Research progress of biological denitrification and nitrogen removal technology promoted by slow release carbon source
-
摘要:
随着污水治理要求的愈加严格与公众健康意识的不断提升,水体硝酸盐污染已引起世界各国的普遍关注。目前,生物异养反硝化是去除水中硝酸盐的主要技术手段,其关键制约因素是碳源,而传统外加碳源的弊端也在不断暴露,于是开发适用于生物脱氮工艺的新型缓释碳源成为国内外学者广泛关注的焦点。从促进生物反硝化脱氮的缓释碳源开发必要性出发,详细分析了缓释碳源的种类、促进反硝化的效果、改性方法、影响因素、作用机理及生物膜特性,比较和揭示了天然缓释碳源、改性缓释碳源、人工合成缓释碳源促进反硝化的性能及生物膜群落结构。提出该领域后续研究方向,包括突破反应动力学的限速步骤、优化骨架材料和空间架构、开发新型缓释碳源促进生物脱氮工艺等,以期为缓释碳源促进生物反硝化效率及推广应用提供参考和依据。
Abstract:With the increasingly stringent requirements for sewage treatment and the continuous improvement of public health awareness, the nitrate pollution in water body has caused widespread concern in the world. At present, biological heterotrophic denitrification as the main technical means to remove nitrate in water, the carbon source has been the key restricting factor, and the disadvantages of traditional external carbon source have also been found. Therefore, the development of new slow-release carbon source suitable for biological denitrification process has become the focus of attention of researchers at home and abroad. Starting from the necessity of developing slow-release carbon sources for promoting biological denitrification, the types of slow-release carbon sources, the effect of promoting denitrification, the modification methods, the influencing factors of nitrogen removal, the mechanism of action and the characteristics of biofilm were analyzed in detail. The denitrification promoting performance and biofilm community structure of natural slow-release carbon source, modified slow-release carbon source and synthetic slow-release carbon source were compared and revealed. At the same time, the prospects of breaking through the speed limiting steps of reaction kinetics, optimizing skeleton materials and spatial framework, developing new slow-release carbon sources and promoting biological denitrification process were put forward for the follow-up researches, so as to provide reference and basis for the dissemination and application of slow-release carbon sources to promote the efficiency of biological denitrification.
-
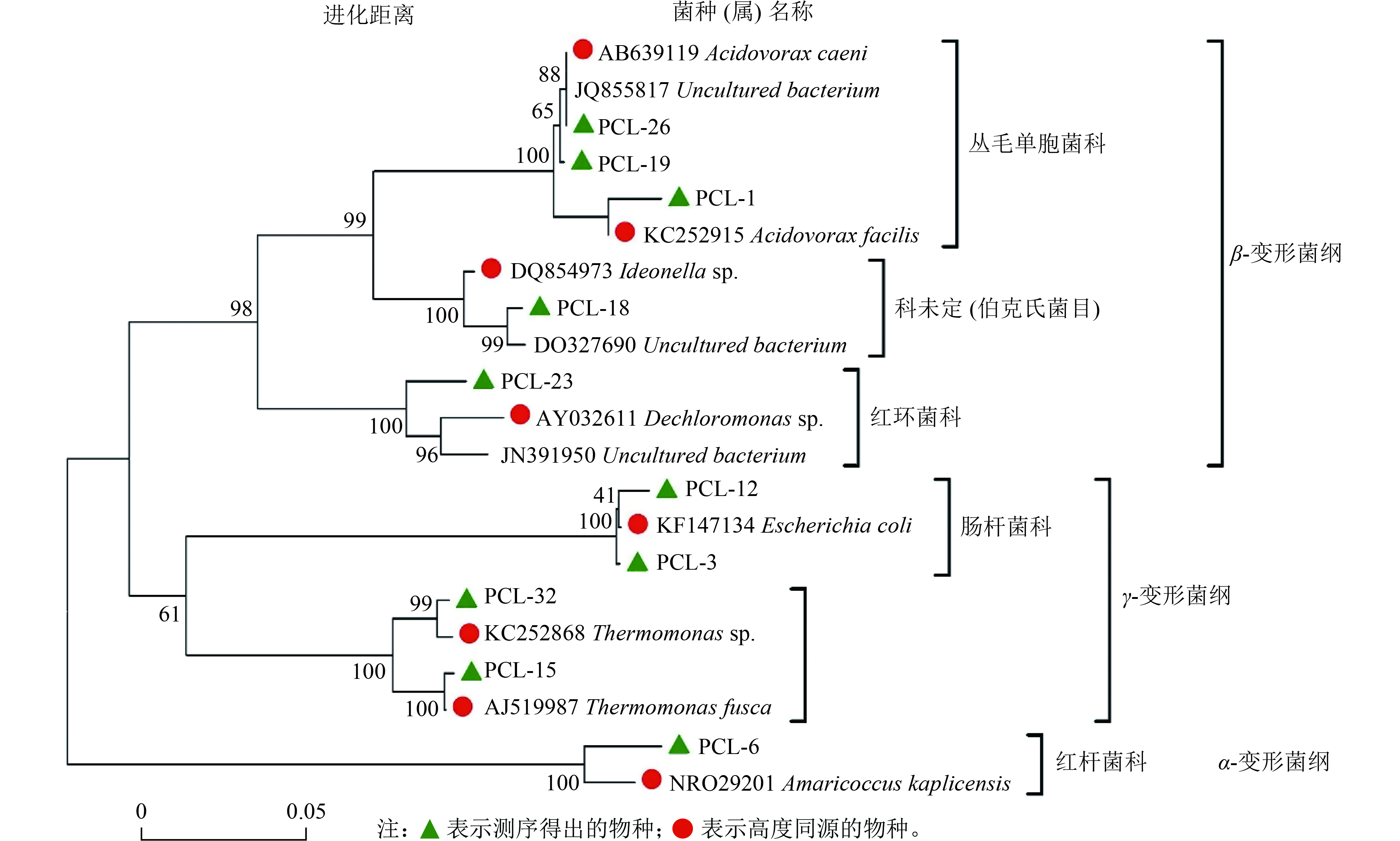
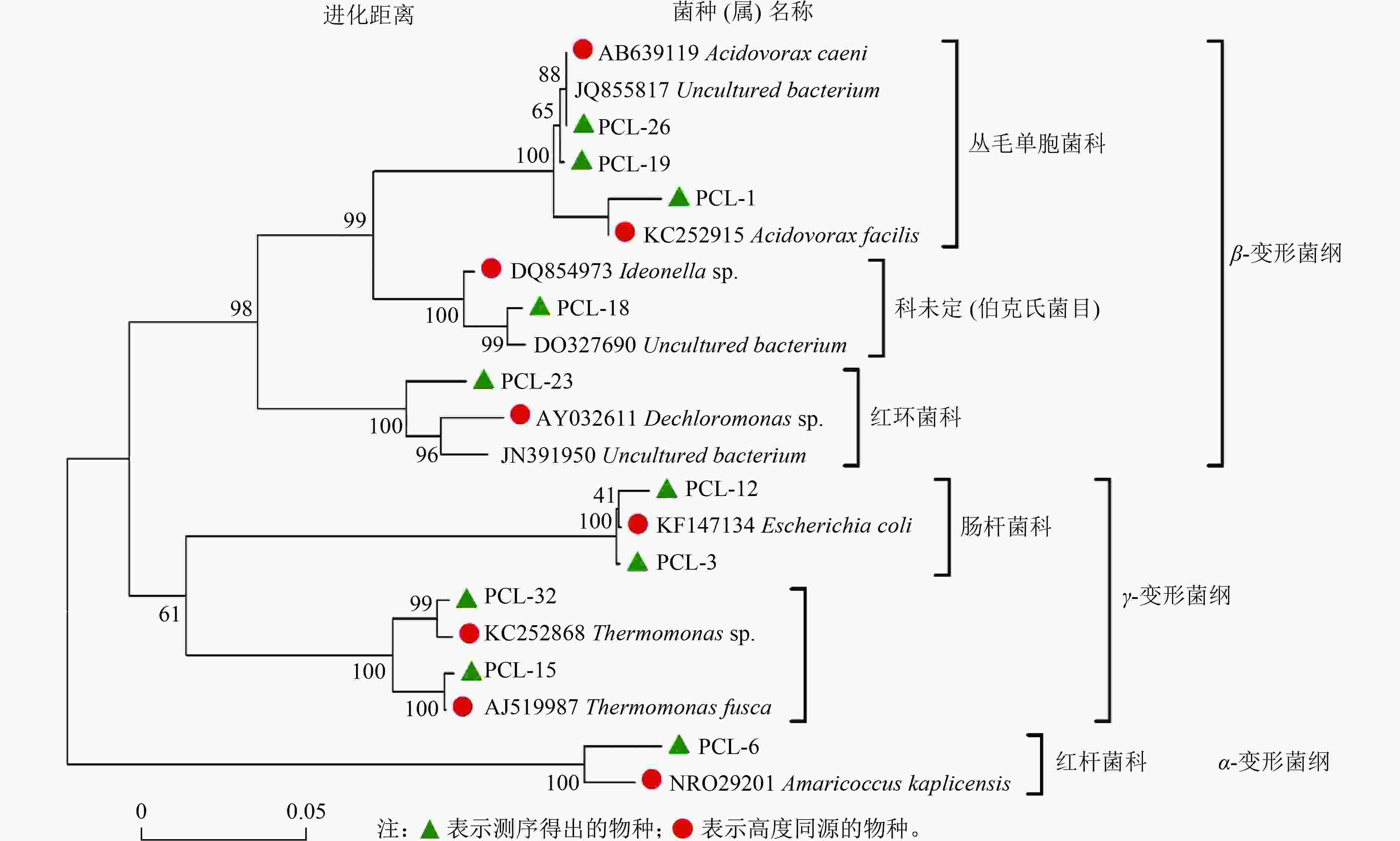
图 1 以PCL为缓释碳源的生物脱氮系统微生物群落系统发育树[59]
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of microbial community in biological nitrogen removal system using PCL as slow-release carbon source
表 1 天然缓释碳源的改性处理方法及处理效果
Table 1. Modified methods and effects of natural slow-release carbon sources
碳源类型 改性处理方法 处理效果 玉米芯[39] 碱处理,采用0.1 g Ca(OH)2处理每g干物质,处理温度
为70 ℃,处理时间为6 h酶解还原糖量提高2.4倍 小麦秸秆[39] 碱处理,采用0.1 g Ca(OH)2处理每g干物质,处理温度
为95 ℃,处理时间为24 h酶解还原糖量提高3.3倍 稻草、稻壳[40] 25 ℃,pH为7.2~7.5,缓释碳源投加量为5 g/L,NO3 −-N初始浓度为8.8 mg/L NO3 −-N去除率大于80% 小麦秸秆[41] 采用钴-60为辐射源进行辐照,源强为1.11×1015 Bq,
剂量为244.53 Gy/min,钴-60射线平均能力为1.25 MeV反硝化速率提高20% 马铃薯和小麦淀粉[42] 采用溶液湿法共混合低温冻胶成型技术,将淀粉与乙烯
醇溶液冷冻—解冻反复4次脱氮率大于90% 樟树叶[43] 温度为25 ℃,NO3 −-N浓度
为60 mg/L,缓释碳源投加量为12.5 g/L脱氮率大于96% 银杏叶、香樟叶、菖蒲、芦苇花、秸秆、木屑、树皮和松枝[42] 碱处理,3%NaOH溶液浸煮,过滤、水洗,调节pH至中性后于40 ℃烘干至恒定质量 除树皮脱氮率不高(75%)外,其他缓释碳源的脱氮率均在96%~98% 玉米秆[44] 碱处理,3%NaOH溶液浸煮 TN去除率
大于97%表 2 不同类型缓释碳源的反硝化速率对比
Table 2. Comparison of denitrification rates of different slow-release carbon sources
碳源类别 碳源名称 表面积/(m2/L) 温度/℃ 流速/(L/h) 投加量/(g/L) 孔隙率/% 反硝化速率/〔mg/(L·d)〕 天然 原棉[26] 14~30 0.037~0.045 22.1~38.0 87~95 49~82 麦秆[41] 24~26 <0.086 25.4~36.3 79~91 38~53 稻壳[29] 10~30 23.7~35.6 82~96 65~142 人工合成 PHB[55] 1.49 20~25 0.4~0.6 17.5~23.1 65~78 168~980 PCL[58] 0.87 20~25 0.2~0.3 7.2~12.9 15~21 504~3 980 黏结共混聚合物[59] 1.22 20~25 0.3~0.6 10.4~15.3 23~35 36~185 -
[1] 谢希, 何圣兵, 崔洪升, 等.固体缓释碳源强化污水土地处理系统的反硝化效能[J]. 中国给水排水,2014,30(3):84-86.XIE X, HE S B, CUI H S, et al. Improving denitrification efficiency of wastewater land treatment system with solid sustained-release carbon source[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2014,30(3):84-86. [2] 张妍, 毕直磊, 张鑫, 等.土地利用类型对渭河流域关中段地表水硝酸盐污染的影响[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(12):4319-4327.ZHANG Y, BI Z L, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of land-use types on nitrate pollution of surface water in Guanzhong area in the Weihe River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(12):4319-4327. [3] ILINITCH O M, NOSOVA L V, GORODETSKII V V, et al. Catalytic reduction of nitrate and nitrite ions by hydrogen: investigation of the reaction mechanism over Pd and Pd-Cu catalysts[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical,2000,158(1):237-249. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(00)00070-4 [4] 崔玉玮. 基于电化学与生物膜耦合深度处理受污染地下水中含氮物质的研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018. [5] DEHGHANI M, HAIDARI E, SHAHSAVANI S, et al. Removal of nitrate in the aqueous phase using granular ferric hydroxide[J]. Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences,2015,7(2):25-31. [6] GUESMI F, HARBI S, AMOURI S, et al. Application of response surface methodology to optimize nitrate removal from water by electrodialysis[J]. Chemistry Letters,2016,45(12):1369-1372. doi: 10.1246/cl.160764 [7] 李德生, 张超, 邓时海, 等.基于铁基质高效催化还原污水中硝酸盐氮的实验研究[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(3):1065-1074.LI D S, ZHANG C, DENG S H, et al. Experimental study on effective nitrate removal from sewage by ZVI-based catalyzed reduction[J]. CIESC Journal,2019,70(3):1065-1074. [8] SAEED T, SUN G Z. A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2012,112:429-448. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.08.011 [9] 陈雷, 姜玉, 龚斌, 等.可生物降解塑料与沸石载体体系对硝酸盐氮污染地下水的生物修复研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2017,39(4):345-351.CHEN L, JIANG Y, GONG B, et al. Study on the bioremediation of nitrate nitrogen contaminated groundwater by biodegradable plastic-zeolite system[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2017,39(4):345-351. [10] 何媛. 电极强化人工湿地处理低碳氮比污水效果及机理研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016. [11] 李学尧, 周宇权, 赵信.地下水生物反硝化的纤维素碳源选择研究[J]. 环境科学与管理,2013,38(2):56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2013.02.015LI X Y, ZHOU Y Q, ZHAO X. Selection of cellulose carbon sources for biological groundwater denitrification[J]. Environmental Science and Management,2013,38(2):56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2013.02.015 [12] 李航, 董立春, 方建飞, 等.初沉池优化运行对改良型A2/O工艺脱氮除磷的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(6):1189-1195. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210038LI H, DONG L C, FANG J F, et al. Effect of optimizing operation of primary sedimentation tank on nitrogen and phosphorus removal of modified A2/O process[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(6):1189-1195. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210038 [13] 李跃平. 固体碳源作为外加碳源提高低C/N污水脱氮性能研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021. [14] 李桂荣, 李雪, 许文峰, 等.解决城镇污水处理厂生物脱氮除磷所需碳源不足的方法综述[J]. 广东化工,2011,38(4):149-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2011.04.073LI G R, LI X, XU W F, et al. A review on shortage of carbon sources for N and P removal of biological systems in municipal wastewater treatment plant[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2011,38(4):149-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2011.04.073 [15] ZHANG Y M, WANG X C, CHENG Z, et al. Effect of fermentation liquid from food waste as a carbon source for enhancing denitrification in wastewater treatment[J]. Chemosphere,2016,144:689-696. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.036 [16] SUN H H, WU Q, YU P, et al. Denitrification using excess activated sludge as carbon source: performance and the microbial community dynamics[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,238:624-632. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.105 [17] 李晓崴, 贾亚红, 李冰, 等.人工湿地植物缓释碳源的预处理方式及释碳性能研究[J]. 水处理技术,2013,39(12):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.12.011LI X W, JIA Y H, LI B, et al. Research on pretreatment methods and carbon releasing property of constructed wetland plant as slow-releasing carbon source[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2013,39(12):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.12.011 [18] 沈志强, 周岳溪, 王建龙.利用淀粉/PCL共混物作为反硝化固体碳源和生物膜载体的研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2014,4(2):129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2014.02.022SHEN Z Q, ZHOU Y X, WANG J L. Denitrification using starch/PCL blends as solid carbon source and biofilm carrier[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2014,4(2):129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2014.02.022 [19] 张恒亮, 朱铁群, 王海燕, 等.芦苇碳源投加量对表面流人工湿地中试系统强化脱氮启动的影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(3):332-339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.03.047ZHANG H L, ZHU T Q, WANG H Y, et al. Influence of Phragmites australis carbon dosage on enhanced nitrogen removal start-up of pilot-scale surface flow constructed wetland[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(3):332-339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.03.047 [20] 白乌云, 张宝林, 塔娜.有机固体废弃物资源化利用探究[J]. 北方环境,2013,25(3):76-77.BAI W Y, ZHANG B L, TA N. On the utilization of organic solid wastes[J]. Northern Environment,2013,25(3):76-77. [21] 冯延申, 黄天寅, 刘锋, 等.反硝化脱氮新型外加碳源研究进展[J]. 现代化工,2013,33(10):52-57.FENG Y S, HUANG T Y, LIU F, et al. New types of extra carbon sources for denitrification[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2013,33(10):52-57. [22] LEE D U, LEE I S, CHOI Y D, et al. Effects of external carbon source and empty bed contact time on simultaneous heterotrophic and sulfur-utilizing autotrophic denitrification[J]. Process Biochemistry,2001,36(12):1215-1224. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00163-7 [23] ASLAN Ş, TÜRKMAN A. Simultaneous biological removal of endosulfan (α+β) and nitrates from drinking waters using wheat straw as substrate[J]. Environment International,2004,30(4):449-455. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00092-8 [24] SU C M, PULS R W. Removal of added nitrate in cotton burr compost, mulch compost, and peat: mechanisms and potential use for groundwater nitrate remediation[J]. Chemosphere,2007,66(1):91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.015 [25] OVEZ B, OZGEN S, YUKSEL M. Biological denitrification in drinking water using Glycyrrhiza glabra and Arunda donax as the carbon source[J]. Process Biochemistry,2006,41(7):1539-1544. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2006.02.015 [26] VOLOKITA M, BELKIN S, ABELIOVICH A, et al. Biological denitrification of drinking water using newspaper[J]. Water Research,1996,30(4):965-971. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00242-1 [27] 杨磊, 郭军, 王岩, 等.农林废弃物制备环境友好型缓释碳源生物膜载体材料[J]. 湖北农业科学,2021,60(18):68-71.YANG L, GUO J, WANG Y, et al. Preparation of environment-friendly slow-release carbon source biofilm carrier material from agricultural and forestry wastes[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2021,60(18):68-71. [28] 孙雅丽, 张国臣, 阎中, 等.以腐朽木为碳源去除废水中硝酸盐氮的研究[J]. 环境科学,2010,31(6):1494-1498.SUN Y L, ZHANG G C, YAN Z, et al. Removing nitrate-nitrogen from wastewater using rotten wood as carbon source[J]. Environmental Science,2010,31(6):1494-1498. [29] 徐锁洪, 施巍.以稻壳为载体培养反硝化菌及硝酸盐氮的去除[J]. 大连铁道学院学报,2001,22(4):98-101.XU S H, SHI W. Nitrate removal and denitrification bacteria cultivation using rice chaff as a medium[J]. Journal of Dalian Railway Institute,2001,22(4):98-101. [30] ROBERTSON W D, BLOWES D W, PTACEK C J, et al. Long-term performance of in situ reactive barriers for nitrate remediation[J]. Ground Water,2000,38(5):689-695. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2000.tb02704.x [31] SCHIPPER L A, VOJVODIĆ-VUKOVIĆ M. Nitrate removal from groundwater and denitrification rates in a porous treatment wall amended with sawdust[J]. Ecological Engineering,2000,14(3):269-278. doi: 10.1016/S0925-8574(99)00002-6 [32] 曲久辉, 范彬, 刘锁祥, 等.电解产氢自养反硝化去除地下水中硝酸盐氮的研究[J]. 环境科学,2001,22(6):49-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2001.06.010QU J H, FAN B, LIU S X, et al. Autotrophic denitrification of groundwater by electrochemical process[J]. Enviromental Science,2001,22(6):49-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2001.06.010 [33] SAKAKIBARA Y, NAKAYAMA T. A novel multi-electrode system for electrolytic and biological water treatments: electric charge transfer and application to denitrification[J]. Water Research,2001,35(3):768-778. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00327-4 [34] VOLOKITA M, ABEHOVICH A, SOARES M I M. Denitrification of groundwater using cotton as energy source[J]. Water Science and Technology,1996,34(1/2):379-385. [35] OVEZ B. Batch biological denitrification using Arundo donax, Glycyrrhiza glabra, and Gracilaria verrucosa as carbon source[J]. Process Biochemistry,2006,41(6):1289-1295. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.12.030 [36] 王尉, 常雅军, 崔键, 等.改性丝瓜络填料对富营养化水体的高效脱氮特性[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(1):130-137.WANG W, CHANG Y J, CUI J, et al. High-efficiency nitrogen removal of eutrophic water by modified loofah fillers[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(1):130-137. [37] 王登敏.玉米芯固体碳源生物膜SND处理低碳源城市污水脱氮性能研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2019. [38] 任琦.以农业废弃物为固体碳源强化SC-MBBR脱氮性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2019. [39] 马雨阳, 纪鸿飞, 孙昭玥, 等.碱预处理对固体碳源生物可利用性及其强化生物脱氮效能的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(6):95-103.MA Y Y, JI H F, SUN Z Y, et al. Effect of alkali pretreatment on solid carbon source bio-availability and enhancing biological denitrification efficiency[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2019,49(6):95-103. [40] 邵留, 徐祖信, 金伟, 等.农业废物反硝化固体碳源的优选[J]. 中国环境科学,2011,31(5):748-754.SHAO L, XU Z X, JIN W, et al. Optimization of solid carbon source for denitrification of agriculture wastes[J]. China Environmental Science,2011,31(5):748-754. [41] 范振兴, 赵璇, 王建龙.利用辐照预处理麦秆作为反硝化固体碳源的研究[J]. 环境科学,2009,30(4):1090-1094. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.04.025FAN Z X, ZHAO X, WANG J L. Denitrification using radiation-pretreated wheat straw as solid carbon source[J]. Environmental Science,2009,30(4):1090-1094. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.04.025 [42] 孙磊, 廖家林, 阮文权, 等.用于地表水反硝化的淀粉碳源选择研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(28):17365-17368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.28.096SUN L, LIAO J L, RUAN W Q, et al. Starch carbon source selection for denitrification in surface water[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(28):17365-17368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.28.096 [43] 郑丽银, 缪恒锋, 严群, 等.用于地表水反硝化的纤维素碳源选择研究[J]. 环境工程学报,2011,5(9):1926-1932.ZHENG L Y, MIAO H F, YAN Q, et al. Selection of cellulose carbon sources for biological denitrification of surface water[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2011,5(9):1926-1932. [44] 李同燕, 李文奇, 胡伟武, 等.玉米秆碳源去除地下水硝酸盐[J]. 环境工程学报,2015,9(9):4245-4251. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150925LI T Y, LI W Q, HU W W, et al. Performances of bio-denitrfication using maize stalks as carbon source for nitrate-contaminated groundwater in situ remediation[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2015,9(9):4245-4251. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150925 [45] CAO S B, WANG L, YAN W W, et al. Primary sludge as solid carbon source for biological denitrification: system optimization at micro-level[J]. Environmental Research,2020,191:110160. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110160 [46] BOLEY A, MÜLLER W R. Denitrification with polycaprolactone as solid substrate in a laboratory-scale recirculated aquaculture system[J]. Water Science and Technology,2005,52(10/11):495-502. [47] 封羽涛, 吴为中. 可降解聚合物PCL、PBS在低有机污染水中固相反硝化脱氮效果比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(增刊1): 1127-1132.FENG Y T, WU W Z. The comparison of nitrogen removal effect between biodegradable polymers of PCL and PBS in the low organic pollution water[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(Suppl 1): 1127-1132. [48] 闫续, 许柯, 耿金菊, 等.两种释碳材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2012,32(11):1984-1990. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.11.009YAN X, XU K, GENG J J, et al. Preparation and properties of two kinds of carbon releasing material[J]. China Environmental Science,2012,32(11):1984-1990. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.11.009 [49] 王允, 张旭, 张大奕, 等.用于地下水原位生物脱氮的缓释碳源材料性能研究[J]. 环境科学,2008,29(8):2183-2188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.08.017WANG Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG D Y, et al. Performance of slow-release organic carbon-source (SOC) materials forin situ biological denitrification in groundwater[J]. Environmental Science,2008,29(8):2183-2188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.08.017 [50] 唐丹琦, 王娟, 郑天龙, 等.聚乳酸/淀粉固体缓释碳源生物反硝化研究[J]. 环境科学,2014,35(6):2236-2240.TANG D Q, WANG J, ZHENG T L, et al. Effect of PLA/starch slow-release carbon source on biological denitrification[J]. Environmental Science,2014,35(6):2236-2240. [51] 张大奕, 李广贺, 王允, 等.缓释碳源材料释碳与脱氮性能[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2009,49(9):75-79.ZHANG D Y, LI G H, WANG Y, et al. Slow-release organic carbon-source materials for groundwater in situ denitrification[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2009,49(9):75-79. [52] 李彭, 唐蕾, 左剑恶, 等.以PHAs为固体碳源的城镇二级出水深度脱氮研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2014,34(2):331-336.LI P,TANG L,ZUO J E, et al. Tertiary nitrogen removal of the municipal secondary effluent using PHAs as solid carbon sources[J]. China Environmental Science,2014,34(2):331-336. [53] 张晓丹, 宋乾武, 代晋国, 等.温度及碳源对NPR工艺脱氮除磷效果的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2007,20(4):125-129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2007.04.022ZHANG X D, SONG Q W, DAI J G, et al. Effect of sewage temperature and carbon source for nitrogen and phosphorus removal rate of NPR process[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2007,20(4):125-129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2007.04.022 [54] ZHENG X H, ZHANG J, LI M T, et al. Optimization of the pollutant removal in partially unsaturated constructed wetland by adding microfiber and solid carbon source based on oxygen and carbon regulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,752:141919. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141919 [55] BOLEY A, MÜLLER W R, HAIDER G. Biodegradable polymers as solid substrate and biofilm carrier for denitrification in recirculated aquaculture systems[J]. Aquacultural Engineering,2000,22(1/2):75-85. [56] 周海红, 王建龙, 赵璇.pH对以PBS为反硝化碳源和生物膜载体去除饮用水源水中硝酸盐的影响[J]. 环境科学,2006,27(2):290-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.02.018ZHOU H H, WANG J L, ZHAO X. Denitrification using PBS as carbon source and biofilm supporter: effect of pH[J]. Environmental Science,2006,27(2):290-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.02.018 [57] 周海红, 赵璇, 王建龙.利用可生物降解聚合物去除饮用水源水中硝酸盐[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2006,46(3):434-436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2006.03.033ZHOU H H, ZHAO X, WANG J L. Removal of nitrates from drinking water using biodegradable polymers as both substrate and biofilm carrier[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2006,46(3):434-436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2006.03.033 [58] 张立秋, 雷志娟, 李淑更, 等.固体碳源生物膜处理地下水硝酸盐污染的脱氮性能研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2020,42(8):937-942.ZHANG L Q, LEI Z J, LI S G, et al. Nitrogen removal performance of solid carbon source biofilm reactor for treatment of nitrate-contaminated groundwater[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2020,42(8):937-942. [59] 李彭. 不同电子供体深度脱氮工艺及微生物群落特征研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2014. [60] MÜLLER R. Biodegradability of polymers: regulations and methods for testing[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, 2005: 365-374. [61] 王旭明, 孙立娇, 仇天雷, 等.固相反硝化技术同时去除地下水中的硝酸盐与农药进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2012,32(12):125-129.WANG X M, SUN L J, QIU T L, et al. Research progress on the simultaneous removal of nitrate and pesticides from groundwater using solid-phase denitrification process[J]. China Biotechnology,2012,32(12):125-129. [62] 杨帆, 王鹤立.缓释碳源复合材料的制备及其用于地下水硝酸盐污染修复的研究[J]. 水处理技术,2013,39(4):75-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.04.018YANG F, WANG H L. Preparation of slow-release carbon source composite materials and their use for groundwater nitrate pollution restoration[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2013,39(4):75-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.04.018 [63] 周梦娟, 缪恒锋, 陆震明, 等.碳源对反硝化细菌的反硝化速率和群落结构的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(12):2047-2054.ZHOU M J, MIAO H F, LU Z M, et al. The influence of different carbon sources on denitrification rate and community structure of denitrifying bacteria[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(12):2047-2054. [64] 裴廷权, 杨小毛, 刘欢, 等.不同缓释碳源对低碳氮比污水反硝化的影响[J]. 工业水处理,2013,33(5):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2013.05.011PEI T Q, YANG X M, LIU H, et al. Effect of different sustained-release carbon source on the denitrification of low C/N wastewater[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,2013,33(5):40-43. ◇ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2013.05.011 -




 下载:
下载: