Forecasting CODMn of Poyang Lake based on empirical wavelet transform
-
摘要:
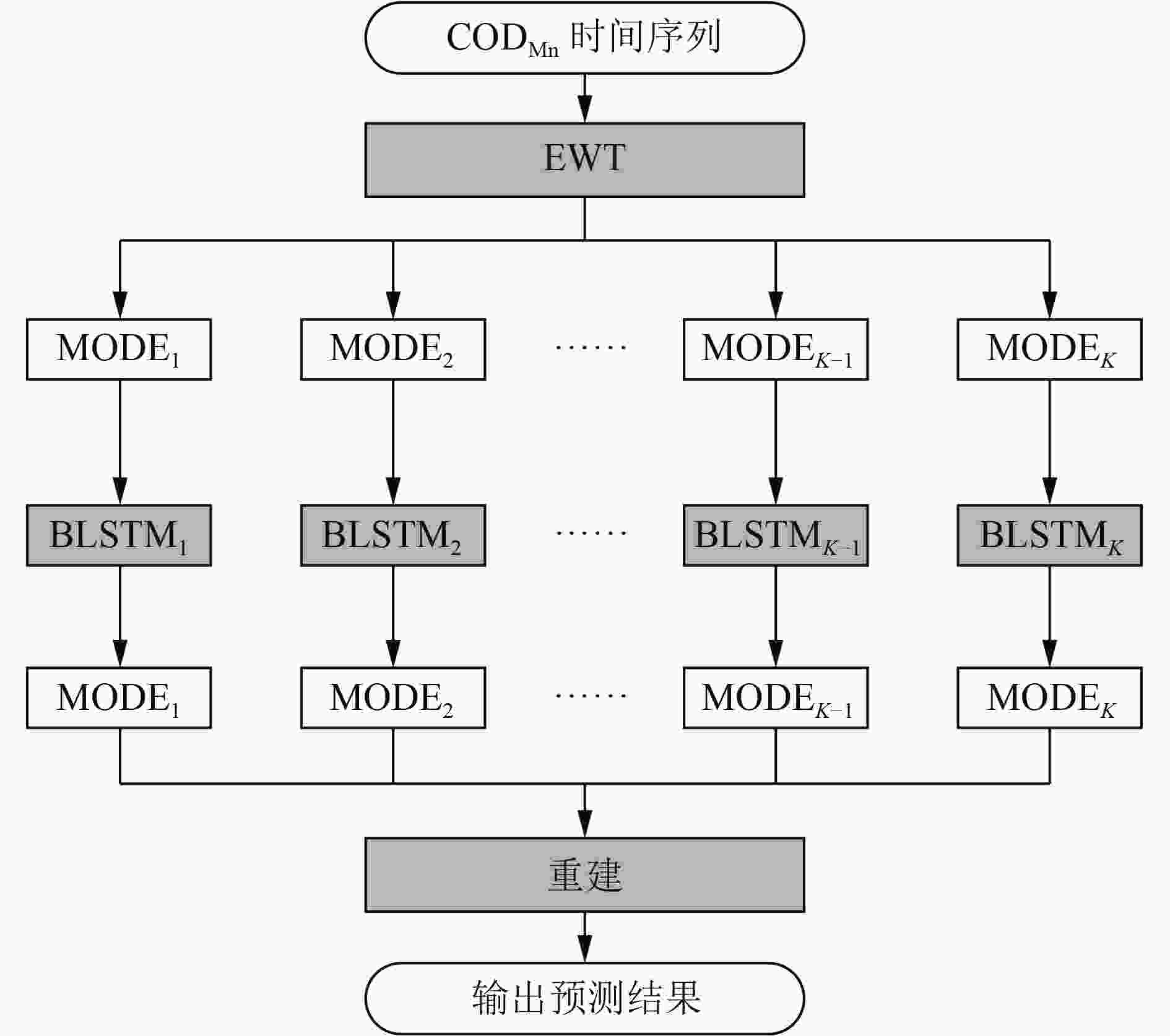
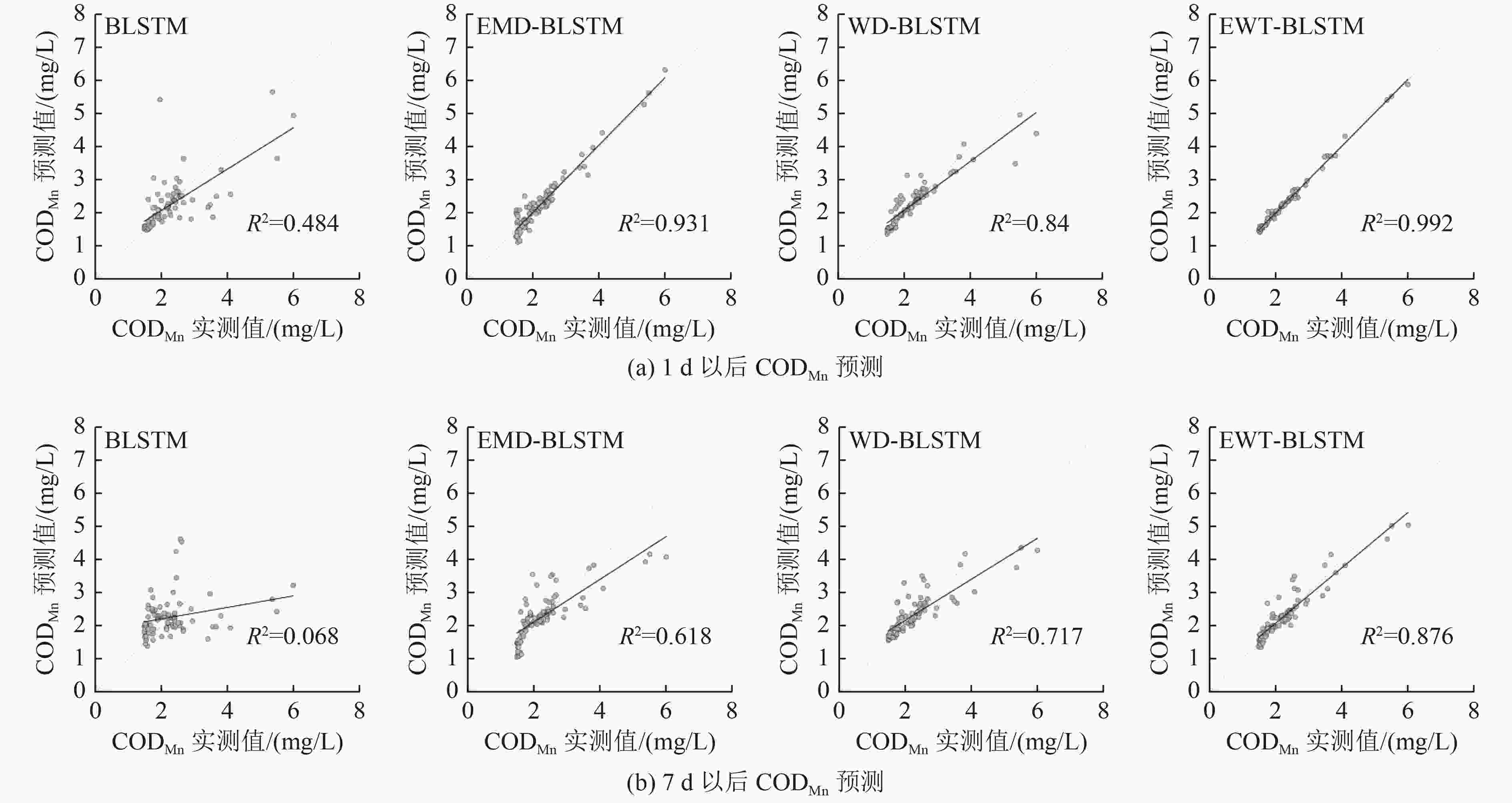
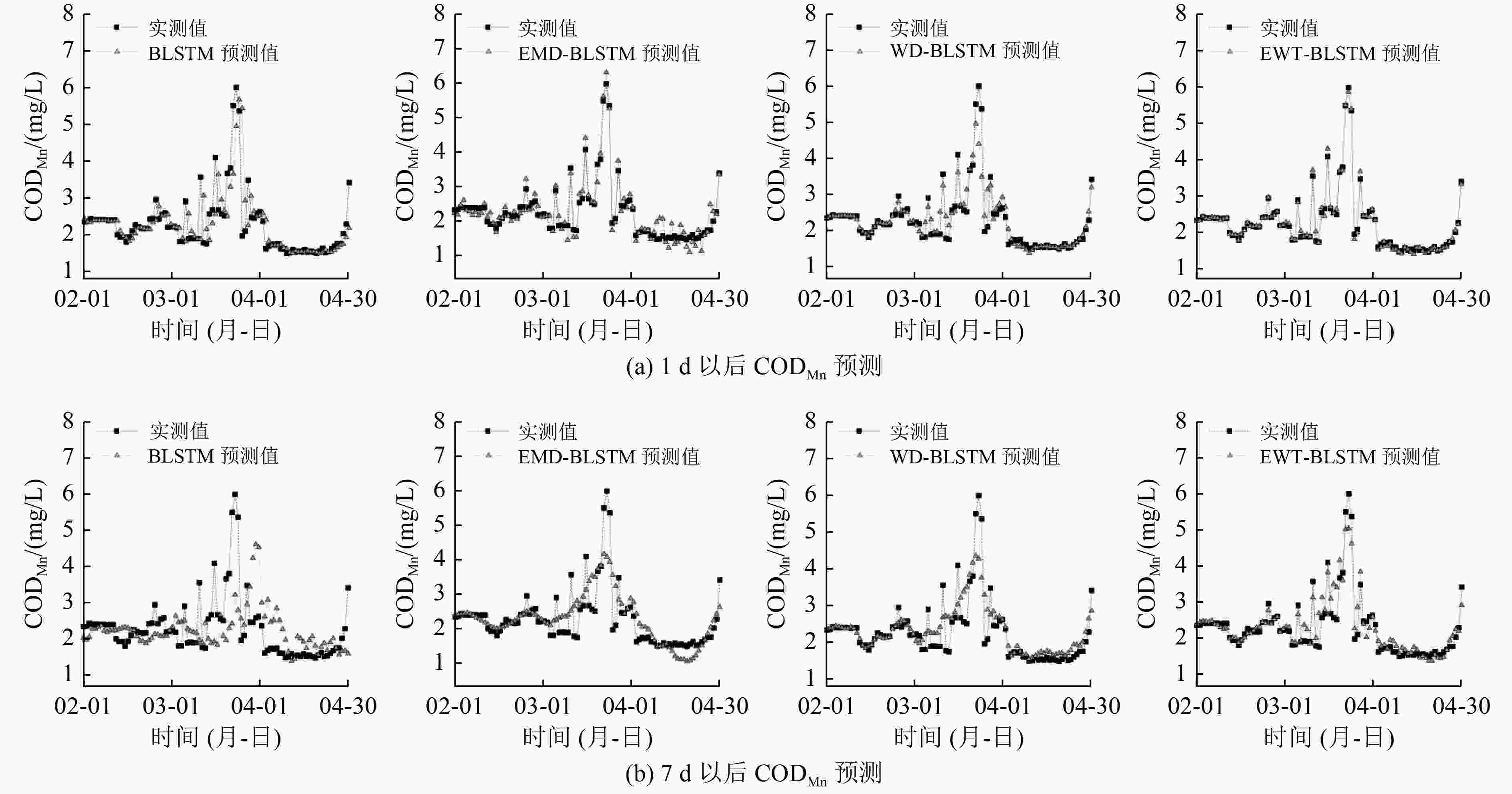
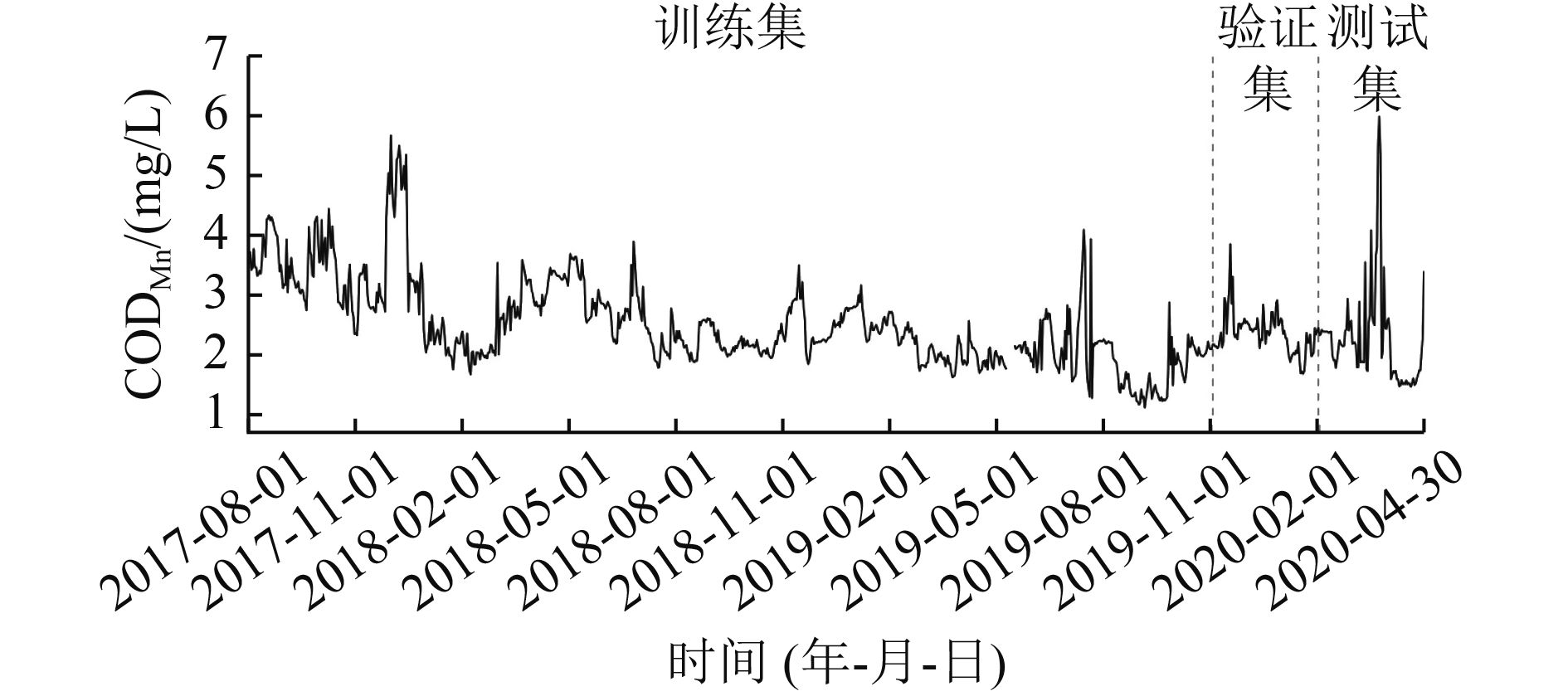
高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)是衡量水质状况的最重要参数之一,能反映水体受还原性物质污染的程度。结合经验小波变换(EWT)和双向长短期记忆(BLSTM)神经网络,提出了一种先利用EWT将原始的CODMn时间序列分解成若干成分,然后利用BLSTM神经网络对分解出来的每个成分进行预测,最后将所有成分的预测结果重建获得最终CODMn预测值的新的混合模型EWT-BLSTM;并以2017年8月—2020年4月鄱阳湖CODMn监测数据为研究对象,进行模型性能验证。结果表明:EWT-BLSTM模型具有良好的预测性能,预测未来1 d以后的CODMn时,EWT-BLSTM模型的平均绝对百分比误差为2.25%,与单一BLSTM神经网络模型相比降低了10.53%;预测未来7 d以后的CODMn时,EWT-BLSTM模型的平均绝对百分比误差为8.36%,与单一BLSTM神经网络模型相比降低了16.16%。在CODMn峰值处,该模型依然保持较高稳定的预测性能,说明在数据相对复杂、极端的情况下,该模型依然适用。
-
关键词:
- 水质预测 /
- CODMn /
- 经验小波变换(EWT) /
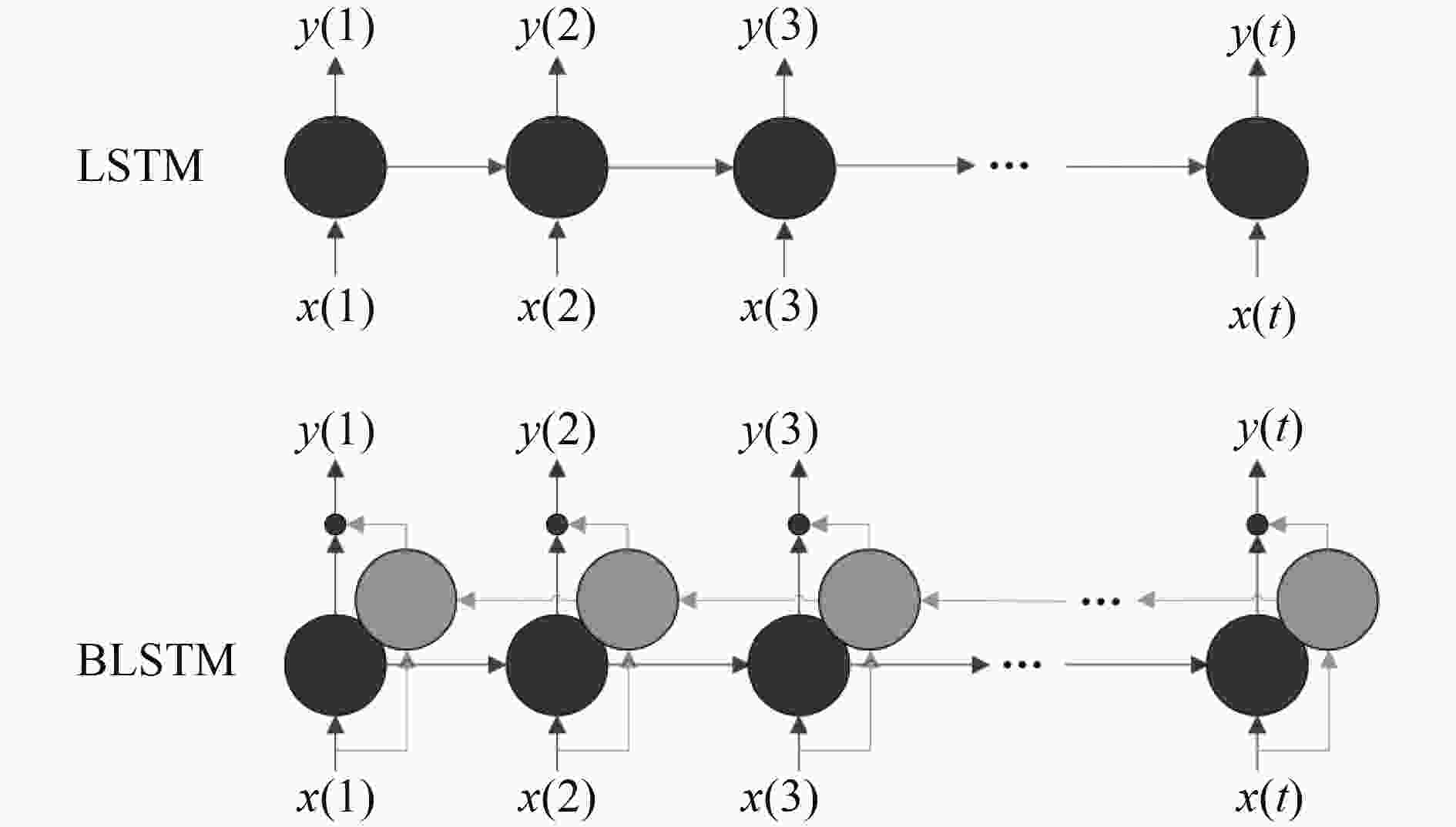
- 双向长短期记忆(BLSTM) /
- 机器学习 /
- 数学模拟 /
- 鄱阳湖
Abstract:Permanganate index (CODMn) is one of the most important parameters to measure water quality and could reflect the degree of water pollution by reducing substances. A novel CODMn forecast model (EWT-BLSTM) by combining empirical wavelet transform (EWT) and bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM) neural network was proposed. First, the original CODMn time series was decomposed into several components by EWT. Next, BLSTM neural network was employed to predict each decomposed component. Finally, the predictions of all components were reconstructed to obtain the new hybrid model EWT-BLSTM for the final CODMn predictions. CODMn data of Poyang Lake was used to evaluate the proposed forecast model. The results showed that EWT-BLSTM model had a powerful forecast capacity. For 1, 7-day ahead forecasting, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of the forecast by EWT-BLSTM was 2.25% and 8.36%, respectively. The MAPE reduced by EWT-BLSTM over BLSTM was 10.53% for 1-day ahead forecasting and 16.16% for 7-day ahead forecasting. Furthermore, the proposed model showed highly stable forecasting performance for CODMn peak points, indicating that the proposed method was still applicable in the case of relatively complex data with extreme points.
-
表 1 参与比较的模型的结构
Table 1. Structure of the competitor models
模型 数据分解算法 神经网络算法 BLSTM 不使用 BLSTM WD-BLSTM WD BLSTM EMD-BLSTM EMD BLSTM EWT-SVR EWT SVR EWT-ELM EWT ELM EWT-LSTM EWT LSTM 表 2 ICEEMDAN分解成分的样本熵
Table 2. Sample entropy calculation of ICEEMDAN modes
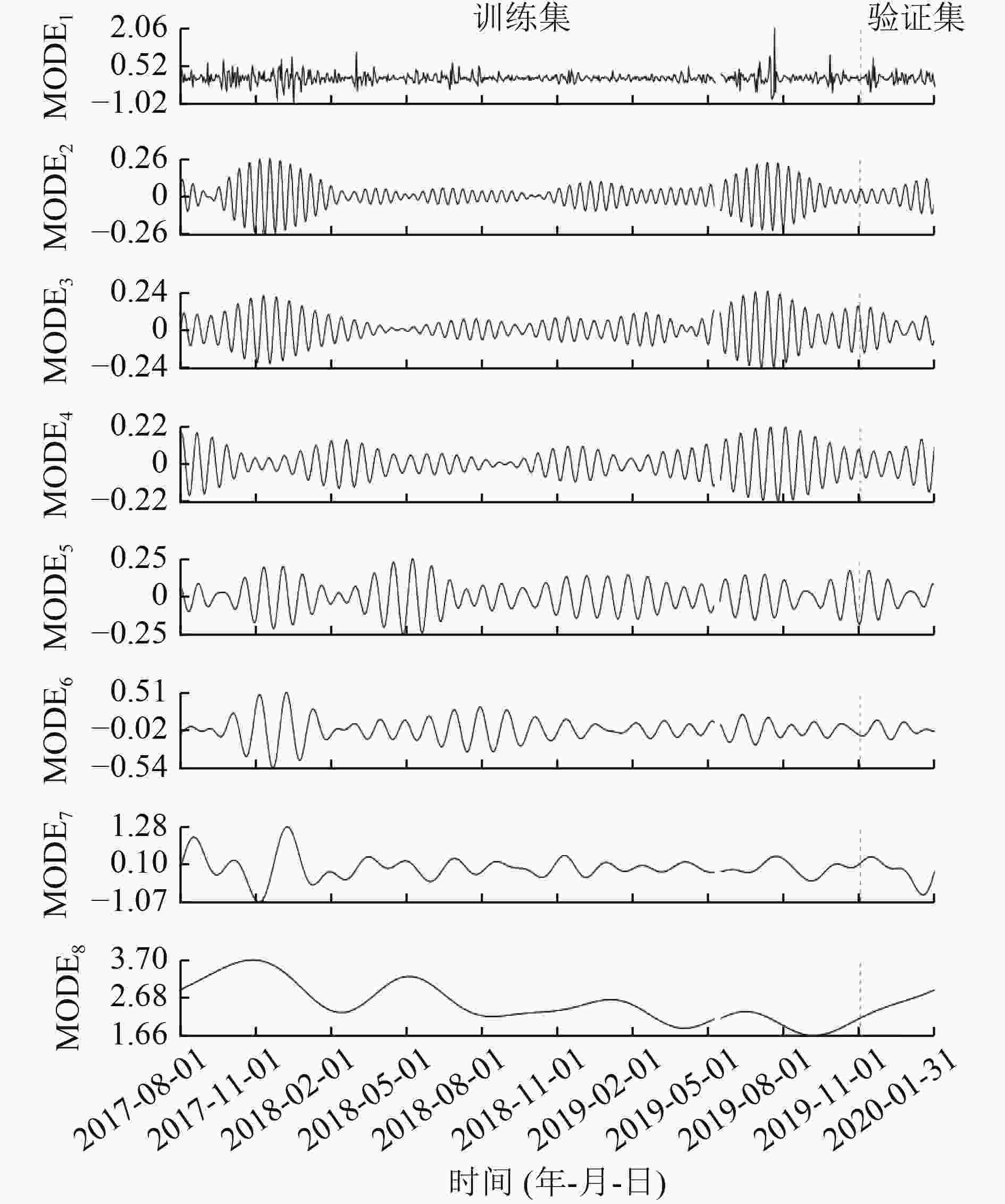
成分类型 样本熵 原始数据 0.85 MODE1 0.81 MODE2 0.72 MODE3 0.57 MODE4 0.45 MODE5 0.19 MODE6 0.09 MODE7 0.04 MODE8 0.00 表 3 CODMn时间序列以分解成分的预测模型的时间滞后值
Table 3. Time lags of the prediction model of the decomposition components of CODMn time series
成分类型 1 d以后预测 7 d以后预测 MODE1 47 41 MODE2 52 46 MODE3 49 43 MODE4 36 30 MODE5 54 48 MODE6 41 35 MODE7 54 48 MODE8 56 50 表 4 BLSTM神经网络的超参数
Table 4. Hyperparameters of BLSTM neural network
参数 数值 BLSTM层数 2 第一层的神经元数 输入大小×2 第二层的神经元数 输入大小 最小批量大小 16 学习率 0.01 最大迭代次数 100 表 5 测试阶段EWT-BLSTM模型的预测性能
Table 5. Forecast performance of EWT-BLSTM model in the testing stage
预测类型 MAE/(mg/L) RMSE/(mg/L) MAPE/% 1 d以后预测 0.05 0.07 2.25 7 d以后预测 0.20 0.32 8.36 表 6 各模型的预测性能比较
Table 6. Comparison of the prediction performance of different models
模型 1 d以后预测 7 d以后预测 MAE
/(mg/L)RMSE
/(mg/L)MAPE
/%MAE
/(mg/L)RMSE
/(mg/L)MAPE
/%BLSTM 0.32 0.62 12.78 0.60 0.87 24.52 WD-BLSTM 0.17 0.35 6.77 0.28 0.46 11.72 EMD-BLSTM 0.19 0.23 9.33 0.34 0.52 14.70 EWT-SVR 0.30 0.5 12.49 0.49 0.67 23.75 EWT-ELM 0.23 0.36 9.79 0.29 0.49 11.69 EWT-LSTM 0.05 0.08 2.34 0.25 0.35 11.42 EWT-BLSTM 0.05 0.07 2.25 0.20 0.32 8.36 -
[1] CARVALHO L, POIKANE S, LYCHE SOLHEIM A, et al. Strength and uncertainty of phytoplankton metrics for assessing eutrophication impacts in lakes[J]. Hydrobiologia,2013,704(1):127-140. doi: 10.1007/s10750-012-1344-1 [2] WU Z S, ZHANG D W, CAI Y J, et al. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: the largest freshwater lake in China[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:17999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18285-y [3] 王圣瑞, 舒俭民, 倪兆奎, 等.鄱阳湖水污染现状调查及防治对策[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(4):342-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.04.054WANG S R, SHU J M, NI Z K, et al. Investigation on pollution situation and countermeasures in Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(4):342-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.04.054 [4] ZHANG S S, WEI J, LI Y P, et al. The Influence of seasonal water level fluctuations on the soil nutrients in a typical wetland reserve in Poyang Lake, China[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(7):3846. doi: 10.3390/su13073846 [5] PU J, WANG S R, NI Z K, et al. Implications of phosphorus partitioning at the suspended particle-water interface for lake eutrophication in China's largest freshwater lake, Poyang Lake[J]. Chemosphere,2021,263:128334. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128334 [6] 许加星, 徐力刚, 姜加虎, 等.鄱阳湖典型洲滩植物群落结构变化及其与土壤养分的关系[J]. 湿地科学,2013,11(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5948.2013.02.006XU J X, XU L G, JIANG J H, et al. Change of vegetation community structure and the relationship between it and soil nutrients in typical beaches in Poyang Lake area[J]. Wetland Science,2013,11(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5948.2013.02.006 [7] 王子为, 林佳宁, 张远, 等.鄱阳湖入湖河流氮磷水质控制限值研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(5):1163-1169. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.03.45WANG Z W, LIN J N, ZHANG Y, et al. Water quality limits of nitrogen and phosphorus in the inflow rivers of Poyang Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(5):1163-1169. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.03.45 [8] 谢培, 高峰, 王书航, 等.入湖河流对千岛湖水质影响研究: 以CODMn为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):692-700. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.04.300XIE P, GAO F, WANG S H, et al. Study on the influence of inflowing rivers on the water quality of Qiandao Lake: taking CODMn as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):692-700. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.04.300 [9] 王业耀, 姜明岑, 李茜, 等.流域水质预警体系研究与应用进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(7):1126-1133. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.01WANG Y Y, JIANG M C, LI Q, et al. Advances in watershed water quality early-warning system[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(7):1126-1133. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.01 [10] RUBEN G B, ZHANG K, BAO H J, et al. Application and sensitivity analysis of artificial neural network for prediction of chemical oxygen demand[J]. Water Resources Management,2018,32(1):273-283. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1809-0 [11] MIAO S, ZHOU C L, ALQAHTANI S A, et al. Applying machine learning in intelligent sewage treatment: a case study of chemical plant in sustainable cities[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society,2021,72:103009. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103009 [12] Khullar S, Singh N. Water quality assessment of a river using deep learning Bi-LSTM methodology: forecasting and validation[J/OL]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-13875-w. [13] EZE E, AJMAL T. Dissolved oxygen forecasting in aquaculture: a hybrid model approach[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(20):7079. doi: 10.3390/app10207079 [14] ZOU Q H, XIONG Q Y, LI Q D, et al. A water quality prediction method based on the multi-time scale bidirectional long short-term memory network[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2020,27(14):16853-16864. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08087-7 [15] FIJANI E, BARZEGAR R, DEO R, et al. Design and implementation of a hybrid model based on two-layer decomposition method coupled with extreme learning machines to support real-time environmental monitoring of water quality parameters[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,648:839-853. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.221 [16] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,1998,454(1971):903-995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [17] LIU S Y, XU L Q, LI D L. Multi-scale prediction of water temperature using empirical mode decomposition with back-propagation neural networks[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering,2016,49:1-8. [18] LIANG N, ZOU Z H, WEI Y G. Regression models (SVR, EMD and FastICA) in forecasting water quality of the Haihe River of China[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2019,154:147-159. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2019.24034 [19] WANG Y X, YUAN Y, PAN Y, et al. Modeling daily and monthly water quality indicators in a canal using a hybrid wavelet-based support vector regression structure[J]. Water,2020,12(5):1476. doi: 10.3390/w12051476 [20] GILLES J. Empirical wavelet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2013,61(16):3999-4010. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2265222 [21] LIU H, YANG R, DUAN Z, et al. A hybrid neural network model for marine dissolved oxygen concentrations time-series forecasting based on multi-factor analysis and a multi-model ensemble[J/OL]. Engineering, 2021. DOI: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.10.005. [22] NONG X Z, SHAO D G, SHANG Y M, et al. Analysis of spatio-temporal variation in phytoplankton and its relationship with water quality parameters in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2021,193(9):1-18. [23] SIT M, DEMIRAY B Z, XIANG Z, et al. A comprehensive review of deep learning applications in hydrology and water resources[J]. Water Science and Technology,2020,82(12):2635-2670. doi: 10.2166/wst.2020.369 [24] CHEN Y Y, SONG L H, LIU Y Q, et al. A review of the artificial neural network models for water quality prediction[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(17):5776. doi: 10.3390/app10175776 [25] YE Q Q, YANG X Q, CHEN C B, et al. River water quality parameters prediction method based on LSTM-RNN Model[J]. 2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC),2019:3024-3028. [26] LIU Y Q, ZHANG Q, SONG L H, et al. Attention-based recurrent neural networks for accurate short-term and long-term dissolved oxygen prediction[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2019,165:104964. ◇ doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.104964 -




 下载:
下载: