Enhanced denitrification performance and microbial distribution characteristics of Tubular Bio-reactor Device filled with slow-release carbon source
-
摘要:
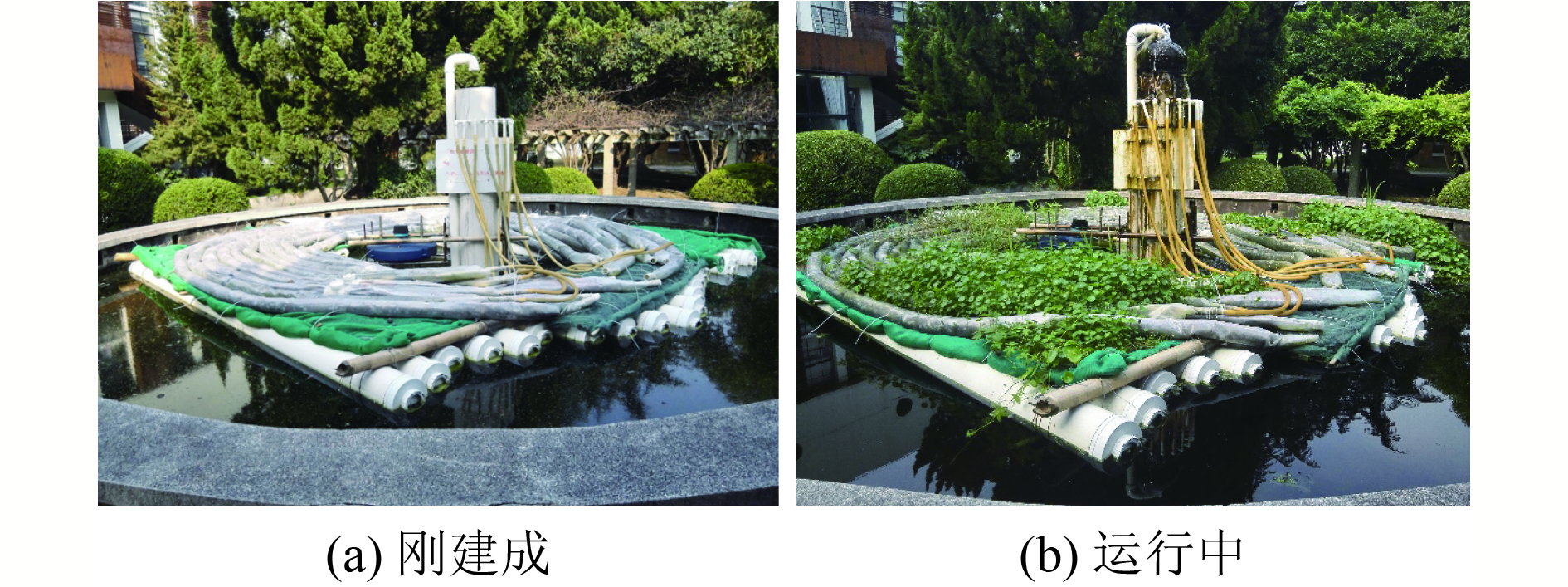
为研究缓释碳源填充管式生物反应装置(TBD)对不同氮组分生活污水的脱氮性能及机理,考察中试规模的TBD在3种不同溶解氧(DO)、氨氮(NH4 +-N)及硝氮(NO3 −-N)浓度工况下的实际运行效果,同时监测TBD沿程的DO浓度、碳氮比(C/N)、碳源等环境因子变化情况,并在运行期末对TBD的管内基质进行16S rRNA多样性高通量测序。结果表明:3种工况条件下TBD对污水中NH4 +-N、NO3 −-N和总氮(TN)的去除率均达90%以上,TBD具有良好的脱氮性能;缓释碳源有助于TBD沿程C/N的增加,且TBD出水CODCr始终低于GB 3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准》Ⅴ类水质标准限值,表明TBD在强化脱氮的同时不会产生有机质过量排放问题。此外,TBD中DO浓度沿程递减,形成了好氧-缺氧沿程分布的特征,且该特征促进了好氧反硝化-缺氧反硝化菌属在TBD的沿程分布。
Abstract:To study the denitrification performance and mechanism of tubular bio-reactor device (TBD) filled with slow-release carbon source for domestic sewage with different nitrogen components, the actual operation effect of TBD in pilot scale under three different concentrations of dissolved oxygen (DO), ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3 −-N) was investigated. At the same time, the change trends of environmental factors such as DO concentration, carbon-nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio), and carbon source along the TBD were monitored, and 16S rRNA diversity high-throughput sequencing of the matrix in the tube of TBD was conducted at the end of the operation period. The results showed that the removal rates of NH4 +-N, NO3 −-N and total nitrogen (TN) in sewage by TBD under three working conditions were more than 90%, proving that TBD had good denitrification performance. The slow-release carbon source contributed to the increase of C/N ratio along the TBD, and CODCr of TBD effluent was always lower than the Class Ⅴ standard of Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002), which indicated that the TBD did not produce excessive organic matter emission during enhanced nitrogen removal. Furthermore, the decrease of DO concentration along the process formed the characteristics of aerobic hypoxia distribution along the TBD and promoted the distribution of aerobic denitrification-anoxic denitrification bacteria along the TBD.
-
表 1 TBD中试装置不同工况下的供试水质及运行条件
Table 1. Water quality and operation conditions of pilot-scale TBD in different operating modes
工况 运行
时段初始NH4 +-N浓度/
(mg/L)初始NO3 −-N浓度/
(mg/L)初始TN浓度/
(mg/L)进水DO浓度/
(mg/L)供水方式 工况1 2016-08—2017-01 8.8 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 0.9 20.0 ± 1.7 6.0 ± 1.0 射流曝气机供水,
50%功率运转工况2 2017-02—2017-07 1.6 ± 0.3 12.1 ± 1.0 15.0 ± 1.3 3.0 ± 1.0 水泵供水,
满功率运转工况3 2017-08—2018-01 12.0 ± 1.2 6.6 ± 0.7 20.0 ± 1.9 9.0 ± 1.0 射流曝气机供水,
满功率运转表 2 TBD生物膜样品的微生物丰度占比和多样性指数
Table 2. Microbial richness and diversity index of the biofilm samples from the TBD
样品编号 高质量序列数 覆盖率/% OTUs Chao1指数 ACE指数 Simpson指数 Shannon多样性指数 Z1 73 151 97.7 5 701 26 217 43 217 0.036 5.37 Z2 80 206 95.3 6 312 32 217 52 805 0.021 6.12 表 3 TBD生物膜样品中的脱氮相关菌属的丰度占比
Table 3. Abundance of nitrogen removal functional genera in the biofilm samples from the TBD
% 菌属类别 菌属名 Z1 Z2 好氧反硝化相关菌属 Citrobacter 13.4 0.5 Acinetobacter 11.1 0.7 Rhizobium 9.2 0.5 Pseudomonas 5.5 0.3 Bacillus 0.9 0.2 Achromobacter 0.3 0.0 Enterobacter 0.1 0.0 合计 40.5 2.2 缺氧反硝化相关菌属 Thermomonas 0.67 9.35 Steroidobacter 0.15 5.15 Hyphomicrobium 0.76 2.37 Flavobacterium 0.1 0.7 Azospira 0.1 0.6 Dechloromonas 0.1 0.4 Hyphomicrobium 0.1 0.4 合计 2.0 19.0 -
[1] 王丽君, 夏训峰, 朱建超, 等.农村生活污水处理设施水污染物排放标准制订探讨[J]. 环境科学研究,2019,32(6):921-928.WANG L J, XIA X F, ZHU J C, et al. Discussion on the drafting of water pollutants discharge standard for rural domestic sewage treatment facilities[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(6):921-928. [2] 王幸智, 年跃刚, 张宪奇, 等.曝气生物净化塘处理农村生活污水效果: 以豫南地区商城县为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):484-492. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210042WANG X Z, NIAN Y G, ZHANG X Q, et al. Treatment effect of rural domestic sewage by aerated biological purification pond: taking Shangcheng County in southern Henan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):484-492. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210042 [3] 张曼雪, 邓玉, 倪福全.农村生活污水处理技术研究进展[J]. 水处理技术,2017,43(6):5-10.ZHANG M X, DENG Y, NI F Q. Research progress of rural domestic sewage treatment technology[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2017,43(6):5-10. [4] 刘晓慧.我国农村生活污水排放现状初析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2015,43(23):234-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.23.086LIU X H. Analysis on emission status of rural domestic sewage in China[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2015,43(23):234-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.23.086 [5] 庞燕, 项颂, 储昭升, 等.洱海流域城镇化对农村生活污水排放量的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2015,28(8):1246-1252.PANG Y, XIANG S, CHU Z S, et al. Impacts of urbanization on rural domestic sewage emissions in Erhai Lake Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2015,28(8):1246-1252. [6] 吴红斌, 张斌, 林晓霖.山林地表慢渗系统处理农村生活污水厂尾水研究[J]. 环境保护科学,2017,43(5):51-56.WU H B, ZHANG B, LIN X L. Study of the treatment of tail water from rural domestic wastewater treatment plants by forest surface infiltration system[J]. Environmental Protection Science,2017,43(5):51-56. [7] 张悦. 江苏省农村生活污水处理设施运行及尾水稻田利用的安全性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. [8] 王俊能, 赵学涛, 蔡楠, 等.我国农村生活污水污染排放及环境治理效率[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(12):2665-2674.WANG J N, ZHAO X T, CAI N, et al. Pollution discharge and environmental treatment efficiency of rural domestic sewage in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(12):2665-2674. [9] 马鲁铭, 王云龙, 刘志刚, 等.南方农村生活污水处理目标及工艺模式探讨[J]. 中国环境科学,2013,33(1):118-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.01.017MA L M, WANG Y L, LIU Z G, et al. Discussion on objective of rural domestic wastewater treatment and technology system in Southern China[J]. China Environmental Science,2013,33(1):118-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.01.017 [10] 徐志荣, 叶红玉, 卓明, 等.浙江省农村生活污水处理现状及其对策[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2015,31(4):473-477. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.04.005XU Z R, YE H Y, ZHUO M, et al. Status quo and strategies of rural sewage treatment in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2015,31(4):473-477. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.04.005 [11] 吕锡武.可持续发展的农村生活污水生物生态组合治理技术[J]. 给水排水,2018,54(12):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2018.12.002 [12] 刘君, 邱敬贤, 邓刚.农村生活污水处理技术探讨[J]. 中国环保产业,2018(10):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2018.10.010LIU J, QIU J X, DENG G. Application of domestic sewage treatment technology in rural areas[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry,2018(10):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5377.2018.10.010 [13] 高立洪, 蒋滔, 杨小玲, 等.农村生活污水常见处理技术及设备现状分析[J]. 农业技术与装备,2017(9):81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2017.09.039GAO L H, JIANG T, YANG X L, et al. Analysis of common treatment technology and equipment for rural domestic sewage[J]. Agricultural Technology & Equipment,2017(9):81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2017.09.039 [14] 贾小宁, 何小娟, 韩凯旋, 等.农村生活污水处理技术研究进展[J]. 水处理技术,2018,44(9):22-26.JIA X N, HE X J, HAN K X, et al. Research progress of sewage treatment technology in rural areas[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2018,44(9):22-26. [15] 凌宇, 赵远哲, 王海燕, 等.HRT对A/O-BF处理低碳氮比农村生活污水脱氮的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(4):927-935.LING Y, ZHAO Y Z, WANG H Y, et al. Effects of HRT on A/O-BF nitrogen removal of low C/N rural domestic sewage[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(4):927-935. [16] 陈翰, 马放, 李昂, 等.低温条件下污水生物脱氮处理研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水,2016,32(8):37-43.CHEN H, MA F, LI A, et al. Research progress in biological nitrogen removal from wastewater under low temperature condition[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2016,32(8):37-43. [17] 王建华, 陈永志, 彭永臻.低碳氮比实际生活污水A2O-BAF工艺低温脱氮除磷[J]. 中国环境科学,2010,30(9):1195-1200.WANG J H, CHEN Y Z, PENG Y Z. Biological nutrients removal from domestic wastewater with low carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in A2O-BAF system at low temperature[J]. China Environmental Science,2010,30(9):1195-1200. [18] 胡述浩. 管式反应器反应失控的CFD技术分析[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2008. [19] 赵宇. 蛇形回路热管在化学反应器中的传热性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京工业大学, 2004. [20] 张海涛, 丁百全.返混:重要的化学工程概念[J]. 化学工程师,2000,14(3):24-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1124.2000.03.010 [21] 顾平道, 庄琛, 李英娜.热管化学反应器的应用研究进展[J]. 化学工程师,2004,18(6):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1124.2004.06.018GU P D, ZHUANG C, LI Y N. Development of heat pipe type chemical reactor[J]. Chemical Engineer,2004,18(6):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1124.2004.06.018 [22] 温瑞媛, 严世强. 化学工程基础[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2002. [23] 黄民生, 崔贺, 常越亚, 等. 一种管式生物净水装置及其净水方法: CN104973689B[P]. 2017-04-19. [24] LI D, CHU Z S, ZENG Z Z, et al. Effects of design parameters, microbial community and nitrogen removal on the field-scale multi-pond constructed wetlands[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,797:148989. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148989 [25] LI D, YE B B, HOU Z Y, et al. Long-term performance and microbial distribution of a filed-scale storing multi-pond constructed wetland with Ottelia acuminata for the treatment of non-point source pollution[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,262:121367. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121367 [26] LI D, ZHENG B H, LIU Y, et al. Use of multiple water surface flow constructed wetlands for non-point source water pollution control[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2018,102(13):5355-5368. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9011-8 [27] HUANG X, DONG W Y, WANG H J, et al. Biological nutrient removal and molecular biological characteristics in an anaerobic-multistage anaerobic/oxic (A-MAO) process to treat municipal wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,241:969-978. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.161 [28] 李怀正, 姚淑君, 徐祖信, 等.曝气稳定塘处理农村生活污水曝气控制条件研究[J]. 环境科学,2012,33(10):3484-3488.LI H Z, YAO S J, XU Z X, et al. Research of controlling condition for aeration stabilization pond dealing with sanitary waste of countryside[J]. Environmental Science,2012,33(10):3484-3488. [29] ZHI W, JI G D. Quantitative response relationships between nitrogen transformation rates and nitrogen functional genes in a tidal flow constructed wetland under C/N ratio constraints[J]. Water Research,2014,64:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.035 [30] SOBIESZUK P, SZEWCZYK K W. Estimation of (C/N) ratio for microbial denitrification[J]. Environmental Technology,2006,27(1):103-108. doi: 10.1080/09593332708618624 [31] YU G L, PENG H Y, FU Y J, et al. Enhanced nitrogen removal of low C/N wastewater in constructed wetlands with co-immobilizing solid carbon source and denitrifying bacteria[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,280:337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.043 [32] SHENG S X, LIU B, HOU X Y, et al. Effects of different carbon sources and C/N ratios on the simultaneous anammox and denitrification process[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation,2018,127:26-34. [33] LE T, PENG B, SU C Y, et al. Impact of carbon source and COD/N on the concurrent operation of partial denitrification and anammox[J]. Water Environment Research,2019,91(3):185-197. doi: 10.1002/wer.1016 [34] KIM E, SHIN S G, JANNAT M, et al. Use of food waste-recycling wastewater as an alternative carbon source for denitrification process: a full-scale study[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,245:1016-1021. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.168 [35] HUANG X, DONG W Y, WANG H J, et al. Role of acid/alkali-treatment in primary sludge anaerobic fermentation: insights into microbial community structure, functional shifts and metabolic output by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Bioresource Technology,2018,249:943-952. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.104 [36] XING W, WANG Y, HAO T Y, et al. pH control and microbial community analysis with HCl or CO2 addition in H2-based autotrophic denitrification[J]. Water Research,2020,168:115200. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115200 [37] CHEN D Y, GU X S, ZHU W Y, et al. Denitrification- and anammox-dominant simultaneous nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process in subsurface flow constructed wetlands[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,271:298-305. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.123 [38] DENNEHY C, LAWLOR P G, GARDINER G E, et al. Process stability and microbial community composition in pig manure and food waste anaerobic co-digesters operated at low HRTs[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2017,11(3):1-13. [39] ZHANG P, GUO J S, SHEN Y, et al. Microbial communities, extracellular proteomics and polysaccharides: a comparative investigation on biofilm and suspended sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology,2015,190:21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.058 [40] WANG L M, GUO F H, ZHENG Z, et al. Enhancement of rural domestic sewage treatment performance, and assessment of microbial community diversity and structure using tower vermifiltration[J]. Bioresource Technology,2011,102(20):9462-9470. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.085 [41] HUANG X, ZHU J, DUAN W Y, et al. Biological nitrogen removal and metabolic characteristics in a full-scale two-staged anoxic-oxic (A/O) system to treat optoelectronic wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,300:122595. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122595 [42] WANG J L, GONG B Z, HUANG W, et al. Bacterial community structure in simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and organic matter removal process treating saline mustard tuber wastewater as revealed by 16S rRNA sequencing[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,228:31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.071 [43] SUN L, ZHAO X X, ZHANG H F, et al. Biological characteristics of a denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating bacterium[J]. Ecological Engineering,2015,81:82-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.030 [44] SLIEKERS A O, DERWORT N, GOMEZ J L C, et al. Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor[J]. Water Research,2002,36(10):2475-2482. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00476-6 [45] DC RUBIN S S, MARÍN I, GÓMEZ M J, et al. Prokaryotic diversity and community composition in the Salar de Uyuni, a large scale, chaotropic salt flat[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2017,19(9):3745-3754. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13876 [46] TIAN M, ZHAO F Q, SHEN X, et al. The first metagenome of activated sludge from full-scale anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2O) nitrogen and phosphorus removal reactor using Illumina sequencing[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2015,35:181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.12.027 [47] 酒卫敬, 汪苹, 岳建伟.好氧反硝化菌处理高浓度氨氮废水研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2011,1(2):111-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2011.02.019JIU W J, WANG P, YUE J W. Study on the treatment of wastewater containing high-concentration ammonia nitrogen with aerobic denitrifying bacteria[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2011,1(2):111-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2011.02.019 [48] 金位栋, 焦巨龙, 李剑屏, 等.微生物菌剂强化A/O脱氮反应器运行效果及微生物群落变化[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):354-364. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200083JIN W D, JIAO J L, LI J P, et al. Operation effect and microbial community changes of A/O denitrification reactor enhanced by microbial agents[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):354-364. ◇ doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200083 -





 下载:
下载: