Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of invasive herbaceous plants in the coastal zone of Daqing River system
-
摘要:
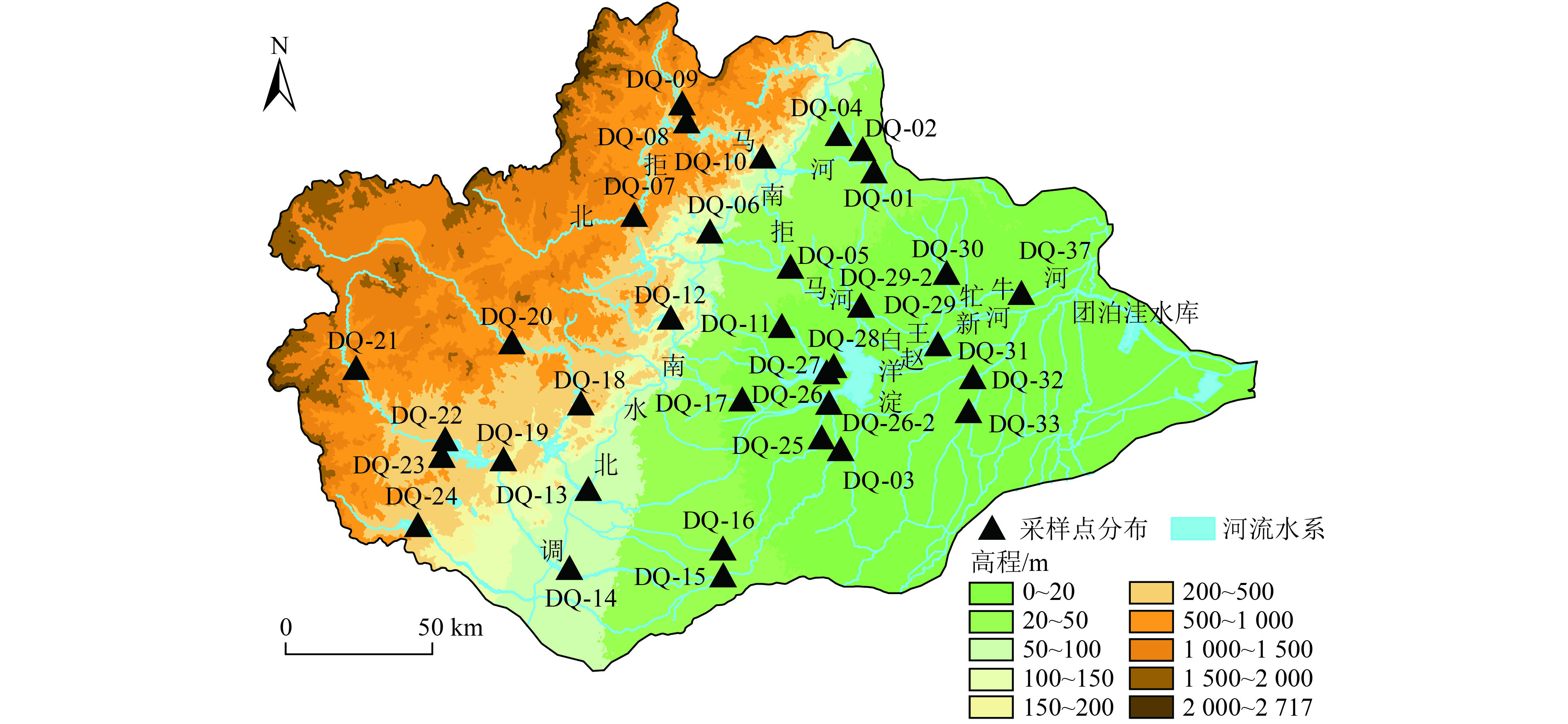
在雄安新区建设大背景下,保障大清河水系生物安全十分重要。为研究大清河水系入侵植物分布规律,探讨影响入侵植物分布的驱动因子,对大清河水系河湖滨岸带开展植被调查,识别滨岸带入侵植物,判定物种的入侵等级,分析物种入侵分布与环境因子和人类活动因素之间的相关性,并提出雄安新区面临的植物入侵风险及防范措施。结果表明:大清河水系有24种入侵植物,其中苋科和菊科合计占54.2%,一年生物种、无意引入物种分别占83.3%、62.5%,原产地为美洲的占62.5%,反枝苋、鬼针草、圆叶牵牛、鳢肠、大狼杷草、苘麻6种植物为流域内广布种;入侵植物种数和入侵性在流域中游的拒马河上游房山山区段、流域下游的牤牛河霸州城市段以及100 m高程分界线附近的山区—平原交接区明显高于其他区域;人类活动是影响植物入侵程度的主要因素,路网密度、建设用地面积占比越高,越有利于入侵植物的分布与扩散;大清河水系植物入侵程度尚可控,但需要在雄安新区建设过程中重视植物入侵定居及扩散风险,早做防范。
Abstract:In the context of the construction of Xiong'an New Area, it is very important to ensure the biological safety of Daqing River system. In order to study the distribution of invasive plants in Daqing River system and explore the driving factors affecting the distribution, the vegetation in the river/lake riparian zone of Daqing River system was investigated. The invasive plants in the riparian zone were identified, the invasion grade of each species determined, the correlation between the distribution of species invasion and influencing factors including natural environment and human activities analyzed, and the risk of plant invasion and preventive measures in Xiong'an New Area put forward. The results showed that there were 24 species of invasive plants in Daqing River system, 54.2% of the invasive species were amaranth and compositae, the annual species and unintroduced species accounted for 83.3% and 62.5%, respectively, and 62.5% of the invasive plants originated from American. Six kinds of plants, including Amaranthus retroflexus, Bidens pilosa, Pharbitis purpurea, Eclipta prostrata, Bidens frondosa, Abutilon theophrasti, were widely distributed in the basin. There were three regions in which the number of species and invasiveness of invasive plants were significantly higher than that in other regions, including Fangshan mountain section in the upper reaches of Juma River in the middle reaches of the basin, Bazhou urban section of Mangniu River in the lower reaches of the basin, and the plain and mountain junction area near the 100 m elevation boundary. Human activity was the main factor affecting the degree of plant invasion. The higher the road network density and the proportion of construction land, the more conducive to the distribution and diffusion of invasive plants. The degree of plant invasion in Daqing River system could be controlled currently, but it was necessary to pay attention to the risk of plant invasion, settlement, and diffusion during the construction of Xiong'an New Area and take early precautions.
-
Key words:
- Daqing River system /
- Xiong'an New Area /
- riparian zone /
- invasive plants /
- human activities
-
表 1 大清河水系滨岸带入侵植物性状
Table 1. Characteristics of invasive plants in riparian area of Daqing river system
科 属 物种 生活型 果实类型 原产地 入侵途径 入侵等级 苋科 莲子草属 空心莲子草(Alternanthera philoxeroides) 多年生草本 胞果 南美洲 有意引进 1 苋属 凹头苋(Amaranthus lividus) 一年生草本 胞果 热带美洲 无意引进 2 刺苋(Amaranthus spinosus) 一年生草本 胞果 热带美洲 无意引进 1 反枝苋(Amaranthus retroflexus) 一年生草本 胞果 热带美洲 人工引种 1 合被苋(Amaranthus polygonoides) 一年生草本 胞果 热带美洲、墨西哥 无意引进 2 苋(Amaranthus tricolor) 一年生草本 胞果 印度 人工引种 3 皱果苋(Amaranthus viridis) 一年生草本 胞果 热带非洲 无意引进 2 菊科 白酒草属 小蓬草(Conyza canadensi) 一年生草本 瘦果 北美洲 无意引进或自然扩散 1 鬼针草属 大狼杷草(Bidens frondosa) 一年生草本 瘦果 北美洲 无意引进 1 鬼针草(Bidens pilosa) 一年生草本 瘦果 美洲 无意引进 1 鳢肠属 鳢肠(Eclipta prostrata) 一年生草本 瘦果 美洲 无意引进 4 向日葵属 菊芋(Helianthus tuberosus) 多年生草本 瘦果 北美洲 有意引进 4 紫菀属 钻叶紫菀(Aster subulatus) 一年生草本 瘦果 北美洲 无意引进 1 藜科 藜属 灰绿藜(Chenopodium glaucum) 一年生草本 胞果 不详 无意引进 4 小藜(Chenopodium serotinum) 一年生草本 胞果 欧洲 无意引进 4 旋花科 牵牛属 牵牛(Pharbitis nil) 一年生缠绕草本 蒴果 南美洲 人工引种 2 圆叶牵牛(Pharbitis purpurea) 一年生缠绕草本 蒴果 热带美洲 人工引种 1 锦葵科 木槿属 野西瓜苗(Hibiscus trionum) 一年生直立或平卧草本 蒴果 非洲 无意引进 4 苘麻属 苘麻(Abutilon theophrasti) 一年生亚灌木状草本 蒴果 印度 无意引进 3 大戟科 大戟属 通奶草(Euphorbia hypericifolia) 一年生草本 蒴果 美洲 无意引进 3 豆科 草木犀属 草木犀(Melilotus officinalis) 二年生草本 荚果 西亚—南欧 有意引进 4 禾本科 虎尾草属 虎尾草(Chloris virgata) 一年生草本 颖果 非洲 无意引进 4 茄科 曼陀罗属 曼陀罗(Datura stramonium) 一年生草本或半灌木状草本 蒴果 热带美洲、墨西哥 有意引进 2 莎草科 莎草属 香附子(Carex heterostachya) 多年生草本 小坚果 印度 不详 4 表 2 不同类别采样点的入侵植物情况
Table 2. Invasive plants at different classification points
采样点类别 入侵物种名称 入侵物种
总数/种采样点入侵
物种数均值/种采样点入侵
强度均值L1 反枝苋、小蓬草、大狼杷草、鬼针草、鳢肠、小藜、牵牛、圆叶牵牛、苘麻、通奶草、曼陀罗、香附子、合被苋、灰绿藜 14 6 14.1 L2 反枝苋、小蓬草、大狼杷草、鬼针草、鳢肠、小藜、牵牛、圆叶牵牛、苘麻、曼陀罗、凹头苋、合被苋、皱果苋、草木犀 14 5 11.2 L3 反枝苋、小蓬草、大狼杷草、鬼针草、鳢肠、菊芋、小藜、牵牛、圆叶牵牛、苘麻、曼陀罗、香附子、空心莲子草、刺苋、苋、皱果苋、钻叶紫菀、野西瓜苗、虎尾草 19 4 7 L4 反枝苋、大狼杷草、鳢肠、小藜、苘麻、曼陀罗、香附子、皱果苋、草木犀 9 2 2.9 表 3 各环境因素多重比较的差异显著性
Table 3. Significance of difference of multiple comparisons of various environmental factors
环境因素 海拔 蜿蜒度 年均降水量 路网密度 建设用地面积占比 耕地面积占比 差异
显著性0.274 0.239 0.248 0.003* 0.05* 0.85 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 表 4 各类采样点的环境因素差异显著性检验
Table 4. Significance test of environmental factors of various sample points
环境因素 采样点类别 L1 L2 L3 L4 海拔 L1 1 L2 0.11 1 L3 0.084 0.906 1 L4 0.103 0.902 0.988 1 蜿蜒度 L1 1 L2 0.065 1 L3 0.188 0.51 1 L4 0.081 0.987 0.546 1 年均降水量 L1 1 L2 0.263 1 L3 0.167 0.781 1 L4 0.048* 0.296 0.418 1 路网密度 L1 1 L2 0.679 1 L3 0.091 0.155 1 L4 0.001** 0.001** 0.029* 1 建设用地面积占比 L1 1 L2 0.06 1 L3 0.038* 0.843 1 L4 0.007** 0.276 0.353 1 耕地面积占比 L1 1 L2 0.976 1 L3 0.597 0.582 1 L4 0.499 0.481 0.838 1 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 表 5 入侵植物分布与各环境指标间的相关系数
Table 5. Correlation coefficient between the distribution of invasive plants and each environmental index
项目 海拔 蜿蜒度 年均降水量 路网密度 建设用地面积占比1) 耕地面积占比1) 入侵物种数 0.083 0.052 −0.289 0.529** 0.352* −0.138 入侵强度 0.298 0.228 −0.309 0.560** 0.385* −0.140 1)为采样点周围1 km缓冲区范围内的指标值。 -
[1] WESTPHAL M I, BROWNE M, MACKINNON K, et al. The link between international trade and the global distribution of invasive alien species[J]. Biological Invasions,2008,10(4):391-398. doi: 10.1007/s10530-007-9138-5 [2] 万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉.中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策[J]. 生物多样性,2002,10(1):119-125. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2002.01.015WAN F H, GUO J Y, WANG D H. Alien invasive species in China: their damages and management strategies[J]. Chinese Biodiversity,2002,10(1):119-125. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2002.01.015 [3] XU H G, DING H, LI M Y, et al. The distribution and economic losses of alien species invasion to China[J]. Biological Invasions,2006,8(7):1495-1500. doi: 10.1007/s10530-005-5841-2 [4] 陈宝雄, 孙玉芳, 韩智华, 等.我国外来入侵生物防控现状、问题和对策[J]. 生物安全学报,2020,29(3):157-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2020.03.001CHEN B X, SUN Y F, HAN Z H, et al. Challenges in preventing and controlling invasive alien species in China[J]. Journal of Biosafety,2020,29(3):157-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2020.03.001 [5] 马玉忠.外来物种入侵 中国每年损失2 000亿[J]. 中国经济周刊,2009(21):43-45. [6] 2019中国生态环境状况公报[A/OL]. (2020-06-02)[2021-06-20]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202006/P020200602509464172096.pdf. [7] LIU J, DONG M, MIAO S L, et al. Invasive alien plants in China: role of clonality and geographical origin[J]. Biological Invasions,2006,8(7):1461-1470. doi: 10.1007/s10530-005-5838-x [8] 常瑞英, 王仁卿, 张依然, 等.入侵植物空心莲子草的入侵机制及综合管理[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2013,29(1):17-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2013.01.003CHANG R Y, WANG R Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. Invasion mechanism and integrated management of invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2013,29(1):17-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2013.01.003 [9] HUFBAUER R A, TORCHIN M E. Integrating ecological and evolutionary theory of biological invasions[M]//Ecological Studies. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2008 : 79-96. [10] RICHARDS C L, PENNINGS S C, DONOVAN L A. Habitat range and phenotypic variation in salt marsh plants[J]. Plant Ecology,2005,176(2):263-273. doi: 10.1007/s11258-004-0841-3 [11] 吴晓雯, 罗晶, 陈家宽, 等.中国外来入侵植物的分布格局及其与环境因子和人类活动的关系[J]. 植物生态学报,2006,30(4):576-584. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2006.04.006WU X W, LUO J, CHEN J K, et al. Spatial patterns of invasive alien plants in China and its relationship with environmental and anthropological factors[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2006,30(4):576-584. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2006.04.006 [12] WEBER E, SUN S G, LI B. Invasive alien plants in China: diversity and ecological insights[J]. Biological Invasions,2008,10(8):1411-1429. doi: 10.1007/s10530-008-9216-3 [13] MCKINNEY M L. Influence of settlement time, human population, park shape and age, visitation and roads on the number of alien plant species in protected areas in the USA[J]. Diversity and Distributions,2002,8(6):311-318. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-4642.2002.00153.x [14] DAWSON F H, HOLLAND D. The distribution in bankside habitats of three alien invasive plants in the U. K. in relation to the development of control strategies[M]//Biology, Ecology and Management of Aquatic Plants. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1999: 193-201. [15] 王静文. 生境破碎化和河流影响下的芦苇种群表型与遗传多样性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. [16] 任颖, 何萍, 侯利萍.海河流域河流滨岸带入侵植物等级与分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2015,28(9):1430-1438.REN Y, HE P, HOU L P. Grading and distribution patterns of invasive plants in riparian area of Hai Basin[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2015,28(9):1430-1438. [17] 马金双. 中国入侵植物名录[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013. [18] 任颖, 何萍, 徐杰, 等.滦河流域河岸带入侵植物分布特征及其与环境的关系[J]. 应用生态学报,2017,28(6):1843-1850.REN Y, HE P, XU J, et al. Distribution pattern of riparian invasive plants in Luanhe Basin, North China and its relationship with environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2017,28(6):1843-1850. [19] 孙然好, 程先, 陈利顶.海河流域河流生境功能识别及区域差异[J]. 生态学报,2018,38(12):4473-4481.SUN R H, CHENG X, CHEN L D. Identification of aquatic ecosystems and regional characteristics in the Haihe River Basin, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(12):4473-4481. [20] 闫小玲, 刘全儒, 寿海洋, 等.中国外来入侵植物的等级划分与地理分布格局分析[J]. 生物多样性,2014,22(5):667-676. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14069YAN X L, LIU Q R, SHOU H Y, et al. The categorization and analysis on the geographic distribution patterns of Chinese alien invasive plants[J]. Biodiversity Science,2014,22(5):667-676. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14069 [21] 王宁, 李卫芳, 周兵, 等.中国入侵克隆植物入侵性、克隆方式及地理起源[J]. 生物多样性,2016,24(1):12-19. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015190WANG N, LI W F, ZHOU B, et al. Invasiveness, clonal form and geographical origin of invasive clonal plant species in China[J]. Biodiversity Science,2016,24(1):12-19. doi: 10.17520/biods.2015190 [22] 郝建华. 部分菊科入侵种的有性繁殖特征与入侵性的关系[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2008. [23] 吴锦容, 彭少麟.化感: 外来入侵植物的“Novel Weapons”[J]. 生态学报,2005,25(11):3093-3097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.11.041WU J R, PENG S L. Allelopathy: “Novel Weapons” of exotic invasive plants[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005,25(11):3093-3097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.11.041 [24] GERVILLA C, RITA J, CURSACH J. Contaminant seeds in imported crop seed lots: a non-negligible human-mediated pathway for introduction of plant species to Islands[J]. Weed Research,2019,59(3):245-253. doi: 10.1111/wre.12362 [25] 朱世新, 覃海宁, 陈艺林.中国菊科植物外来种概述[J]. 广西植物,2005,25(1):69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2005.01.014ZHU S X, QIN H N, CHEN Y L. Alien species of compositae in China[J]. Guihaia,2005,25(1):69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2005.01.014 [26] 耿宇鹏, 张文驹, 李博, 等.表型可塑性与外来植物的入侵能力[J]. 生物多样性,2004,12(4):447-455. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2004.04.009GENG Y P, ZHANG W J, LI B, et al. Phenotypic plasticity and invasiveness of alien plants[J]. Chinese Biodiversity,2004,12(4):447-455. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.2004.04.009 [27] SMITH M D, KNAPP A K. Physiological and morphological traits of exotic, invasive exotic, and native plant species in tallgrass prairie[J]. International Journal of Plant Sciences,2001,162(4):785-792. doi: 10.1086/320774 [28] 孔锋, 王一飞, 吕丽莉, 等. 北京“7·21”特大暴雨洪涝特征与成因及对策建议[J]. 人民长江, 2018, 49(增刊1): 15-19.KONG F, WANG Y F, LU L L, et al. Genesis analysis and countermeasures on huge rainstorm and flooding on 21st Aug. in Beijing[J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(Suppl 1): 15-19. [29] 杨景成, 王光美, 姜闯道, 等.城市化影响下北京市外来入侵植物特征及其分布[J]. 生态环境学报,2009,18(5):1857-1862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.05.048YANG J C, WANG G M, JIANG C D, et al. Ecological characters and distribution of invasive plants under the influence of urbanization in Beijing, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2009,18(5):1857-1862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2009.05.048 [30] 王楠, 吕锡斌, 李辉, 等.贵州省河谷型村镇建设中外来植物的入侵风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(7):1719-1727.WANG N, LÜ X B, LI H, et al. Invasion risk assessment of alien plants in valley-type villages and towns in Guizhou Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(7):1719-1727. [31] TROMBULAK S C, FRISSELL C A. Review of ecological effects of roads on terrestrial and aquatic communities[J]. Conservation Biology,2000,14(1):18-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.99084.x [32] 张昶. 城镇化地区河流生态景观带风貌特征及其影响机制[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. [33] PRETTO F, CELESTI-GRAPOW L, CARLI E, et al. Influence of past land use and current human disturbance on non-native plant species on small Italian Islands[J]. Plant Ecology,2010,210(2):225-239. doi: 10.1007/s11258-010-9751-8 [34] 付军. 大清河流域土地利用变化对洪水影响的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2010. [35] ZEDLER J B, KERCHER S. Causes and consequences of invasive plants in wetlands: opportunities, opportunists, and outcomes[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,2004,23(5):431-452. doi: 10.1080/07352680490514673 [36] 王坤. 1980—2017年大清河流域水系连通性变化分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. [37] 高末, 胡仁勇, 陈贤兴, 等.干扰、地形和土壤对温州入侵植物分布的影响[J]. 生物多样性,2011,19(4):424-431. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08325GAO M, HU R Y, CHEN X X, et al. Effects of disturbance, topography, and soil conditions on the distribution of invasive plants in Wenzhou[J]. Biodiversity Science,2011,19(4):424-431. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08325 [38] 朱慧, 吴双桃.空心莲子草在污染治理中的应用[J]. 河北化工,2006,29(6):55-57.ZHU H, WU S T. Application of alternan Thera philoxeroides in pollution control[J]. Hebei Chemical Engineering and Industry,2006,29(6):55-57. [39] 王芳, 王瑞江, 庄平弟, 等.广东外来入侵植物现状和防治策略[J]. 生态学杂志,2009,28(10):2088-2093.WANG F, WANG R J, ZHUANG P D, et al. Present status and management strategies of alien invasive plants in Guangdong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2009,28(10):2088-2093. [40] PRITEKEL C, WHITTEMORE-OLSON A, SNOW N, et al. Impacts from invasive plant species and their control on the plant community and belowground ecosystem at Rocky Mountain National Park, USA[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,2006,32(1):132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.01.010 [41] 谢勇, 徐永福, 游健荣, 等.黄金河国家湿地公园外来植物种类组成、区系与入侵危害[J]. 生态学杂志,2020,39(11):3613-3622.XIE Y, XU Y F, YOU J R, et al. Species composition, flora and invasion hazard of alien plants in Huangjinhe National Wetland Park[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(11):3613-3622. ◇ -





 下载:
下载: