Accumulation characteristics of cadmium in farmland soil by Pueraria thomsonii
-
摘要:
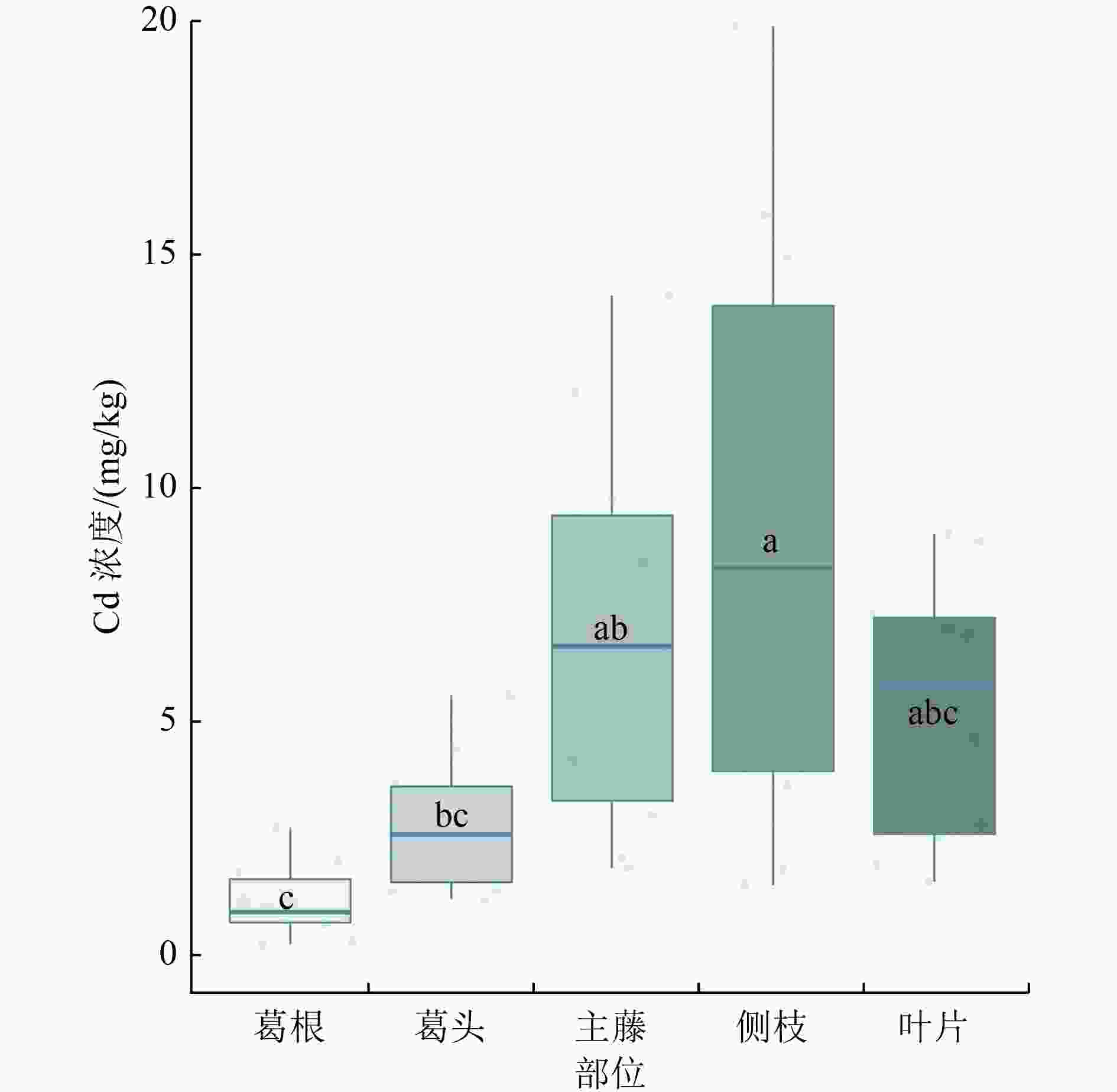
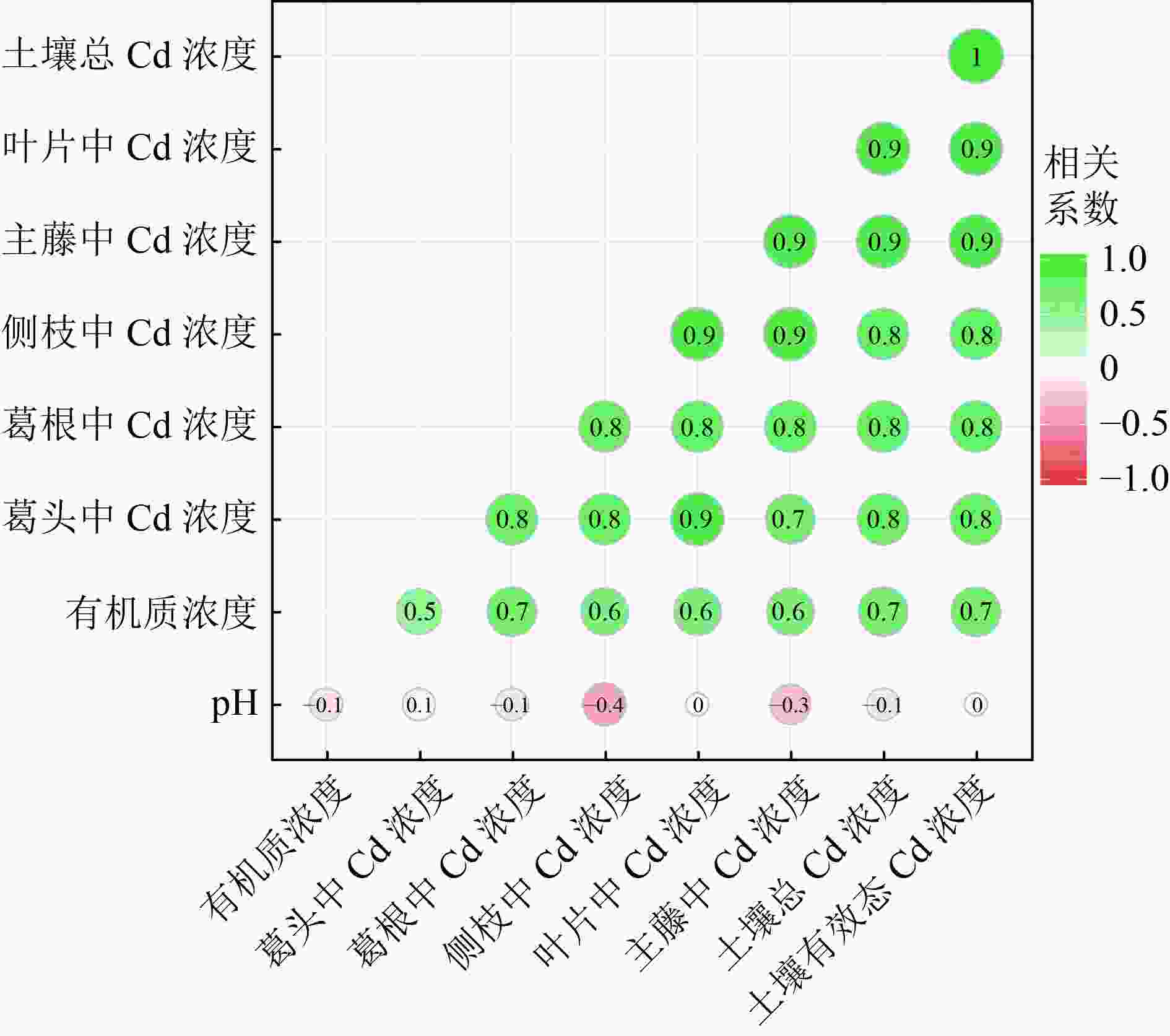
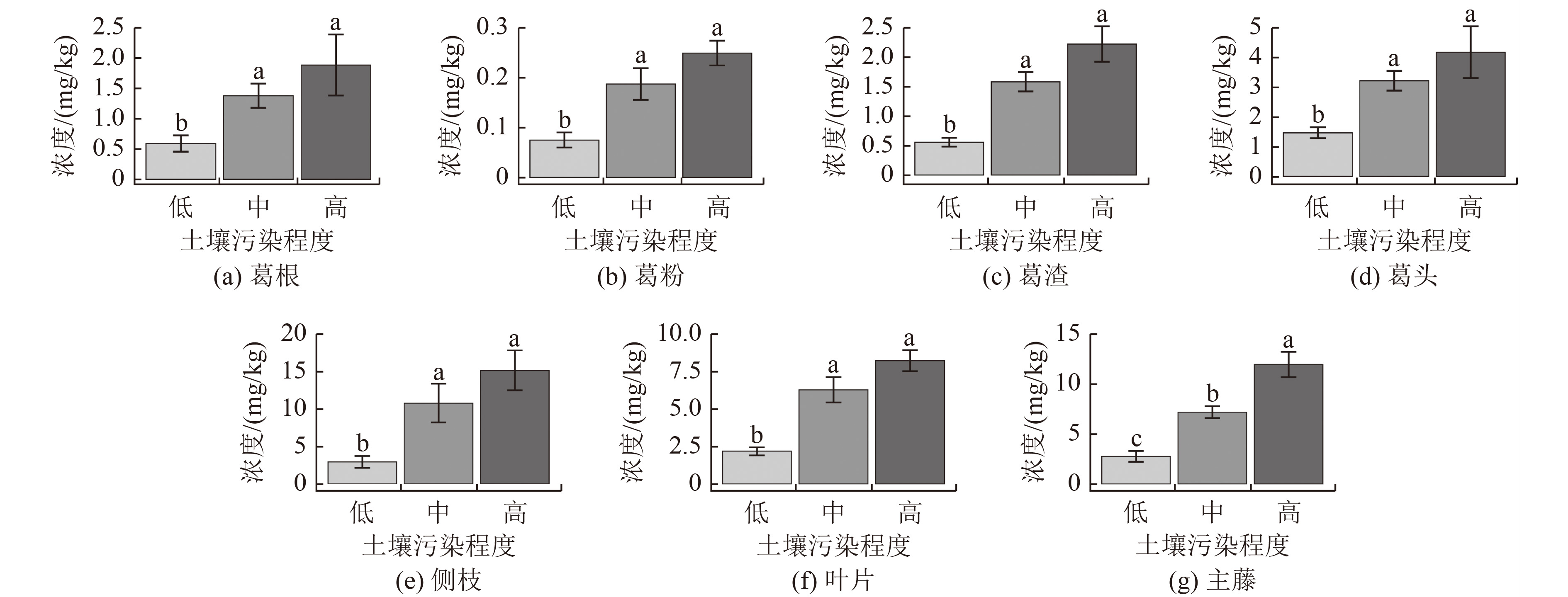
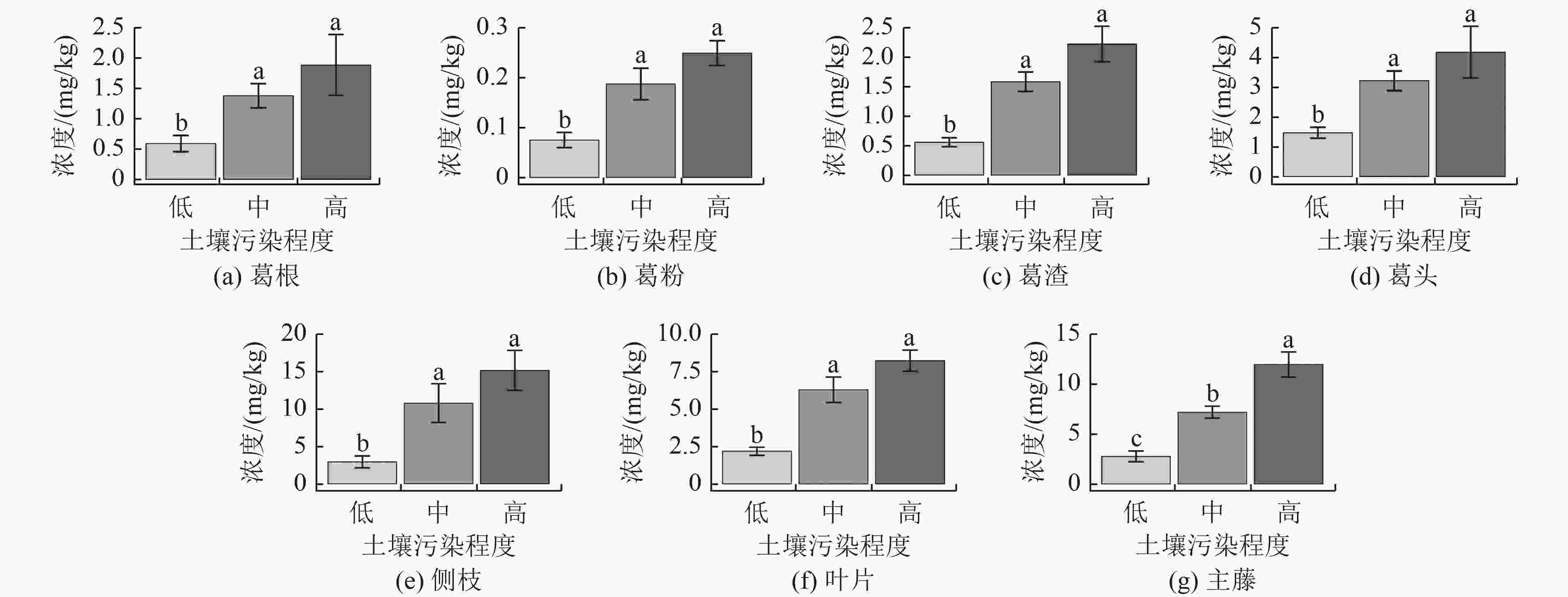
选用生长速度快、生物量大、经济价值高的富集植物是重金属生物修复新的突破口。为研究粉葛对农田土壤镉(Cd)的富集特征,采用大田试验探讨3种污染程度下粉葛不同部位葛根(葛粉和葛渣)、葛头、主藤、侧枝和叶片中Cd浓度。结果表明:粉葛不同部位中Cd浓度表现为侧枝(8.96 mg/kg)>主藤(6.85 mg/kg)>叶片(5.22 mg/kg)>葛头(2.80 mg/kg)>葛渣(1.36 mg/kg)>葛根(1.21 mg/kg)>葛粉(0.16 mg/kg),且随土壤污染程度增加而增加,表现为中、高污染显著高于低污染(P<0.05)。除葛根外,粉葛其他部位对土壤Cd的富集系数均大于1(1.09~8.65),转运系数为2.59~8.98。粉葛各部位中Cd的分配率表现为侧枝(35.64%~43.81%)>主藤(21.55%~25.49%)>叶片(15.40%~23.63%)>葛根(7.03%~9.94%)>葛头(5.99%~9.57%)。粉葛各部位生物量表现为葛根>侧枝>叶片>主藤>葛头,粉葛对Cd移除量随土壤污染程度递增,具体为高污染(45.39 g/hm2)>中污染(39.96 g/hm2)>低污染(16.56 g/hm2)。总体上,粉葛各部位中Cd浓度与土壤有机质、有效态Cd、总Cd浓度呈显著正相关,而与土壤pH均呈负相关。在Cd污染农田土壤治理中,粉葛(用作葛粉)对Cd污染农田土壤修复具有应用价值。
Abstract:The selection of rich plants with high growth, high biomass, and high economic value is a new breakthrough in the bioremediation of heavy metals. To study the accumulation characteristic of cadmium (Cd) by Pueraria thomsonii in farmland soil, field experiments were conducted to investigate Cd contents in tuber (radix pueraria and arrowroot), basal part of stem, main vine, lateral branch, and leaf of Pueraria thomsonii under three pollution levels. The results showed that Cd contents in different parts of Pueraria thomsonii were lateral branch (8.96 mg/kg) > main vine (6.85 mg/kg) > leaf (5.22 mg/kg) > basal part of stem (2.80 mg/kg) > radix pueraria (1.36 mg/kg)> tuber (1.21 mg/kg)> arrowroot (0.16 mg/kg). Cd contents increased with the increase of soil pollution, showing that Cd contents in medium and high pollution were significantly higher than in low pollution (P < 0.05). Except for tuber, the accumulation coefficient of Cd in other parts of the plant was higher than 1 (1.09-8.65), and the transport coefficient was 2.59-8.98. The distribution rates of Cd content in various parts of Pueraria thomsonii were as follows: lateral branch (35.64%-43.81%) > main vine (21.55%-25.49%) > leaf (15.40%-23.63%) > tuber (7.03%-9.94%) > basal part of stem (5.99%-9.57%). The biomass in various parts of Pueraria thomsonii was tuber > lateral branch > leaf > main vine > basal part of stem. The removal amount of Cd increased with the pollution level, which was high pollution (45.39 g/hm2) > medium pollution (39.96 g/hm2) > low pollution (16.56 g/hm2). In general, Cd contents in various parts of Pueraria thomsonii were significantly positively correlated with soil organic matter, available Cd, and total Cd, but negatively correlated with soil pH. In the treatment of Cd contaminated farmland soil, Pueraria thomsonii (used as arrowroot) has application value for Cd contaminated farmland soil remediation.
-
Key words:
- Pueraria thomsonii /
- cadmium /
- pollution level /
- accumulation characteristics /
- biomass
-
图 2 粉葛不同部位Cd浓度比较
注:同图1。
Figure 2. Comparison of Cd contents in different parts of Pueraria thomsonii
表 1 土壤理化性质及Cd污染程度
Table 1. Physiochemical properties and Cd pollution level in soil
土壤污染程度 总Cd浓度/
(mg/kg)有效Cd浓度/
(mg/kg)有机质浓度/
(g/kg)pH 低 0.53 0.39 26.69 4.64 中 1.28 1.13 34.35 4.60 高 1.93 1.38 34.36 4.64 表 2 不同土壤污染程度下粉葛各部分富集系数
Table 2. Accumulation coefficients of various parts of Pueraria thomsonii under different soil pollution levels
土壤污染程度 葛根/土壤 葛头/土壤 主藤/土壤 侧枝/土壤 叶片/土壤 低 1.12±0.42 3.15±1.22 5.47±1.20 5.43±0.90 4.63±1.97 中 1.09±0.35 2.56±0.70 5.68±1.18 8.65±4.10 5.03±1.63 高 0.98±0.45 2.15±0.76 6.20±1.23 7.86±2.40 4.25±0.57 表 3 不同土壤污染程度下粉葛各部位转运系数
Table 3. Transport coefficients of various parts of Pueraria thomsonii under different soil pollution levels
土壤污染程度 葛头/葛根 主藤/葛根 侧枝/葛根 叶片/葛根 低 3.14±1.96 5.65±3.00 5.59±2.49 4.87±3.46 中 2.59±0.54 6.01±2.02 8.98±4.75 5.04±1.14 高 2.63±1.71 7.21±2.81 8.65±2.08 5.31±3.32 表 4 不同土壤污染程度下粉葛各部分中Cd的分配率
Table 4. Distribution rates of Cd in different parts of Pueraria thomsonii under different soil pollution levels
% 土壤污染
程度葛根 葛头 主藤 侧枝 叶片 低 9.94±7.64 9.57±4.26 25.24±5.56 39.84±10.13 15.40±6.17 中 7.03±0.31 5.99±1.32 21.55±4.67 43.81±12.01 21.61±13.58 高 7.99±3.16 7.25±2.73 25.49±6.22 35.64±13.91 23.63±12.35 表 5 不同土壤污染程度下粉葛各部位生物量
Table 5. Biomass in different parts of Pueraria thomsonii under different soil pollution levels
g/株 土壤污染程度 葛根 葛头 主藤 侧枝 叶片 地上部分 低 119.38±18.31 52.01±20.73 85.50±43.74 134.75±70.46 73.12±67.71 345.26±181.13 中 114.74±13.34 44.75±24.86 68.33±27.06 94.60±34.07 82.33±59.37 290.02±123.22 高 102.62±24.62 44.69±21.89 51.11±7.55 61.01±33.41 64.32±33.05 220.69±26.89 表 6 不同土壤污染程度下粉葛Cd移除量
Table 6. Cd removal amount from Pueraria thomsonii under different soil pollution levels
土壤污染程度 净化率/% 单株移除量/(mg/株) 移除量/(g/hm2) 低 25.27±13.12 0.92±0.55 16.56±9.90 中 19.65±2.36 2.22±0.37 39.96±6.66 高 14.99±5.39 2.52±0.85 45.36±15.30 注:净化率=植株Cd积累量/土壤有效态Cd浓度×100%[19]。 -
[1] 郭广慧, 雷梅, 乔鹏炜.北京市城市发展中土壤重金属的空间分布[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2015,5(5):424-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2015.05.067GUO G H, LEI M, QIAO P W. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils during urban development of Beijing[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2015,5(5):424-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2015.05.067 [2] 环境保护部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[A/OL]. [2021-04-05]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417_270670.htm. [3] 张建, 杨瑞东, 陈蓉, 等.贵州喀斯特地区土壤-辣椒体系重金属元素的生物迁移积累特征[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(21):175-181. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201721028ZHANG J, YANG R D, CHEN R, et al. Bioconcentration of heavy metals in soil-Capsicum annuum L. system in Karst areas of Guizhou Province[J]. Food Science,2017,38(21):175-181. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201721028 [4] YANG Y, ZHOU X H, TIE B Q, et al. Comparison of three types of oil crop rotation systems for effective use and remediation of heavy metal contaminated agricultural soil[J]. Chemosphere,2017,188:148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.140 [5] SHI L, GUO Z H, LIANG F, et al. Effect of liming with various water regimes on both immobilization of cadmium and improvement of bacterial communities in contaminated paddy: a field experiment[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2019,16(3):498. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030498 [6] 谭可夫, 涂鹏飞, 杨洋, 等.烟草—红叶甜菜轮作对镉污染农田的修复潜力试验[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(3):440-448. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-9991X.20190167TAN K F, TU P F, YANG Y, et al. Phytoextraction of cadmium contaminated agricultural soil by tobacco and swiss chard rotation systems[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(3):440-448. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-9991X.20190167 [7] 徐剑锋, 王雷, 熊瑛, 等.土壤重金属污染强化植物修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(3):366-373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.03.051XU J F, WANG L, XIONG Y, et al. Research progress on strengthening phytoremediation technologies for heavy metals contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(3):366-373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.03.051 [8] KRÄMER U. Metal hyperaccumulation in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology,2010,61:517-534. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112156 [9] 王艳, 杨远宁, 王学礼, 等.施用含硒有机肥对粉葛产量及硒吸收转运的影响[J]. 热带作物学报,2021,42(2):449-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.02.021WANG Y, YANG Y N, WANG X L, et al. Effects of selenium-containing organic fertilizer on the yield and selenium absorption and transport of Pueraria thomsonii Benth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2021,42(2):449-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.02.021 [10] 田国政.葛中重金属元素铅和镉的分析与评价[J]. 湖北民族学院学报(自然科学版),2004,22(4):42-44.TIAN G Z. The analysis and evaluation of lead and cadmium of kudzu vine[J]. Journal of Hubei Institute for Nationalities,2004,22(4):42-44. [11] 何绍浪, 黄欠如, 成艳红, 等.江西省葛产业发展现状及对策[J]. 湖北农业科学,2019,58(22):130-133. doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.22.030HE S L, HUANG Q R, CHENG Y H, et al. Current situation and strategies on the development of Pueraria industry in Jiangxi Province[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2019,58(22):130-133. doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.22.030 [12] 章丽娟. 大理葛根及其种植土壤中主要金属元素的调查[D]. 大理: 大理学院, 2012. [13] 陆金, 赵兴青, 黄健, 等.铜陵狮子山矿区尾矿库及周边17种乡土植物重金属含量及富集特征[J]. 环境化学,2019,38(1):78-86. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018021302LU J, ZHAO X Q, HUANG J, et al. Heavy metal contents and enrichment characteristics of 17 species indigenous plants in the tailing surrounding in Shizishan, Tongling[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,38(1):78-86. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018021302 [14] 叶惠煊, 谭舟, 刘向前, 等.湿法消解-原子荧光光谱法测定湘葛一号中的砷、汞、铅[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(4):151-154. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201404031YE H X, TAN Z, LIU X Q, et al. Determination of arsenic, mercury and lead in Radix puerariae by atomic florescence spectrophotometry with wet digestion[J]. Food Science,2014,35(4):151-154. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201404031 [15] 国土资源部. 生态地球化学评价动植物样品分析方法 第1部分: 锂、硼、钒等19个元素量的测定 电感耦合等离子体质谱: DZ/T 0253.1—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. [16] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. [17] 刘冲, 赵玲, 李秀华, 等.苎麻对农田土壤中汞、镉的吸收累积特征研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2020,39(5):1034-1042. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1249LIU C, ZHAO L, LI X H, et al. Accumulation and transfer of mercury and cadmium in ramie from agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2020,39(5):1034-1042. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1249 [18] 龙玉梅, 刘杰, 傅校锋, 等.4种Cd超富集/富集植物修复性能的比较[J]. 江苏农业科学,2019,47(8):296-300.LONG Y M, LIU J, FU X F, et al. Comparative study on remediation performance of 4 kinds of Cd hyperaccumulators[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(8):296-300. [19] 郑陶, 李廷轩, 张锡洲, 等.水稻镉高积累品种对镉的富集特性[J]. 中国农业科学,2013,46(7):1492-1500. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.07.020ZHENG T, LI T X, ZHANG X Z, et al. Accumulation characteristics of cadmium-accumulated rice cultivars with high cadmium accumulation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2013,46(7):1492-1500. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.07.020 [20] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量: GB 2762—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [21] 中华人民共和国商务部. 药用植物及制剂外经贸绿色行业标准: WM/T 2—2004[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004. [22] 李广云, 曹永富, 赵书民, 等.土壤重金属危害及修复措施[J]. 山东林业科技,2011,41(6):96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2724.2011.06.031 [23] 孙正国.龙葵对镉污染土壤的响应及其修复效应研究[J]. 江苏农业科学,2015,43(10):397-401. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2015.10.126 [24] 潘雨齐, 黄仁志, 雷鸣, 等.镉在桑树体内的迁移与分布特征研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2016,35(8):1480-1487. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015-1725PAN Y Q, HUANG R Z, LEI M, et al. Transportation and distribution of Cd in different varieties of mulberry (Moms alba L.)[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2016,35(8):1480-1487. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015-1725 [25] SALT D E, SMITH R D, RASKIN I. Phytoremediation[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology,1998,49:643-668. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.643 [26] 佘玮, 揭雨成, 邢虎成, 等.不同程度污染农田苎麻吸收积累镉特性研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2012,28(14):275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.14.054SHE W, JIE Y C, XING H C, et al. Cd uptake and accumulation of ramie planting in contaminated soil in Anhua and Zhuzhou of Hunan Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(14):275-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.14.054 [27] 龙新宪, 王艳红, 刘洪彦.不同生态型东南景天对土壤中Cd的生长反应及吸收积累的差异性[J]. 植物生态学报,2008,32(1):168-175. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2008.01.019LONG X X, WANG Y H, LIU H Y. Growth response and uptake differences between two ecotypes of sedum alfredii to soils cd[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2008,32(1):168-175. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2008.01.019 [28] 郭媛, 邱财生, 龙松华, 等.不同黄麻品种对重金属污染农田镉的富集和转移效率研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2019,38(8):1929-1935. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0597GUO Y, QIU C S, LONG S H, et al. Cadmium accumulation and translocation in different jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) cultivars growing in heavy metal contaminated paddy soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2019,38(8):1929-1935. ⊕ doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0597 -




 下载:
下载: