Cause analysis of water quality fluctuation of Yixun River in spring flood season
-
摘要:
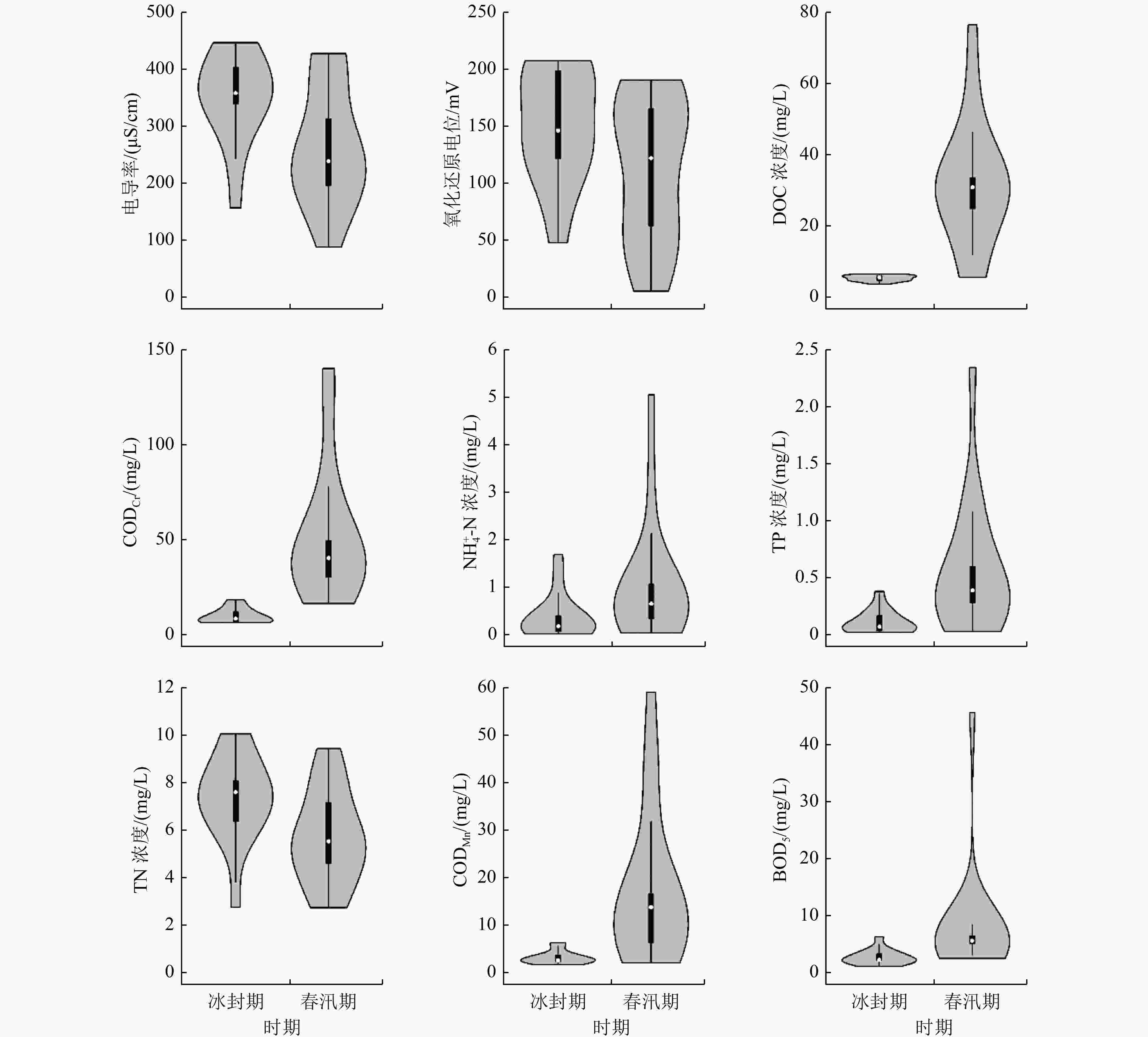
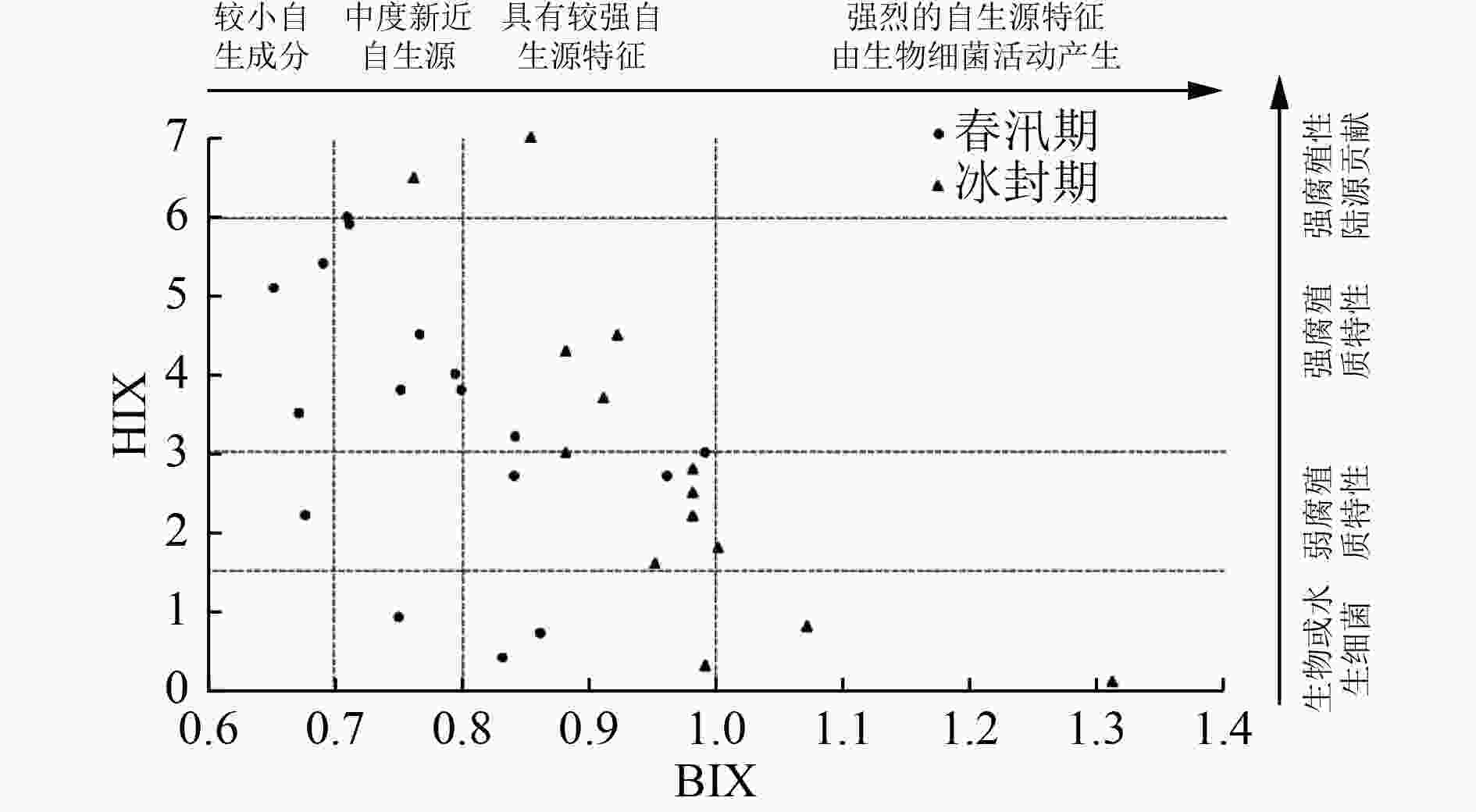
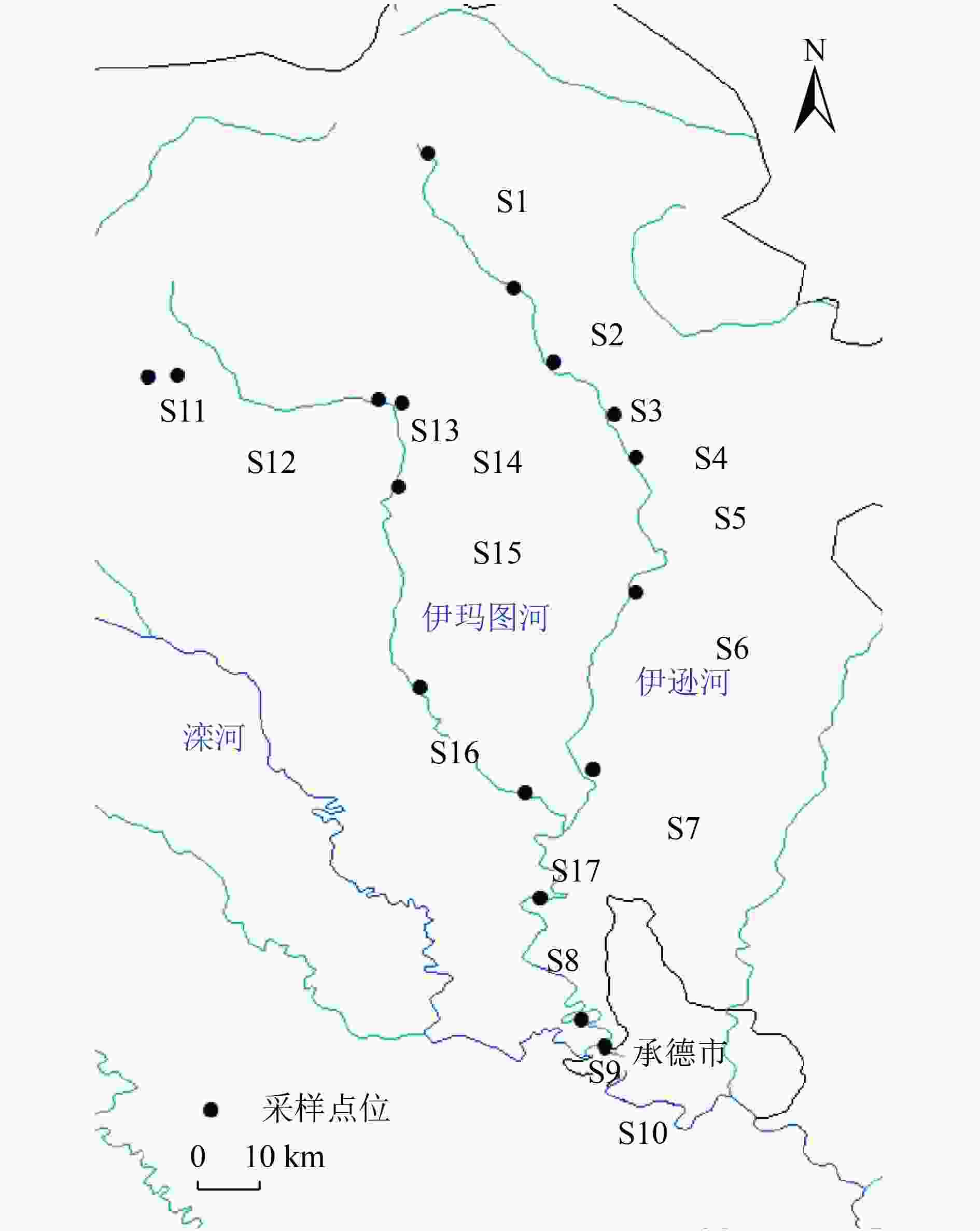
为探究伊逊河春汛期水质波动的主要原因,分别于2020年12月和2021年3月对伊逊河流域进行采样调查,在水环境因子时空特征分析的基础上,使用三维荧光光谱结合平行因子分析、荧光特征分析和Spearman秩相关分析,解析水体污染物的荧光特性和来源特征。结果表明:伊逊河春汛期水质明显恶化,Ⅴ类及劣Ⅴ类水体占比由14.29%升至88.24%,主要超标因子为CODCr、TP和CODMn;水体溶解性有机物(DOM)识别出3种荧光组分〔UVC类腐殖质(C1)、UVA类腐殖质(C2)和类色氨酸(C3)〕,类腐殖质总贡献率接近80%;冰封期和春汛期各采样点位水体溶解性有机物的荧光指数(FI)分别为1.65~1.88和1.49~1.75,自生源指数(BIX)分别为0.76~1.31和0.65~0.99,腐殖化指数(HIX)分别为0.10~7.00和0.40~6.00;春汛期伊逊河水体DOM表现出更强的腐殖性和较弱的近期自生源特性,陆源贡献比例显著提高;荧光参数FI、BIX与DOC、TP、CODCr和CODMn等水质参数呈显著负相关(R>0.6,P<0.01),春汛期水体DOC、TP等污染物浓度升高主要受高腐殖质背景、水土流失及农业面源污染的影响。
Abstract:In order to explore the main reasons for water quality fluctuation in the Yixun River in the spring flood season, Yixun River Basin was sampled and investigated in December 2020 and March 2021, respectively. Based on an analysis of the spatial and temporal characteristics of water environment factors, the excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy combined with parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC), fluorescence characteristic analysis and Spearman rank correlation analysis were used in fluorescence characteristics studies and source characteristics studies. The results showed that the water quality of the Yixun River in the spring flood season deteriorated significantly, which was mainly reflected in the increase in the proportion of Class V and worse water bodies of the national standard from 14.29% to 88.24%. The main over-standard factors were CODCr, TP and CODMn. Three fluorescence components, including UVC humic-like substances (C1), UVA humic-like substances (C2), and tryptophan-like substances (C3) were detected in the dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the water body, of which the total contribution of humic-like substances accounted for nearly 80%. The fluorescence index (FI) of DOM during the freezing and spring flood seasons were 1.65-1.88 and 1.49-1.75, the biological source index (BIX) was 0.76-1.31 and 0.65-0.99, and the humification index (HIX) was 0.10-7.00 and 0.40-6.00, respectively. During the spring flood season, the DOM of the Yixun River body showed stronger humility and weaker recent autochthonous characteristics, and the proportion of land source contribution significantly increased. The fluorescence parameters of FI and BIX were significantly negatively correlated (R>0.6, P<0.01) with the water quality parameters such as DOC, TP, CODCr and CODMn. The increase of the concentration of DOC, TP and other pollutants in water bodies during the spring flood season was mainly affected by three factors, including high humus background, soil erosion and agricultural non-point source pollution.
-
Key words:
- Yixun River /
- PARAFAC /
- fluorescence characteristics /
- dissolved organic matter /
- humus-like substances
-
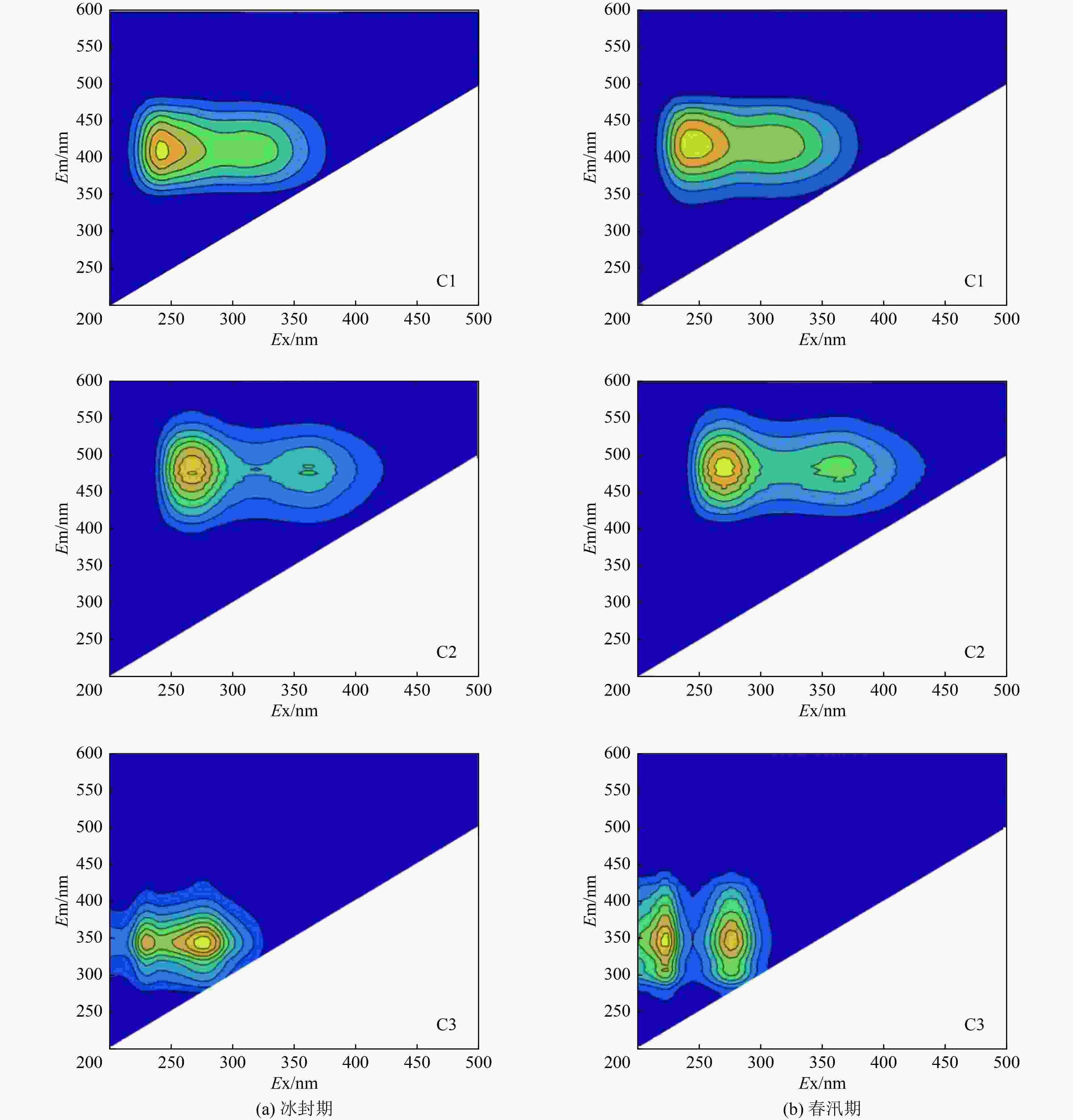
表 1 伊逊河水体DOM荧光组分特征
Table 1. Characteristics of DOM fluorescent components in Yixun River
荧光组分 Ex/Em/nm 数据来源 UVC类腐殖质(C1) 240(315)/410 本研究(冰封期) 245(310)/420 本研究(春汛期) <250(<325)/438 文献[27] <250(<305)/412~420 文献[12] 250(305)/412 文献[28] 250(325)/416 文献[29] UVA类腐殖质(C2) 270(365)/480 本研究(冰封期) 270(365)/480 本研究(春汛期) 240(370)/480 文献[30] 270(360)/478 文献[29] 255(350)/471 文献[22] 类色氨酸(C3) 230(275)/345 本研究(冰封期) 225(275)/345 本研究(春汛期) <250(<280)/340 文献[27] <250(<280)/360 文献[18] <225(<285)/344 文献[22] 表 2 水体荧光参数与水质参数的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation between water quality parameters and fluorescence parameters of DOM samples
项目 EC ORP DOC浓度 CODCr NH4 +-N浓度 TP浓度 TN浓度 CODMn BOD5 FI BIX ORP 0.34 DOC浓度 −0.41 −0.13 CODCr −0.30 −0.05 0.86* NH4 +-N浓度 −0.23 −0.14 0.57* 0.58* TP浓度 −0.56* −0.10 0.67* 0.67* 0.72* TN浓度 0.56* 0.31 −0.40 −0.34 0.08 −0.29 CODMn −0.61* −0.17 0.81* 0.80* 0.61* 0.81* −0.52* BOD5 −0.20 −0.27 0.65* 0.79* 0.65* 0.60* −0.20 0.75* FI 0.66* 0.48 −0.66* −0.58* −0.37 −0.65* 0.57* −0.77* −0.57* BIX 0.81* 0.22 −0.66* −0.63* −0.40 −0.73* 0.60* −0.72* −0.36 0.76* HIX −0.53* −0.12 0.03 0.00 −0.21 0.24 −0.49 0.07 −0.25 −0.22 −0.56* 注:*表示P<0.01。 -
[1] 任晓庆, 杨中文, 张远, 等.滦河流域水生态承载力评估研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2019,30(5):72-79.REN X Q, YANG Z W, ZHANG Y, et al. Evaluation of hydro-ecological carrying capacity (HECC) in Luanhe River Basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2019,30(5):72-79. [2] 杨志勇, 于赢东, 王建华, 等.气候变化对伊逊河流域水资源量的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2011,22(2):175-181.YANG Z Y, YU Y D, WANG J H, et al. Climate change and its impact on water resources in Yixun River Basin[J]. Advances in Water Science,2011,22(2):175-181. [3] SILVA M M V G, GOMES E M C, ISAÍAS M, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of surface and groundwater quality in a fast-growing city: Lubango, Angola[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(23):1-17. [4] XU G Y, REN X D, YANG Z H, et al. Influence of landscape structures on water quality at multiple temporal and spatial scales: a case study of Wujiang River Watershed in Guizhou[J]. Water,2019,11(1):159. doi: 10.3390/w11010159 [5] 张道萍, 张铃松, 孟凡生, 等.黑龙江流域典型断面水体DOM荧光特性分析[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(5):1099-1110. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.08.08ZHANG D P, ZHANG L S, MENG F S, et al. Fluorescence characteristics analysis of DOM in typical section of Heilongjiang River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(5):1099-1110. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.08.08 [6] 邵田田, 李柳阳, 王涛, 等.辽河流域河流秋季CDOM光学特性及影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2018,38(4):1558-1568. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0410SHAO T T, LI L Y, WANG T, et al. CDOM optical characteristics and influences factors affected on them for rivers in Liaohe River Watershed in autumn[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2018,38(4):1558-1568. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0410 [7] PARK J H, KALBITZ K, MATZNER E. Resource control on the production of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a deciduous forest floor[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2002,34(6):813-822. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00011-1 [8] 白小梅, 李悦昭, 姚志鹏, 等.三维荧光指纹谱在水体污染溯源中的应用进展[J]. 环境科学与技术,2020,43(1):172-180. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.01.025BAI X M, LI Y Z, YAO Z P, et al. Application progress of three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy in source tracing of water pollution[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,43(1):172-180. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.01.025 [9] 郭旭晶, 席北斗, 谢森, 等.乌梁素海沉积物孔隙水中溶解有机质的荧光及紫外光谱研究[J]. 环境工程学报,2012,6(2):440-444.GUO X J, XI B D, XIE S, et al. Study on fluorescence spectra and UV-vis spectra of dissolved organic matter collected from sediment pore water in Wuliangsuhai Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2012,6(2):440-444. [10] 隋志男, 郅二铨, 姚杰, 等.三维荧光光谱区域积分法解析辽河七星湿地水体DOM组成及来源[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2015,5(2):114-120.SUI Z N, ZHI E Q, YAO J, et al. Characterization of DOM composition and origin using three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with region integration method in Qixing Wetland[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2015,5(2):114-120. [11] STEDMON C A, BRO R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods,2008,6(11):572-579. doi: 10.4319/lom.2008.6.572 [12] 吕丽莎, 赵卫红, 苗辉.三维荧光结合平行因子分析在东海溶解有机物研究中的应用[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2013,33(3):653-658. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)03-0653-06LÜ L S, ZHAO W H, MIAO H. Application of excitation-emission matrix spectrum combined with parallel factor analysis in dissolved organic matter in East China Sea[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2013,33(3):653-658. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)03-0653-06 [13] SANCHEZ N P, SKERIOTIS A T, MILLER C M. A PARAFAC-based long-term assessment of DOM in a multi-coagulant drinking water treatment scheme[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(3):1582-1591. [14] MORADI S, SAWADE E, ARYAL R, et al. Tracking changes in organic matter during nitrification using fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy coupled with parallel factor analysis (FEEM/PARAFAC)[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2018,6(1):1522-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.02.003 [15] HUA B, YANG J, LIU F J, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter/nitrogen by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for watershed management[J]. Chemosphere,2018,201:708-715. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.043 [16] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [17] 陈毅忠, 杜尔登, 王聿琳, 等.三维荧光组合PARAFAC分析评估城市水体DOM特征分布与来源[J]. 常州大学学报(自然科学版),2017,29(6):55-62.CHEN Y Z, DU E D, WANG Y L, et al. Distribution and source of DOM in urban water bodies by EEMs spectrum and PARAFAC analysis[J]. Journal of Changzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2017,29(6):55-62. [18] YANG X L, YU X B, CHENG J R, et al. Impacts of land-use on surface waters at the watershed scale in southeastern China: Insight from fluorescence excitation-emission matrix and PARAFAC[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:647-657. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.279 [19] 刘东萍, 高红杰, 崔兵, 等.白塔堡河底泥DOM组成结构的荧光光谱与多元统计模型表征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):249-257. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200204LIU D P, GAO H J, CUI B, et al. Fluorescence spectra and multivariate statistical model characterization of DOM composition structure of Baitapu River Sediment[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):249-257. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200204 [20] 张欢. 派河和南淝河溶解性有机质(DOM)光谱分析及污染源解析[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. [21] 王迪, 张飞, 张兆永, 等.新疆艾比湖流域枯、丰水期三维荧光光谱特性及其与水质的关系[J]. 湖泊科学,2020,32(2):483-495. doi: 10.18307/2020.0217WANG D, ZHANG F, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Characteristics of three-dimensional fluorescence spectra and its correlation with water quality of surface water during dry and wet seasons in Lake Ebinur Watershed, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2020,32(2):483-495. doi: 10.18307/2020.0217 [22] ZHANG Y L, ZHANG E L, YIN Y, et al. Characteristics and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in lakes of the Yungui Plateau, China, differing in trophic state and altitude[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2010,55(6):2645-2659. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2645 [23] 薛浩, 王业耀, 孟凡生, 等.汤旺河着生硅藻群落及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(3):1256-1264.XUE H, WANG Y Y, MENG F S, et al. Community of benthic diatoms and their relationship with aquatic environmental factors in the Tangwang River, China[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(3):1256-1264. [24] 林田野.基于滦河流域水环境治理与保护的思考[J]. 水资源开发与管理,2020,18(1):14-17. doi: 10.16616/j.cnki.10-1326/TV.2020.01.04LIN T Y. Thinking on water environment management and protection in the Luanhe River Basin[J]. Water Resources Development and Management,2020,18(1):14-17. doi: 10.16616/j.cnki.10-1326/TV.2020.01.04 [25] 王子为, 钱昶, 张成波, 等.伊逊河流域总磷污染来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(10):2290-2297. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.05.12WANG Z W, QIAN C, ZHANG C B, et al. Source apportionment of total phosphorus pollution in Yixun River Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(10):2290-2297. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.05.12 [26] 陈庆锋, 郭贝贝. 我国北方山区河流生态综合治理模式探究[C]//2015年水资源生态保护与水污染控制研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国环境科学学会, 2015: 241-246. [27] HOSEN J D, MCDONOUGH O T, FEBRIA C M, et al. Dissolved organic matter quality and bioavailability changes across an urbanization gradient in headwater streams[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(14):7817-7824. [28] STEDMON C A, MARKAGER S. Resolving the variability in dissolved organic matter fluorescence in a temperate estuary and its catchment using PARAFAC analysis[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2005,50(2):686-697. doi: 10.4319/lo.2005.50.2.0686 [29] STEDMON C A, MARKAGER S, BRO R. Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry,2003,82(3/4):239-254. [30] KOWALCZUK P, TILSTONE G H, ZABŁOCKA M, et al. Composition of dissolved organic matter along an atlantic meridional transect from fluorescence spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis[J]. Marine Chemistry,2013,157:170-184. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.10.004 [31] 颜秉斐, 彭剑峰, 邓齐玉, 等.白塔堡河水体DOM分布特征及来源[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(3):225-232. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.02.190YAN B F, PENG J F, DENG Q Y, et al. DOM distribution characteristics and source analysis of Baitabu River[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(3):225-232. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.02.190 [32] BAKER A, INVERARITY R. Protein-like fluorescence intensity as a possible tool for determining river water quality[J]. Hydrological Processes,2004,18(15):2927-2945. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5597 [33] 张博, 高建文, 范绍锦, 等.南湖水系溶解性有机质来源及时空分布特征[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):912-919. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200066ZHANG B, GAO J W, FAN S J, et al. Origin and spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of dissolved organic matter in Nanhu Lake water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):912-919. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200066 [34] HUGUET A, VACHER L, RELEXANS S, et al. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2009,40(6):706-719. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002 [35] 陶澍, 陈静生, 邓宝山, 等.中国东部主要河流河水腐殖酸的起源、含量及地域分异规律[J]. 环境科学学报,1988,8(3):286-294. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.1988.03.004TAO S, CHEN J S, DENG B S, et al. Contents of stream humic substances in the east of China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,1988,8(3):286-294. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.1988.03.004 [36] 吴立钰, 张璇, 李冲, 等.气候变化和人类活动对伊逊河流域径流变化的影响[J]. 自然资源学报,2020,35(7):1744-1756. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200717WU L Y, ZHANG X A, LI C, et al. Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff variations in Yixun River Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2020,35(7):1744-1756. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20200717 [37] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 张晓敏, 等.河北承德中部伊逊河红旗地区土壤生源要素空间分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 矿产勘查,2021,12(4):1008-1018. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.04.023SUN H Y, WEI X F, ZHANG X M, et al. Spatial variation and influencing factors of soil biogenic elements distribution in Hongqi Town of Yixun River Basin in Chengde City[J]. Mineral Exploration,2021,12(4):1008-1018. □ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.04.023 -




 下载:
下载: