Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals of a certain river in headwater stream of Xiangjiang River
-
摘要: 为探究湘江源头某河段水体重金属分布特征并探讨其对沿岸居民健康的影响,在丰水期、枯水期以及平水期对该河段13个地表水样品中的5种重金属(As、Cu、Pb、Zn、和Cd)进行监测,通过内梅罗综合污染指数法、健康风险评价模型评价了该河段水体中5种重金属的污染现状、分布特征和可能产生的健康风险。结果表明,该河段水体中重金属浓度表现为Zn>As>Pb>Cd>Cu,污染程度为平水期≈枯水期>丰水期,且上游≈中游>下游。内梅罗综合污染指数法评价结果表明,该河段水体86.1%的采样点全年处于重度污染状态。健康风险评价结果表明,该河段地表水体中重金属引起的环境健康风险主要来自于As、Cd,二者浓度表现为上游>中游>下游,枯水期>平水期>丰水期,且儿童所面临的健康风险约为成人的2.1倍。Abstract: To investigate the distribution characteristics of heavy metal elements in a river section in headwater stream of Xiangjiang River and assess their health risks to coastal residents, five heavy metal elements (As, Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd) in 13 surface water samples of the river were collected and monitored at three periods (wet, dry and normal). The Nemero comprehensive pollution index method and the health risk assessment model were employed to study the pollution levels, distribution characteristics and potential health risks of these heavy metals. The results showed that the average metal concentrations in the surface water samples in the river followed the order of Zn > As > Pb > Cd > Cu. The pollution levels of these heavy metals were arranged as follows: normal period ≈ dry period > wet period, and upstream ≈ midstream > downstream. The results of Nemero comprehensive pollution index method showed that 86.1% of the sampling sites in the river were heavily polluted by heavy metals throughout the year. The result of health risk assessment indicated that the environmental health risks in the surface water in the study area were mainly caused by As and Cd. The health risk level of these heavy metals in study area followed the order of upstream > midstream > downstream and dry period > normal period > wet period. And the children were nearly 2.1 times more susceptible to health effects than adults.
-
表 1 水体重金属污染评价标准[17]
Table 1. Evaluation criteria for heavy metal pollution
Pi Pn 污染程度 ≤1 ≤0.7 安全 1~2 0.7~1.0 警戒 2~3 1.0~2.0 轻度污染 >3 >2.0 重度污染 表 2 致癌物质的致癌系数和非致癌物质参考剂量
Table 2. Carcinogenic coefficient of carcinogens and reference dose of non-carcinogens
类别 元素 致癌系数/参考剂量 致癌 As 15 Cd 6.1 非致癌 Zn 0.3000 Cu 0.0050 Pb 0.0014 注:致癌系数计量单位为kg∙d/mg,参考剂量单位为mg/(kg∙d)。 表 3 研究河段水体重金属监测结果统计
Table 3. Statistical analysis of heavy metal monitoring results in the study river section
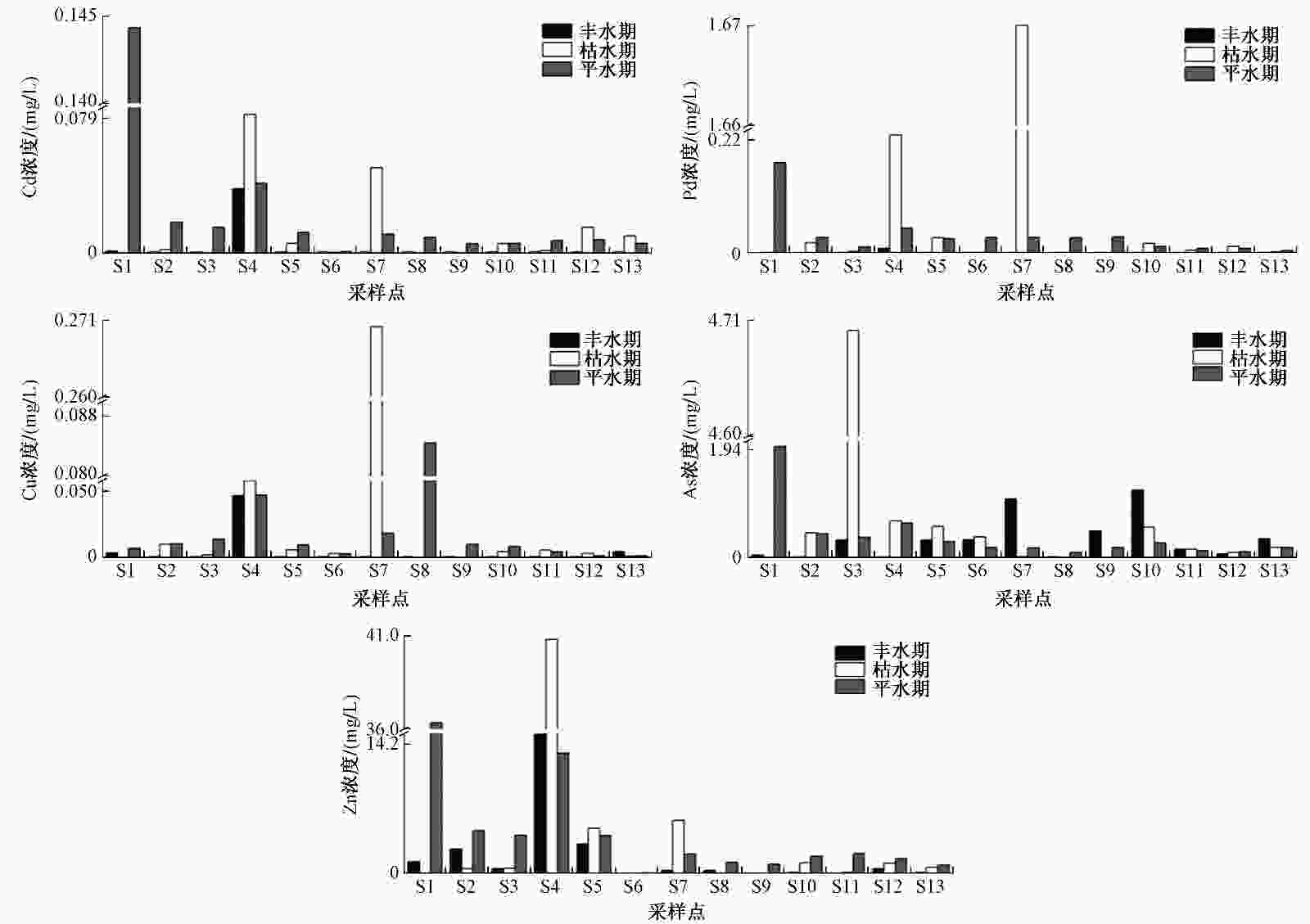
重金属 水期 浓度/(mg/L) 标准差/(mg/L) 变异系数 标准值1)/(mg/L) 超标采样点数/个 超标率/% 最小值 最大值 均值 Cu 丰水期 0.0005 0.05 0.005 0.01 2.68 1.00 0 枯水期 0.001 0.27 0.04 0.08 2.20 1.00 0 平水期 0.001 0.08 0.02 0.02 1.36 1.00 0 Zn 丰水期 0.03 15.30 1.92 3.99 2.08 1.00 4 31 枯水期 0.04 40.83 5.62 11.90 2.12 1.00 5 50 平水期 0.07 31.27 6.55 7.71 1.18 1.00 10 77 Pb 丰水期 0.0005 0.009 0.001 0.002 1.99 0.05 0 枯水期 0.001 1.67 0.20 0.50 2.48 0.05 2 20 平水期 0.001 0.13 0.03 0.04 1.23 0.05 2 15 As 丰水期 0.008 1.21 0.33 0.38 1.13 0.05 9 69 枯水期 0.02 4.74 0.78 1.34 1.73 0.05 9 90 平水期 0.02 1.62 0.44 0.48 1.09 0.05 12 92 Cd 丰水期 0.0005 0.04 0.003 0.01 2.89 0.005 1 8 枯水期 0.0002 0.08 0.02 0.03 1.49 0.005 6 60 平水期 0.001 0.08 0.02 0.02 0.91 0.005 11 85 1) GB 3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准》Ⅲ类水质标准[25]。 表 4 研究河段水体重金属污染评价结果
Table 4. Evaluation results of heavy metals contamination in the study river section
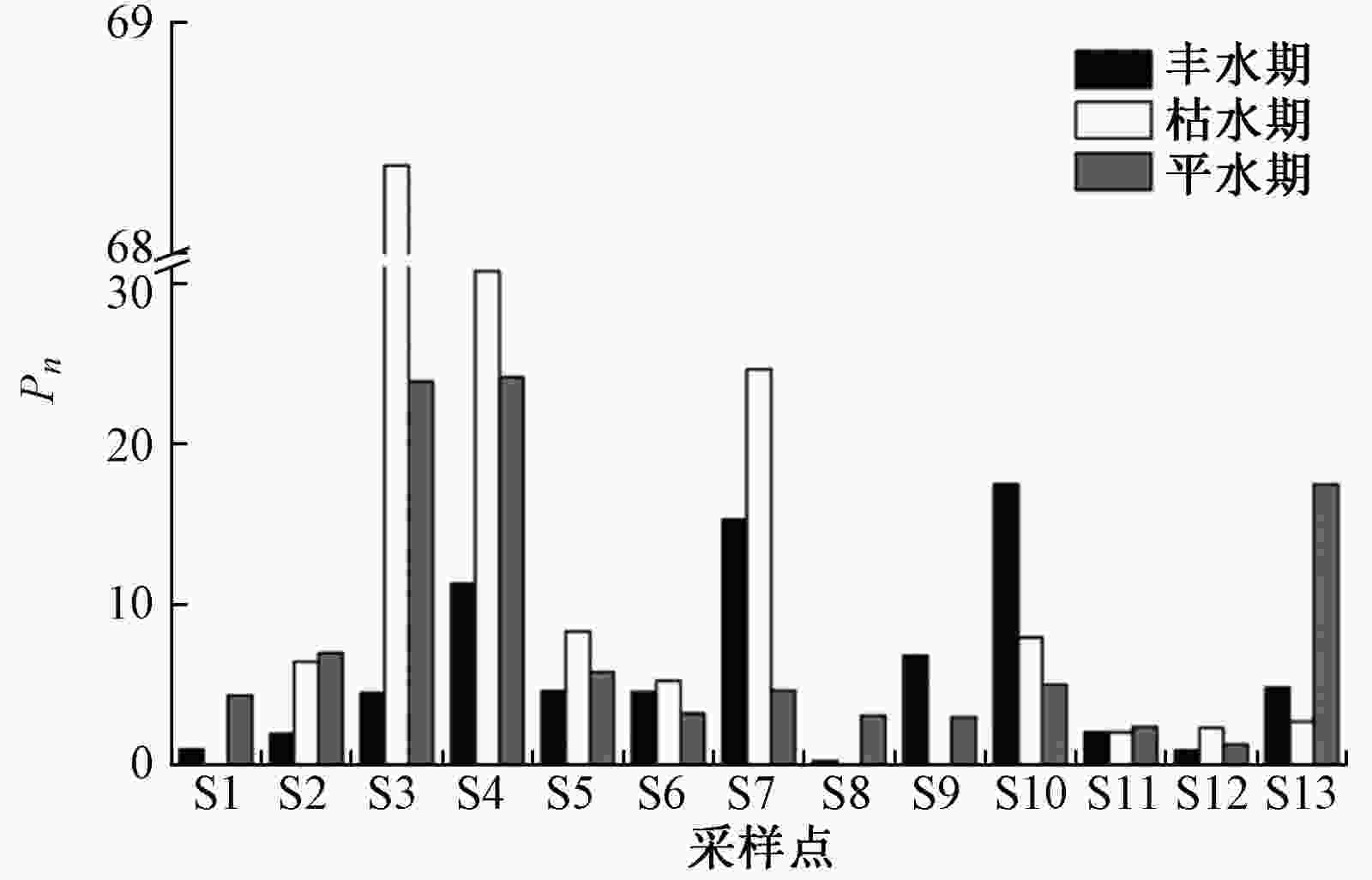
河段 水期 单因子污染指数 内梅罗综合污染指数及评价结果 Cu Zn Pb As Cd Pn 评价结果 上游 丰水期 0.013 4.983 0.055 1.828 1.988 4.705 重度污染 枯水期 0.017 10.498 1.265 29.208 4.155 26.394 重度污染 平水期 0.019 13.730 1.068 14.928 8.098 14.860 重度污染 中游 丰水期 0.001 0.717 0.010 11.313 0.100 8.187 重度污染 枯水期 0.047 2.017 5.735 4.963 2.043 7.704 重度污染 平水期 0.022 4.330 0.735 4.523 3.055 4.147 重度污染 下游 丰水期 0.002 0.267 0.010 3.613 0.100 2.617 重度污染 枯水期 0.003 0.690 0.137 2.773 1.767 2.384 重度污染 平水期 0.002 1.417 0.093 9.287 1.153 7.054 重度污染 表 5 饮用水引起的致癌健康风险评价结果
Table 5. Results of health risk assessment of carcinogenesis caused by drinking water
a−1 水期 重金属 上游 中游 下游 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 丰水期 As 2.88×10−4 6.49×10−4 1.78×10−3 4.02×10−3 5.69×10−4 1.28×10−3 Cd 1.27×10−5 2.87×10−5 6.41×10−7 1.44×10−6 6.41×10−7 1.44×10−6 致癌总风险 3.01×10−4 6.78×10−4 1.78×10−3 4.02×10−3 5.70×10−4 1.28×10−3 枯水期 As 4.12×10−3 6.61×10−3 1.17×10−3 2.64×10−3 4.37×10−4 9.85×10−4 Cd 3.55×10−5 8.00×10−5 1.96×10−5 4.43×10−5 1.13×10−5 2.55×10−5 致癌总风险 4.15×10−3 6.69×10−3 1.19×10−3 2.69×10−3 4.48×10−4 1.01×10−3 平水期 As 2.35×10−3 5.30×10−3 7.13×10−4 1.61×10−3 1.46×10−3 3.30×10−3 Cd 5.19×10−5 1.17×10−4 1.96×10−5 4.41×10−5 7.40×10−6 1.67×10−5 致癌总风险 2.40×10−3 5.42×10−3 7.33×10−4 1.65×10−3 1.47×10−3 3.31×10−3 表 6 饮用水引起的非致癌健康风险评价结果
Table 6. Results of health risk assessment of non-carcinogen caused by drinking water
a−1 时期 重金属 上游 中游 下游 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 丰水期 Cu 5.33×10−10 1.20×10−9 2.10×10−11 4.73×10−11 7.36×10−11 4.73×10−11 Zn 3.49×10−9 7.86×10−9 5.00×10−10 1.13×10−9 1.86×10−10 4.18×10−10 Pb 4.03×10−10 9.09×10−10 7.51×10−11 1.69×10−10 7.51×10−11 1.69×10−10 非致癌总风险 4.43×10−9 9.97×10−9 5.96×10−10 1.34×10−9 3.34×10−10 6.35×10−10 枯水期 Cu 9.78×10−10 2.20×10−9 2.97×10−9 6.70×10−9 1.33×10−10 3.00×10−10 Zn 9.80×10−9 2.21×10−8 2.12×10−9 4.78×10−9 4.83×10−10 1.09×10−9 Pb 1.26×10−8 2.85×10−8 6.46×10−8 1.45×10−7 1.00×10−9 2.25×10−9 非致癌总风险 2.34×10−8 5.28×10−8 6.97×10−8 1.57×10−7 1.62×10−9 3.64×10−9 平水期 Cu 8.18×10−10 1.84×10−9 9.30×10−10 2.09×10−9 3.05×10−10 6.88×10−10 Zn 9.62×10−9 2.17×10−8 3.03×10−9 6.84×10−9 9.91×10−10 2.23×10−9 Pb 8.01×10−9 1.81×10−8 5.52×10−9 1.24×10−8 6.93×10−10 1.56×10−9 非致癌总风险 1.84×10−8 4.16×10−8 9.48×10−9 2.14×10−8 1.99×10−9 4.48×10−9 -
[1] DAVE D, SARMA S, PARMAR P, et al. Microbes as a boon for the bane of heavy metals[J]. Environmental Sustainability,2020,3(3):233-255. doi: 10.1007/s42398-020-00112-2 [2] 辛成林, 任景玲, 张桂玲, 等.海南东部河流、河口及近岸水域颗粒态重金属的分布及污染状况[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(4):1315-1323.XIN C L, REN J L, ZHANG G L, et al. Distributions and pollution status of heavy metals in the suspended particles of the estuaries and coastal area of eastern Hainan[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(4):1315-1323. [3] 张智慧, 李宝, 梁仁君.南四湖南阳湖区河口与湖心沉积物重金属形态对比研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2015,35(5):1408-1416.ZHANG Z H, LI B, LIANG R J. Comparison of sediment heavy metal fractions at estuary and center of Nanyang Zone from Nansi Lake, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2015,35(5):1408-1416. [4] XIA F, NIU X, QU L, et al. Integrated source-risk and uncertainty assessment for metals contamination in sediments of an urban river system in eastern China[J]. CATENA,2021,203(8):105-113. [5] 曾晨, 郭少娟, 杨立新.汞、镉、铅、砷单一和混合暴露的毒性效应及机理研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2018,8(2):221-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2018.02.030ZENG C, GUO S J, YANG L X. Toxic effects and mechanisms of exposure to single and mixture of mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2018,8(2):221-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2018.02.030 [6] ZHANG J, LI X, GUO L, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and water quality characteristics of the reservoir control reaches in the middle Han River, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,799(4):149-156. [7] YAN C, QU Z, WANG J, et al. Microalgal bioremediation of heavy metal pollution in water: recent advances, challenges, and prospects[J]. Chemosphere,2022,286:131870. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131870 [8] TANG J, CHAI L, LI H, et al. A 10-year statistical analysis of heavy metals in river and sediment in Hengyang Segment, Xiangjiang River Basin, China[J]. Sustainability,2018,10(4):1057. doi: 10.3390/su10041057 [9] HUANG Z, LIU C, ZHAO X, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment at the drinking water source of the Xiangjiang River in South China[J]. Environmental Sciences Europe,2020,32(1):23-29. doi: 10.1186/s12302-020-00305-w [10] XU J, CHEN Y, ZHENG L, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediment of the main tributaries of Dongting Lake, China[J]. Water,2018,10(8):1060. doi: 10.3390/w10081060 [11] FANG X, PENG B, SONG Z, et al. Geochemistry of heavy metal-contaminated sediments from the four river inlets of Dongting Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(22):27593-27613. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12635-0 [12] 徐冰冰, 许秋瑾, 梁存珍, 等.湖南郴州柿竹园矿区乡镇地下饮用水源重金属水质评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(2):113-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.02.019XÜ B B, XÜ Q J, LIANG C Z, et al. Water quality assessment for heavy metals in rural groundwater sources around Shizhuyuan Polymetallic Mine in Chenzhou, Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(2):113-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.02.019 [13] 肖双.湘江长沙段地表水源生活饮用水PAEs健康风险评估[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2019,37(6):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.06.004XIAO S. Health risk assessment of PAEs in the drinking water for Changsha Section of Xiangjiang River[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2019,37(6):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.06.004 [14] 杨海君, 许云海, 刘亚宾, 等.湘江流域衡阳水口山段水环境健康风险评估[J]. 环境化学,2018,37(9):2061-2070.YANG H J, XÜ Y H, LIU Y B, et al. Environmental health risk assessment of Shuikou Mountain Section of Hengyang in Xiangjiang River Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2018,37(9):2061-2070. [15] WU J, LU J, ZHANG C, et al. Pollution, sources, and risks of heavy metals in coastal waters of China[J]. Human and ecological risk assessment,2020,26(8):2011-2026. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2019.1634466 [16] 张清华, 韦永著, 曹建华, 等.柳江流域饮用水源地重金属污染与健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(4):1598-1607.ZHANG Q H, WEI Y Z, CAO J H, et al. Heavy metal pollution of the drinking water sources in the Liujiang River Basin, and related health risk assessments[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(4):1598-1607. [17] 丁婷婷, 李强, 杜士林, 等.沙颍河流域水环境重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学,2019,38(10):2386-2401. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121806DING T T, LI Q, DU S L, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Shaying River Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,38(10):2386-2401. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121806 [18] 王进军, 刘占旗, 古晓娜, 等.环境致癌物的健康风险评价方法[J]. 国外医学(卫生学分册),2009,36(1):50-58. [19] 李丽娜. 上海市多介质环境中持久性毒害污染物的健康风险评价[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2007. [20] 生态环境部. 建设用地土壤污染风险评估技术导则: HJ 25.3—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2019. [21] 孙超, 陈振楼, 张翠, 等.上海市主要饮用水源地水重金属健康风险初步评价[J]. 环境科学研究,2009,22(1):61-65.SUN C, CHEN Z L, ZHANG C, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water sources in Shanghai, China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2009,22(1):61-65. [22] 刘昭, 周宏, 曹文佳, 等.清江流域地表水重金属季节性分布特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(1):175-183.LIU Z, ZHOU H, CAO W J, et al. Seasonal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of Qingjiang River[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(1):175-183. [23] 王晓东,田伟,张雪艳.宁夏地区地下水金属元素分布特征及健康风险评价[J/OL].环境科学.[2021-07-09].https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202105037. [24] 韦振丽, 吴湘滨, 刘悟辉, 等.三十六湾矿区的水环境问题研究[J]. 湖南有色金属,2008(1):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2008.01.015 [25] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [26] 吴蕾, 刘桂建, 周春财, 等.巢湖水体可溶态重金属时空分布及污染评价[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(2):738-747.WU L, LIU G J, ZHOU C C, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of dissolved heavy metals in Chaohu Lake[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(2):738-747. [27] 陈艳卿, 孟伟, 武雪芳, 等.美国水环境质量基准体系[J]. 环境科学研究,2011,24(4):468-474.CHEN Y Q, MENG W, WU X F, et al. Ambient water quality criteria system in the United States[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2011,24(4):468-474. [28] YIN S, FENG C, LI Y, et al. Heavy metal pollution in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: a 5-year follow-up study[J]. Chemosphere,2015,138:718-725. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.060 [29] LI C, SUN L, JIA J, et al. Risk assessment of water pollution sources based on an integrated k-means clustering and set pair analysis method in the region of Shiyan, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,557/558:307-316. □ doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.069 -




 下载:
下载: