Research status and development trend of the technology for arsenic removal from groundwater
-
摘要:
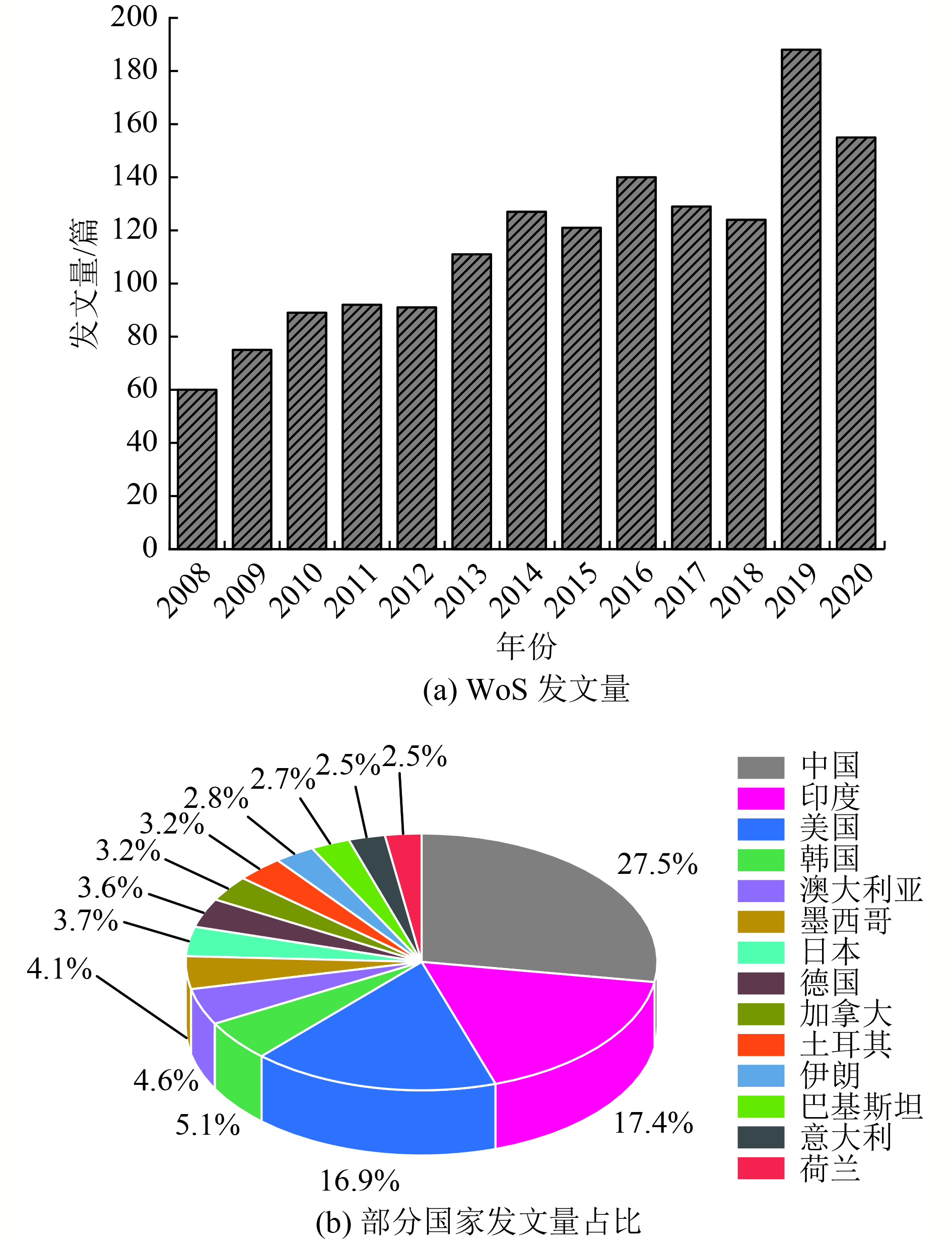
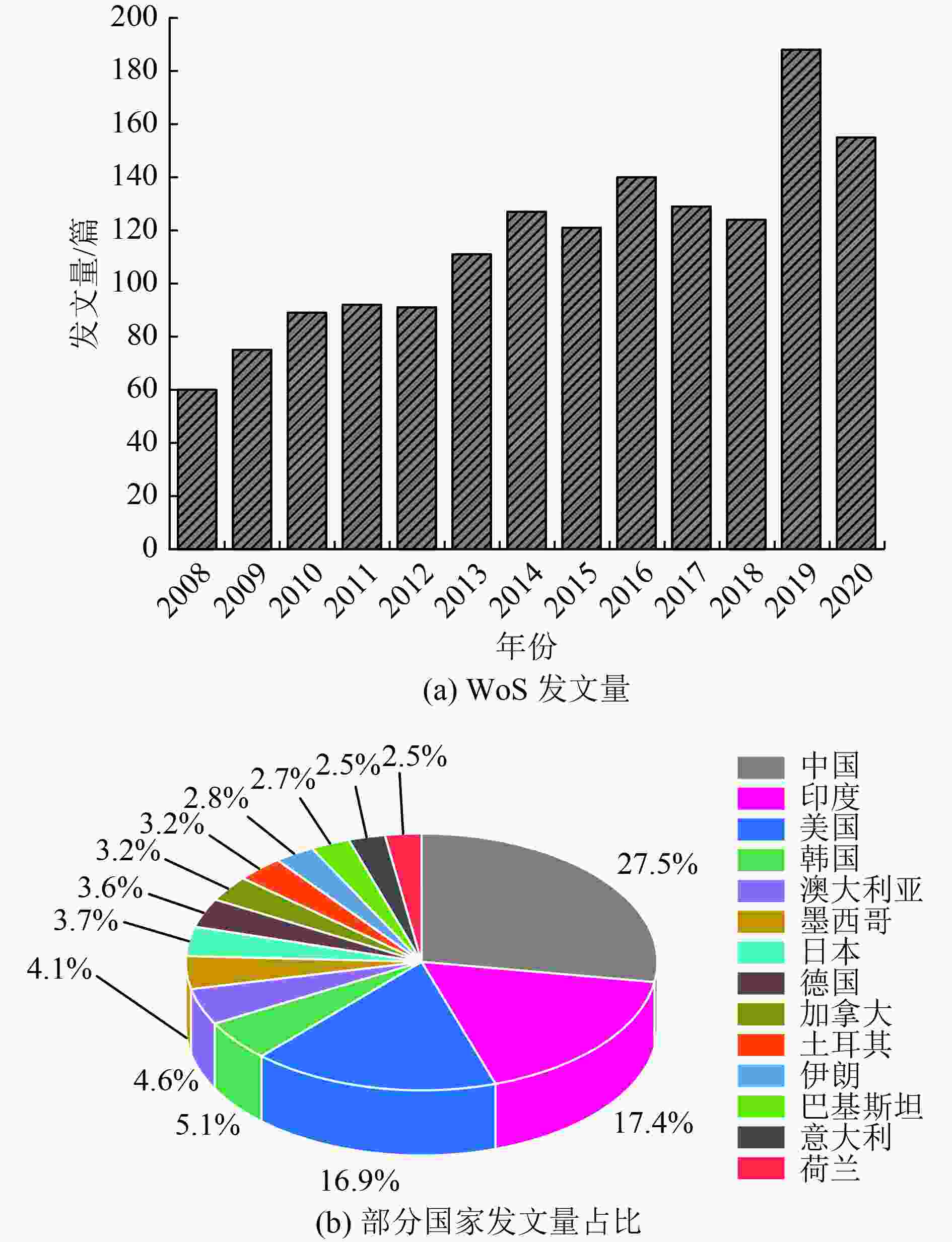
为明确地下水脱砷技术研究现状及未来发展趋势,采用文献计量学方法统计分析了Web of Science(WoS)数据库中2008—2020年发表的关于地下水脱砷技术的文献资料,并从年度发文量、发文机构、发文期刊、发文作者以及论文关键词等方面进行分析。结果表明:WoS数据库中地下水脱砷技术方面的研究型论文共1 501篇,年度发文量总体呈上升趋势;中国、美国和印度为发文量排名前3的国家;共计1 503家研究机构、4 875名作者参与地下水脱砷技术研究,其中高等院校为主要研究机构,而高校教师与硕士、博士研究生则为研究的主力军;关键词分析表明,吸附和电絮凝技术是地下水脱砷的主流方法,其中零价铁材料作为吸附剂是贯穿2008—2020年的研究热点;通过突现分析得出,二元甚至多元氧化物和纳米复合材料的制备将成为未来地下水脱砷技术研究的热点方向。
-
关键词:
- 地下水 /
- 除砷 /
- 文献计量 /
- 研究趋势 /
- Web of Science(WoS)数据库
Abstract:To clarify the research status and future development trend of arsenic removal from groundwater, the bibliometric method was used to analyze the literature on arsenic removal from groundwater published in the Web of Science (WoS) database from 2008 to 2020, and the comprehensive analysis was conducted from the aspects of the annual number of articles published, publishing organizations, journals, authors, and keywords. The results indicated that: in WoS database, there were 1 501 research papers on arsenic removal from groundwater, and the annual number of publications was on an overall upward trend; the top three countries in terms of publication volume were China, the United States and India; a total of 1 503 research institutions and 4 875 authors participated in the research of arsenic removal from groundwater, in which universities were the main research bases, and university teachers, postgraduate students werethe main force of the research. Keywords analysis showed that the adsorption and electrocoagulation technology were the mainstream methods for arsenic removal from groundwater, the zero-valent iron materials were popular adsorbents applied in the research from 2008 to 2020. At the same time, the emergence analysis showed that the preparation of binary or even multiple oxides and nanocomposites would become the frontier hotspot in the research of arsenic removal from groundwater.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- arsenic removal /
- bibliometrics /
- researching trends /
- Web of Science (WoS) database
-
表 1 2008—2020年发文量排名前5的国家及其发文量
Table 1. Top 5 countries and their annual number of publications from 2008 to 2020
篇 年份 中国 印度 美国 韩国 澳大利亚 2008 5 12 20 5 0 2009 9 12 19 8 3 2010 15 22 18 3 1 2011 19 17 18 4 0 2012 30 21 19 4 1 2013 26 21 21 4 4 2014 34 18 27 3 2 2015 30 20 23 3 5 2016 40 26 29 6 9 2017 47 15 16 8 3 2018 33 16 16 9 7 2019 46 36 14 8 16 2020 35 30 19 11 17 表 2 2008—2020年地下水脱砷技术研究发文量排名前10的期刊
Table 2. Top 10 journals in the number of articles published on groundwater arsenic removal technology from 2008 to 2020
期刊名称 发文
量/篇发文量
占比/%2020年影响因子 科学网
学科类别Journal of Hazardous Materials 94 6.26 9.04 工程技术 Desalination and Water Treatment 60 4.00 0.85 工程技术 Water Research 58 3.86 9.13 环境科学
与生态学Chemical Engineering Journal 51 3.40 10.65 工程技术 Chemosphere 48 3.20 5.78 环境科学与
生态学Environmental Science & Technology 48 3.20 4.36 环境科学
与生态学Environmental Science and Pollution Research 42 2.80 3.06 环境科学
与生态学Science of the Total Environmental 41 2.73 6.55 环境科学
与生态学Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances Environmental Engineering 28 1.87 0.97 环境科学
与生态学RSC Advances 28 1.87 3.12 化学 表 3 2008—2020年地下水脱砷技术研究发文量排名前20的发文机构
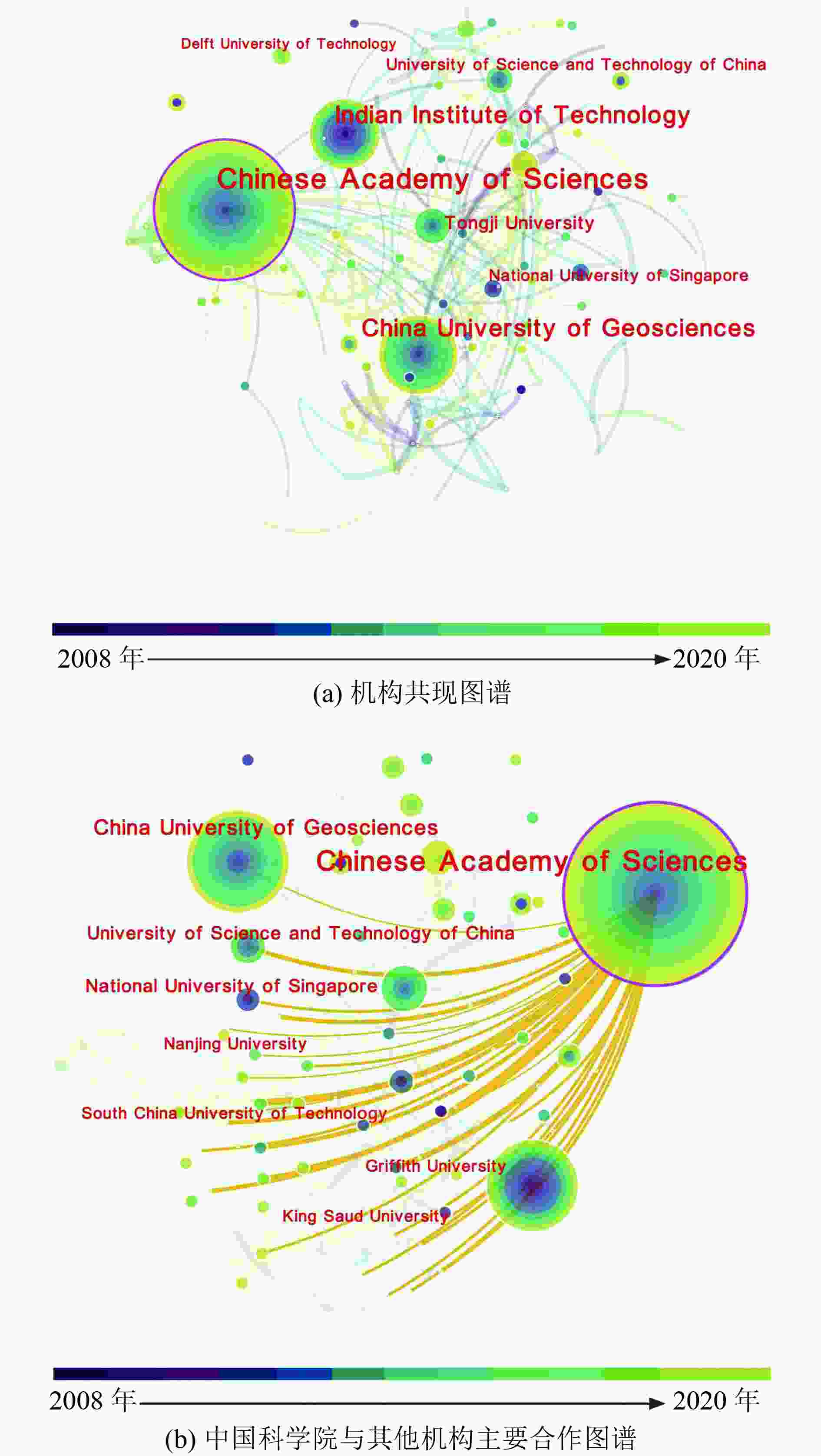
Table 3. Top 20 institutions in the number of articles published in groundwater arsenic removal technology from 2008 to 2020
机构名称 发文量/篇 占比/
%排名 英文名称 中文名称 Chinese Academy of Sciences 中国科学院 83 5.53 1 China University of Geosciences 中国地质大学 52 3.46 2 Indian Institute of Technology 印度理工学院 46 3.07 3 Tongji University 同济大学 23 1.53 4 Indian Institute of Technology 印度国立理工学院 18 1.20 5 National University of Singapore 新加坡国立大学 16 1.07 6 University Guanajuato 瓜纳华托大学 16 1.07 6 Nanjing University 南京大学 15 1.00 8 University of California, Berkeley 加州大学伯克利分校 15 1.00 8 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences 中国科学院大学 15 1.00 8 University of Science and Technology of China 中国科学技术大学 15 1.00 8 University of Southern Queensland 南昆士兰大学 15 1.00 8 Delft University of Technology 代尔夫特大学技术学院 14 0.93 13 Taiwan University 台湾大学 14 0.93 13 University of Belgrade 贝尔格莱德大学 14 0.93 13 University of Novi Sad 诺维萨德大学 14 0.93 13 US Environmental Protection Agency 美国国家环境保护局 14 0.93 13 Central South University 中南大学 12 0.80 18 Cheng Kung University 台湾成功大学 12 0.80 18 Tsinghua University 清华大学 12 0.80 18 表 4 2008—2020年出现频次排名前20的地下水脱砷技术研究的关键词
Table 4. Keywords of groundwater arsenic removal technology with top 20 occurrences in 2008-2020
排序 关键词 出现频次/次 中心性 英文名称 中文名称 1 groundwater 地下水 961 0.00 2 adsorption 吸附 717 0.00 3 arsenic 砷 539 0.00 4 drinking water 饮用水 421 0.01 5 removal 去除 421 0.00 6 water 水资源 388 0.01 7 arsenic removal 砷去除 370 0.01 8 aqueous solution 水溶液 336 0.02 9 sorption 吸附作用 299 0.02 10 iron 铁矿 285 0.01 11 oxidation 氧化 225 0.02 12 adsorbent 吸附剂 211 0.02 13 kinetics 动力学 205 0.02 14 As(Ⅲ) 三价砷 199 0.02 15 nanoparticle 纳米颗粒 151 0.02 16 contamination 污染物 150 0.02 17 As(Ⅴ) 五价砷 138 0.04 18 zero valent iron 零价铁 124 0.04 19 remediation 修复 121 0.04 20 speciation 物种形成 120 0.02 表 5 2008—2020年地下水脱砷技术研究关键词突现图谱
Table 5. Keywords of groundwater arsenic removal technology from 2008 to 2020
关键词 年份 突现图谱 英文名称 中文名称 zerovalent iron 零价铁 2008—2010 
hydroxide 羟化物 2008—2011 
Bangladesh 孟加拉国 2008—2010 
phosphate 磷酸 2008—2009 
alumina 氧化铝 2008—2011 
carbonate 碳酸盐 2008—2011 
binary oxide 二元氧化物 2016—2020 
electrode 电极 2016—2020 
iron electrocoagulation 铁电凝法 2016—2018 
Fe(Ⅱ) 二价铁 2017—2018 
hexavalent chromium 六价铬 2017—2018 
in situ 原位 2017—2018 
Fe 铁 2017—2018 
graphene oxide 石墨烯氧化物 2017—2020 
pollution 污染 2017—2020 
contaminant 污染物 2017—2020 
biochar 生物炭 2018—2020 
adsorptive removal 吸附去除 2018—2020 
health risk 健康风险 2018—2020 
risk assessment 风险评估 2018—2020 
response surface methodology 响应面法 2018—2020 
methylene blue 亚甲蓝 2018—2020 
simultaneous removal 同时去除 2018—2020 
waste water 废水 2018—2020 
nanocomposite 纳米复合材料 2018—2020 
-
[1] SINHA D, PRASAD P. Health effects inflicted by chronic low-level arsenic contamination in groundwater: a global public health challenge[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2020,40(1):87-131. doi: 10.1002/jat.3823 [2] CHEN Q Y, COSTA M. Arsenic: a global environmental challenge[J]. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology,2021,61:47-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030220-013418 [3] ALKA S, SHAHIR S, IBRAHIM N, et al. Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: a mini review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,278:123805. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123805 [4] GHOSH S, DEBSARKAR A, DUTTA A. Technology alternatives for decontamination of arsenic-rich groundwater: a critical review[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2019,13:277-303. [5] SIDDIQ O M, TAWABINI B S, SOUPIOS P, et al. Removal of arsenic from contaminated groundwater using biochar: a technical review[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2022,19(1):651-664. doi: 10.1007/s13762-020-03116-x [6] 郭丽, 王延荣.地下水污染环境评价探讨[J]. 当代化工研究,2021(13):129-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.13.061GUO L, WANG Y R. Discussion on environmental assessment of groundwater pollution[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2021(13):129-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.13.061 [7] 王宝燕, 肖巍.地下水污染现状与防治对策研究[J]. 环境与发展,2020,32(10):38-39.WANG B Y, XIAO W. Study on the status quo of groundwater pollution and countermeasures[J]. Environment and Development,2020,32(10):38-39. [8] SHAJI E, SANTOSH M, SARATH K V, et al. Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(3):101079. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.08.015 [9] 生态环境部. 2018中国生态环境状况公报[A/OL]. (2019-05-29)[2021-06-02].https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/tpxw/201905/t20190529_704841.shtml. [10] 曾祥裕, 张春燕.印度应对水危机的政策措施评析[J]. 南亚研究季刊,2015(2):84-93. doi: 10.13252/j.cnki.sasq.2015.02.012ZENG X Y, ZHANG C Y. Water crisis: the Indian response[J]. South Asian Studies Quarterly,2015(2):84-93. doi: 10.13252/j.cnki.sasq.2015.02.012 [11] 环境保护部. 2016中国环境状况公报[A/OL]. (2017-06-05)[2021-06-02].https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201706/t20170605_415442.htm. [12] SIK E, KOBYA M, DEMIRBAS E, et al. Combined effects of co-existing anions on the removal of arsenic from groundwater by electrocoagulation process: optimization through response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5(4):3792-3802. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.004 [13] MOHORA E, RONČEVIĆ S, AGBABA J, et al. Arsenic removal from groundwater by horizontal-flow continuous electrocoagulation (EC) as a standalone process[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2018,6(1):512-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.042 [14] CASTAÑEDA L F, COREÑO O, NAVA J L. Arsenic and hydrated silica removal from groundwater by electrocoagulation using an up-flow reactor in a serpentine array[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2019,7(5):103353. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103353 [15] GUO H M, STÜBEN D, BERNER Z, et al. Adsorption of arsenic species from water using activated siderite-hematite column filters[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,151(2/3):628-635. [16] LI F L, GUO H M, ZHAO K, et al. Modeling transport of arsenic through modified granular natural siderite filters for arsenic removal[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2019,10(5):1755-1764. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.12.002 [17] CHENG Y, ZHANG S S, HUANG T L, et al. Arsenite removal from groundwater by iron-manganese oxides filter media: behavior and mechanism[J]. Water Environment Research,2019,91(6):536-545. doi: 10.1002/wer.1056 [18] WU K, WANG M, LI A Z, et al. The enhanced As(Ⅲ) removal by Fe-Mn-Cu ternary oxide via synergistic oxidation: performances and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,406:126739. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126739 [19] PAL M, CHAKRABORTTY S, NAYAK J, et al. Removing toxic contaminants from groundwater by graphene oxide nanocomposite in a membrane module under response surface optimization[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2019,16(8):4583-4594. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-1924-3 [20] CHOWDHURY T, ZHANG L, ZHANG J Q, et al. Removal of arsenic(Ⅲ) from aqueous solution using metal organic framework-graphene oxide nanocomposite[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland),2018,8(12):1062. doi: 10.3390/nano8121062 [21] GIFFORD M, HRISTOVSKI K, WESTERHOFF P. Ranking traditional and nano-enabled sorbents for simultaneous removal of arsenic and chromium from simulated groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,601/602:1008-1014. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.126 [22] CHOWDHURY S R, YANFUL E K. Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2010,91(11):2238-2247. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.06.003 [23] GUZMÁN A, NAVA J L, COREÑO O, et al. Arsenic and fluoride removal from groundwater by electrocoagulation using a continuous filter-press reactor[J]. Chemosphere,2016,144:2113-2120. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.108 [24] NEMADE P D, KADAM A M, SHANKAR H S. Removal of iron, arsenic and coliform bacteria from water by novel constructed soil filter system[J]. Ecological Engineering,2009,35(8):1152-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.03.013 [25] YANG L, LI X K, CHU Z R, et al. Distribution and genetic diversity of the microorganisms in the biofilter for the simultaneous removal of arsenic, iron and manganese from simulated groundwater[J]. Bioresource Technology,2014,156:384-388. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.067 [26] SHAKYA A K, GHOSH P K. Concurrent removal of nitrate, arsenic and iron from simulated and real-life groundwater to meet drinking water standards: effects of operational and environmental parameters[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,235:9-18. [27] THAKUR L S, MONDAL P. Simultaneous arsenic and fluoride removal from synthetic and real groundwater by electrocoagulation process: parametric and cost evaluation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2017,190:102-112. [28] POONIA T, SINGH N, GARG M C. Contamination of arsenic, chromium and fluoride in the Indian groundwater: a review, meta-analysis and cancer risk assessment[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2021,18(9):2891-2902. ◇ doi: 10.1007/s13762-020-03043-x -




 下载:
下载: