Microbial community structure characteristics and influencing factors in sediments of Hengshui Lake in winter
-
摘要:
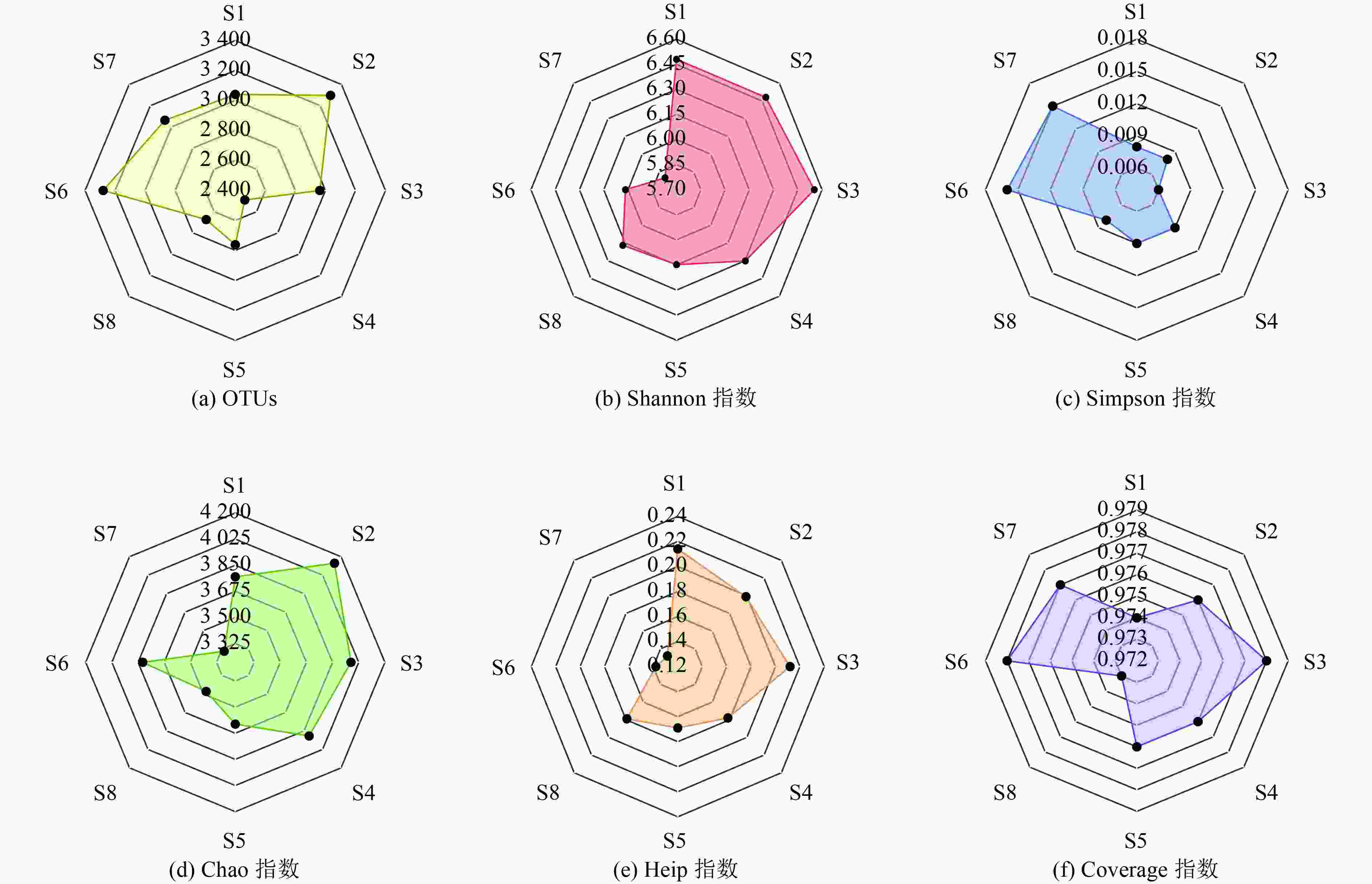
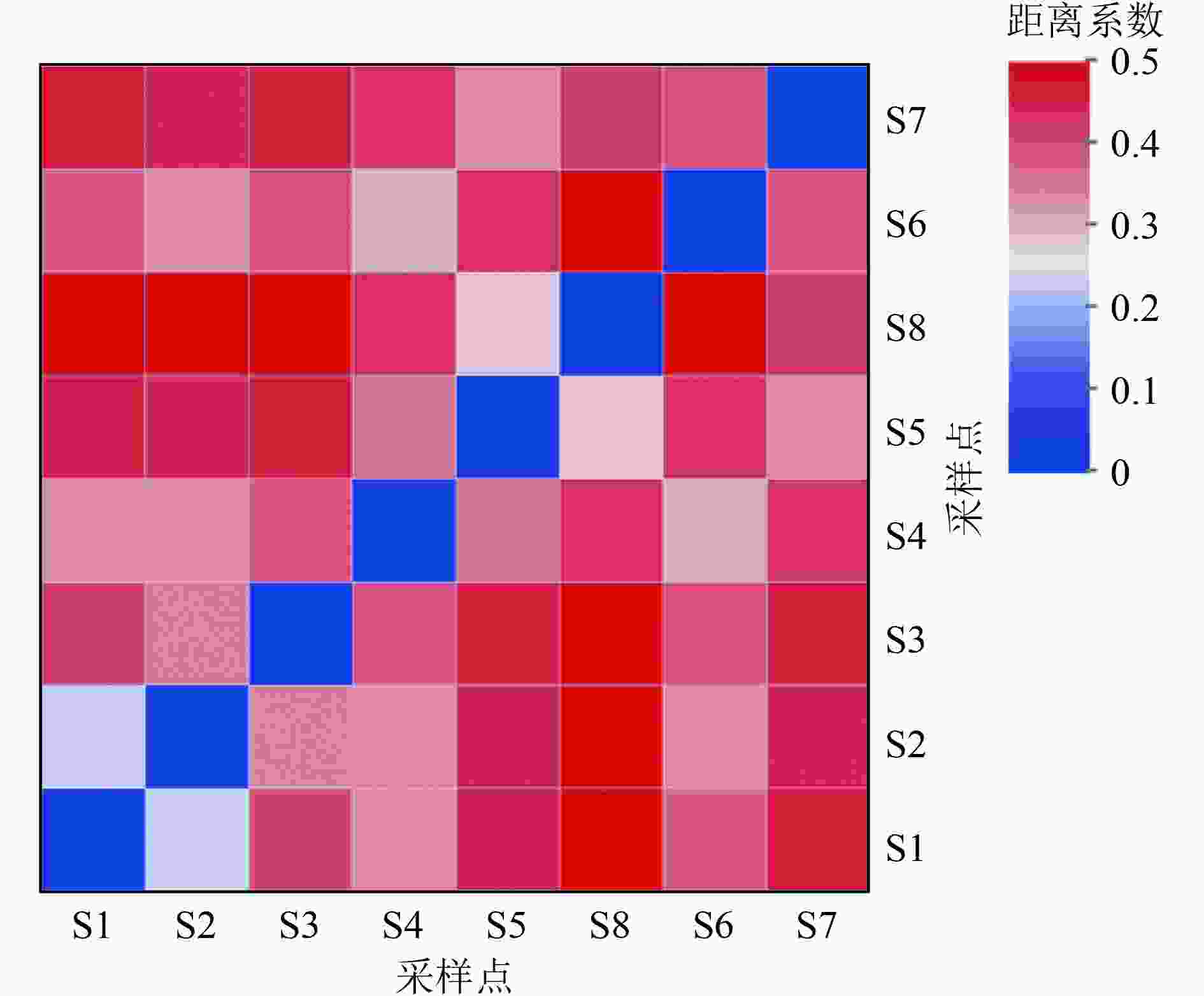
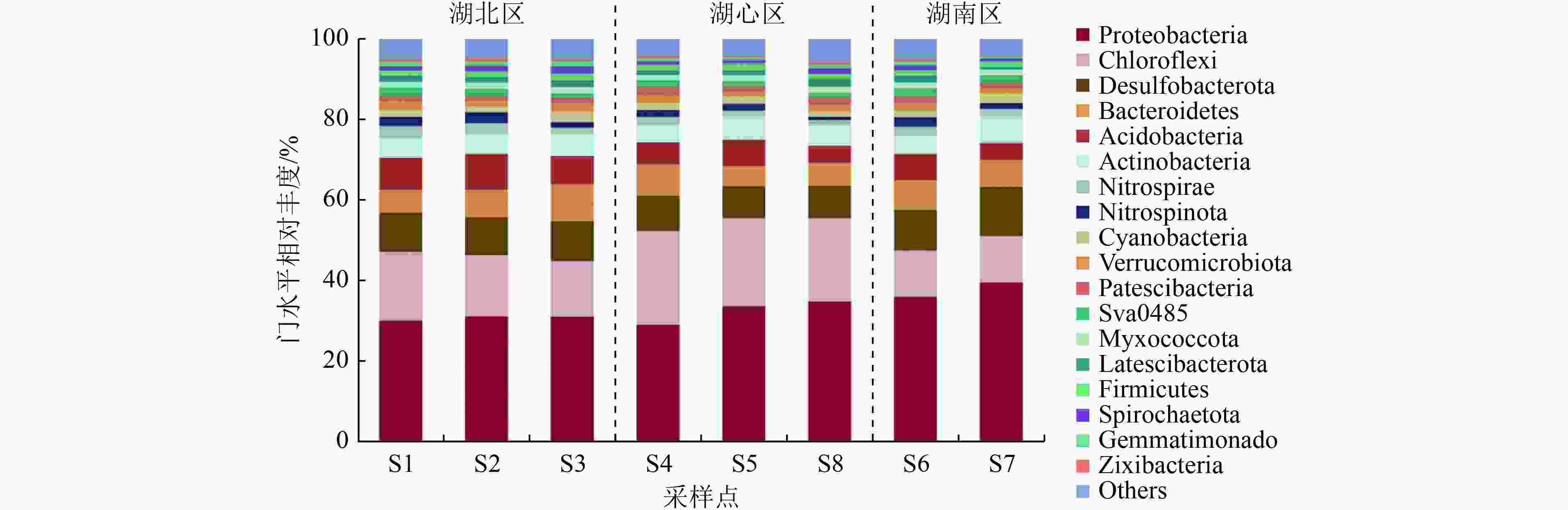
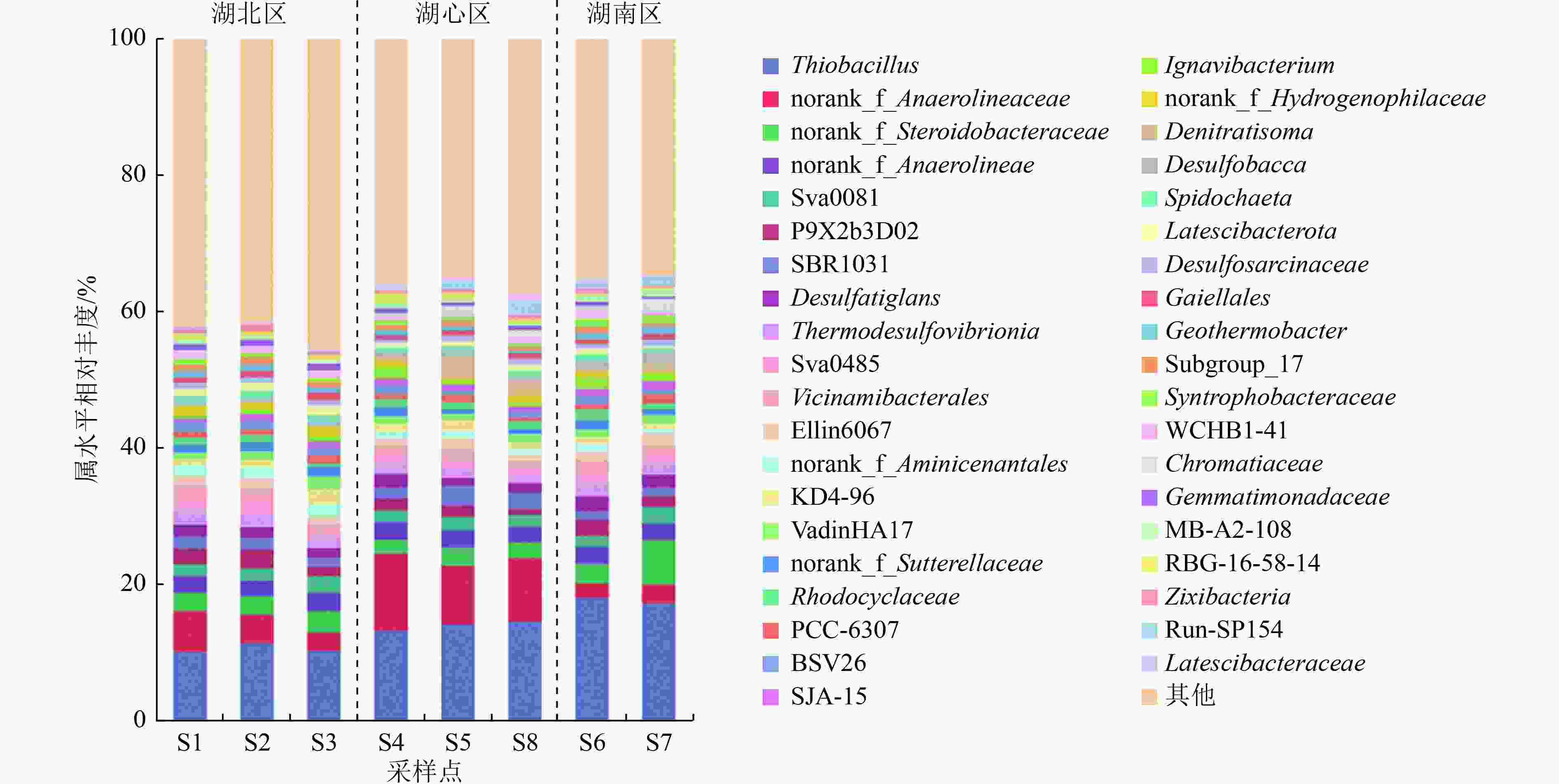
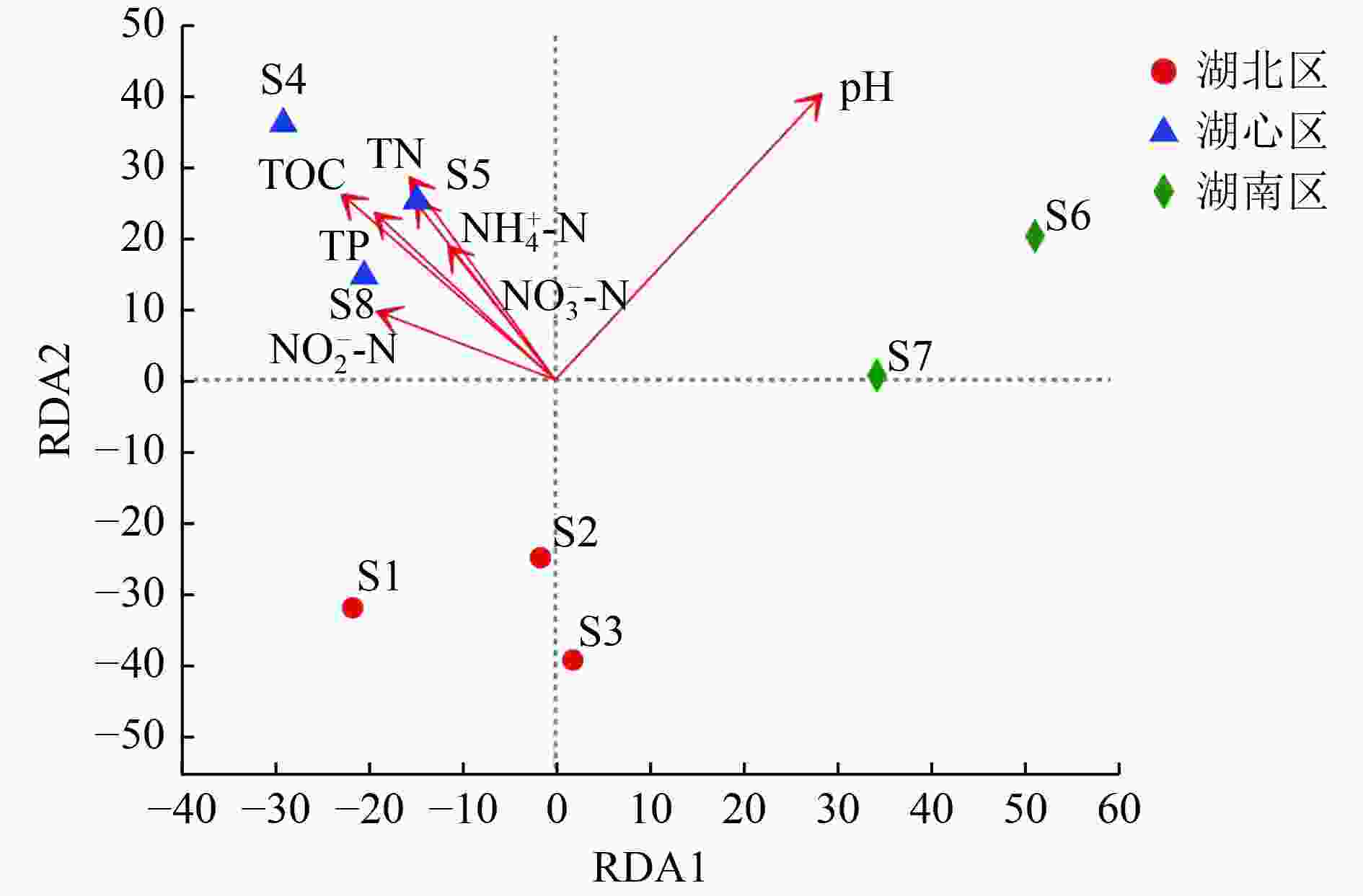
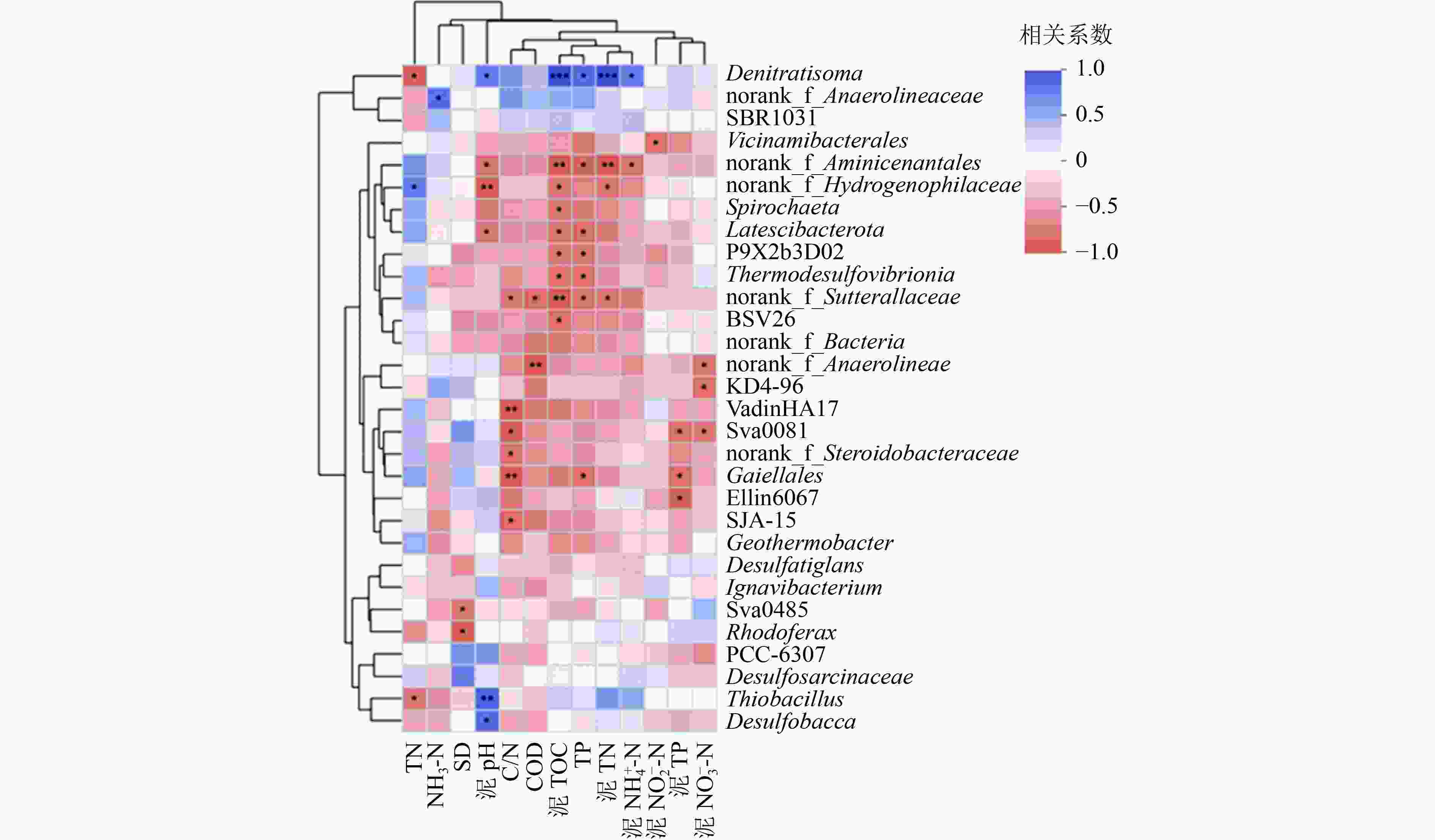
湖泊沉积物中的微生物对有机物和营养盐的转化起着重要作用,其群落结构也会受环境因子的影响。为探究冬季衡水湖沉积物中微生物群落结构差异及影响因素,基于16S rRNA基因高通量测序,分析衡水湖不同湖区表层沉积物中微生物群落结构组成、多样性及与环境因子之间的响应关系。结果表明:不同湖区沉积物中微生物群落多样性表现为湖北区>湖心区>湖南区,湖北区与湖心区沉积物的微生物群落结构存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。在门水平上,湖心区沉积物中绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)的相对丰度显著高于其他湖区,这与湖心区有机污染严重有关;在属水平上,湖北区沉积物中P9X2b3D02相对丰度显著高于其他湖区,说明该菌属更适宜在水生植物丰富的环境下生长繁衍。有机碳(TOC)浓度是衡水湖水体沉积物微生物群落结构的关键影响因素,TOC浓度与微生物菌属相对丰度的高相关性与沉积物有机污染严重有关。
Abstract:The microorganism of lake sediments plays an important role in the transformation of organic matter and nutrients, and the microbial community structure is also affected by various environmental factors. In order to explore the differences of the microbial community structure and the influencing factors in the sediments of Hengshui Lake in winter, based on 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing, the microbial community structure composition, diversity and response relationship with environmental factors in various lake areas were analyzed. The results showed that the microbial community diversity in the sediments of various lake areas was in the order of the north area of lake>the center area of lake>the south area of lake. There were extremely significant differences (P<0.01) in the microbial community structure of sediments in the north area of lake and the center area of lake. At the phylum level, the relative abundance of Chloroflexi in the sediment samples in the center area of lake was significantly higher than that in other lake areas, which was related to the serious organic pollution in the center area of lake. At the genus level, the relative abundance of P9X2b3D02 in sediment samples of the north area was significantly higher than that in other areas, indicating that this genus was more suitable for growth and reproduction in an environment with rich aquatic plants. The total organic carbon (TOC) content of the sediments was the key influencing factor of microbial community structure in lake sediments. The high correlation between TOC concentration and the relative abundance of microbial species was related to the heavy organic pollution of the sediments.
-
Key words:
- Hengshui Lake /
- sediments /
- microorganism /
- community structure /
- habitat heterogeneity
-
表 1 PCR扩增引物信息
Table 1. PCR amplification primer information
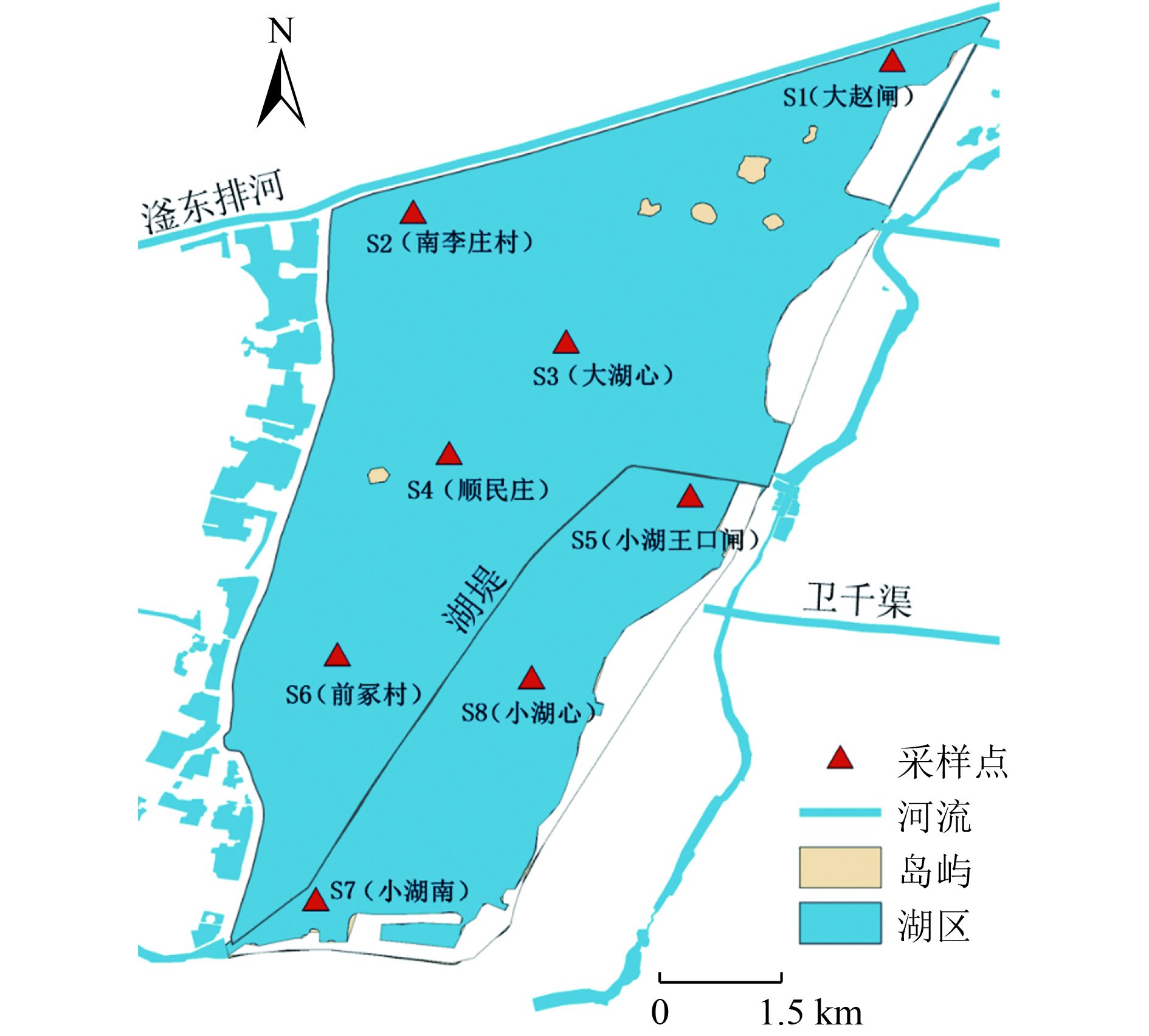
测序区域 引物名称 引物序列 338F_806R 338F ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG 806R GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT 表 2 衡水湖冬季不同湖区表层沉积物理化指标统计
Table 2. Statistics of physicochemical indexes of surface sediments in different areas of Hengshui Lake in winter
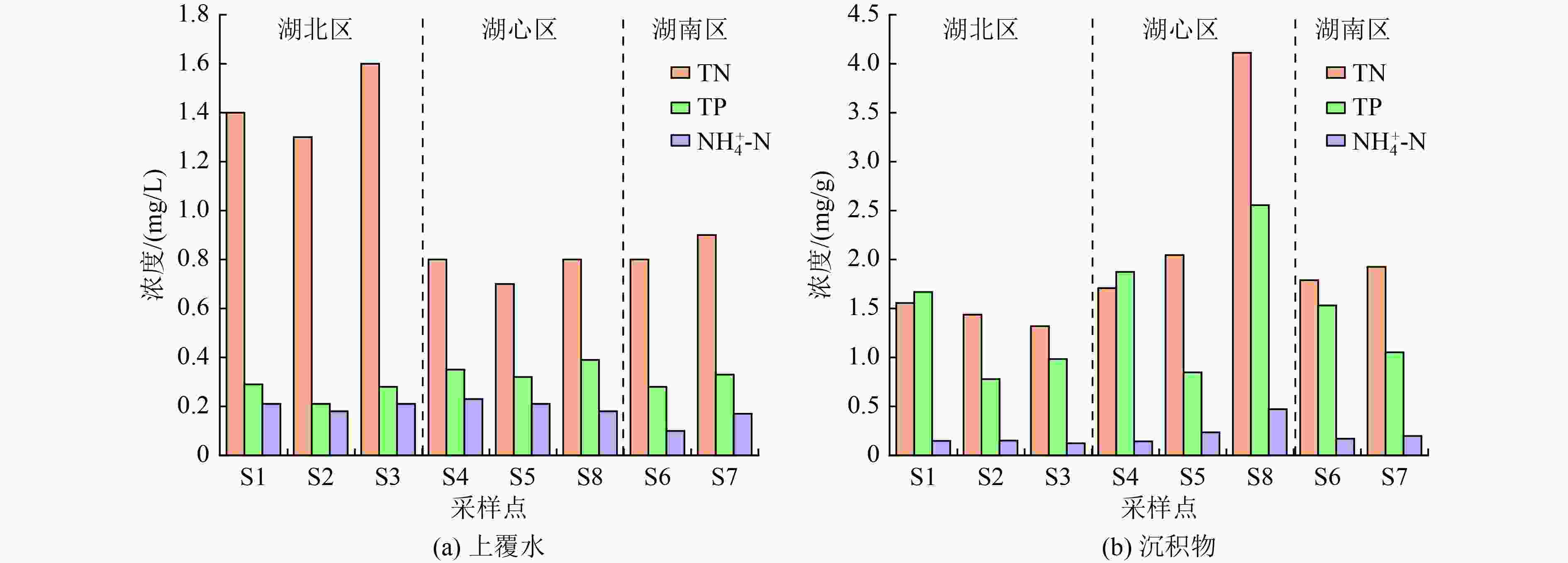
湖区 采样点 pH TP浓度/
(mg/g)TOC浓度/
(mg/g)TN浓度/
(mg/g)NH4 +-N浓度/
(mg/g)NO3 −-N浓度/
(mg/g)NO2 −-N浓度/
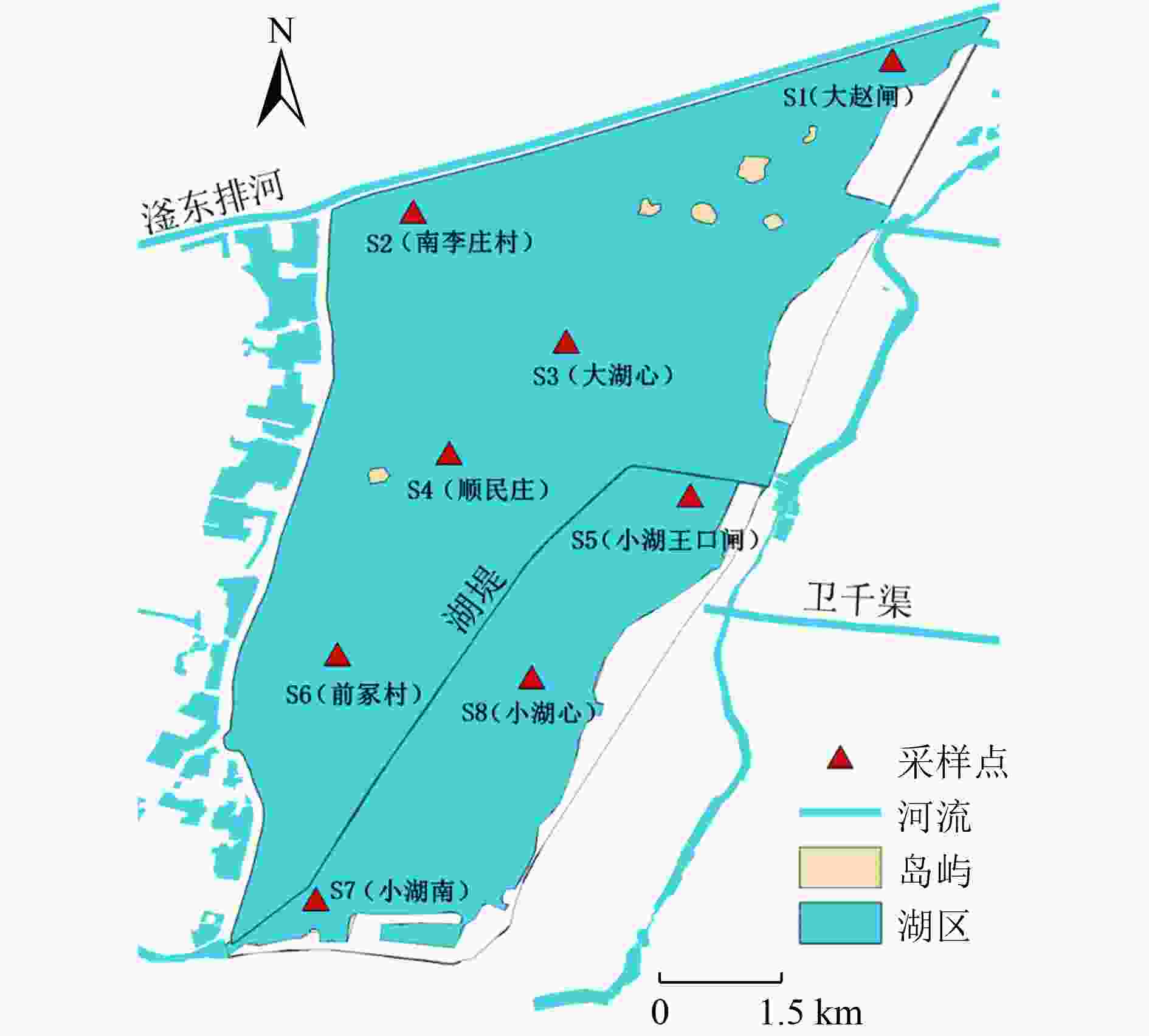
(10−4 mg/g)湖北区 S1 7.64 1.668 37.016 1.557 0.147 0.058 4.67 S2 7.68 0.779 12.465 1.437 0.152 0.042 5.84 S3 7.78 0.984 22.640 1.320 0.123 0.011 6.57 湖心区 S4 7.83 1.873 37.645 1.708 0.142 0.038 7.35 S5 7.91 0.847 45.010 2.045 0.235 0.032 4.04 S8 7.81 2.556 174.772 4.110 0.472 0.164 9.51 湖南区 S6 7.83 1.531 36.910 1.789 0.171 0.058 4.67 S7 8.01 1.052 41.121 1.926 0.199 0.052 6.71 -
[1] 金相灿, 王圣瑞, 姜霞.湖泊水-沉积物界面三相结构模式的初步研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2004,17(增刊 1):1-5.JIN X C, WANG S R, JIANG X. Preliminary study of the three-dimension model of the lake water-sediment interface[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2004,17(Suppl 1):1-5. [2] 刘昔, 邓兆林, 张露, 等.洪湖沉积物内源污染及其氮磷释放特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(1):80-88.LIU X, DENG Z L, ZHANG L, et al. Sediment endogenous pollution and release characteristics of Honghu Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(1):80-88. [3] di CESARE A, PJEVAC P, ECKERT E, et al. The role of metal contamination in shaping microbial communities in heavily polluted marine sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:114823. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114823 [4] SEKIGUCHI H, WATANABE M, NAKAHARA T, et al. Succession of bacterial community structure along the Changjiang River determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and clone library analysis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(10):5142-5150. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.10.5142-5150.2002 [5] 潘福霞, 来晓双, 李欣, 等.不同湿地植物脱氮效果与根际土壤微生物群落功能多样性特征分析[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1497-1503.PAN F X, LAI X S, LI X, et al. Nitrogen removal efficiencies and rhizosphere soil microbial community functional diversities of different plants in constructed wetlands[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(6):1497-1503. [6] 寄博华, 李玮, 常军军, 等.滇池湖滨湿地不同挺水植物区沉积物细菌群落结构特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2020,36(3):390-398.JI B H, LI W, CHANG J J, et al. Characteristics of bacterial community structure in sediments with different emergent plants in Dianchi lakeside wetland[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2020,36(3):390-398. [7] 于妍, 王悦悦, 方杜贤, 等.白洋淀表层沉积物细菌多样性及影响因素[J]. 环境工程学报,2021,15(3):1121-1130.YU Y, WANG Y Y, FANG D X, et al. Bacterial diversity in surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake and its influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2021,15(3):1121-1130. [8] 朱婷婷, 田从魁.水库底泥中微生物多样性及其与环境因子相关性分析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(3):625-632.ZHU T T, TIAN C K. Analysis on microbial diversity in the sediments and its relationship with environmental factors in a reservoir[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2018,54(3):625-632. [9] 刘利, 张嘉雯, 陈奋飞, 等.衡水湖底泥重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(2):205-211.LIU L, ZHANG J W, CHEN F F, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Hengshui Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(2):205-211. [10] 张嘉雯, 魏健, 刘利, 等.衡水湖沉积物营养盐形态分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(12):5389-5399.ZHANG J W, WEI J, LIU L, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nutrients in Hengshui Lake sediments[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(12):5389-5399. [11] 王贺年, 张曼胤, 郭子良, 等.衡水湖底泥中7种重金属元素含量的分布及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 湿地科学,2020,18(2):191-199.WANG H N, ZHANG M Y, GUO Z L, et al. Distribution of contents of 7 kinds of heavy metal elements in the sediments of Hengshui Lake and their ecological risk assessment[J]. Wetland Science,2020,18(2):191-199. [12] 王倩, 甄志磊, 王春玲, 等. 汾河太原段沉积物中细菌群落的分布特征[J/OL]. 水生态学杂志, 2021. https://doi.org/10.15928/j.1674-3075.202108030266.WANG Q, ZHEN Z L, WANG C L, et al. Distribution characteristics of bacterial communities in the sediments of the Taiyuan section of the Fenhe River[J/OL]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2021. https://doi.org/10.15928/j.1674-3075.202108030266. [13] 国家环境保护总局.水和废水监测分析方法[M]4版. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2002. [14] 全国农业分析标准化技术委员会. 土壤全磷测定法: NY/T 88—1988[S/OL]. [2021-11-01]. https://www.doc88.com/p-6951358370813.html?r=1. [15] PARDO P, RAURET G, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F. Shortened screening method for phosphorus fractionation in sediments: a complementary approach to the standards, measurements and testing harmonised protocol[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2004,508(2):201-206. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2003.11.005 [16] 胡彩莉, 马玉贞, 郭超, 等.烧失量法测定土壤有机质含量的实验条件探究[J]. 地球与环境,2016,44(1):110-118.HU C L, MA Y Z, GUO C, et al. Optimization of the experiment conditions for estimating organic matter content with loss-on-ignition method[J]. Earth and Environment,2016,44(1):110-118. [17] 包宇飞, 胡明明, 王殿常, 等.黄柏河梯级水库沉积物营养盐与重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报,2021,30(5):1005-1016.BAO Y F, HU M M, WANG D C, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of the cascade reservoirs in Huangbai River[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2021,30(5):1005-1016. [18] WANG W J, YUJUNYI, YANG Y F, et al. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the sediment microbial communities of Baiyangdian shallow lake[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,2020,35(2):180-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.10.006 [19] TONG T L, LI R L, WU S J, et al. The distribution of sediment bacterial community in mangroves across China was governed by geographic location and eutrophication[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2019,140:198-203. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.046 [20] 李鹏洋, 安启睿, 王新皓, 等.辽河四平段流域河流沉积物微生物群落多样性和结构分析[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(5):2586-2594.LI P Y, AN Q R, WANG X H, et al. Analysis on diversity and structure of microbial community in river sediment of Siping section of Liaohe River[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(5):2586-2594. [21] WAN Y, BAI Y, HE J, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of aquatic environmental characteristics and sediment bacterial community in five regions of Lake Taihu[J]. Aquatic Ecology,2017,51(3):343-358. doi: 10.1007/s10452-017-9621-8 [22] YANG J, JIANG H C, WU G, et al. Distinct factors shape aquatic and sedimentary microbial community structures in the lakes of Western China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2016,7:1782. [23] DAI Y, YANG Y Y, WU Z, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2016,100(9):4161-4175. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7253-2 [24] 姚美辰, 段亮, 张恒亮, 等.辽河保护区人工湿地微生物群落结构及分布规律[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(3):233-238. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.03.040YAO M C, DUAN L, ZHANG H L, et al. Microbial community structure and distribution of constructed wetlands in Liaohe Conservation Area[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(3):233-238. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.03.040 [25] 阴星望, 田伟, 丁一, 等.丹江口库区表层沉积物细菌多样性及功能预测分析[J]. 湖泊科学,2018,30(4):1052-1063. doi: 10.18307/2018.0418YIN X W, TIAN W, DING Y, et al. Composition and predictive functional analysis of bacterial communities in surface sediments of the Danjiangkou Reservoir[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2018,30(4):1052-1063. doi: 10.18307/2018.0418 [26] 王鹏, 肖汉玉, 张华, 等.鄱阳湖入湖河口沉积物细菌群落特征[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(4):1481-1489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.035WANG P, XIAO H Y, ZHANG H, et al. Bacterial communities in the estuarine sediment of Poyang Lake[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(4):1481-1489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.035 [27] WU H, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Sediment bacterial communities in a eutrophic lake influenced by multiple inflow-rivers[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research,2017,24(24):19795-19806. [28] 朱粟锋, 刘煜杰, 张强, 等.生态恢复模式对若尔盖高寒沙化草地土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(1):199-206. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210138ZHU S F, LIU Y J, ZHANG Q, et al. Effects of ecological restoration patterns on soil microbial community functional diversity in Zoige alpine desertification grassland[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(1):199-206. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210138 [29] ZHANG Y W, WEI D Y, MORRISON L, et al. Nutrient removal through pyrrhotite autotrophic denitrification: implications for eutrophication control[J]. The Science of the Total Environment,2019,662:287-296. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.230 [30] KUEVER J. The family Desulfobacteraceae[M]//The Prokaryotes. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2014: 45-73. [31] BOVIO P, CABEZAS A, ETCHEBEHERE C. Preliminary analysis of Chloroflexi populations in full-scale UASB methanogenic reactors[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2019,126(2):667-683. doi: 10.1111/jam.14115 [32] YAMADA T, SEKIGUCHI Y. Anaerolineaceae[M]//Bergey's manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria. New York : John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2018. [33] HUA D L, FAN Q W, ZHAO Y X, et al. Comparison of methanogenic potential of wood vinegar with gradient loads in batch and continuous anaerobic digestion and microbial community analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,739:139943. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139943 [34] WANG X L, YAN Y G, GAO D W. The threshold of influent ammonium concentration for nitrate over-accumulation in a one-stage deammonification system with granular sludge without aeration[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,634:843-852. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.053 [35] 高志伟, 刘凡惠, 贾美清, 等.基于Illumina高通量测序的天津北大港湿地沉积物细菌群落特征和多样性分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,41(4):45-52.GAO Z W, LIU F H, JIA M Q, et al. Illumina-based high-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial community structure and diversity in Beidagang wetland sediment, Tianjin[J]. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2021,41(4):45-52. [36] 周思聪, 赵宇, 沈汇超, 等.洪泽湖西北部湿地富营养化特征研究[J]. 环境科技,2020,33(5):8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2020.05.003ZHOU S C, ZHAO Y, SHEN H C, et al. Eutrophication characteristics of the northwest wetland in Hongze Lake[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2020,33(5):8-12. ◇ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2020.05.003 -




 下载:
下载: