Effects of dredging on nutrients in sediments in Xiashan Daxi Basin of Lianjiang River
-
摘要:
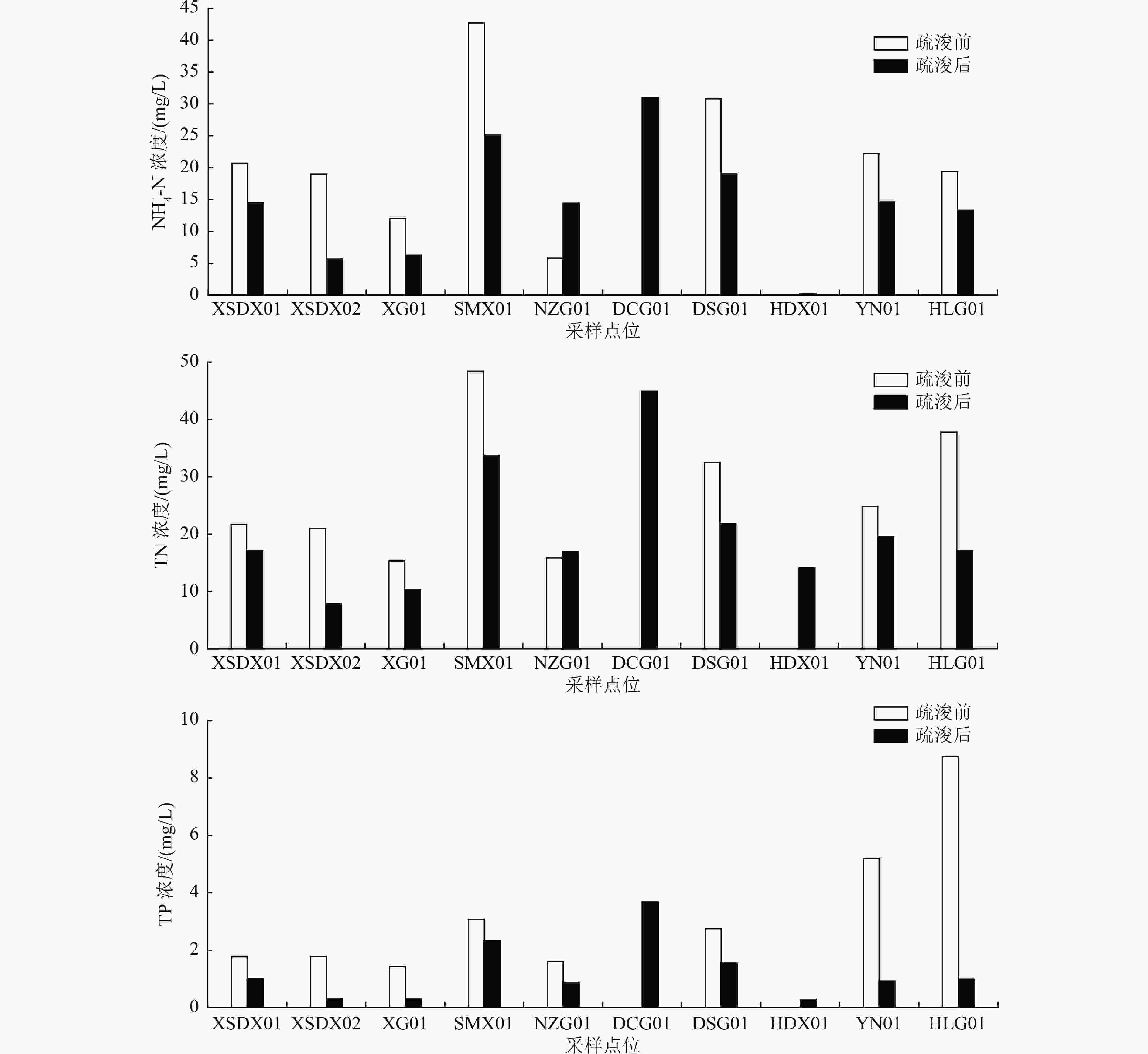
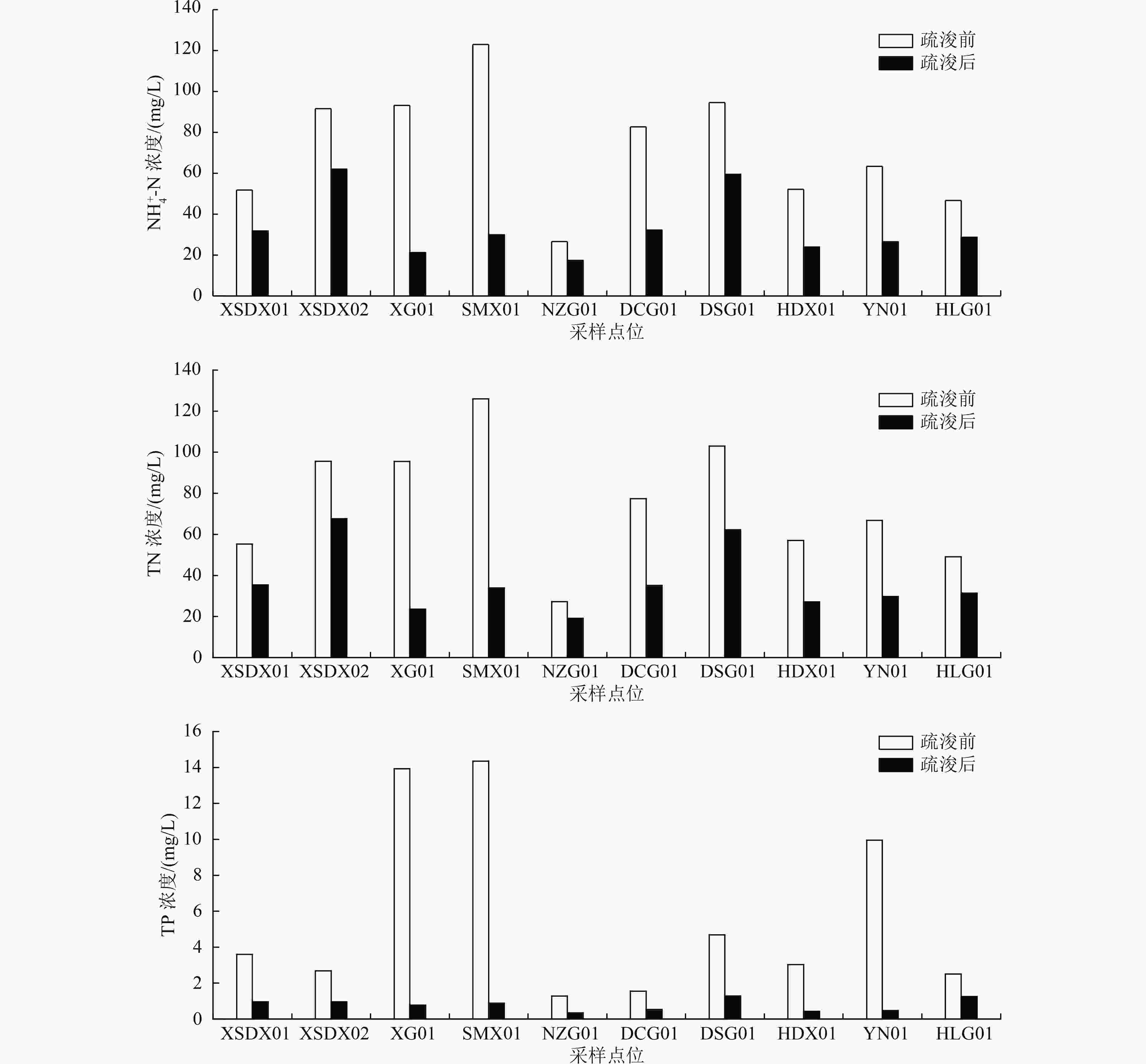
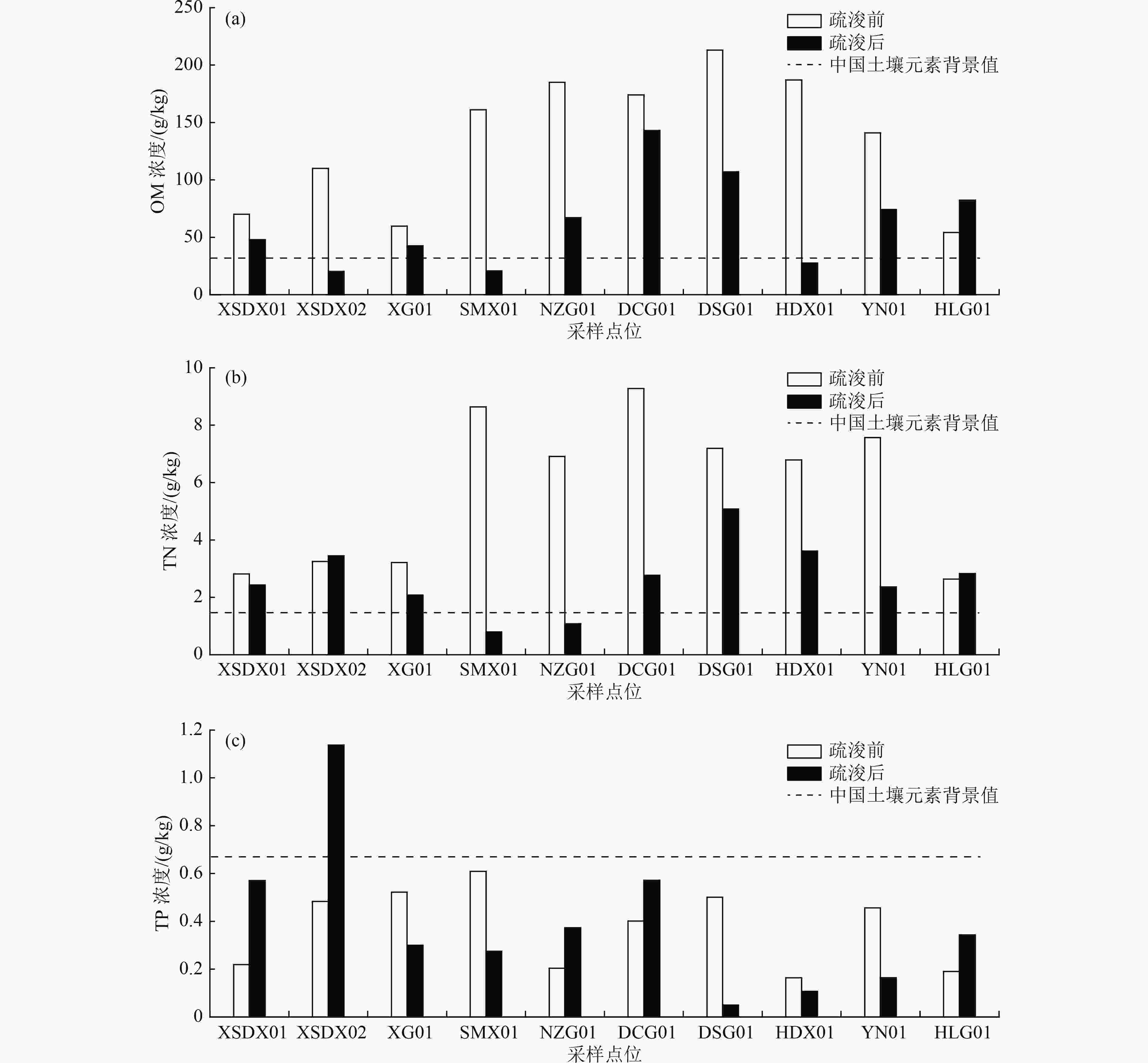
以练江峡山大溪流域为研究对象,通过分析疏浚前后10个点位表层沉积物有机质(OM)、总氮(TN)和总磷(TP)浓度以及间隙水和上覆水中氨氮(NH4 +-N)、TN和TP浓度,以揭示疏浚对表层沉积物营养盐的时空分布及释放过程的影响,并对疏浚后表层沉积物污染状况进行评价。结果表明:疏浚后间隙水和上覆水中TP、TN、NH4 +-N浓度均显著下降,表层沉积物中OM和TN平均浓度较疏浚前分别下降53.3%、54.5%,有接近1/2点位的表层沉积物出现TP浓度高于疏浚前的现象,疏浚对表层沉积物中营养物移除能力为TN>OM>TP;疏浚后表层沉积物OM、TN和TP污染情况较疏浚前有所改观,但污染程度依然处于较高等级;疏浚后,沉积物中的氮表现为“源”,而磷经历了从“源”到“汇”的转换,表明本次疏浚对表层沉积物间隙水中氮的内源释放有促进作用,对磷的内源释放存在抑制作用,这与本次疏浚的深度、沉积物的理化性质及赋存环境的改变有关。
Abstract:To reveal the effects of dredging on the temporal and spatial distribution and the release process of nutrients in surface sediments, the contents of organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) of the surface sediments as well as the concentrations of ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +-N), TN and TP of the interstitial water and the overlying water at 10 points from Xiashan Daxi Basin of Lianjiang River were analyzed before and after dredging, and the pollution status of surface sediments after dredging was also evaluated. The results showed that TP, TN, and NH4 +-N concentrations in interstitial water and overlying water decreased significantly after dredging. The average concentrations of OM and TN of surface sediments decreased by 53.3% and 54.5%, respectively, compared with those before dredging. TP concentration of surface sediment was higher than that before dredging at nearly half of the points, and the ability of dredging to remove nutrients in surface sediments was TN>OM>TP. The pollution of OM, TN and TP in surface sediments after dredging improved compared with that before dredging, but the pollution level was still high. After dredging, the nitrogen in the sediments displayed as "source", and phosphorus changed from "source" to "sink", indicating that this dredging promoted the internal release of nitrogen in the interstitial water of surface sediment and inhibited the internal release of phosphorus. This was related to the dredging depth, the changes in the physicochemical characteristics of the sediments and the occurrence environment.
-
Key words:
- dredging /
- Xiashan Daxi Basin /
- surface sediments /
- nutrients /
- endogenous release
-
表 1 沉积物OI评价标准[18]
Table 1. Assessment standards of sediment organic pollution index
OI 污染程度 污染等级 <0.05 清洁 Ⅰ 0.05~0.2 轻度污染 Ⅱ 0.2~0.5 中度污染 Ⅲ ≥0.5 重度污染 Ⅳ 表 2 沉积物FF分级标准
Table 2. Classification standards of comprehensive pollution of sediments
FF 污染程度 污染等级 <1.0 清洁 Ⅰ 1.0~1.5 轻度污染 Ⅱ 1.5~2.0 中度污染 Ⅲ ≥2.0 重度污染 Ⅳ 表 3 疏浚前后峡山大溪流域表层沉积物理化特性
Table 3. Physico-chemical characteristics of surface sediments in Xiashan Daxi Basin before and after dredging
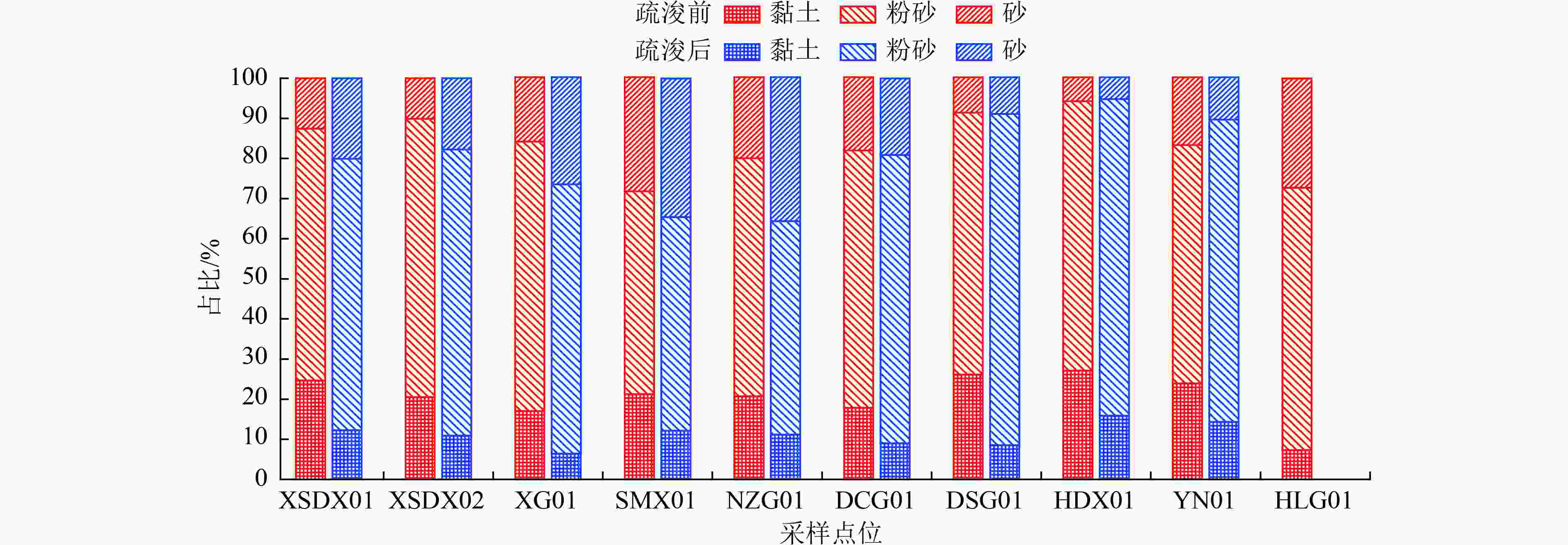
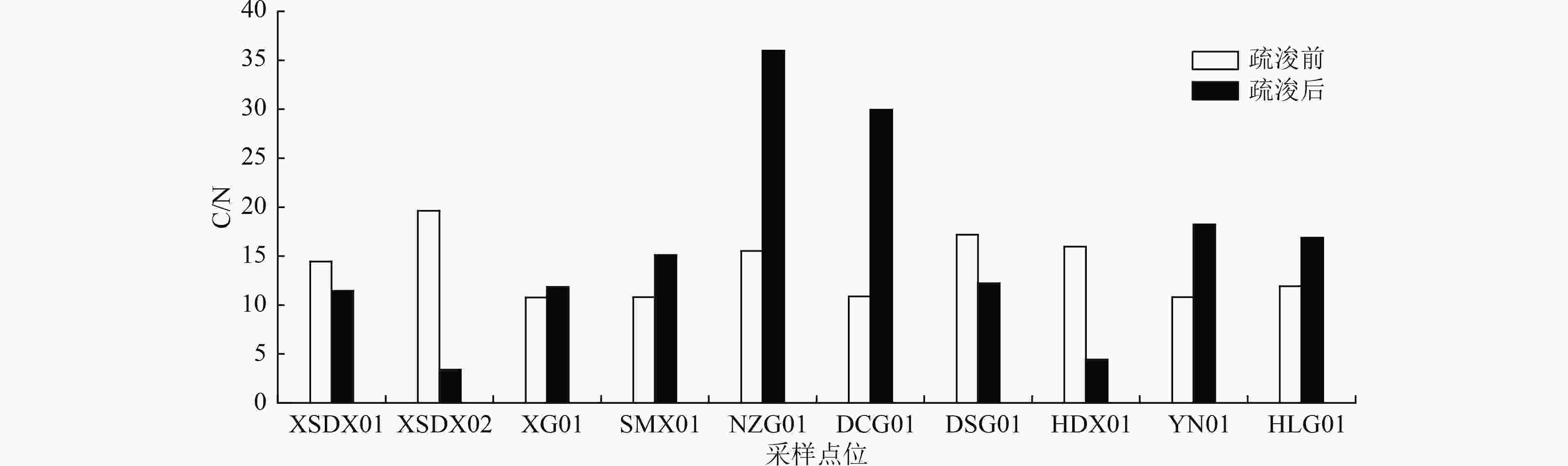
阶段 浓度/(g/kg) 含水率/% 占比/% OM TN TP 砂 粉砂 黏土 疏浚前 范围 54.2~185 2.64~9.28 0.19~0.609 57.1~87.2 5.73~28.18 50.57~69.39 17.03~27.11 均值 135.5 5.83 0.375 72.95 15.05 62.81 22.14 疏浚后 范围 20.2~143 0.8~5.08 0.05~1.137 47.9~80.2 5.21~35.64 53.2~91.31 6.38~15.88 均值 63.23 2.65 0.389 63.41 20.53 69.91 10.80 表 4 疏浚前后各采样点位沉积物OI和FF污染程度分级
Table 4. Pollution levels classification of OI and FF indexes of sediments at various sampling points before and after dredging
采样点位 疏浚前OI 疏浚后OI 疏浚前FF 疏浚后FF 数值 污染程度 数值 污染程度 数值 污染程度 数值 污染程度 XSDX01 1.09 重度污染 0.64 重度污染 2.10 重度污染 2.13 重度污染 XSDX02 1.97 重度污染 0.38 中度污染 2.61 重度污染 3.32 重度污染 XG01 1.06 重度污染 0.49 中度污染 2.62 重度污染 1.66 中度污染 SMX01 7.67 重度污染 0.09 轻度污染 6.39 重度污染 0.78 清洁 NZG01 7.04 重度污染 0.40 中度污染 4.89 重度污染 1.06 轻度污染 DCG01 8.90 重度污染 2.18 重度污染 6.66 重度污染 2.36 重度污染 DSG01 8.44 重度污染 3.00 重度污染 5.31 重度污染 3.52 重度污染 HDX01 7.00 重度污染 0.55 重度污染 4.77 重度污染 2.55 重度污染 YN01 5.88 重度污染 0.96 重度污染 5.53 重度污染 1.74 中度污染 HLG01 0.79 重度污染 1.28 重度污染 1.96 中度污染 2.21 重度污染 -
[1] 姜霞, 王书航, 张晴波, 等.污染底泥环保疏浚工程的理念·应用条件·关键问题[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(10):1497-1504. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.83JIANG X, WANG S H, ZHANG Q B, et al. Analysis of concepts, conditions and critical problems in environmental dredging[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(10):1497-1504. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.83 [2] JASKUŁA J, SOJKA M, FIEDLER M, et al. Analysis of spatial variability of river bottom sediment pollution with heavy metals and assessment of potential ecological hazard for the Warta River, Poland[J]. Minerals,2021,11(3):327. doi: 10.3390/min11030327 [3] WEN S L, WANG H W, WU T, et al. Vertical profiles of phosphorus fractions in the sediment in a chain of reservoirs in North China: implications for pollution source, bioavailability, and eutrophication[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,704:135318. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135318 [4] TANG X Q, LI R, HAN D, et al. Impacts of electrokinetic isolation of phosphorus through pore water drainage on sediment phosphorus storage dynamics[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,266:115210. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115210 [5] EVANS J L, MURDOCK J N, TAYLOR J M, et al. Sediment nutrient flux rates in a shallow, turbid lake are more dependent on water quality than lake depth[J]. Water,2021,13(10):1344. doi: 10.3390/w13101344 [6] YANG Y, CHEN W, YI Z Y, et al. The integrative effect of periphyton biofilm and tape grass (Vallisneria natans) on internal loading of shallow eutrophic lakes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2018,25(2):1773-1783. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0623-9 [7] TONG Y L, LIANG T, WANG L Q, et al. Simulation on phosphorus release characteristics of Poyang Lake sediments under variable water levels and velocities[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences,2017,27(6):697-710. doi: 10.1007/s11442-017-1401-9 [8] YENILMEZ F, AKSOY A. Comparison of phosphorus reduction alternatives in control of nutrient concentrations in Lake Uluabat (Bursa, Turkey): partial versus full sediment dredging[J]. Limnologica,2013,43(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.limno.2012.05.003 [9] CHEN M S, CUI J Z, LIN J, et al. Successful control of internal phosphorus loading after sediment dredging for 6 years: a field assessment using high-resolution sampling techniques[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,616/617:927-936. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.227 [10] LI Y, WANG L G, YAN Z W, et al. Effectiveness of dredging on internal phosphorus loading in a typical aquacultural lake[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,744:140883. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140883 [11] 王英丽, 杨晶, 黄显东.练江流域(汕头)段底泥污染物分布特征及污染评价[J]. 广东水利水电,2020(7):6-10. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2020.07.002WANG Y L, YANG J, HUANG X D. Distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of sediment pollutants in Lianjiang River Basin (Shantou reaches)[J]. Guangdong Water Resources and Hydropower,2020(7):6-10. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2020.07.002 [12] 田秀芳, 胡兆华, 邱家诚, 等.凤眼莲对练江水体重金属的去除效果和富集能力研究[J]. 农业与技术,2021,41(3):96-101. doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20210215030 [13] 刘翔宇.河道清淤工程余方处置方案探讨: 以韩江-榕江-练江水系连通潮水溪疏浚工程为例[J]. 亚热带水土保持,2021,33(1):50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2651.2021.01.012LIU X Y. Probe into the disposal plan of rest in the river desilting project[J]. Subtropical Soil and Water Conservation,2021,33(1):50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2651.2021.01.012 [14] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. [15] 刘俊, 田学达, 王琳杰, 等.洞庭湖表层沉积物营养盐空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):701-706. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.180LIU J, TIAN X D, WANG L J, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of surface sediment nutrients in Lake Dongting[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):701-706. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.180 [16] 张紫霞, 刘鹏, 王妍, 等.普者黑岩溶湿地干湿季沉积物氮、磷、有机质分布及污染风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报,2019,39(12):4088-4095. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0311ZHANG Z X, LIU P, WANG Y, et al. Distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in sediments of Puzhehei Karst wetland in dry and wet season and pollution risk assessment[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2019,39(12):4088-4095. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0311 [17] 李芬芳, 黄代中, 连花, 等.洞庭湖及其入湖口表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的分布及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报,2018,27(12):2307-2313. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.12.017LI F F, HUANG D Z, LIAN H, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in the surface sediments of Dongting Lake and its lake inlets[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2018,27(12):2307-2313. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.12.017 [18] 孙顺才. 太湖[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993. [19] 尹宇莹, 彭高卓, 谢意南, 等.洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养元素、重金属的污染特征与评价分析[J]. 环境化学,2021,40(8):2399-2409. doi: 10.18307/2021.0511YIN Y Y, PENG G Z, XIE Y N, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2021,40(8):2399-2409. doi: 10.18307/2021.0511 [20] YU J H, DING S M, ZHONG J C, et al. Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,592:662-673. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.219 [21] LIU C, SHAO S G, SHEN Q S, et al. Use of multi-objective dredging for remediation of contaminated sediments: a case study of a typical heavily polluted confluence area in China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2015,22(22):17839-17849. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4978-5 [22] 王宁, 张刚, 王瑗.湖泊内源污染的环保疏浚及其效果: 以长春南湖清淤工程为例[J]. 环境科学研究,2004,17(2):34-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2004.02.009WANG N, ZHANG G, WANG Y. Environmental protection dredging and its effects for intrinsic pollution of lake: case study of Nanhu lake in Changchun[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2004,17(2):34-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2004.02.009 [23] ZHONG J C, YOU B S, FAN C X, et al. Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus[J]. Pedosphere,2008,18(1):34-44. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60100-3 [24] JING L D, WU C X, LIU J T, et al. The effects of dredging on nitrogen balance in sediment-water microcosms and implications to dredging projects[J]. Ecological Engineering,2013,52:167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.109 [25] 钟继承, 刘国锋, 范成新, 等.湖泊底泥疏浚环境效应: Ⅱ. 内源氮释放控制作用[J]. 湖泊科学,2009,21(3):335-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.03.004ZHONG J C, LIU G F, FAN C X, et al. Environmental effect of sediment dredging in lake: Ⅱ. the role of sediment dredging in reducing internal nitrogen release[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2009,21(3):335-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.03.004 [26] WU H P, HAO B B, ZHOU Q C, et al. Contribution of various categories of environmental factors to sediment nitrogen-removal in a low C/N ratio river[J]. Ecological Engineering,2021,159:106121. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.106121 [27] TANG F, HUANG T, FAN R, et al. Temporal variation in sediment C, N, and P stoichiometry in a plateau lake during sediment burial[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2020,20(3):1706-1718. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02501-5 [28] MEYERS P A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter[J]. Chemical Geology,1994,114(3/4):289-302. [29] FAN C X, ZHANG L, WANG J J, et al. Processes and mechanism of effects of sludge dredging on internal source release in lakes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(17):1853-1859. doi: 10.1007/BF03183413 [30] LIU C, DU Y H, YIN H B, et al. Exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface influenced by the external suspended particulate matter and the residual matter after dredging[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,246:207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.092 [31] LOUREY M J, ALONGI D M, RYAN D A J, et al. Variability of nutrient regeneration rates and nutrient concentrations in surface sediments of the northern Great Barrier Reef shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2001,21(2):145-155. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00084-4 [32] 余居华, 钟继承, 张银龙, 等.湖泊底泥疏浚对沉积物再悬浮及营养盐负荷影响的模拟[J]. 湖泊科学,2012,24(1):34-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.01.005YU J H, ZHONG J C, ZHANG Y L, et al. Simulation of influence of dredging on sediment resuspension and nutrient loading in lake[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2012,24(1):34-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.01.005 [33] BEUTEL M W. Inhibition of ammonia release from anoxic profundal sediments in lakes using hypolimnetic oxygenation[J]. Ecological Engineering,2006,28(3):271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2006.05.009 [34] 陈超, 钟继承, 范成新, 等.湖泊疏浚方式对内源释放影响的模拟研究[J]. 环境科学,2013,34(10):3872-3878. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.10.031CHEN C, ZHONG J C, FAN C X, et al. Simulation research on the release of internal nutrients affected by different dredging methods in lake[J]. Environmental Science,2013,34(10):3872-3878. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.10.031 [35] 魏伟伟, 李春华, 叶春, 等.基于底泥重金属污染及生态风险评价的星云湖疏浚深度判定[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(3):385-391. doi: 10.18307/2020.0506WEI W W, LI C H, YE C, et al. Determination of dredging depth of Xingyun Lake based on heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of sediment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(3):385-391. doi: 10.18307/2020.0506 [36] CAO X Y, SONG C L, LI Q M, et al. Dredging effects on P status and phytoplankton density and composition during winter and spring in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Hydrobiologia,2007,581(1):287-295. ◇ doi: 10.1007/s10750-006-0516-2 -




 下载:
下载: