Research hot spots and trends on the impacts of global agricultural production on groundwater in the past two decades
-
摘要:
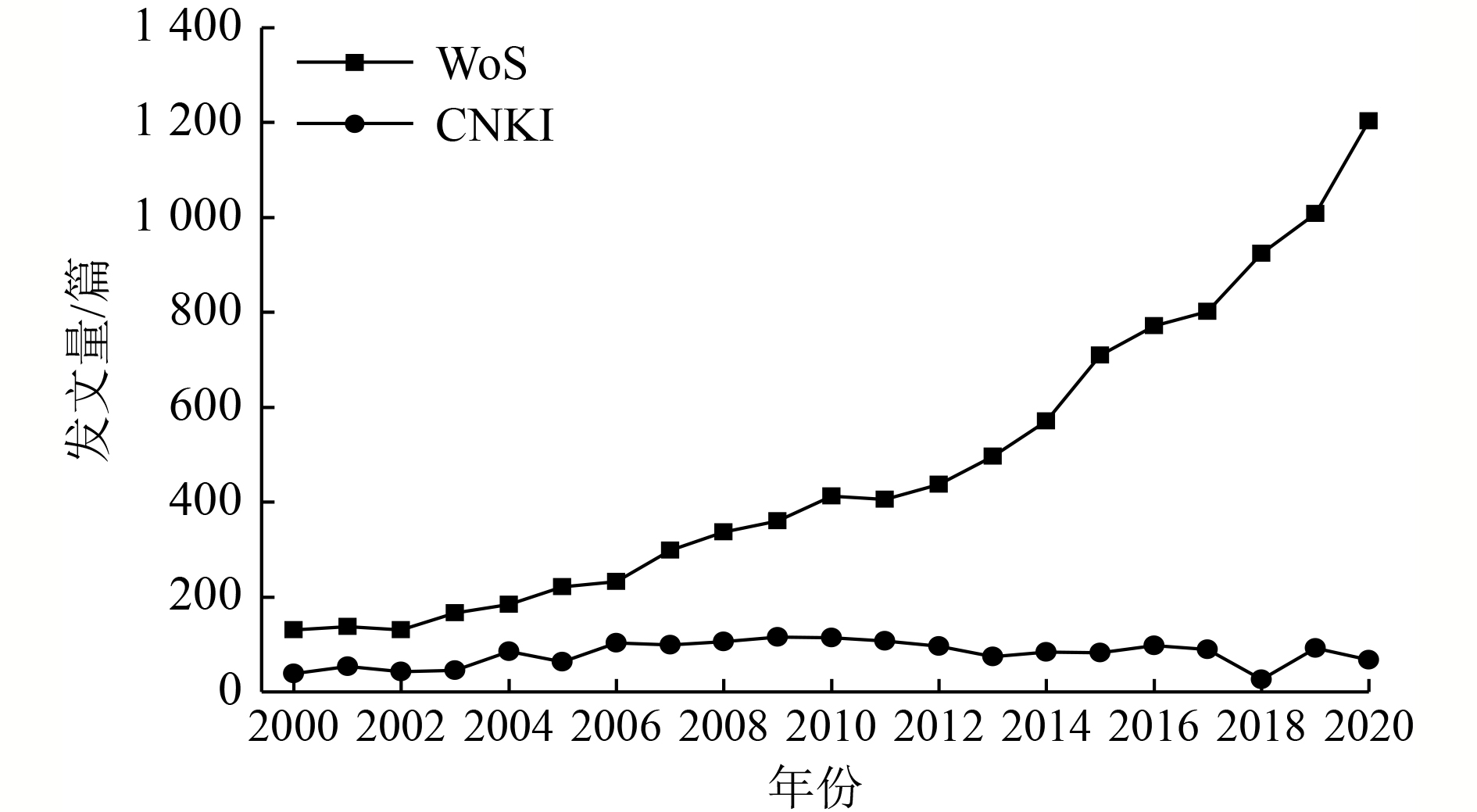
全球地下水开采总量的90%以上都被用于农业生产,地下水资源已成为事关全球粮食安全的重要战略资源。因此,明确全球农业生产对地下水影响研究的热点演进过程与未来趋势,对于灌溉农业的可持续发展和地下水资源的保护与利用具有重要意义。基于中国知网(CNKI)核心期刊数据库和Web of Science(WoS)数据库,通过可视化文献分析工具CiteSpace,对2000—2020年全球范围内农业生产对地下水影响研究领域的相关文献进行分析,总结该领域近20年的研究进展、研究热点和发展趋势。结果显示:在农业生产对地下水影响的研究中,CNKI和WoS发文量平均增速分别为1.45和53.7篇/a,美国和中国是该研究领域发文的主导国家,其发文量分别占总发文量的24.94%和15.70%;在全球各大研究机构中,中国科学院是该领域最具国际影响力的研究机构;农业面源污染和地下水健康风险评价是当前全球在该领域中的研究热点,并在人口激增、水资源匮乏、粮食短缺等以及全球气候变化的背景下将继续保持一定的热度;地下水超采是农业生产对地下水影响领域中重要的研究主题,Scanlon和Taylor等专家的高被引文章在该领域影响力较大。
Abstract:More than 90% of global groundwater exploitation is used for agricultural production, and groundwater has become an important strategic resource concerning global food security. Hence, understanding the research hot spots and the trends on the impacts of global agricultural production on groundwater is critical for sustainable irrigated agricultural development and groundwater resource protection and utilization. The article is based on China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) core journal database and Web of Science (WoS) database, the CiteSpace tool was employed to analyze the research papers concerning the impacts of agricultural production on groundwater globally from 2000 to 2020. This study aimed to summarize the frontier, hot spots, and trends of the research field in the past two decades. The results indicated that in the study of the impact of agricultural production on groundwater, the average annual increases of the number of CNKI and WoS papers reached 1.45 and 53.7, respectively. The United States and China were the leading countries in the research field on the impact of agricultural production on groundwater, accounting for 24.94% and 15.70% of published papers, respectively. Among the major research institutions in the world, Chinese Academy of Sciences was the most internationally influential academic institution. The themes of non-point agricultural pollution and groundwater health risk assessment both were the research hot spots worldwide, and would continue to be the hot research topics under the background of population increase, water resource shortage, food crisis and global climate change. Groundwater overexploitation was an important research theme in the field of the impacts of global agricultural production on groundwater, and the highly cited papers by experts Scanlon and Taylor et al were the most influential papers in this research field.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- agricultural production /
- CiteSpace /
- visual analysis /
- research hot spots
-
表 1 全球农业生产对地下水影响研究高频关键词
Table 1. High-frequency keywords of the research on the impact of global agricultural production on groundwater
CNKI WoS 关键词 年份 频次 关键词 年份 频次 地下水 2000 221 groundwater 2000 2890 水资源 2000 208 water 2000 1390 再生水 2006 65 soil 2000 1056 灌溉 2000 62 nitrate 2000 982 地下水埋深 2007 44 management 2000 915 对策 2000 31 irrigation 2000 855 可持续利用 2000 31 contamination 2000 792 土壤 2004 30 aquifer 2000 775 浅层地下水 2006 29 water quality 2000 767 硝态氮 2006 29 model 2000 719 生态环境 2004 24 nitrogen 2000 716 土壤水 2004 21 impact 2004 715 农业 2000 21 quality 2000 631 节水 2000 17 climate change 2006 608 河套灌区 2010 16 pollution 2000 602 地下水超采 2016 16 agriculture 2000 588 石羊河流域 2006 15 system 2000 583 硝酸盐 2008 13 land use 2000 547 可持续发展 2000 13 basin 2004 521 灌区 2000 12 surface water 2000 506 表 2 WoS农业生产对地下水影响研究被引次数排名前10的论文
Table 2. Top 10 articles in WoS on the research of the impact of agricultural production on groundwater
篇名 发表年份 作者 被引频次 所属聚类 Guidelines for drinking-water quality,4th ed 2011 World Health Organization(WHO) 73 #0 Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and indudtrial activities,mid-west China 2016 Wu J H 69 #0 Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley 2012 Scanlon B R 55 #6 Evidence of the dependence of groundwater resources on extreme rainfall in East Africa 2013 Taylor R G 51 #6 Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major infuencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County,China 2016 Li P Y 48 #0 The global groundwater crisis 2014 Famiglietti J S 48 #6 Water balance of global aquifers revealed by groundwater footprint 2012 Gleeson T 47 #6 Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India 2009 Rodell M 40 #6 Groundwater depletion embedded in international food trade 2017 Dalin C 38 #9 Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes 2008 Rivett M O 33 #3 -
[1] 胡汝骥, 陈曦, 姜逢清, 等.人类活动对亚洲中部水环境安全的威胁[J]. 干旱区研究,2011,28(2):189-197.HU R J, CHEN X, JIANG F Q, et al. Threat of human activities to hydrological regime in central Asia[J]. Arid Zone Research,2011,28(2):189-197. [2] 裴宏伟, 王彦芳, 沈彦俊, 等.美国高平原农业发展对地下水资源的影响及启示[J]. 农业现代化研究,2016,37(1):166-173.PEI H W, WANG Y F, SHEN Y J, et al. The impacts and enlightenments of irrigated agriculture on groundwater resources in the US High Plains[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization,2016,37(1):166-173. [3] 杨胜天, 于心怡, 丁建丽, 等.中亚地区水问题研究综述[J]. 地理学报,2017,72(1):79-93. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701007YANG S T, YU X Y, DING J L, et al. A review of water issues research in Central Asia[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2017,72(1):79-93. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701007 [4] PEI H W, SCANLON B R, SHEN Y J, et al. Impacts of varying agricultural intensification on crop yield and groundwater resources: comparison of the North China Plain and US High Plains[J]. Environmental Research Letters,2015,10(4):044013. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/10/4/044013 [5] 石建省, 王昭, 张兆吉, 等.华北平原深层地下水超采程度计算与分析[J]. 地学前缘,2010,17(6):215-220.SHI J S, WANG Z, ZHANG Z J, et al. Assessment of over-exploitation of deep groundwater in the North China Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2010,17(6):215-220. [6] CALISKAN S, OZKAYA I, CALISKAN M E, et al. The effects of nitrogen and iron fertilization on growth, yield and fertilizer use efficiency of soybean in a Mediterranean-type soil[J]. Field Crops Research,2008,108(2):126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2008.04.005 [7] GRILLO R, PEREIRA A E S, NISHISAKA C S, et al. Chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles loaded with paraquat herbicide: an environmentally safer alternative for weed control[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,278:163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.079 [8] SCHOUMANS O F, CHARDON W J, BECHMANN M E, et al. Mitigation options to reduce phosphorus losses from the agricultural sector and improve surface water quality: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,468/469:1255-1266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.061 [9] 裴宏伟, 沈彦俊, 刘昌明.华北平原典型农田氮素与水分循环[J]. 应用生态学报,2015,26(1):283-296.PEI H W, SHEN Y J, LIU C M. Nitrogen and water cycling of typical cropland in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2015,26(1):283-296. [10] DÖLL P, HOFFMANN-DOBREV H, PORTMANN F T, et al. Impact of water withdrawals from groundwater and surface water on continental water storage variations[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,2012,59/60:143-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2011.05.001 [11] HAO A B, ZHANG Y L, ZHANG E Y, et al. Review: groundwater resources and related environmental issues in China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(5):1325-1337. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1787-1 [12] 喻朝庆.水-氮耦合机制下的中国粮食与环境安全[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(12):2018-2036. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0041YU C Q. The coupled effects of water and nitrogen on China's food and environmental securities[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2019,49(12):2018-2036. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0041 [13] 安源, 张玲.文献计量学在我国图书情报领域的应用研究进展综述[J]. 图书馆,2014(5):63-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1558.2014.05.018AN Y, ZHANG L. Applied research summary on bibliometrics in library and information field[J]. Library,2014(5):63-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1558.2014.05.018 [14] ZOU X, YUE W L, VU H L. Visualization and analysis of mapping knowledge domain of road safety studies[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention,2018,118:131-145. [15] 曹树金, 吴育冰, 韦景竹, 等.知识图谱研究的脉络、流派与趋势: 基于SSCI与CSSCI期刊论文的计量与可视化[J]. 中国图书馆学报,2015,41(5):16-34.CAO S J, WU Y B, WEI J Z, et al. History, schools and trend in knowledge map: investigation and visualization based on SSCI and CSSCI[J]. Journal of Library Science in China,2015,41(5):16-34. [16] CHEN C M. CiteSpace Ⅱ: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2006,57(3):359-377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317 [17] 陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2053.2015.02.009CHEN Y, CHEN C M, LIU Z Y, et al. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains[J]. Studies in Science of Science,2015,33(2):242-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2053.2015.02.009 [18] 侯剑华, 胡志刚.CiteSpace软件应用研究的回顾与展望[J]. 现代情报,2013,33(4):99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2013.04.022HOU J H, HU Z G. Review on the application of CiteSpace at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Modern Information,2013,33(4):99-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2013.04.022 [19] CHEN C M. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(Suppl 1): 5303-5310. [20] 李杰, 陈超美. CiteSpace: 科技文本挖掘及可视化[M]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学出版社, 2016. [21] 李思奇, 邬娜, 吴佳, 等.基于CiteSpace的中国产业转移研究热点与趋势分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):599-608. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200182LI S Q, WU N, WU J, et al. Analysis of research hotspots and trends of China's industrial transfer based on CiteSpace[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):599-608. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200182 [22] 谢浩, 李军, 邹胜章, 等.基于文献计量学的地下水污染研究现状[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2021,19(1):168-178.XIE H, LI J, ZOU S Z, et al. Research status of groundwater pollution based on bibliometrics[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2021,19(1):168-178. [23] 林德明, 陈超美, 刘则渊.共被引网络中介中心性的Zipf-Pareto分布研究[J]. 情报学报,2011,30(1):76-82. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1000-0135.2011.01.011LIN D M, CHEN C M, LIU Z Y. Study on Zipf-Pareto distribution of the betweenness centrality of a co-citation network[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information,2011,30(1):76-82. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1000-0135.2011.01.011 [24] 何书金, 刘昌明, 袁振杰.从《地理学报》创刊85年载文审视中国地理学发展特征[J]. 地理学报,2019,74(11):2209-2229. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201911002HE S J, LIU C M, YUAN Z J. Development of geographical research in China through the lens of publication in the Acta Geographica Sinica between 1934 and 2018[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2019,74(11):2209-2229. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201911002 [25] ZHONG S H, CHEN R, SONG F, et al. Knowledge mapping of carbon footprint research in a LCA perspective: a visual analysis using CiteSpace[J]. Processes,2019,7(11):818. doi: 10.3390/pr7110818 [26] 孟凡乔, 王坤, 肖广敏, 等.华北平原潮土区粮田氮淋失阻控措施及效果分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2021,29(1):141-153.MENG F Q, WANG K, XIAO G M, et al. Nitrogen leaching mitigation in fluvo-aquic soil in the North China Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2021,29(1):141-153. [27] 曹文杰, 赵瑞莹.国际农业面源污染研究演进与前沿: 基于CiteSpace的量化分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(7):1-9.CAO W J, ZHAO R Y. Evolution and frontiers of international agricultural diffused pollution research: quantitative analysis based on CiteSpace[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2019,33(7):1-9. [28] 陈悦, 陈超美, 胡志刚. 引文空间分析原理与应用: CiteSpace实用指南[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. [29] WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quality[S]. 4th ed. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2011. [30] SCANLON B R, FAUNT C C, LONGUEVERGNE L, et al. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2012,109(24):9320-9325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200311109 [31] TAYLOR R G, TODD M C, KONGOLA L, et al. Evidence of the dependence of groundwater resources on extreme rainfall in East Africa[J]. Nature Climate Change,2013,3(4):374-378. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1731 [32] FAMIGLIETTI J S. The global groundwater crisis[J]. Nature Climate Change,2014,4(11):945-948. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2425 [33] GLEESON T, WADA Y, BIERKENS M F P, et al. Water balance of global aquifers revealed by groundwater footprint[J]. Nature,2012,488(7410):197-200. doi: 10.1038/nature11295 [34] RODELL M, VELICOGNA I, FAMIGLIETTI J S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India[J]. Nature,2009,460(7258):999-1002. doi: 10.1038/nature08238 [35] DALIN C, WADA Y, KASTNER T, et al. Groundwater depletion embedded in international food trade[J]. Nature,2017,543(7647):700-704. doi: 10.1038/nature21403 [36] DÖLL P, MÜLLER SCHMIED H, SCHUH C, et al. Global-scale assessment of groundwater depletion and related groundwater abstractions: combining hydrological modeling with information from well observations and GRACE satellites[J]. Water Resources Research,2014,50(7):5698-5720. doi: 10.1002/2014WR015595 [37] FENG W, ZHONG M, LEMOINE J M, et al. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the gravity recovery and climate experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements[J]. Water Resources Research,2013,49(4):2110-2118. doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20192 [38] 陈飞, 丁跃元, 李原园, 等.华北地区地下水超采治理实践与思考[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2020,18(2):191-198.CHEN F, DING Y Y, LI Y Y, et al. Practice and consideration of groundwater overexploitation in North China Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020,18(2):191-198. [39] 贺亚雪, 代朝猛, 苏益明, 等.地下水重金属污染修复技术研究进展[J]. 水处理技术,2016,42(2):1-5.HE Y X, DAI C M, SU Y M, et al. Research progress of remediation technologies on heavy metal pollution in groundwater[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2016,42(2):1-5. [40] 李元杰, 王森杰, 张敏, 等.土壤和地下水污染的监控自然衰减修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(3):1185-1193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.047LI Y J, WANG S J, ZHANG M, et al. Research progress of monitored natural attenuation remediation technology for soil and groundwater pollution[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(3):1185-1193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.047 [41] LI Y L, LI P Y, CUI X H, et al. Groundwater quality, health risk, and major influencing factors in the lower Beiluo River watershed of northwest China[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: an International Journal,2021,27(7):1987-2013. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2021.1940834 [42] GÜNER E D, CEKIM H O, SEÇKIN G. Determination of water quality assessment in wells of the Göksu plains using multivariate statistical techniques[J]. Environmental Forensics,2021,22(1/2):172-188. ⊗ -





 下载:
下载: