Study on the inhibitory effect of phenol on anammox granular sludge denitrification performance
-
摘要:
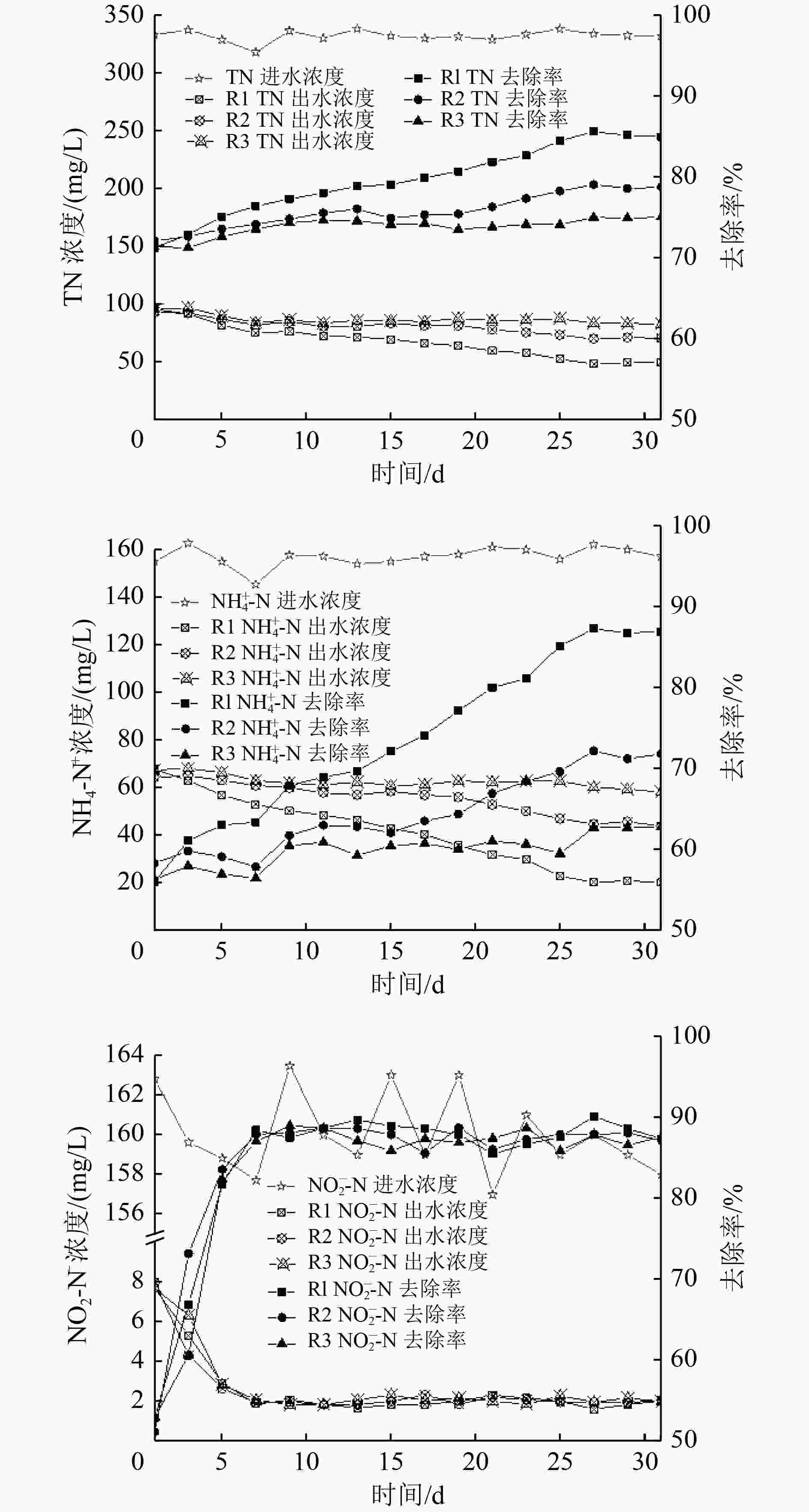
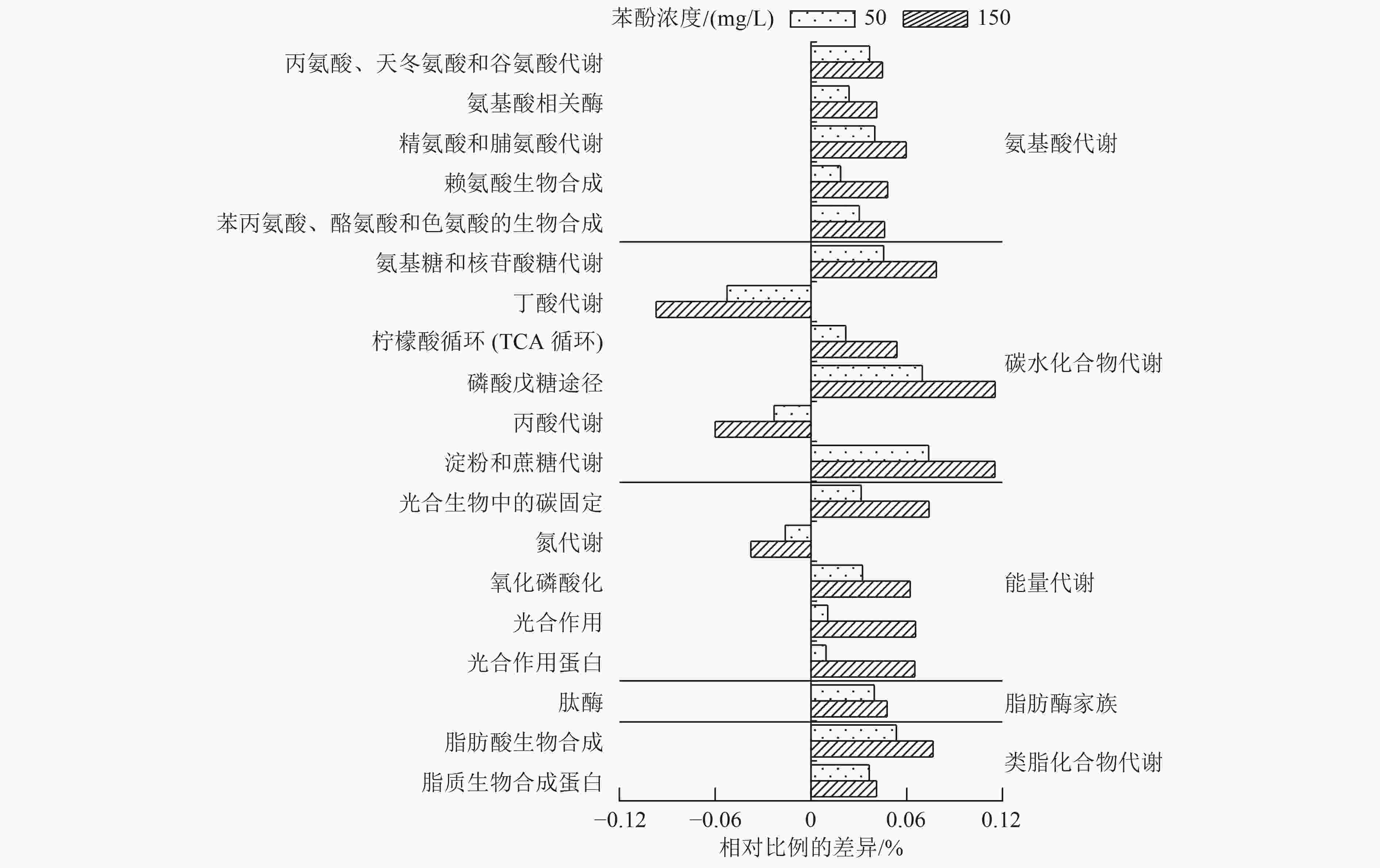
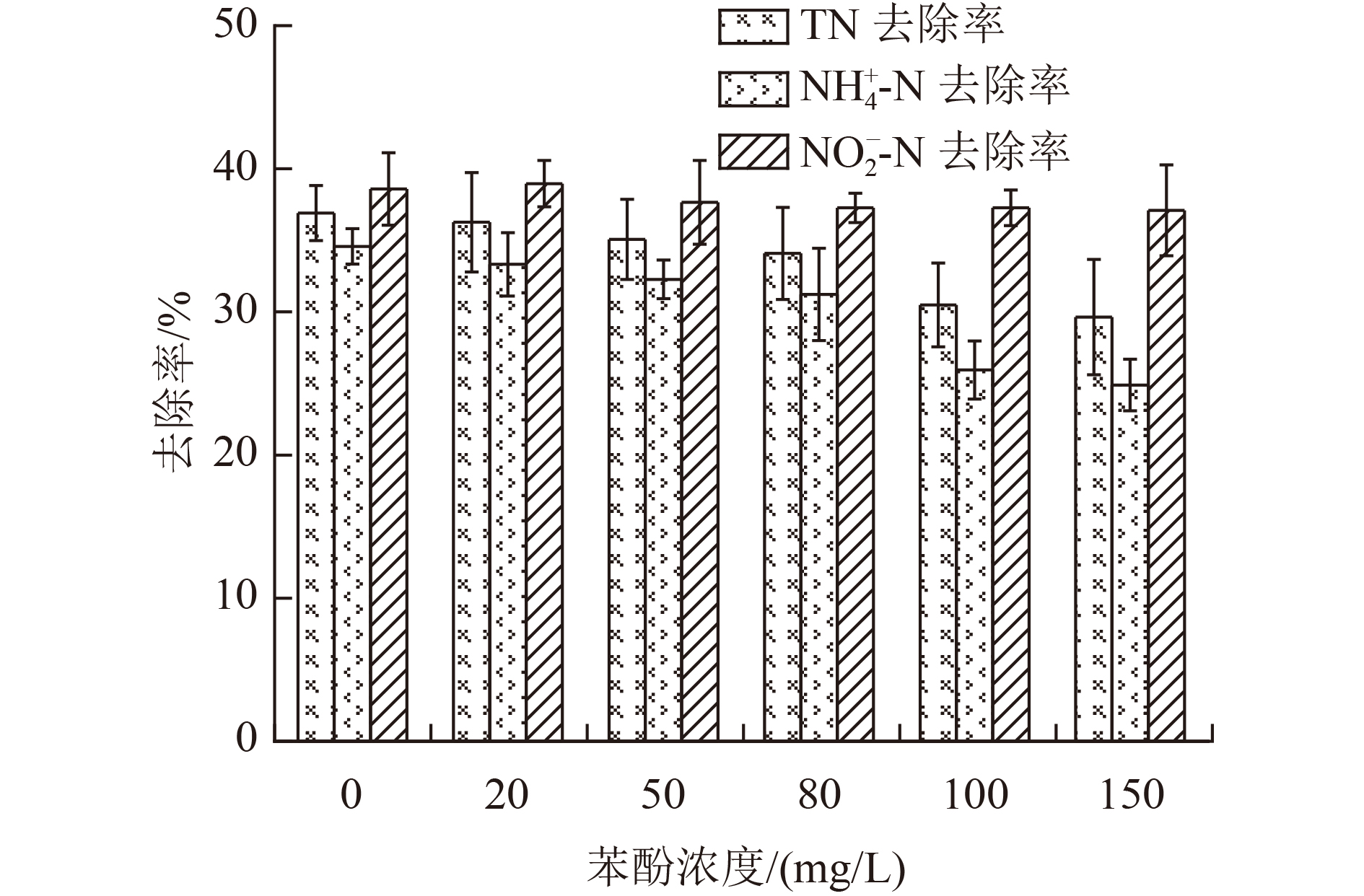
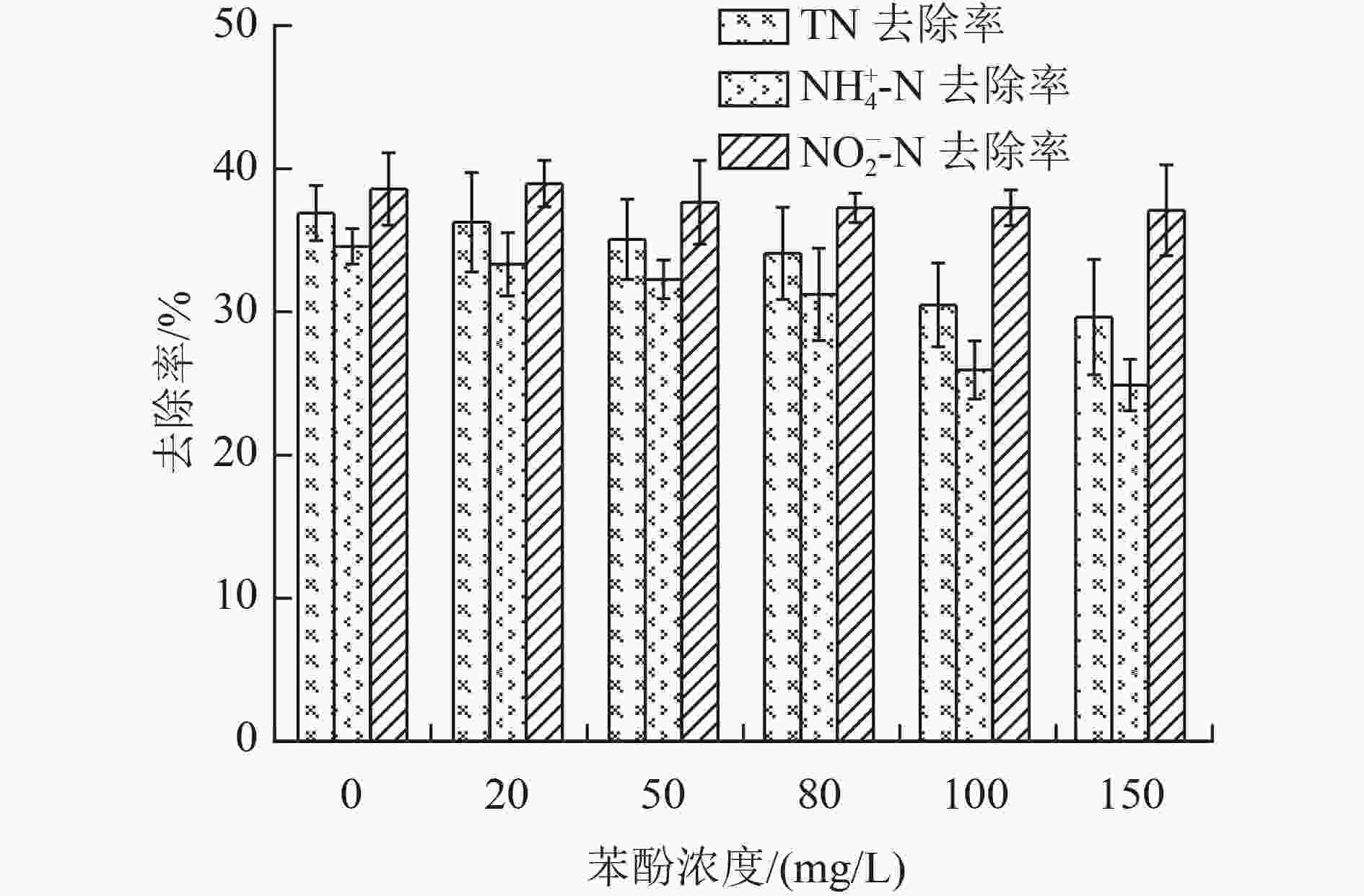
为了考察有毒有机物苯酚对厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥活性的抑制作用,研究了不同苯酚浓度(50和100 mg/L)条件下厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥对氨氮(
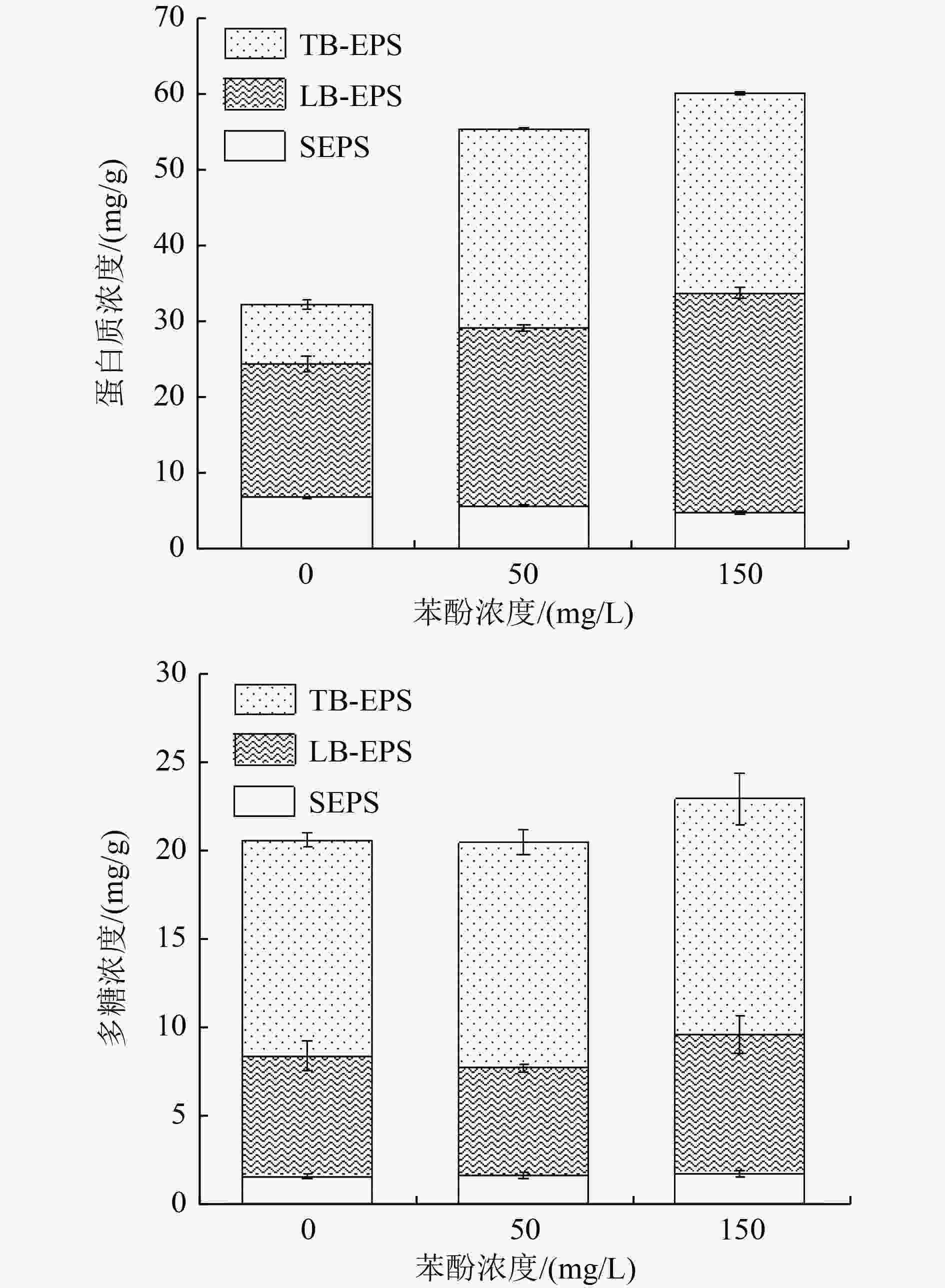
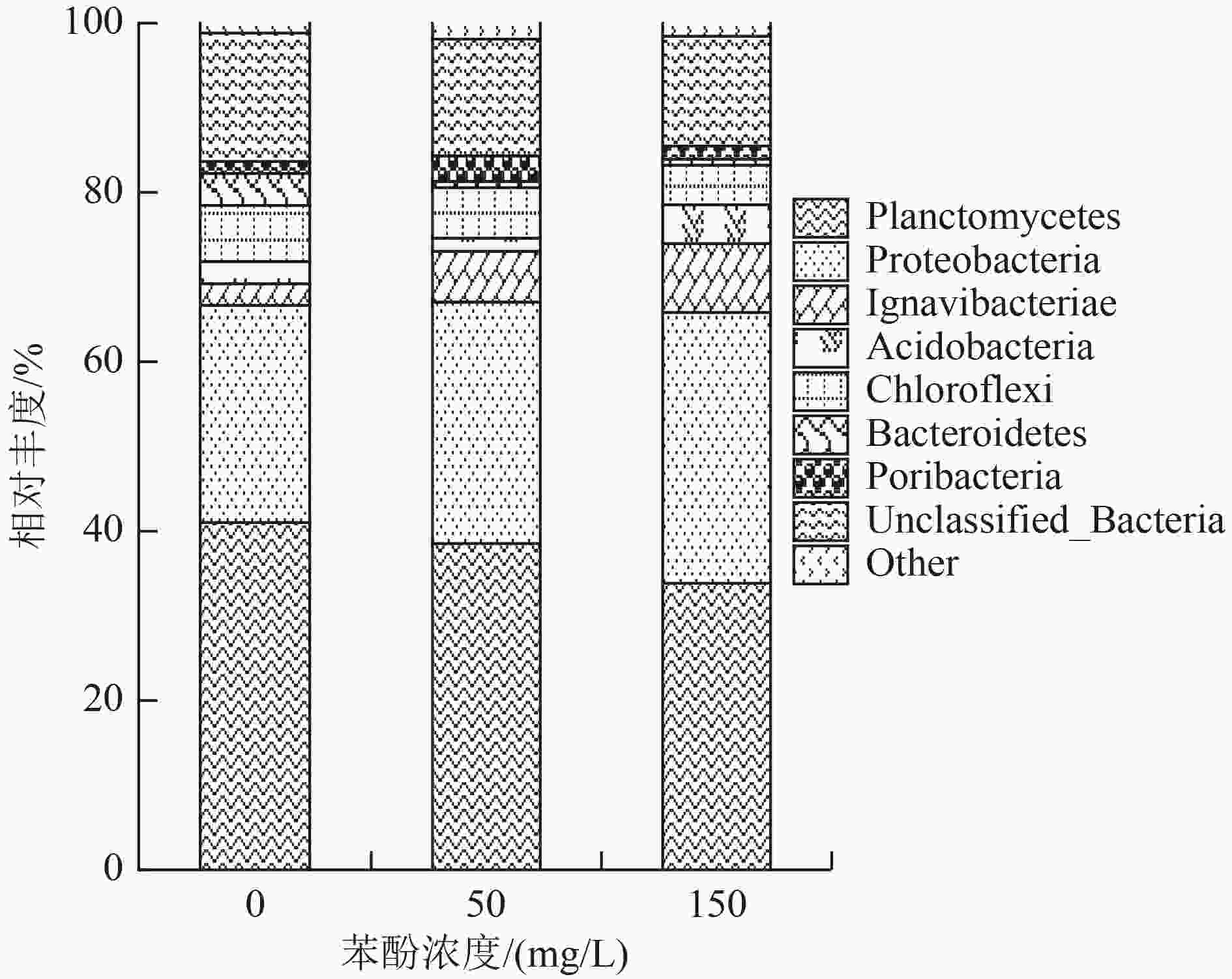
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N)和亚硝酸盐氮(NO2 −-N)去除率的影响,并综合胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)分泌情况和微生物群落变化趋势,分析颗粒污泥脱氮性能退化的原因。结果表明,苯酚抑制了厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的脱氮性能,当苯酚浓度为50和150 mg/L时,$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率分别降低了15.05%和24.35%。苯酚刺激了颗粒污泥中微生物胞外聚合物的分泌,以抵御其毒性胁迫,当苯酚浓度为50、150 mg/L时,颗粒污泥的总EPS含量分别增加了43.62%和57.29%。苯酚导致厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥中微生物群落发生变化,在苯酚浓度为50、150 mg/L时,厌氧氨氧化细菌所属的浮霉菌门的相对丰度由41.01%分别降至38.52%、33.84%。通过PICRUSt(Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States)预测分析发现,在苯酚胁迫下与厌氧氨氧化细菌相关的关键代谢通路受到了抑制,苯酚影响了与颗粒污泥脱氮性能相关的功能性细菌的代谢。Abstract:In order to investigate the inhibitory effect of the toxic organic matter of phenol on anammox granular sludge, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen (
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N) and nitrite nitrogen (NO2 −-N) in anammox granular sludge under different phenol conditions (50 and 100 mg/L) was studied. The reasons for the degradation of granular sludge performance were analyzed by integrating the secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and the change trend of microbial community. The results showed that phenol inhibited the denitrification performance of anammox granular sludge. When the phenol concentration was 50 and 150 mg/L, the removal rate of$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N was reduced by 15.05% and 24.35%, respectively. Phenol stimulated the secretion of microbial EPS in granular sludge to resist its toxic stress. When the phenol concentration was 50 and 150 mg/L, the total EPS content of granular sludge increased by 43.62% and 57.29%, respectively. The microbial community of the anammox granular sludge changed under different phenol conditions. Under the phenol concentration of 50 and 150 mg/L, the relative abundance of Planctomycetes distributed by anammox bacteria decreased from 41.01% to 38.52% and 33.84%, respectively. Through the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) prediction analysis, it was found that the key metabolic pathways related to anammox bacteria was inhibited, and the metabolism of functional bacteria related to the denitrification of granular sludge was affected by phenol. -
表 1 不同浓度苯酚胁迫下的EPS浓度
Table 1. EPS contents under stress of different concentrations of phenol of phenol
苯酚浓度/(mg/L) SEPS/(mg/g) LB-EPS/(mg/g) TB-EPS/(mg/g) 0 8.23±0.20 24.42±1.83 20.06±1.07 50 7.12±0.24 29.54±0.54 39.04±0.79 150 6.31±0.46 36.94±1.84 39.66±1.65 表 2 16S rRNA多样性指数
Table 2. 16S rRNA diversity indexes
苯酚浓度/
(mg/L)丰富度 Shannon
指数Simpson
指数Pielou
指数Chao1
指数ACE
指数覆盖率 0 177 2.48 0.81 0.48 198.33 195.06 0.99 50 189 2.81 0.86 0.54 192.06 193.23 0.99 150 198 2.79 0.83 0.53 200.25 201.33 0.99 -
[1] RONGSAYAMANONT C, KHONGKHAEM P, LUEPROMCHAI E, et al. Inhibitory effect of phenol on wastewater ammonification[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,309:123312. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123312 [2] CHEN R, REN L F, SHAO J H, et al. Changes in degrading ability, populations and metabolism of microbes in activated sludge in the treatment of phenol wastewater[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(83):52841-52851. doi: 10.1039/C7RA09225C [3] ZHOU X, WANG G L, YIN Z Y, et al. Performance and microbial community in a single-stage simultaneous carbon oxidation, partial nitritation, denitritation and anammox system treating synthetic coking wastewater under the stress of phenol[J]. Chemosphere,2020,243:125382. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125382 [4] 姚宏, 王钰楷, 何永淼, 等.两级厌氧-好氧-厌氧氨氧化组合工艺处理制药和淀粉混合废水[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(3):183-188.YAO H,WANG Y K,HE Y M, et al. Study on Antibiotic and Starch Mixed Wastewater Treatment by Combined Two-phase Anaerobic, Aerobic and ANAMMOX Process[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(3):183-188. [5] TOH S K, ASHBOLT N J. Adaptation of anaerobic ammonium-oxidising consortium to synthetic coke-ovens wastewater[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2002,59(2/3):344-352. [6] XIAO R, NI B J, LIU S T, et al. Impacts of organics on the microbial ecology of wastewater anammox processes: recent advances and meta-analysis[J]. Water Research,2021,191:116817. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116817 [7] van de GRAAF A A, de BRUIJN P, ROBERTSON L A, et al. Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor[J]. Microbiology,1996,142(8):2187-2196. doi: 10.1099/13500872-142-8-2187 [8] NHAT P T, BIEC H N, TUYET MAI N T, et al. Application of a partial nitritation and anammox system for the old landfill leachate treatment[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation,2014,95:144-150. [9] LÜ L T, ZHANG K, LI Z J, et al. Inhibition of anammox activity by phenol: suppression effect, community analysis and mechanism simulation[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation,2019,141:30-38. [10] 杨朋兵, 李祥, 黄勇, 等.苯酚对厌氧氨氧化污泥脱氮效能长短期影响[J]. 环境科学,2015,36(10):3771-3777.YANG P B, LI X, HUANG Y, et al. Short or long term influence of phenol on nitrogen removal efficiency of ANAMMOX sludge[J]. Environmental Science,2015,36(10):3771-3777. [11] 王晗. NaCl盐度对ANAMMOX-EGSB反应器性能及AnAOB的影响机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. [12] 李惠娟, 彭党聪, 陈国燕, 等.ANAMMOX的快速启动及EPS在ANAMMOX颗粒污泥中的空间分布[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(7):2931-2940. [13] PEREIRA A D, LEAL C D, DIAS M F, et al. Effect of phenol on the nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure and composition of an anammox reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology,2014,166:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.043 [14] WANG W G, XIE H C, WANG H, et al. Organic compounds evolution and sludge properties variation along partial nitritation and subsequent anammox processes treating reject water[J]. Water Research,2020,184:116197. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116197 [15] HOU X L, LIU S T, ZHANG Z T. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in determining the high aggregation ability of anammox sludge[J]. Water Research,2015,75:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.031 [16] WANG S, LIU L J, LI H X, et al. The branched chains and branching degree of exopolysaccharides affecting the stability of anammox granular sludge[J]. Water Research,2020,178:115818. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115818 [17] YANG G F, GUO X L, CHEN S X, et al. The evolution of Anammox performance and granular sludge characteristics under the stress of phenol[J]. Bioresource Technology,2013,137:332-339. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.145 [18] BHATTACHARJEE A S, WU S, LAWSON C E, et al. Whole-community metagenomics in two different anammox configurations: process performance and community structure[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,51(8):4317-4327. [19] GONZALEZ-GIL G, SOUGRAT R, BEHZAD A R, et al. Microbial community composition and ultrastructure of granules from a full-scale anammox reactor[J]. Microbial Ecology,2015,70(1):118-131. doi: 10.1007/s00248-014-0546-7 [20] ZHENG M Q, ZHU H, HAN Y X, et al. Comparative investigation on carbon-based moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) for synchronous removal of phenols and ammonia in treating coal pyrolysis wastewater at pilot-scale[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,288:121590. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121590 [21] FENG Y, ZHAO Y P, GUO Y Z, et al. Microbial transcript and metabolome analysis uncover discrepant metabolic pathways in autotrophic and mixotrophic anammox consortia[J]. Water Research,2018,128:402-411. ⊗ doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.069 -







 下载:
下载: