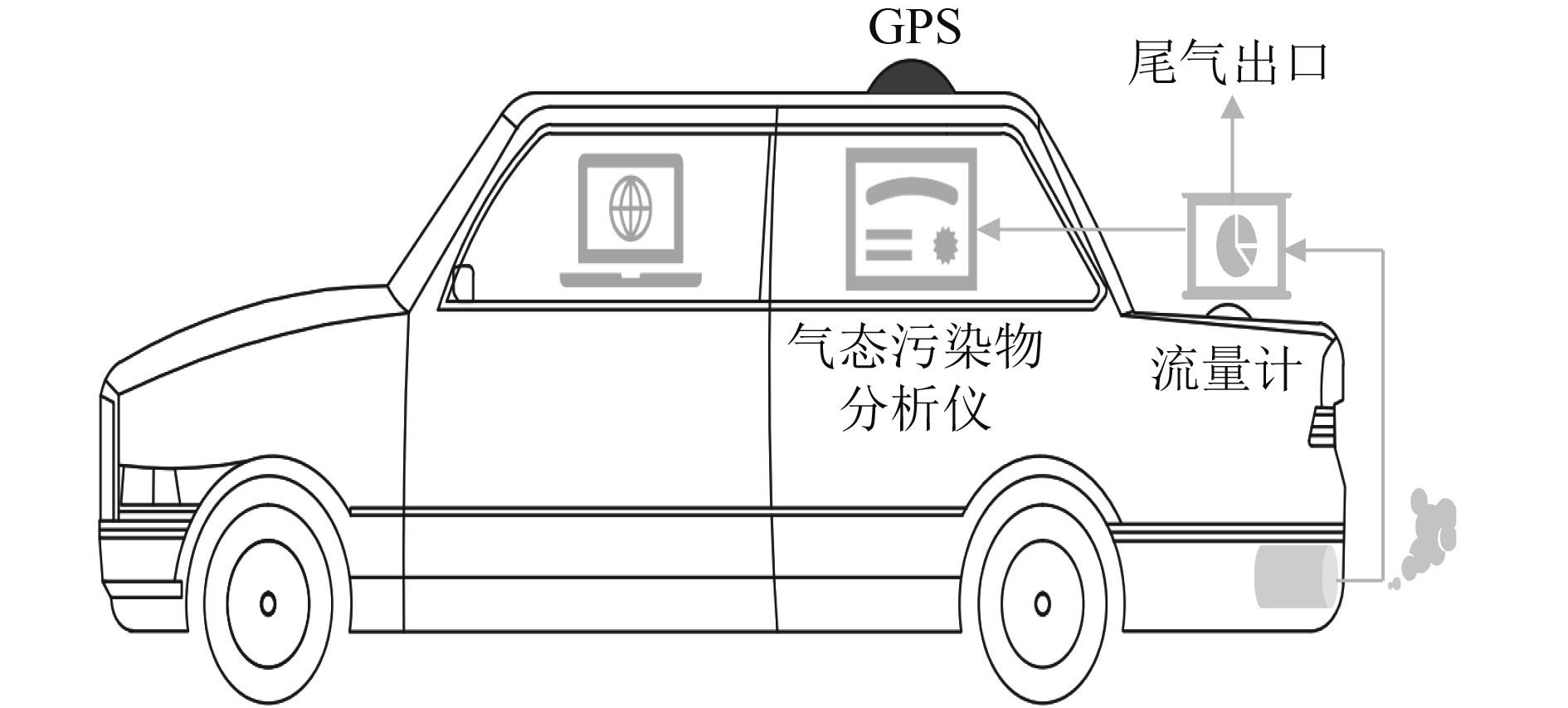
Emission characteristics of light-duty vehicles based on portable emission measurement system (PEMS)
-
摘要:
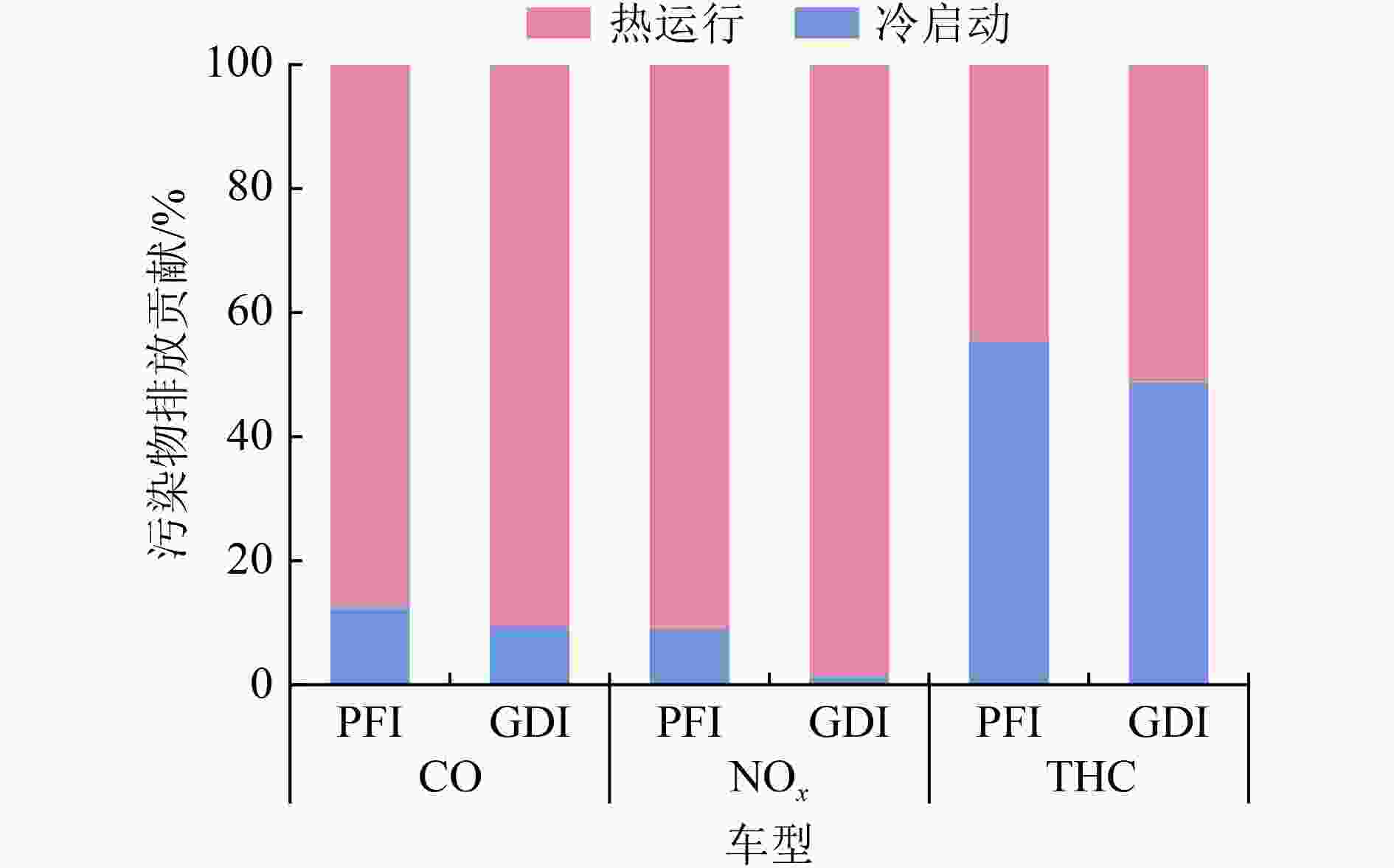
选择11辆轻型汽车作为研究对象,利用车载测试系统(portable emission measurement system,PEMS)研究了轻型汽车气态污染物排放和油耗特征。结果表明:轻型汽车一氧化碳(carbon monoxide,CO)、氮氧化物(nitrogen oxides,NOx)和总碳氢化合物(total hydrocarbons,THC)的排放因子分别为(910.4±822.6)、(58.0±48.3)和(21.6±16.1)mg/km,且其排放速率随发动机比功率-速度(vehicle specific power-velocity,VSP-v)增大而增加,冷启动期间CO、NOx和THC的排放量占排放总量的11.2%±2.1%、3.7%±5.4%和52.7%±4.6%。轻型汽车瞬态油耗速率随VSP-v的增大而增加,车辆相对油耗在平均车速低于15 km/h时显著上升,车速在40 km/h以上时油耗随车速变化呈平稳的趋势。20 ℃时CO、NOx和THC排放速率高于1 ℃时的排放速率;1 ℃的环境温度使油耗速率增加,尤其在车辆高速行驶时,1 ℃时其油耗速率比20 ℃时高27.1%±24.5%。
Abstract:The emission characteristics of gaseous pollutants and the fuel consumption from eleven gasoline light-duty gasoline cars were studied, using the portable emission measurement system (PEMS). The results showed that the emission factors of light-duty gasoline cars were (910.4±822.6) mg/km for carbon monoxide (CO), (58.0±48.3) mg/km for nitrogen oxides (NOx), and (21.6±16.1) mg/km for total hydrocarbons (THC), respectively. The emission rates of CO, NOx, and THC increased with the increase of vehicle specific power-velocity (VSP-v), and the emissions in the cold start phase accounted for 11.2%±2.1%, 3.7%±5.4%, and 52.7%±4.6% of the total CO, NOx, and THC mass, respectively. The transient fuel consumption rates of the light-duty gasoline cars increased with the increase of VSP-v. Vehicle relative fuel consumption increased significantly as the vehicle average speed was less than 15 km/h, and increased slightly as the vehicle average speed was over 40 km/h. The emission rates of CO, NOx, and THC at 20 ℃ were higher than those at 1 ℃. Ambient temperature also dramatically influenced vehicle fuel consumption rate. Especially when the vehicle was running at high speed, the fuel consumption rate at 1 ℃ was 27.1%±24.5% higher than that at 20 ℃.
-
Key words:
- light-duty vehicles /
- gaseous pollutants /
- fuel consumption /
- injection method /
- cold start /
- driving conditions /
- ambient temperature
-
表 1 测试车辆基本信息
Table 1. Details of tested vehicles
车辆编号 品牌 生产年份 排放标准 后处理 行驶里程/(103 km) 排量/L 整备质量/kg 额定功率
/kW喷油方式 1# 别克 2006 国2 TWC 132 1.6 1220 78 PFI 2# 丰田 2012 国4 TWC 59 1.6 1300 90 PFI 3# 别克 2017 国5 TWC 58 1.5 1225 81 PFI 4# 别克 2015 国5 TWC 91 1.4 1430 103 PFI 5# 大众 2016 国5 TWC 105 1.6 1265 87 PFI 6# 大众 2014 国4 TWC 29 1.8 1600 118 GDI 7# 东风 2016 国5 TWC 73 1.2 1305 100 GDI 8# 本田 2018 国5 TWC 11 1.5 1205 96 GDI 9# 雪佛兰 2018 国5 TWC 51 1.5 1520 GDI 10# 福特 2012 国4 TWC 131 1.8 1340 PFI 11# 别克 2015 国4 TWC 118 2.4 1595 PFI 表 2 测试车辆在不同道路上的行驶里程和平均速度
Table 2. Mileage and average speed of tested vehicles on different roads
车辆编号 道路类型 行驶里程/km 平均速度/(km/h) 车辆编号 道路类型 行驶里程/km 平均速度/(km/h) 1# 城市道路 15.2 21 7# 城市道路 15.1 35 市郊道路 15.1 57 市郊道路 15.1 82 高速路 15.1 82 高速路 15.1 100 2# 城市道路 15.2 13 8# 城市道路 15.1 38 市郊道路 15.1 47 市郊道路 15.2 76 高速路 15.3 82 高速路 15.1 102 3# 城市道路 15.1 18 9# 城市道路 15.1 36 市郊道路 15.3 58 市郊道路 15.1 80 高速路 15.2 68 高速路 15.1 102 4# 城市道路 15.2 28 10# 城市道路 15.2 27 市郊道路 15.3 69 市郊道路 15.2 71 高速路 15.2 94 高速路 15.3 85 5# 城市道路 15.2 19 11# 城市道路 15.3 19 市郊道路 15.3 65 市郊道路 15.2 44 高速路 15.2 62 高速路 15.1 80 6# 城市道路 15.1 17 市郊道路 15.2 39 高速路 15.1 81 表 3 轻型汽车Bin划分方法
Table 3. Bin distributions of light vehicles in this study
VSP/(kW/t) v/(km/h) <1.6 1.6~40 40~80 ≥80 ≤−4 Bin1(怠速) Bin11 Bin21 Bin35 −4~−2 Bin1(怠速) Bin12 Bin22 Bin35 −2~0 Bin1(怠速) Bin13 Bin23 Bin35 0~2 Bin1(怠速) Bin14 Bin24 Bin35 2~4 Bin1(怠速) Bin15 Bin25 Bin35 4~6 Bin1(怠速) Bin16 Bin26 Bin36 6~8 Bin1(怠速) Bin17 Bin27 Bin37 8~10 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin28 Bin38 10~12 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin29 Bin38 12~14 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin2X Bin39 14~16 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin2Y Bin39 16~20 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin2Y Bin3X >20 Bin1(怠速) Bin18 Bin2Y Bin3Y -
[1] IODICE P, SENATORE A. Appraisal of pollutant emissions and air quality state in a critical Italian region: methods and results[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy,2015,34(5):1497-1505. [2] TONG Z M, CHEN Y J, MALKAWI A, et al. Energy saving potential of natural ventilation in China: the impact of ambient air pollution[J]. Applied Energy,2016,179:660-668. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.019 [3] DROZD G T, ZHAO Y L, SALIBA G, et al. Detailed speciation of intermediate volatility and semivolatile organic compound emissions from gasoline vehicles: effects of cold-starts and implications for secondary organic aerosol formation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(3):1706-1714. [4] 生态环境部. 中国移动源环境管理年报[A]. 北京: 生态环境部, 2019. [5] MCCAFFERY C, ZHU H W, LI C G, et al. On-road gaseous and particulate emissions from GDI vehicles with and without gasoline particulate filters (GPFs) using portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,710:136366. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136366 [6] YANG Z W, LIU Y, WU L, et al. Real-world gaseous emission characteristics of Euro 6b light-duty gasoline- and diesel-fueled vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2020,78:102215. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2019.102215 [7] CHONG H S, KWON S, LIM Y, et al. Real-world fuel consumption, gaseous pollutants, and CO2 emission of light-duty diesel vehicles[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society,2020,53:101925. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101925 [8] GRAHAM L. Chemical characterization of emissions from advanced technology light-duty vehicles[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(13):2385-2398. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.049 [9] SINGH S. Comparison of fuel economy and gaseous emissions of gas-direct injection versus port fuel injection light duty vehicles based on real-world measurements[D]. North Carolina: North Carolina State University, 2018. [10] 王军方, 尹航, 王宏丽, 等.轻型汽油车国六标准可行性研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(6):661-665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.06.091WANG J F, YIN H, WANG H L, et al. Study on probability of compliance with China 6 standard for the emission from light duty gasoline vehicles[J]. Iournal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(6):661-665. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.06.091 [11] ZHAO F, LAI M C, HARRINGTON D L. Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,1999,25(5):437-562. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(99)00004-0 [12] WEILENMANN M, FAVEZ J Y, ALVAREZ R. Cold-start emissions of modern passenger cars at different low ambient temperatures and their evolution over vehicle legislation categories[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2009,43(15):2419-2429. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.02.005 [13] CLAIROTTE M, ADAM T W, ZARDINI A A, et al. Effects of low temperature on the cold start gaseous emissions from light duty vehicles fuelled by ethanol-blended gasoline[J]. Applied Energy,2013,102:44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.08.010 [14] YAO Z L, WANG Q D, HE K B, et al. Characteristics of real-world vehicular emissions in Chinese cities[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association (1995),2007,57(11):1379-1386. [15] ZHANG S J, WU Y, LIU H, et al. Real-world fuel consumption and CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions by driving conditions for light-duty passenger vehicles in China[J]. Energy,2014,69:247-257. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.02.103 [16] YANG L, WU Y, LI J Q, et al. Mass concentrations and temporal profiles of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 near major urban roads in Beijing[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2014,9(4):675-684. [17] WU Y, ZHANG S J, LI M L, et al. The challenge to NOx emission control for heavy-duty diesel vehicles in China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2012,12(19):9365-9379. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-9365-2012 [18] 环境保护部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 轻型汽车污染物排放限值及测量方法: GB 18352.6—2016[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2020. [19] LUJÁN J M, BERMÚDEZ V, DOLZ V, et al. An assessment of the real-world driving gaseous emissions from a Euro 6 light-duty diesel vehicle using a portable emissions measurement system (PEMS)[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2018,174:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.11.056 [20] 国家发展和改革委员会. 轻型汽车燃料消耗量试验方法: GB/T 19233—2003[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003. [21] IMÉNEZ-PALACIOS J L. Understanding and quantifying motor vehicle emissions with vehicle specific power and TILDAS remote sensing[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1999. [22] 杨柳含子. 基于车载诊断系统的机动车油耗与氮氧化物排放特征研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016: 20-23. [23] US Environmental Protection Agency. Development of emission rates for heavy-duty vehicles in the motor vehicle emissions simulator MOVES2010[R]. Washington DC: Office of Transportation and Air Quality, 2010: 11-12. [24] BISHOP G A, STEDMAN D H, BURGARD D A, et al. High-mileage light-duty fleet vehicle emissions: their potentially overlooked importance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(10):5405-5411. [25] BORKEN-KLEEFELD J, CHEN Y C. New emission deterioration rates for gasoline cars: results from long-term measurements[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2015,101:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.013 [26] SALIBA G, SALEH R, ZHAO Y L, et al. Comparison of gasoline direct-injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicle emissions: emission certification standards, cold-start, secondary organic aerosol formation potential, and potential climate impacts[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,51(11):6542-6552. [27] WU X, ZHANG S J, GUO X, et al. Assessment of ethanol blended fuels for gasoline vehicles in China: fuel economy, regulated gaseous pollutants and particulate matter[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,253:731-740. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.045 [28] DARDIOTIS C, MARTINI G, MAROTTA A, et al. Low-temperature cold-start gaseous emissions of late technology passenger cars[J]. Applied Energy,2013,111:468-478. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.04.093 [29] MAHADEVAN G, SUBRAMANIAN S. Experimental investigation of cold start emission using dynamic catalytic converter with pre-catalyst and hot air injector on a multi cylinder spark ignition engine[C]//SAE Technical Paper Series. 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA, United States: SAE International, 2017. [30] WANG W, MCCOOL G, KAPUR N, et al. Mixed-phase oxide catalyst based on Mn-mullite (Sm, Gd) Mn2O5 for NO oxidation in diesel exhaust[J]. Science,2012,337:832-835. doi: 10.1126/science.1225091 [31] CHAN T W, MELOCHE E, KUBSH J, et al. Impact of ambient temperature on gaseous and particle emissions from a direct injection gasoline vehicle and its implications on particle filtration[J]. SAE International Journal of Fuels and Lubricants,2013,6(2):350-371. doi: 10.4271/2013-01-0527 [32] COLE R L, POOLA R B, SEKAR R. Exhaust emissions of a vehicle with a gasoline direct-injection engine[C]//SAE Technical Paper Series. 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA, United States: SAE International, 1998. [33] ZHU R C, HU J N, BAO X F, et al. Tailpipe emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicles at both low and high ambient temperatures[J]. Environmental Pollution,2016,216:223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.066 [34] ZHENG X, WU Y, ZHANG S J, et al. Evaluating real-world emissions of light-duty gasoline vehicles with deactivated three-way catalyst converters[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research,2018,9(1):126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2017.08.001 [35] 王军方, 丁焰, 王爱娟, 等.北京机动车行驶工况研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2012,2(3):240-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.03.037WANG J F, DING Y, WANG A J, et al. Study of vehicle driving cycle modes on road in Beijing[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2012,2(3):240-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.03.037 [36] National Research Council. Cost, effectiveness, and deployment of fuel economy technologies for light-duty vehicles[M]. Washington DC: National Academies Press, 2015. [37] CONFER K A, KIRWAN J, ENGINEER N. Development and vehicle demonstration of a systems-level approach to fuel economy improvement technologies[C]//SAE Technical Paper Series. 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA, United States: SAE International, 2013. [38] KOBAYASHI S, PLOTKIN S, RIBEIRO S K. Energy efficiency technologies for road vehicles[J]. Energy Efficiency,2009,2(2):125-137. doi: 10.1007/s12053-008-9037-3 [39] GONZÁLEZ PALENCIA J C, FURUBAYASHI T, NAKATA T. Energy use and CO2 emissions reduction potential in passenger car fleet using zero emission vehicles and lightweight materials[J]. Energy,2012,48(1):548-565. □ doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2012.09.041 -





 下载:
下载: