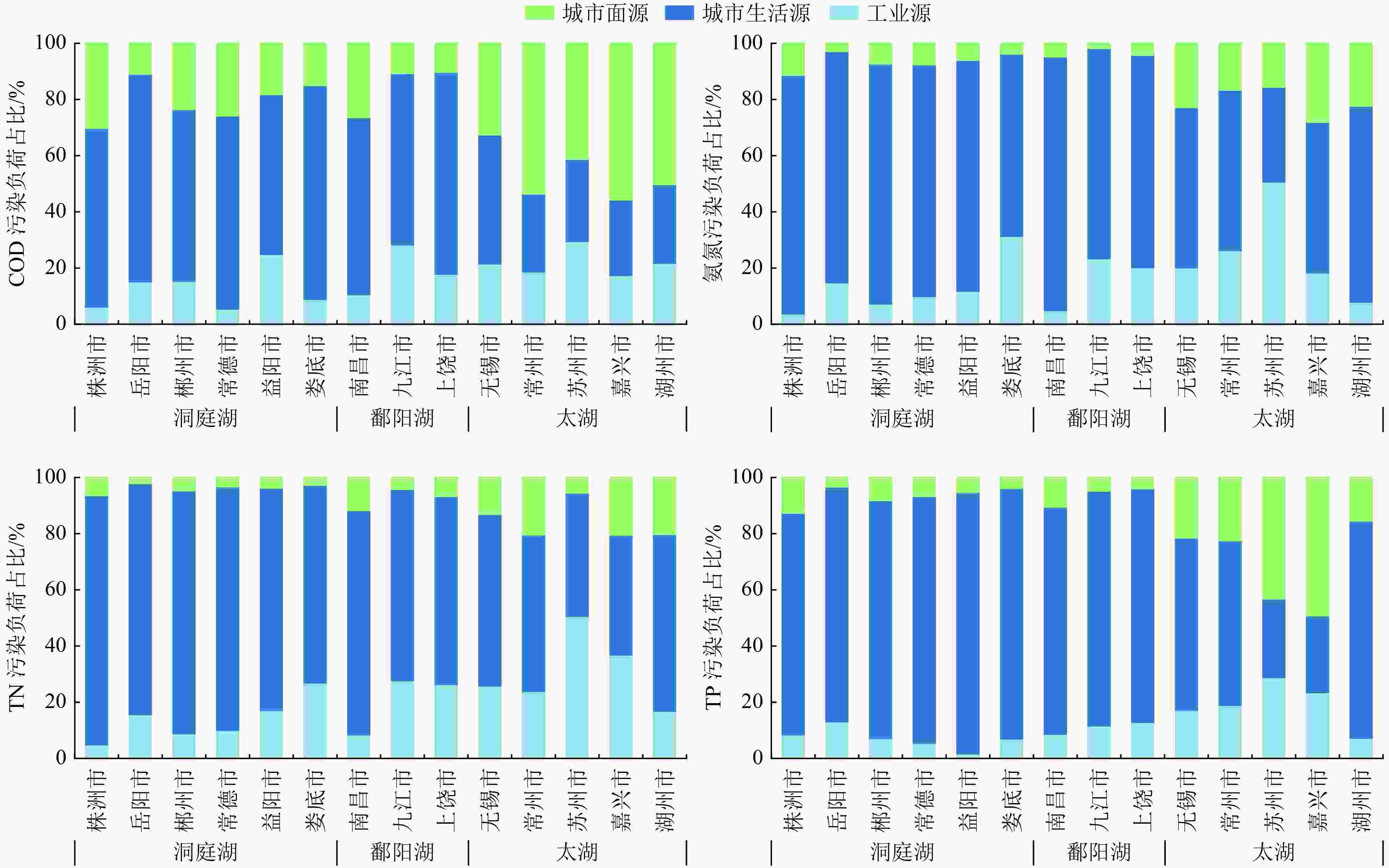
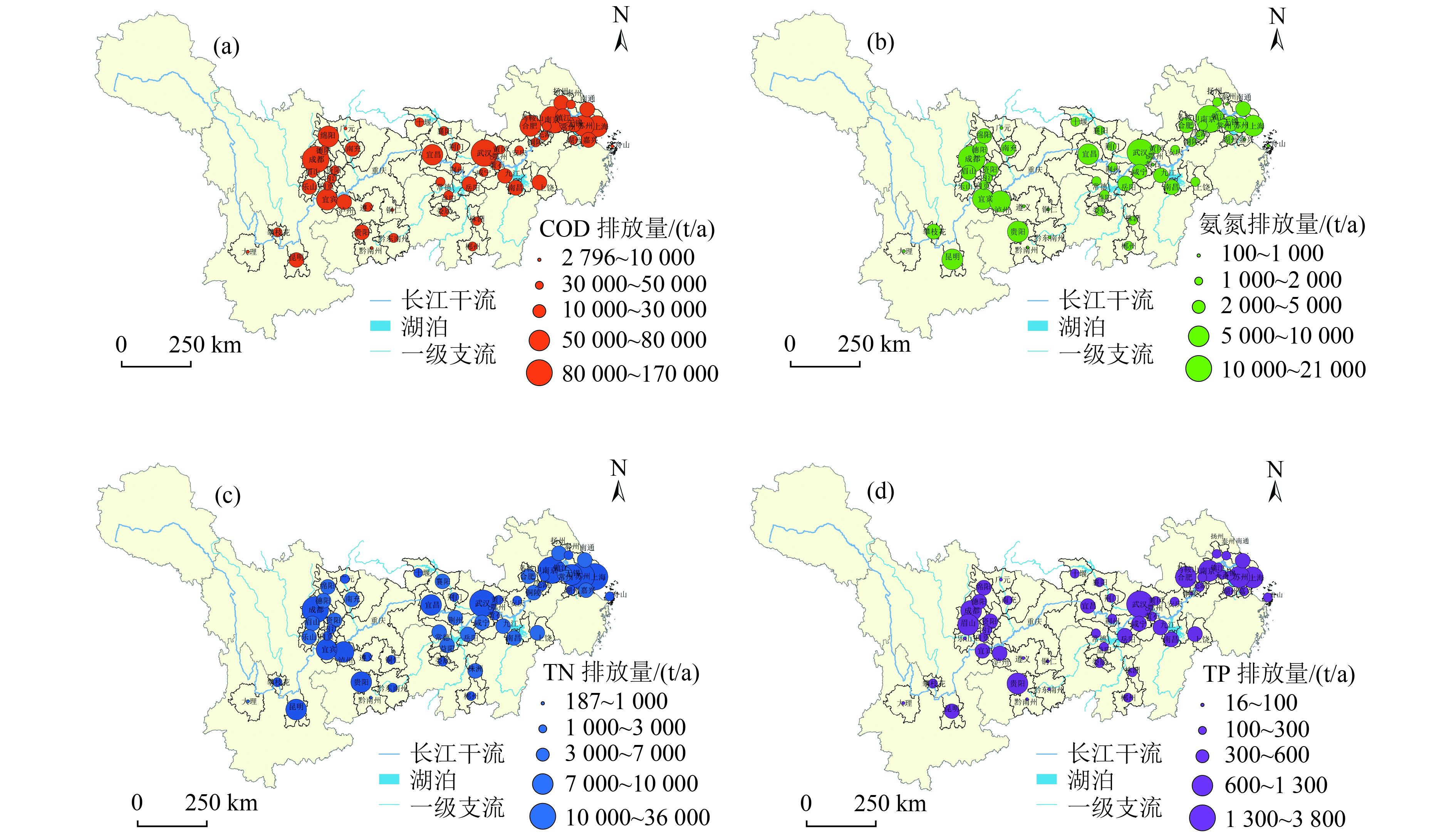
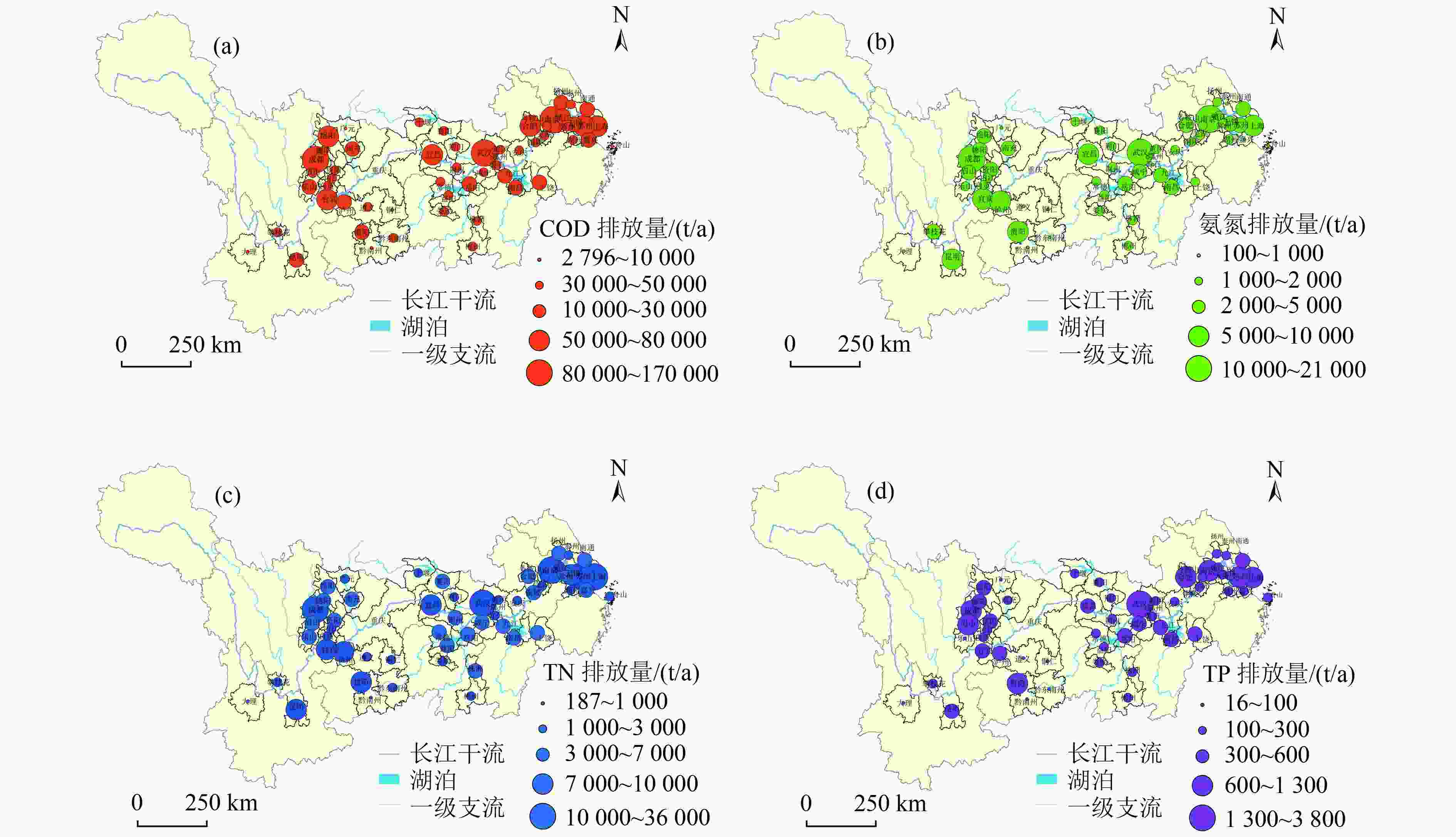
以长江流域典型城市为研究对象,估算长江干流、主要支流和通江湖城市COD、氨氮、TN和TP污染排放负荷,梳理典型城市水环境质量、水生态、水资源和水安全特征。结果表明,长江流域内56个城市COD、氨氮、TN、TP的排放量分别为193.78万、15.57万、31.01万和2.18万t/a,流域内大部分城市主要污染源为城市生活源,但工业源和城市面源不容忽视。近年来,流域内城市面源排放负荷占比升高,部分城市水生态系统遭到破坏,存在水质型和资源型缺水、水资源开发利用不合理、非常规水利用率低等问题,导致部分城市仍存在水生态环境安全风险。在此基础上提出了流域内城市“十四五”时期水生态环境综合整治对策建议。
Abstract:The discharge loads of COD, NH3-N, TN and TP from typical cities at the mainstream, tributary streams and around the lakes connected with the Yangtze River Basin were evaluated. The characteristics of urban water environment quality, water ecology, water resources and water security of the typical cities were analyzed. The results showed that 1937800, 155700, 310100 and 21800 tons of COD, NH3-N, TN and TP, respectively, were discharged from 56 cities in the Yangtze River Basin for each year. The domestic source was the main pollution source for most cities in the Yangtze River Basin, and the pollution from industry and non-point sources was also nonnegligible. In recent years, the increasing non-point source proportion, the general damage of the urban water ecosystem, the shortage of water due to water quality and resources in some cities, the rough use of water and low utilization of unconventional water sources led to the prominent water ecological risk in these cities in the Yangtze River Basin. Finally, comprehensive countermeasures were proposed to improve the urban water eco-environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin in the 14th Five-Year Plan period.
-
表 1 本研究选取的长江流域典型城市
Table 1. Selected typical cities in the Yangtze River Basin in this study
流域 典型城市 干流城市 云南省:昆明市、大理市
贵州省:贵阳市、遵义市、黔东南州、黔南州、铜仁市
四川省:攀枝花市、宜宾市、泸州市
湖北省:武汉市、宜昌市、黄冈市、鄂州市、咸宁市、 荆州市、黄石市
安徽省:合肥市、芜湖市、铜陵市、马鞍山市、安庆市
江苏省:南京市、扬州市、泰州市、南通市、镇江市
上海市
浙江省:舟山市支流城市 岷沱江支流:四川省德阳市、成都市、资阳市、眉山 市、内江市、自贡市、乐山市
嘉陵江支流:四川省绵阳市、广元市、南充市
汉江支流:湖北省十堰市、襄阳市、荆门市通江湖城市 洞庭湖:湖南省株洲市、岳阳市、郴州市、常德市、
益阳市、娄底市
鄱阳湖:江西省南昌市、九江市、上饶市
太湖:江苏省无锡市、常州市、苏州市,浙江省嘉兴 市、湖州市表 2 长江流域56个典型城市污染物排放量
Table 2. Pollutant discharges from 56 typical cities in the Yangtze River Basin
指标 城市生活源 工业源 城市面源 总计/
(万t/a)排放量/
(万t/a)占比/% 排放量/
(万t/a)占比/% 排放量/
(万t/a)占比/% COD 117.25 60.51 27.22 14.04 49.31 25.45 193.78 氨氮 12.24 78.61 2.04 13.10 1.29 8.29 15.57 TN 22.73 73.30 5.14 16.57 3.14 10.13 31.01 TP 1.64 75.23 0.30 13.76 0.24 11.01 2.18 -
[1] 李爽, 周天凯, 樊琳梓.长江流域城市的绿色发展评价及影响因素[J]. 管理现代化,2018,38(4):86-89.LI S, ZHOU T K, FAN L Z. Evaluation and influencing factors of green development of cities in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Modernization of Management,2018,38(4):86-89. [2] 胡洪营, 孙迎雪, 陈卓, 等.城市水环境治理面临的课题与长效治理模式[J]. 环境工程,2019,37(10):6-15. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201910002HU H Y, SUN Y X, CHEN Z, et al. Topics and long-term governance model of urban water environment governance[J]. Environmental Engineering,2019,37(10):6-15. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201910002 [3] 孔令桥, 张路, 郑华, 等.长江流域生态系统格局演变及驱动力[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(3):741-749.KONG L Q, ZHANG L, ZHENG H, et al. Driving forces behind ecosystem spatial changes in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(3):741-749. [4] 王金南, 于雷, 万军, 等.长江三角洲地区城市水环境承载力评估[J]. 中国环境科学,2013,33(6):1147-1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.06.026WANG J N, YU L, WAN J, et al. Assessment on water environmental carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. China Environmental Science,2013,33(6):1147-1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.06.026 [5] 成金华, 王然.基于共抓大保护视角的长江经济带矿业城市水生态环境质量评价研究[J]. 中国地质大学学报(社会科学版),2018,18(4):1-11. doi: 10.16493/j.cnki.42-1627/c.2018.04.001CHENG J H, WANG R. Research on water ecological environment quality evaluation of mining cities in the Yangtze River economic belt from the perspective of common protection[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences (Social Sciences Edition),2018,18(4):1-11. doi: 10.16493/j.cnki.42-1627/c.2018.04.001 [6] CHANG Y J, ZHU D M. Water security of the megacities in the Yangtze River Basin: comparative assessment and policy implications[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,290:125812. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125812 [7] 刘录三, 黄国鲜, 王璠, 等.长江流域水生态环境安全主要问题、形势与对策[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(5):1081-1090.LIU L S, HUANG G X, WANG F, et al. Main problems, situation and countermeasures of water eco-environment security in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(5):1081-1090. [8] 王建华.生态大保护背景下长江流域水资源综合管理思考[J]. 人民长江,2019,50(10):1-6.WANG J H. Discussion on integrated water resources management in Yangtze River Basin under background of ecological protection[J]. Yangtze River,2019,50(10):1-6. [9] DOU P F, ZUO S D, REN Y, et al. Refined water security assessment for sustainable water management: a case study of 15 key cities in the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,290:112588. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112588 [10] 关于发布《排放源统计调查产排污核算方法和系数手册》的公告[A/OL]. 北京: 生态环境部. (2021-06-18)[2021-12-30]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202106/t20210618_839512.html. [11] 杨龙, 孙长虹, 齐珺, 等.城市径流污染负荷动态更新研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展,2014,39(3):135-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2014.03.042YANG L, SUN C H, QI J, et al. Study on the dynamic update of urban surface runoff pollutants load[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development,2014,39(3):135-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2014.03.042 [12] 杨均英, 蒋时兴, 朱俊成, 等.长江流域黑臭水体的成因与治理[J]. 施工技术,2020,49(18):6-8.YANG J Y, JIANG S X, ZHU J C, et al. The formation and treatment of black-odor water in Yangtze River[J]. Construction Technology,2020,49(18):6-8. [13] 长江经济带生态环境保护规划[R]. 北京: 环境保护部, 2017. [14] 朱振肖, 王夏晖, 张箫, 等.湖北省长江三峡地区山水林田湖草生态保护修复实践探索与思考[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(5):769-778. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190187ZHU Z X, WANG X H, ZHANG X, et al. Practice and thinking about the mountain-river-forest-farmland-lake-grassland ecological conservation and restoration in Three Gorges Area of the Yangtze River in Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(5):769-778. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190187 [15] 易雨君, 王文君, 宋劼.长江中下游底泥重金属污染特征、潜在生态风险评价及来源分析[J]. 水利水电技术,2019(2):1-7. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2019.02.001YI Y J, WANG W J, SONG J. Pollution characteristics, potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals of sediment in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2019(2):1-7. ⊗ doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2019.02.001 -




 下载:
下载: