Research progress on pollution and toxic effects of microplastics in freshwater environment
-
摘要:
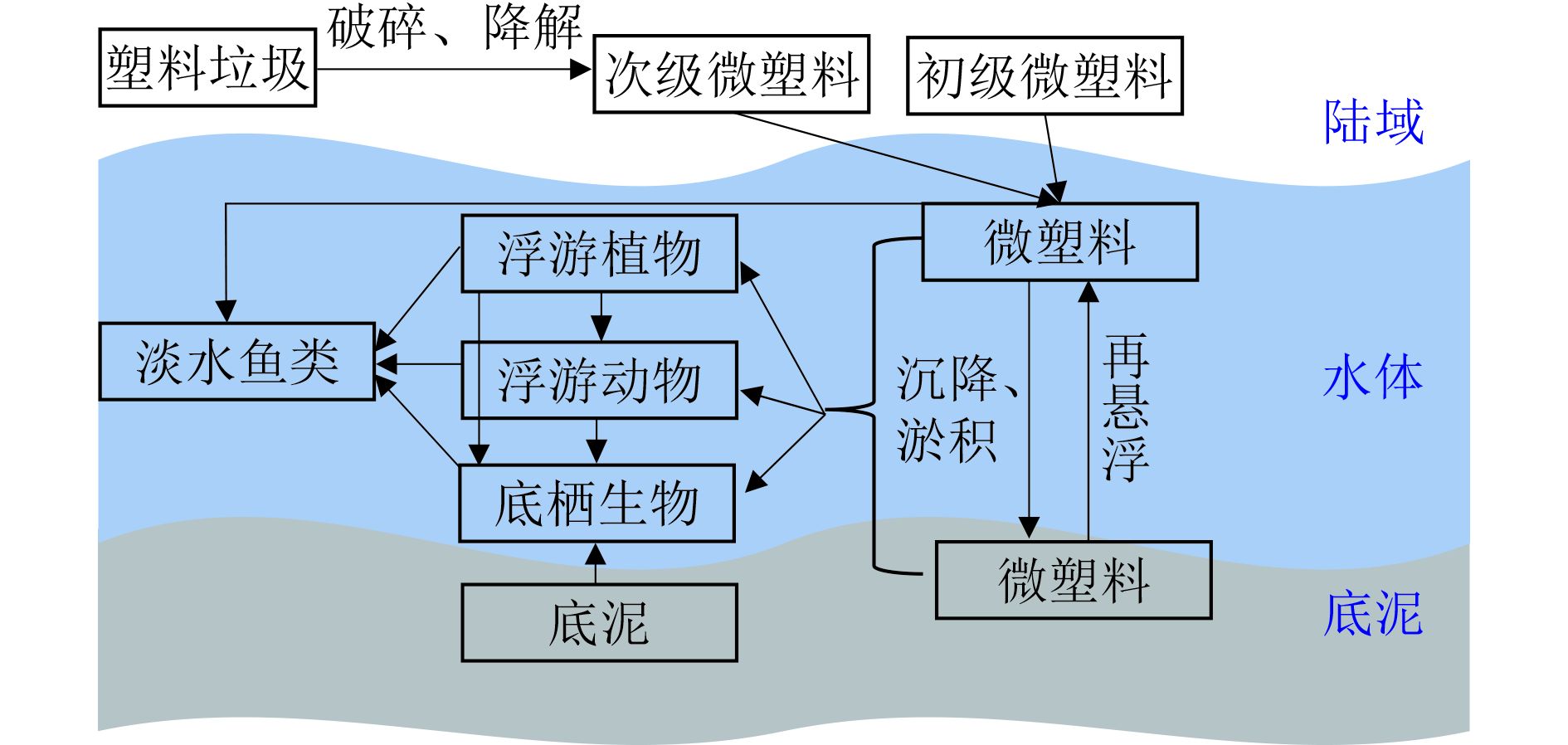
通过梳理淡水环境中微塑料分布现状及毒性效应研究进展,分析淡水环境中微塑料的丰度、类型、粒径、颜色、形状及毒性影响因素,并综述了微塑料对淡水环境生态系统中不同营养级生物的毒性效应。结果表明:微塑料在淡水水体中的分布受人为活动、水文特征、季节及微塑料类型等因素的影响,人类活动较多、水动力条件差及降水较多的水体中微塑料污染严重,不同密度的微塑料在环境介质中赋存存在差异;微塑料毒性与其浓度、粒径、类型密切相关,通过在生物体内富集及携带的化学污染物,影响水生生物的摄食、生长及繁殖能力。我国淡水环境微塑料丰度高于其他国家,建议逐步开展淡水环境微塑料及河流微塑料入海通量的调查及监测。目前国内外微塑料毒性效应研究对象主要关注了浮游植物、大型溞、贻贝及斑马鱼,尚不能满足微塑料生态和健康风险评价要求,亟待开展我国不同营养级本土生物的微塑料毒性效应研究,为将来淡水环境微塑料环境基准的建立提供科技支撑。
Abstract:By summarizing the distribution status and research progress of microplastics in the freshwater environment, the abundance, type, particle size, color, shape and influence factors of microplastics in the freshwater environment were analyzed, and the toxic of microplastics on different trophic organisms in freshwater environment ecosystem were summarized. The results showed that the microplastics distribution in the freshwater bodies was affected by human activities, hydrological characteristics, seasons and microplastics types. Freshwater with more human activities, poor hydrodynamic conditions and more precipitation was seriously polluted by microplastics, and the occurrence of microplastics with different densities was different in environmental media. The toxicity of microplastics was closely related to their concentration, particle size and type, and affected the feeding, growth and reproduction ability of aquatic organisms through the enrichment and carrying of chemical pollutants in organisms. The abundance of microplastics in the freshwater environment in China was higher than that in other countries. It was suggested to gradually carry out the investigation and monitoring of microplastics flux in the freshwater environment and river into the sea. The present microplastics research on the toxic effect at home and abroad mainly focused on phytoplankton, Daphnia magna, mussels and zebrafish, which still could not meet the requirement of the microplastics ecological and health risk assessment. It was urgent to research the microplastics toxicity effect of native organisms at different trophic levels in China, so as to provide scientific and technological support for the establishment of the microplastics environmental benchmark in the freshwater environment in the future.
-
Key words:
- micro plastics /
- abundance /
- fresh water /
- aquatic life /
- environmental risk /
- toxicity effect
-
表 1 淡水环境中微塑料的分布及特征
Table 1. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in freshwater environment
国家 水体名称 介质 丰度 类型 粒径/mm 颜色 主要形状 加拿大 Lake Ontario[17] 地表水 0.8个/L PS、PET、PP 长度(1.0±0.9),
宽度(0.3±0.2)透明色、白色 碎片状、纤维状、薄膜状 雨水径流 15.4个/L PE、PP、PS、PET 长度(0.9±0.9),
宽度(0.2±0.2)透明色、白色 纤维状、薄膜状 农业径流 0.9个/L PS、PP 长度(0.5±0.5),
宽度(0.2±0.2)透明色、白色 纤维状、薄膜状、泡沫状 尾水 13.3个/L PET、PE、PS 长度(1.2±1.0),
宽度(0.07±0.10)蓝色、透明色、白色 纤维状 日本 Awano River[18] 水 102~146个/L PE、PP 50~1 0001) 纤维状 Ayaragi River[18] 水 86~148个/L PE、PET 50~1 0001) 纤维状 Asa River[18] 水 87~172个/L PE、PP 50~1 0001) 纤维状 Majime River[18] 水 99~1 061个/L PE、PET、PP、PS 50~1 0001) 纤维状、碎片状 葡萄牙 Antuă River[19] 水 5.0~8.3 mg/m3
(3月),5.8~51.7 mg/m3(10月)PE、PP 彩色 碎片状、纤维状 美国 St. Lawrence River[20] 沉积物 (13 832±13 677)个/m2 PE 0.40~2.16 球状 中国 长江[21] 水 (3 407.7~13 617.5)×103个/km2 PE、PP、PS 0.112~5 长江[26] 水 0.48~21.52个/L PET <0.5 纤维状 沉积物 35.76~3 185.33个/kg PP <0.5 纤维状、碎片状 长江[27] 水 247~2 686个/m3 PE <0.05 透明色 碎片状 沉积物 15~40个/kg PE、PP 0.048~0.500 透明色 纤维状 黄河[22] 水 930个/L(旱季),497个/L(雨季) PE、PP、PS <2001) 纤维状 釜溪河[23] 沉积物 (232.83±72.83)个/kg PP、PE 片状 虞山河[28] 沉积物 3.5~53 mg/kg PE、PP、PET 透明色 薄膜状 北塘排污河[29] 沉积物 (183.50±11.33)~
(238.00±12.93)个/kg<2 碎片状、纤维状、薄膜 湘西河[30] 水 65.6×105个/km2
(7月),4.5×105个/km2
(1月)PP 1~5 薄片状 丹江口水库[31] 水 467~15 017个/m3 PE、PP 0.5~1.0 蓝色 纤维状 沉积物 15~40个/kg PE、PP 0.048~0.500 透明色 纤维状 三峡水库[31] 水 1 597~12 611个/m3 PE、PP <1 透明色 纤维状 沉积物 25~300个/kg PS 0.5~1 透明色 纤维状 1)单位为μm。 表 2 微塑料对浮游植物的毒性效应
Table 2. Toxic effects of microplastics on phytoplankton
物种名 微塑料类型 粒径 作用时间/h 毒性数据 影响 斜生栅藻[42] PE 200~250 μm 96 8.46×105 μg/L(EC50) 生长抑制 特氏杜氏藻[45] PVC 200~250 μm 96 1.27×105 μg/L(EC50) 生长抑制 PP (5±0.3)mm 24 17 μg/L(EC50) 氧化应激诱导,光合作用降低,生长抑制 中肋骨条藻[46] PP (5±0.3)mm 72 8.5 μg/L(EC50) PE (5±0.3)mm 24 16.5 μg/L(EC50) PE (5±0.3)mm 72 16.4 μg/L(EC50) PS (5±0.3)mm 24 20 μg/L(EC50) PS (5±0.3)mm 72 12.9 μg/L(EC50) PE 74 μm 96 25.3%(生长抑制率) 叶绿素含量降低,光合作用下降,生长抑制 PS 74 μm 96 24.7%(生长抑制率) PVC 74 μm 96 29.3%(生长抑制率) PVC800 1 μm 96 36.2%(生长抑制率) 中肋骨条藻[46] PE、PS、PVC与TCS复合体系 74 μm 96 7×104 μg/L(LC50) 细胞膜破坏,生长抑制,细胞死亡 PVC800与TCS复合体系 1 μm 96 6×104 μg/L(LC50) 斜生栅藻[47] PS 0.1 μm 48、72 藻细胞密度、叶绿素含量、光合作用效率下降 注:EC50为半最大效应浓度;LC50为半数致死浓度。 表 3 微塑料对浮游动物的毒性效应
Table 3. Toxic effects of microplastics on zooplankton
表 4 微塑料对底栖生物的毒性效应
Table 4. Toxic effects of microplastics on benthos
表 5 微塑料对淡水鱼类的毒性效应
Table 5. Toxic effects of microplastics on freshwater fish
-
[1] 丁剑楠, 张闪闪, 邹华, 等.淡水环境中微塑料的赋存、来源和生态毒理效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报,2017,26(9):1619-1626.DING J N, ZHANG S S, ZOU H, et al. Occurrence, source and ecotoxicological effect of microplastics in freshwater environment[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2017,26(9):1619-1626. [2] ZHANG Z Y, MAMAT Z, CHEN Y G. Current research and perspective of microplastics (MPs) in soils (dusts), rivers (lakes), and marine environments in China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2020,202:110976. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110976 [3] 张颖, 金晶, 刘翔.淡水环境中微塑料的来源、赋存研究进展[J]. 科技风,2020(36):143-144. [4] 陈兴兴, 刘敏, 陈滢.淡水环境中微塑料污染研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2020,39(8):3333-3343.CHEN X X, LIU M, CHEN Y. Microplastics pollution in freshwater environment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(8):3333-3343. [5] DING N, AN D, YIN X F, et al. Detection and evaluation of microbeads and other microplastics in wastewater treatment plant samples[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2020,27(13):15878-15887. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08127-2 [6] BIRCH Q T, POTTER P M, PINTO P X, et al. Sources, transport, measurement and impact of nano and microplastics in urban watersheds[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio-Technology,2020,19:275-336. doi: 10.1007/s11157-020-09529-x [7] 李爱峰, 李方晓, 邱江兵, 等.水环境中微塑料的污染现状、生物毒性及控制对策[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(10):88-100.LI A F, LI F X, QIU J B, et al. Pollution status, biological toxicity and control strategy of microplastics in water environments: a review[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2019,49(10):88-100. [8] 汪新.微塑料对海洋环境和渔业生产的影响研究现状及防控措施[J]. 渔业研究,2021,43(1):89-97.WANG X. Research status and prevention and control measures on the impact of microplastics on marine environment and fishery production[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research,2021,43(1):89-97. [9] 荣佳辉, 牛学锐, 韩美, 等.河流微塑料入海通量研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(7):1630-1640.RONG J H, NIU X R, HAN M, et al. Global river microplastics flux into the sea: a review[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(7):1630-1640. [10] 包旭辉, 闫振华, 陆光华.我国淡水中微塑料的污染现状及生物效应研究[J]. 水资源保护,2019,35(6):115-123. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.06.018BAO X H, YAN Z H, LU G H. Study on pollution status and biological effect of microplastics in fresh water of China[J]. Water Resources Protection,2019,35(6):115-123. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.06.018 [11] 夏斌, 杜雨珊, 赵信国, 等.微塑料在海洋渔业水域中的污染现状及其生物效应研究进展[J]. 渔业科学进展,2019,40(3):178-190.XIA B, DU Y S, ZHAO X G, et al. Research progress on microplastics pollution in marine fishery water and their biological effects[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences,2019,40(3):178-190. [12] BOUR A, AVIO C G, GORBI S, et al. Presence of microplastics in benthic and epibenthic organisms: influence of habitat, feeding mode and trophic level[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,243:1217-1225. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.115 [13] 王英雪, 徐熳, 王立新, 等.微塑料在哺乳动物的暴露途径、毒性效应和毒性机制浅述[J]. 环境化学,2021,40(1):41-54. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002WANG Y X, XU M, WANG L X, et al. The exposure routes, organ damage and related mechanism of the microplastics on the mammal[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2021,40(1):41-54. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002 [14] PAROLINI M, FERRARIO C, de FELICE B, et al. Interactive effects between sinking polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics deriving from water bottles and a benthic grazer[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,398:122848. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122848 [15] 郑可. 珠江流域野生淡水鱼类中塑料及有机磷塑料添加剂污染[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2019. [16] 薛云鹏.浅析淡水河流中微塑料的研究进展[J]. 资源节约与环保,2020(1):12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2020.01.012 [17] GRBIĆ J, HELM P, ATHEY S, et al. Microplastics entering northwestern Lake Ontario are diverse and linked to urban sources[J]. Water Research,2020,174:115623. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115623 [18] KABIR A H M E, SEKINE M, IMAI T, et al. Assessing small-scale freshwater microplastics pollution, land-use, source-to-sink conduits, and pollution risks: perspectives from Japanese Rivers polluted with microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,768:144655. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144655 [19] RODRIGUES M O, ABRANTES N, GONÇALVES F J M, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,633:1549-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.233 [20] CREW A, GREGORY-EAVES I, RICCIARDI A. Distribution, abundance, and diversity of microplastics in the upper St. Lawrence River[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,260:113994. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113994 [21] ZHANG K, GONG W, LÜ J Z, et al. Accumulation of floating microplastics behind the Three Gorges Dam[J]. Environmental Pollution,2015,204:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.04.023 [22] HAN M, NIU X R, TANG M, et al. Distribution of microplastics in surface water of the lower Yellow River near estuary[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,707:135601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135601 [23] 张耀丹, 李锡鹏, 王旭, 等.釜溪河沉积物微塑料颗粒调查分析的研究[J]. 四川环境,2019,38(2):46-52.ZHANG Y D, LI X P, WANG X, et al. Study on analysis of the microplastics in the sediments of Fuxi River[J]. Sichuan Environment,2019,38(2):46-52. [24] XIONG X, ZHANG K, CHEN X C, et al. Sources and distribution of microplastics in China's largest inland lake:Qinghai Lake[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,235:899-906. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.081 [25] WANG W F, YUAN W K, CHEN Y L, et al. Microplastics in surface waters of Dongting Lake and Hong Lake, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,633:539-545. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.211 [26] HU L L, CHERNICK M, HINTON D E, et al. Microplastics in small waterbodies and tadpoles from Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(15):8885-8893. [27] 张胜, 潘雄, 林莉, 等.长江源区水体微塑料组成及分布特征初探[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(4):12-18. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200174ZHANG S, PAN X, LIN L, et al. Preliminary study on composition and distribution characteristics of microplastics in water from the source region of Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(4):12-18. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200174 [28] NIU S P, WANG X, RAO Z, et al. Microplastics present in sediments of Yushan River: a case study for urban tributary of the Yangtze River[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal,2021,30(3):314-330. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2020.1841731 [29] 赵艳民, 马迎群, 温泉, 等.基于不确定性的天津市北塘排污河表层沉积物微塑料污染评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(3):554-561. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200098ZHAO Y M, MA Y Q, WEN Q, et al. Evaluation of microplastics pollution in surface sediments of Beitang Drainage River in Tianjin City based on uncertainty[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(3):554-561. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200098 [30] ZHANG K, XIONG X, HU H J, et al. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastic pollution in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,51(7):3794-3801. [31] 底明晓. 长江流域河型水库微塑料污染特征及微塑料与雌二醇的吸附动力学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院武汉植物园), 2019. [32] 冯志桥, 钟伟, 罗鑫, 等.洞庭湖区下新码头水体富营养化评价及微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 环境保护与循环经济,2019,39(4):46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2019.04.011 [33] CAO L, WU D, LIU P, et al. Occurrence, distribution and affecting factors of microplastics in agricultural soils along the lower reaches of Yangtze River, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,794:148694. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148694 [34] WAKKAF T, EL ZRELLI R, KEDZIERSKI M, et al. Characterization of microplastics in the surface waters of an urban lagoon (Bizerte lagoon, Southern Mediterranean Sea): composition, density, distribution, and influence of environmental factors[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,160:111625. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111625 [35] TOUMI H, ABIDLI S, BEJAOUI M. Microplastics in freshwater environment: the first evaluation in sediments from seven water streams surrounding the lagoon of Bizerte (Northern Tunisia)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2019,26(14):14673-14682. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04695-0 [36] 李江南, 凌玮, 沈茜, 等.双台子河与大辽河表层水体微塑料特征与分布研究[J]. 生态毒理学报,2021,16(3):192-199.LI J N, LING W, SHEN Q, et al. Characteristics and distribution of microplastics in surface water from Shuangtaizi River and Daliao River[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2021,16(3):192-199. [37] MOORE C J, LATTIN G L, ZELLERS A F. Quantity and type of plastic debris flowing from two urban rivers to coastal waters and beaches of Southern California[J]. Revista de Gestão Costeira Integrada,2011,11(1):65-73. [38] LIMA A R A, COSTA M F, BARLETTA M. Distribution patterns of microplastics within the plankton of a tropical estuary[J]. Environmental Research,2014,132:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2014.03.031 [39] 牛学锐. 黄河口表层水微塑料赋存特征研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2020. [40] JIANG C B, YIN L S, WEN X F, et al. Microplastics in sediment and surface water of west Dongting Lake and south Dongting Lake: abundance, source and composition[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2018,15(10):2164. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102164 [41] 张辉, 彭宇琼, 邹贤妮, 等.南亚热带特大型水库浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系: 以新丰江水库为例[J]. 湖泊科学,2022,34(2):404-417. doi: 10.18307/2022.0204ZHANG H, PENG Y Q, ZOU X N, et al. The characteristics of phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors of a large reservoir in subtropic of Southern China: a case study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2022,34(2):404-417. doi: 10.18307/2022.0204 [42] 殷岑. 微塑料和有机污染物对水生生物的联合毒性效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2018. [43] WANG Q J, JIN X X, ZHANG Y, et al. The toxicity of virgin and UV-aged PVC microplastics on the growth of freshwater algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,749:141603. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141603 [44] WU Y M, GUO P Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. Effect of microplastics exposure on the photosynthesis system of freshwater algae[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,374:219-227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.039 [45] SCHIAVO S, OLIVIERO M, CHIAVARINI S, et al. Polyethylene, polystyrene, and polypropylene leachate impact upon marine microalgae Dunaliella tertiolectatiolecta[J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A,2021,84(6):249-260. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2020.1860173 [46] 朱志林. 典型微塑料与水环境中PPCPs的复合毒性及吸附行为研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019. [47] 姜航, 丁剑楠, 黄叶菁, 等.聚苯乙烯微塑料和罗红霉素对斜生栅藻(Scenedesmus obliquus)和大型溞(Daphnia magna)的联合效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报,2019,28(7):1457-1465.JIANG H, DING J N, HUANG Y J, et al. Combined effects of polystyrene microplastics and roxithromycin on the green algae (Scenedesmus obliquus) and waterflea (Daphnia magna)[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2019,28(7):1457-1465. [48] 刘同琳, 陈皓若, 洪陈聪, 等.苏州城区河道后生浮游动物群落结构与环境因子的关系[J]. 动物学杂志,2021,56(5):674-685.LIU T L, CHEN H R, HONG C C, et al. Relationship between metazooplankton community structure and environmental factors in Suzhou urban river[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology,2021,56(5):674-685. [49] YIN C, YANG X H, ZHAO T Y, et al. Changes of the acute and chronic toxicity of three antimicrobial agents to Daphnia magna in the presence/absence of micro-polystyrene[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,263:114551. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114551 [50] 李勤, 李尚谕, 熊雄, 等.微塑料对大型溞的急性毒性研究[J]. 水生生物学报,2021,45(2):292-298. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.180LI Q, LI S Y, XIONG X, et al. Study on acute toxicity of microplastic to Daphnia magna[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2021,45(2):292-298. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.180 [51] 贾静. 微塑料在水生食物链中的富集及毒性效应研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2018. [52] 高嘉蔚, 赵莎莎, 李富云, 等.微塑料对大型溞摄食和抗氧化防御系统的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(5):1205-1212.GAO J W, ZHAO S S, LI F Y, et al. Effects of microplastics on feeding behavior and antioxidant system of Daphnia magna[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(5):1205-1212. [53] 巩宁, 韩旭, 李佳璠, 等.不同粒径聚乙烯微粒对大型溞的生物毒性效应[J]. 海洋环境科学,2020,39(2):169-176. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200201GONG N, HAN X, LI J F, et al. Toxic effects of different particle size polyethylene microbeads on Daphnia magna[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2020,39(2):169-176. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200201 [54] 涂烨楠, 凌海波, 吴辰熙, 等.淡水浮游动物摄食微塑料过程及影响研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,2018,41(11):1-8.TU Y N, LING H B, WU C X, et al. Ingestion and effects of microplastics on freshwater zooplankton[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,41(11):1-8. [55] DAWSON A L, KAWAGUCHI S, KING C K, et al. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill[J]. Nature Communications,2018,9:1001. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03465-9 [56] 任中华. 莱州湾及黄河口海域大型底栖生物群落结构多样性及其生态学研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016. [57] KOLANDHASAMY P, SU L, LI J N, et al. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: a novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,610/611:635-640. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.053 [58] ARGAMINO R, JANAIRO J I B. Qualitative assessment and management of microplastics in Asian green mussels (Perna viridis) cultured in Bacoor Bay, Cavite, Phillipines[J]. EnvironmentAsia,2016,9(2):48-54. [59] DÉTRÉE C, GALLARDO-ESCÁRATE C. Single and repetitive microplastics exposures induce immune system modulation and homeostasis alteration in the edible mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2018,83:52-60. [60] BALBI T, CAMISASSI G, MONTAGNA M, et al. Impact of cationic polystyrene nanoparticles (PS-NH2) on early embryo development of Mytilus galloprovincialis: effects on shell formation[J]. Chemosphere,2017,186:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.120 [61] REDONDO-HASSELERHARM P E, GORT G, PEETERS E T H M, et al. Nano- and microplastics affect the composition of freshwater benthic communities in the long term[J]. Science Advances,2020,6(5):eaay4054. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay4054 [62] 马思琦. 鱼类分类和功能多样性研究: 以济南地区鱼类为例[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2020. [63] ZHANG C N, WANG J, ZHOU A G, et al. Species-specific effect of microplastics on fish embryos and observation of toxicity kinetics in larvae[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,403:123948. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123948 [64] WEBER A, von RANDOW M, VOIGT A L, et al. Ingestion and toxicity of microplastics in the freshwater gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis: no microplastic-induced effects alone or in combination with copper[J]. Chemosphere,2021,263:128040. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128040 [65] 何君仪. 微塑料与磷酸三苯酯对斑马鱼的联合毒性效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2019. [66] RAINIERI S, CONLLEDO N, LARSEN B K, et al. Combined effects of microplastics and chemical contaminants on the organ toxicity of zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Environmental Research,2018,162:135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.12.019 [67] 赵佳, 饶本强, 郭秀梅, 等.微塑料对斑马鱼胚胎孵化影响及其在幼鱼肠道中的积累[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(1):485-491.ZHAO J, RAO B Q, GUO X M, et al. Effects of microplastics on embryo hatching and intestinal accumulation in larval zebrafish Danio rerio[J]. Environmental Science,2021,42(1):485-491. [68] 王林林. PVC微塑料对黄河鲤幼鱼的毒理效应研究[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2019. [69] 杨秉倬, 黄河.微塑料对红鲫鱼幼鱼抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术,2019,42(12):23-27.YANG B Z, HUANG H. Effect of microplastics on antioxidant enzyme system in juvenile red crucian carp[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,42(12):23-27. [70] 田莉莉, 文少白, 马旖旎, 等.海水青鳉摄食微塑料的荧光和C-14同位素法示踪定量研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(11):2571-2578.TIAN L L, WEN S B, MA Y N, et al. Quantification of ingestion of microplastics by marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) using fluorescence and C-14 isotope radiotracer[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(11):2571-2578. [71] 李文华, 简敏菲, 余厚平, 等.鄱阳湖流域饶河龙口入湖段优势淡水鱼类对微塑料及重金属污染物的生物累积[J]. 湖泊科学,2020,32(2):357-369. doi: 10.18307/2020.0206LI W H, JIAN M F, YU H P, et al. Bioaccumulation effects of microplastics and heavy metals pollutants in the dominant freshwater fish species in the Longkou entry of Raohe River, Lake Poyang Basin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2020,32(2):357-369. doi: 10.18307/2020.0206 [72] 李佳娜. 贻贝中微塑料的污染特征及其与典型污染物的复合毒性效应[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019. [73] 左优. 聚苯乙烯微塑料与四溴双酚—A对斑马鱼的复合毒性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019. [74] 段鑫越, 关文玲, 程昊东, 等.胚胎绒毛膜对微塑料颗粒与镉联合作用的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2021,41(3):1422-1428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.03.046DUAN X Y, GUAN W L, CHENG H D, et al. Effect of chorionic villi on the combination action of microplastic particles and cadmium[J]. China Environmental Science,2021,41(3):1422-1428. ◇ doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.03.046 -





 下载:
下载: