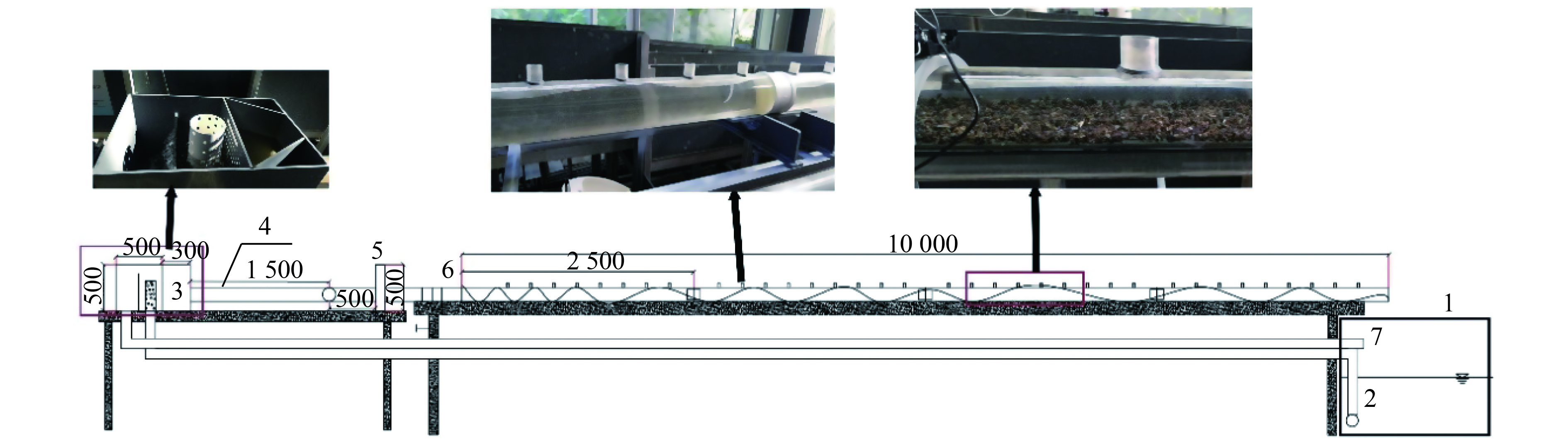
Simulation test on the influence of sediment accumulation on the drainage capacity of rainwater pipeline
-
摘要:
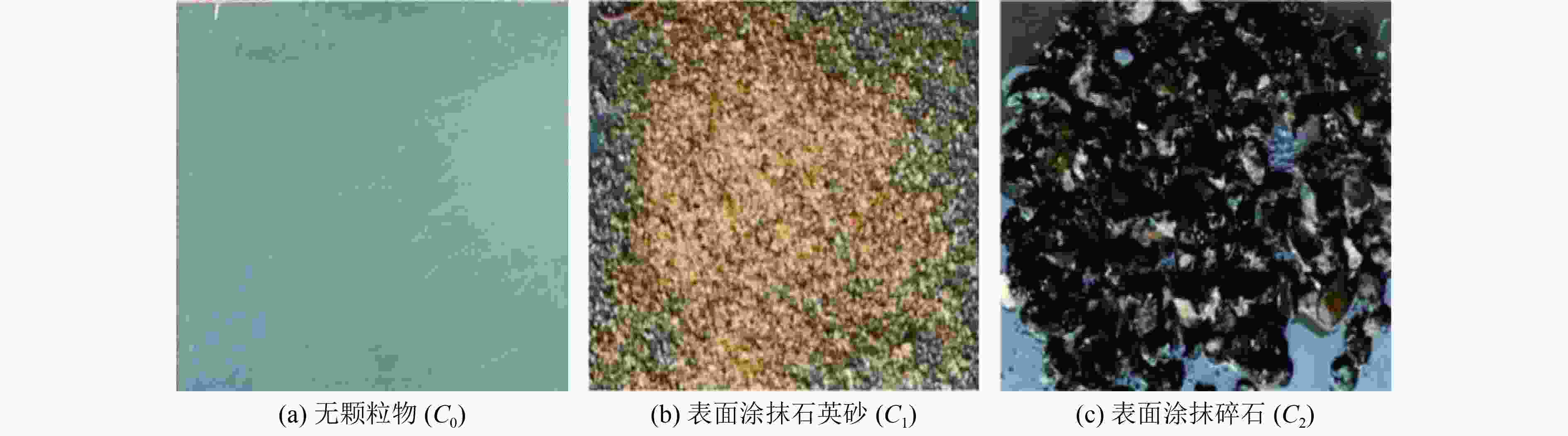
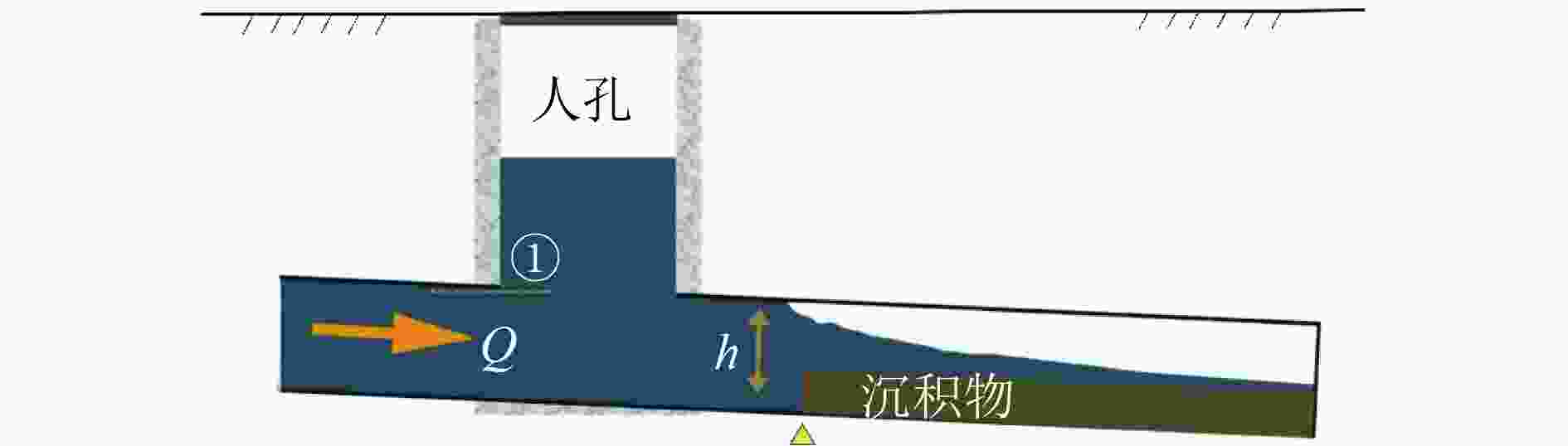
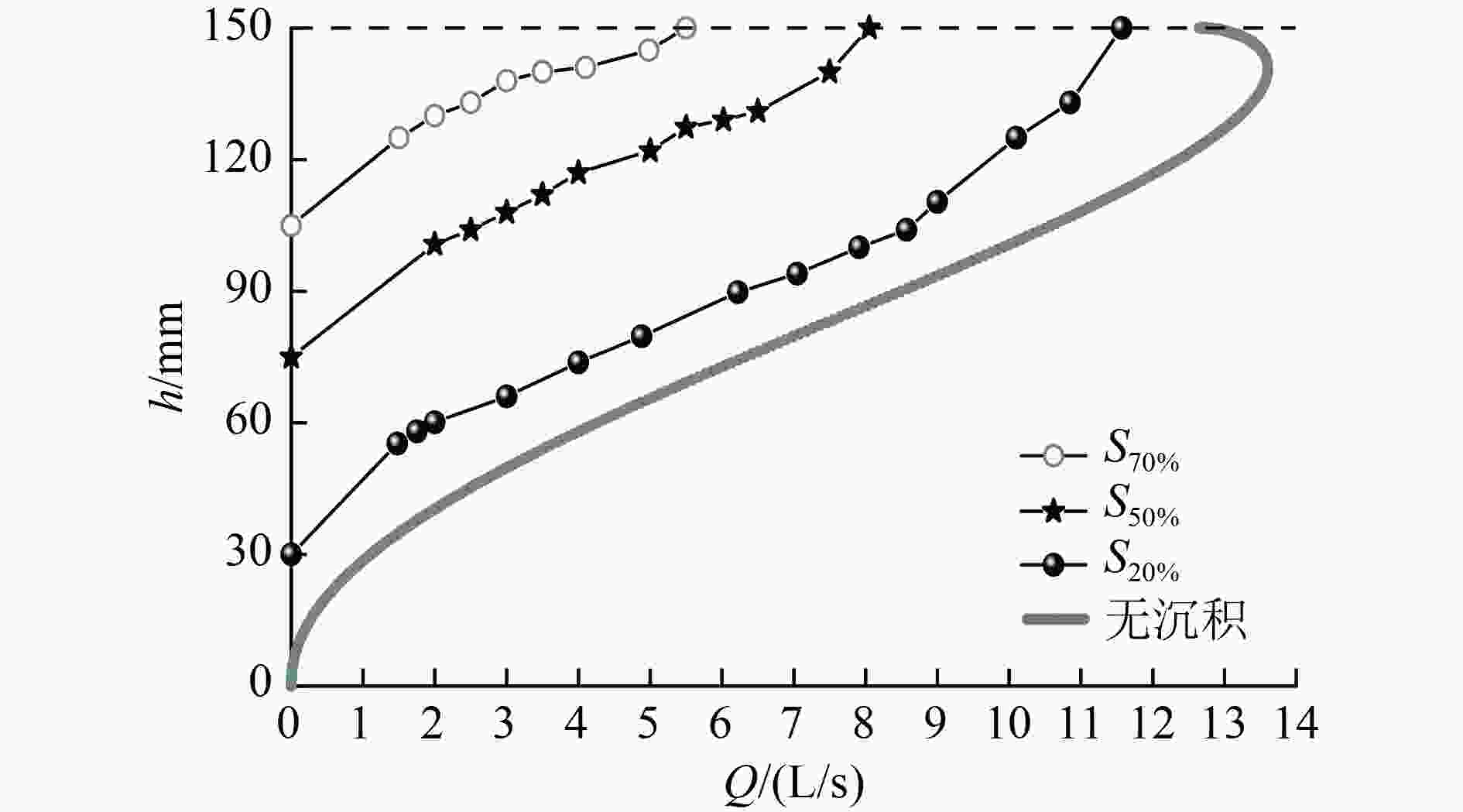
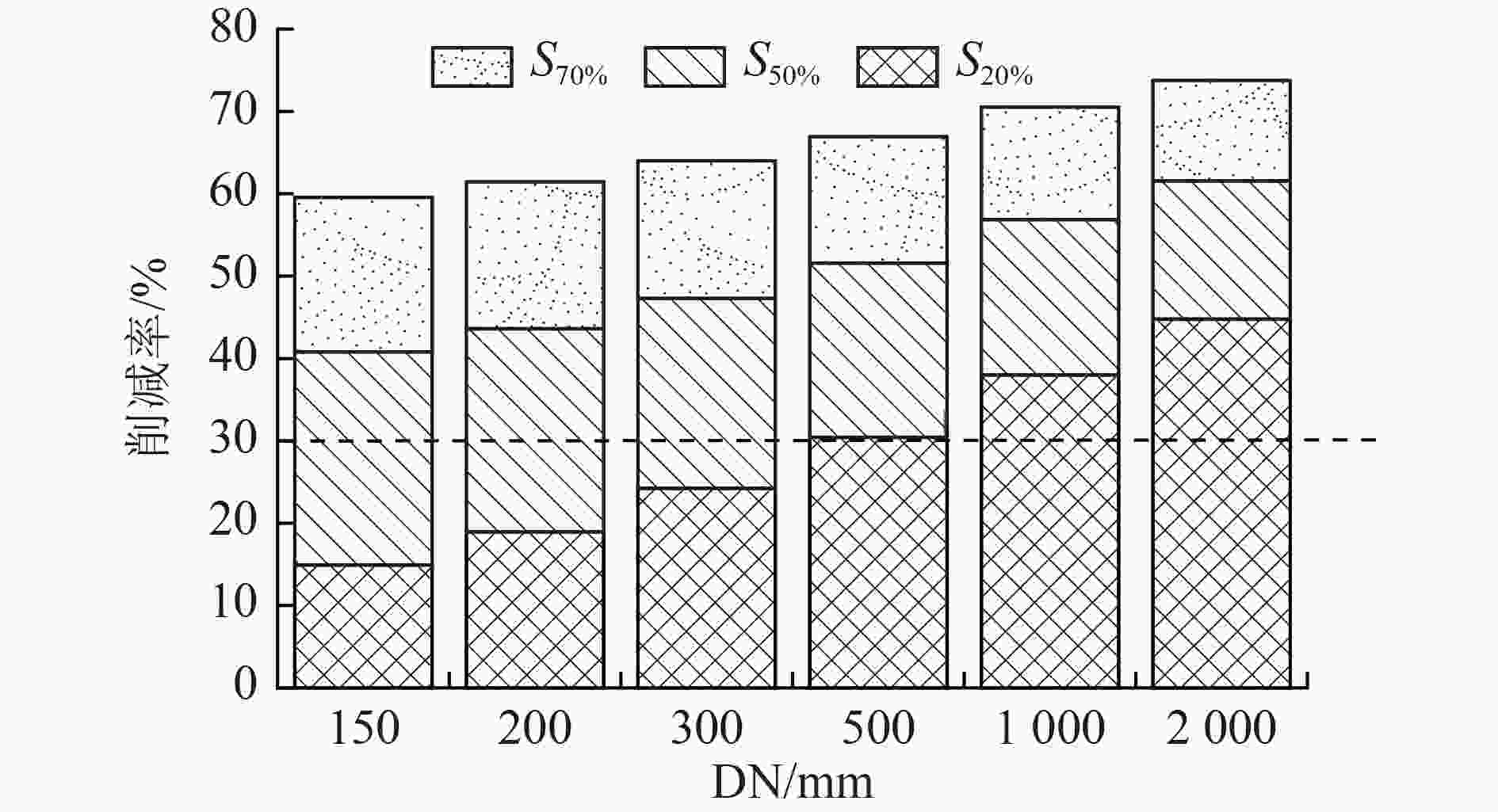
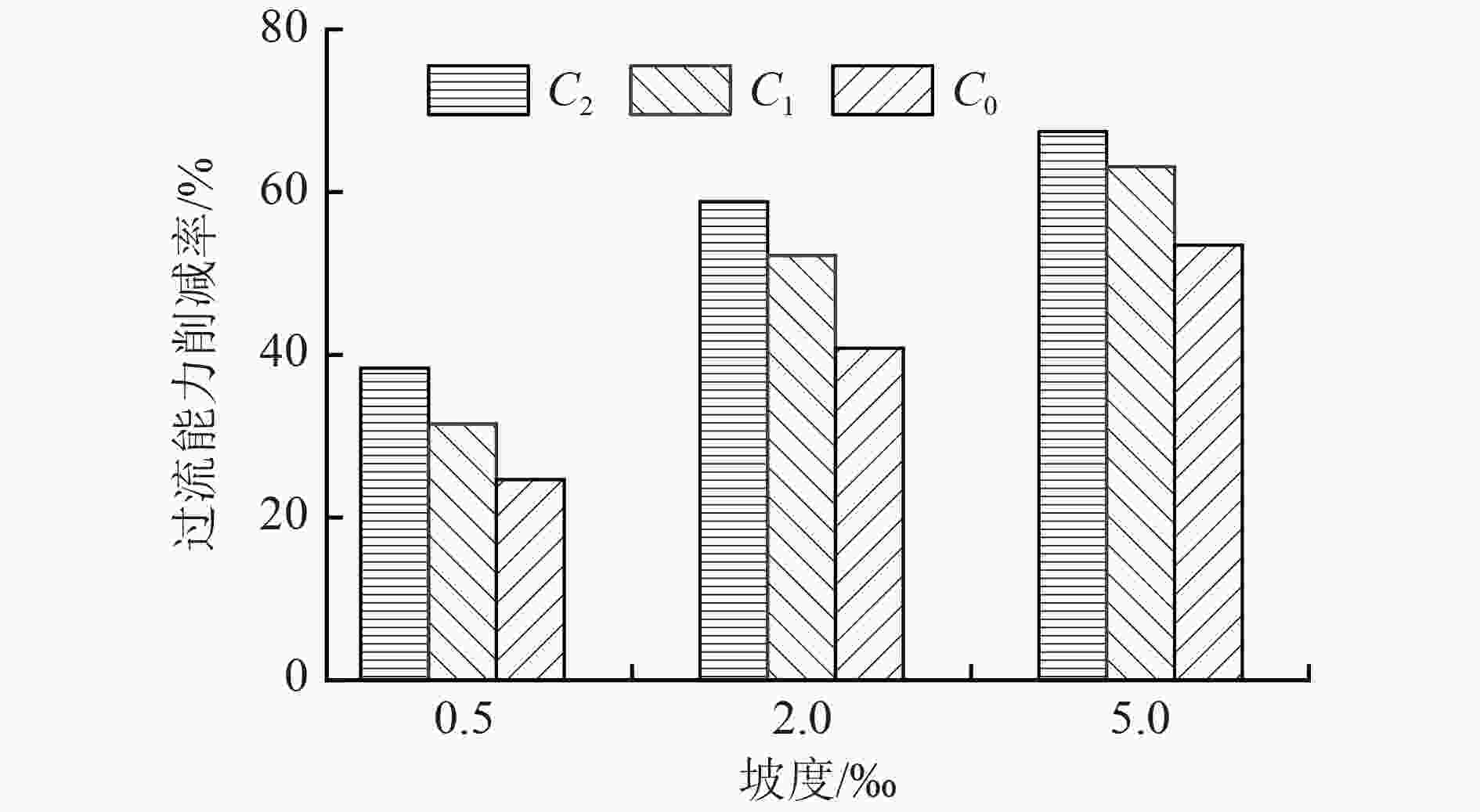
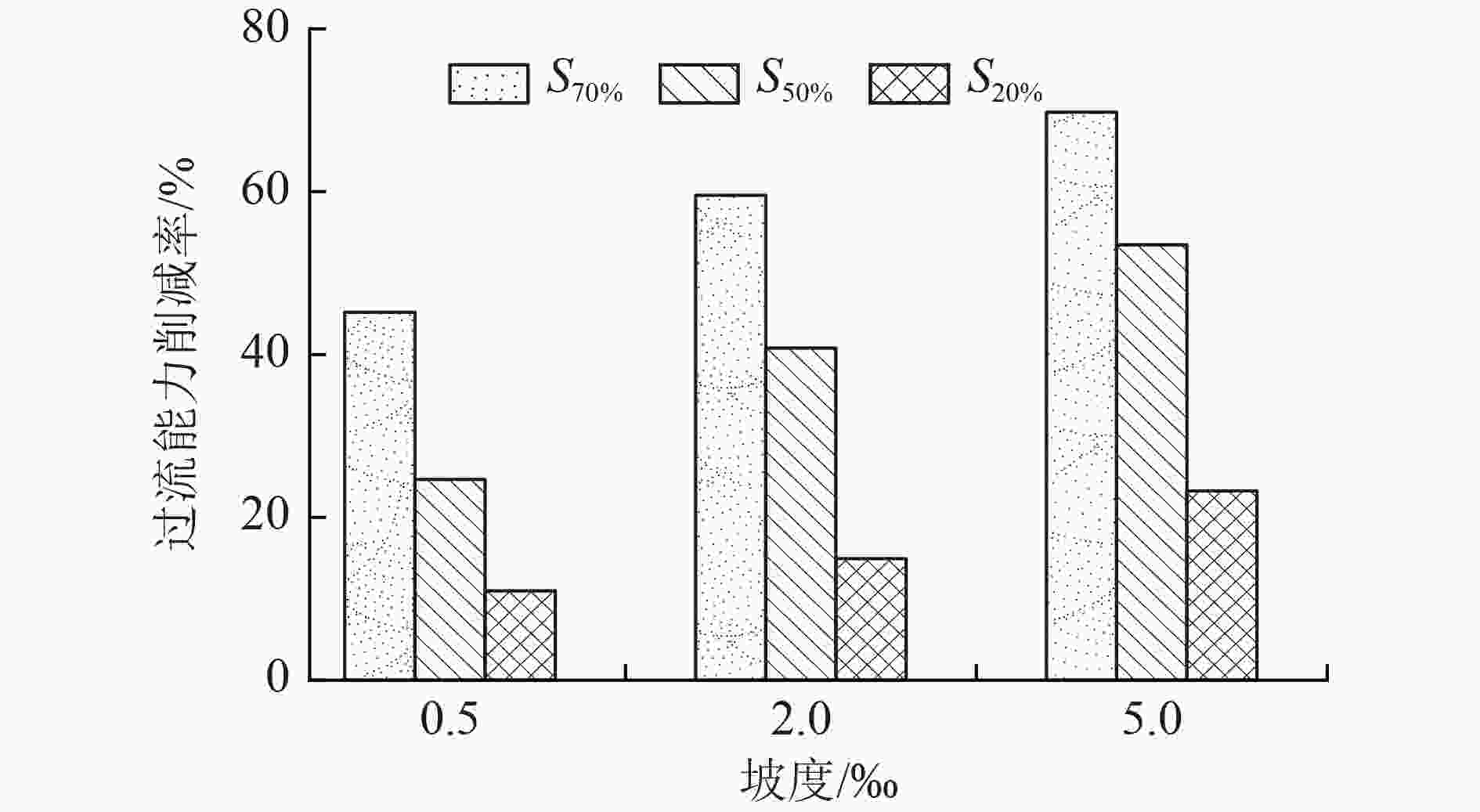
我国大部分城市的雨水管道都存在沉积物累积现象,其一方面阻塞管道,降低过流能力,引发积水内涝,另一方面也是造成受纳水体冲击污染的主要原因之一。针对上述问题,通过实验室试验,研究了沉积物累积厚度、沉积物表面粗糙程度、管道坡度等因素对雨水管道过流能力的影响。结果表明:在坡度为2‰条件下,当管径为150 mm时,沉积物累积厚度从管道直径的20%增至70%,过流能力削减率从14.93%增至59.56%;根据水力学相似准则,当管径为2 000 mm时,沉积物累积厚度从20%增至70%,过流能力削减率从44.78%增至73.75%。因此,过流能力削减率随沉积物累积厚度和管径的增加而增加。试验条件下,沉积物表面粗糙度变化对过流能力无显著影响,随粗糙度增加,过流能力削减率变化幅度的平均值为5.93个百分点;而坡度变化对过流能力的影响较为明显,试验条件下过流能力削减率变化幅度为12.30~28.83个百分点。研究结果可为城市雨水排水管道的优化设计、维护管理、监测评估提供依据。
Abstract:Most rainwater drainage pipelines in China have sediment accumulation phonomenon, which often blocks the pipeline and reduces the drainage capacity, resulting in water logging. Meanwhile, the sediment accumulation is also one of the main sources of abruptly pollution in the receiving water. In view of the above problems, the effects of sediments accumulation thickness, sediment surface roughness and pipeline slope on the drainage capacity of rainwater pipeline were studied through laboratory experiment. The results showed that with the pipeline slope of 2‰, and when pipe diameter was 150 mm, the sediment accumulation thickness increased from 20% to 70%, and the reduction rate of drainage capacity increased from 14.93% to 59.56%. According to the hydraulic similarity criterion, when the diameter of pipeline was 2 000 mm, the sediment accumulation thickness increased from 20% to 70%, and the reduction rate of drainage capacity increased from 44.78% to 73.75%. Therefore, the reduction rate of drainage capacity increased with the increase of sediment cumulative thickness and pipe diameter. The changing of surface roughness of the sediment has no markedly effect on the drainage capacity, under experimental conditions, the average increase in drainage capacity reduction was 5.93 percentage points, while the slope change had a more obvious effect on the drainage capacity. When the slope increased, the reduction range of drainage capacity was 12.30-28.83 percentage points. Overall, the research results could provide a support for the optimization design, maintenance management, monitoring and evaluation of urban rainwater drainage pipeline.
-
Key words:
- sediment /
- rainwater drainage pipeline /
- drainage capacity /
- roughness /
- slope
-
-
[1] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015. [2] 黄乃先, 齐一凡, 金伟.排水管道沉积物控制的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):507-513. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210017HUANG N X, QI Y F, JIN W. Research progress on the control of sediments in the drainage pipe[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):507-513. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210017 [3] 李茂英, 李海燕.城市排水管道中沉积物及其污染研究进展[J]. 给水排水,2008,44(增刊1):88-92. [4] 尹海龙, 王月, 赵刚.分流制系统雨水管网混接旱天排放污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2019,39(10):3551-3558.YIN H L, WANG Y, ZHAO G. A study on characteristics of dry-weather discharge pollution from separate storm drains with inappropriate flow entries[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2019,39(10):3551-3558. [5] YANG L H, LI J Z, ZHOU K K, et al. The effects of surface pollution on urban river water quality under rainfall events in Wuqing District, Tianjin, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,293:126136. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126136 [6] WANG Q, ZHANG Q H, WU Y, et al. Physicochemical conditions and properties of particles in urban runoff and rivers: implications for runoff pollution[J]. Chemosphere,2017,173:318-325. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.066 [7] HANNOUCHE A, CHEBBO G, JOANNIS C. Assessment of the contribution of sewer deposits to suspended solids loads in combined sewer systems during rain events[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2014,21(8):5311-5317. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2395-1 [8] 尚宇, 周毅, 廖安意, 等.雨水管道沉积物沉淀特性及主要污染物含量分布[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(8):3696-3703.SHANG Y, ZHOU Y, LIAO A Y, et al. Sedimentation characteristics and pollutant content distribution of storm drainage sediments[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(8):3696-3703. [9] 司韦, 于江华, 解丽媛.雨水管道沉积物粒径分布与污染特征研究[J]. 环境科技,2021,34(1):35-40.SI W, YU J H, XIE L Y. Study on the particle size distribution and pollution characteristics of rainwater pipe sediments[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2021,34(1):35-40. [10] 桑浪涛, 石烜, 张彤, 等.城市污水管网中污染物冲刷与沉积规律[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(5):1965-1971.SANG L T, SHI X, ZHANG T, et al. Law of pollutant erosion and deposition in urban sewage network[J]. Environmental Science,2017,38(5):1965-1971. [11] 徐强强, 李阳, 马黎, 等.城市雨水管道沉积物氮磷污染溶出特性试验研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(3):646-654.XU Q Q, LI Y, MA L, et al. Experimental study on leaching characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in urban rainwater pipeline sediment[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(3):646-654. [12] 张怡蕾, 操家顺, 薛朝霞, 等.城市排水管道内污染物迁移转化规律研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(1):111-121.ZHANG Y L, CAO J S, XUE Z X, et al. Research progress on the pollutants migration and transformation in municipal sewer[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(1):111-121. [13] TANG Y B, ZHU D Z, RAJARATNAM N, et al. Sediment depositions in a submerged storm sewer pipe[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering,2020,146(10):04020118. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001799 [14] SONG Y, YUN R, LEE E, et al. Predicting sedimentation in urban sewer conduits[J]. Water,2018,10(4):462. doi: 10.3390/w10040462 [15] 桑浪涛. 管道中污染物在污水-沉积物间的迁移转化规律研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017. [16] 付博文. 城市污水管道中污染物沉积特性研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2016. [17] 卢渊博. 排水管道淤积过流特性与点源污染扩散规律研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2020. [18] 王晓静, 陈永祥.城市排水管道结构性缺陷及应对策略[J]. 城乡建设,2020(5):51-53. [19] 王冬梅, 张士林.水平管道淤积断面紊流的速度分布研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2005,7(2):66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2005.02.012WANG D M, ZHANG S L. Research on water velocity in filling up section of horizontal pipe[J]. Engineering Science,2005,7(2):66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2005.02.012 [20] 文碧岚, 李树平, 沈继龙, 等.排水管道淤积状况模拟分析[J]. 给水排水,2015,51(7):151-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2015.07.037WEN B L, LI S P, SHEN J L, et al. Modelling of sewer sedimentation accumulating[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering,2015,51(7):151-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2015.07.037 [21] 龙同云. 城市排水管道内障碍物对过流能力的影响研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2016. [22] 李书友, 冯亚辉.管道无压流的过流能力研究[J]. 水利科技与经济,2012,18(4):11-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2012.04.004LI S Y, FENG Y H. Discharge capacity research on pipeline free flow[J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy,2012,18(4):11-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2012.04.004 [23] 住房和城乡建设部. 室外排水设计标准: GB 50014—2021[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社有限公司, 2021. [24] 张亚琦. 综合管廊排水管道堵塞识别理论与试验研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2019. [25] 李斌, 王以兵, 丁林.山地灌区重力流下管道极限流速探讨[J]. 人民黄河,2013,35(2):81-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.02.029LI B, WANG Y B, DING L. Investigation for the pipeline limit flow rates of gravity flow conditions in mountain irrigation area[J]. Yellow River,2013,35(2):81-82. ◇ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.02.029 -




 下载:
下载: