Effects of vegetation restoration methods on vegetation growth indexes and soil physical and chemical properties of spoil ground in red-soil hilly region
-
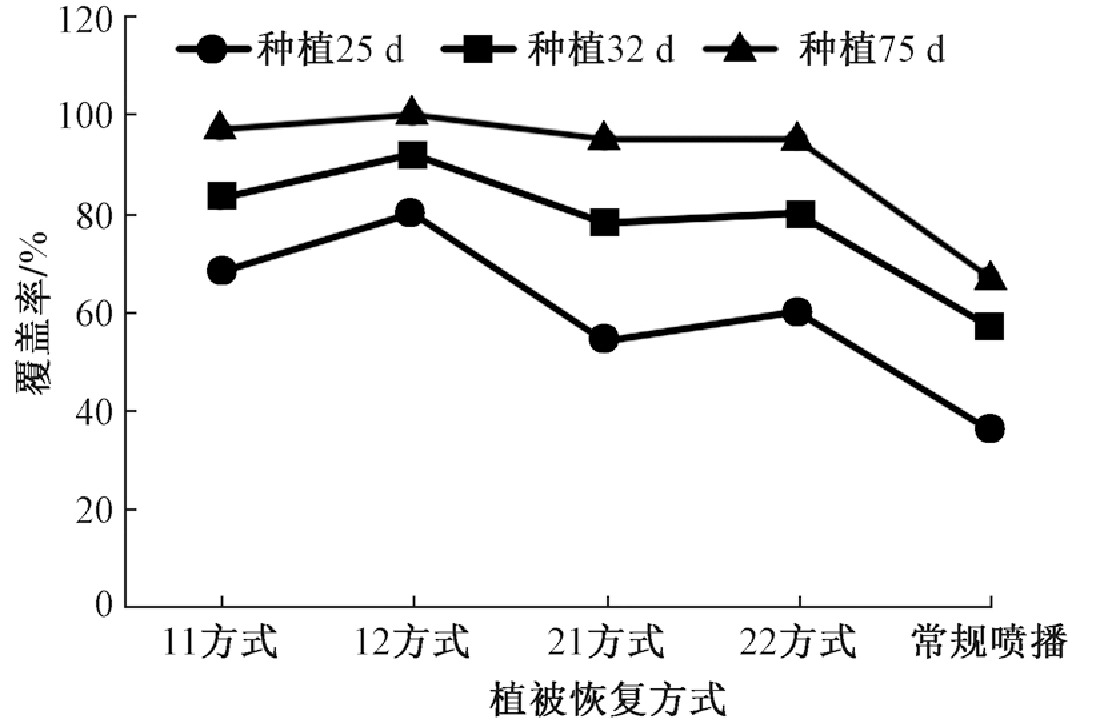
摘要: 以江西高速公路某弃土场为例,探讨红壤丘陵区弃土场植被恢复的关键技术,在了解弃土场气候特点及地质情况的基础上,通过测土配方,采用草灌混播方式,设置3种植被配置方案,包括植被配置1(狗牙根+百喜草+紫花苜蓿+白三叶+伞房决明+紫穗槐)、植被配置2(紫花苜蓿+白三叶+狗牙根+马棘+美丽胡枝子)、常规喷播(狗牙根+紫花苜蓿+马棘),2种基肥配置方案,包括基肥配置1(50 g/m2复合肥)、基肥配置2(100 g/m2复合肥),分析不同处理下植被恢复情况及土壤理化性质,并确定最佳组合。结果表明:植被配置1+基肥配置2恢复方式下植被长势好,密度较大,1个月后覆盖率达到80%,土壤理化性质较其他处理具有显著变化,与常规喷播相比,土壤容重减少0.17 g/cm3,土壤总孔隙度、有机质及碱解氮浓度分别提高了19.68%、62%和8%,有效解决了弃土场复绿覆盖不均匀、时间长的难题,可以起到预防和减轻水土流失的作用,具有一定的经济效益和较好的生态效益。Abstract: Taking an abandoned soil field of Jiangxi expressway as an example, the key techniques of vegetation restoration in the abandoned soil field of red-soil hilly area was discussed. Based on the understanding of the climatic characteristics and geological conditions of the spoil ground, three vegetation schemes and two basic fertilizer schemes were set up by soil testing formula and grass irrigation mixed sowing method. The three vegetation schemes were: Vegetation allocation 1 (Bermudagrass + Bahia grass + Alfalfa + White clover + Cassia corymbosa+ Amorpha fruticosa), Vegetation allocation 2 (Alfalfa + White clover + Bermudagrass + Horse thorn + Beautiful lespedeza), and conventional spray seeding (Bermudagrass + Alfalfa + Horse thorn). The two basic fertilizer schemes were Fertilizer scheme 1 (50 g/m2 compound fertilizer) and Fertilizer scheme 2 (100 g/m2 compound fertilizer). The vegetation restoration and soil physical and chemical properties were analyzed to determine the best combination. The results showed that: under Vegetation allocation 1 + Fertilizer schemes 2, the vegetation grew well, the density was high, and the coverage rate reached 80% after one month. And the physical and chemical properties of soil were significantly changed compared with other treatments. Compared with conventional spray seeding, the soil capacity decreased by 0.17 g/cm3, and the total porosity of soil, organic matter and alkaline nitrogen increased by 19.68%, 62% and 8%, respectively, which could effectively solve the problem of uneven green coverage and long time in the spoil ground, prevent and reduce soil and water loss, and thus have great economic and ecological benefits.
-
表 1 弃土场土壤理化性质
Table 1. Soil physical and chemical properties of abandoned soil site
土壤深度/
cm容重/
(g/cm3)含水率/
%孔隙度/
%pH 有机质浓度/
(g/kg)全氮浓度/
(g/kg)碱解氮浓度/
(mg/kg)有效磷浓度/
(mg/kg)速效钾浓度/
(mg/kg)0~10 1.51 21.08 43.04 5.08 14.91 2.90 67.50 3.57 186.47 10~20 1.74 19.41 34.19 5.12 11.26 2.34 67.53 1.93 205.40 表 2 不同植被恢复方式对地上生物量的影响
Table 2. Effects of different vegetation restoration methods on aboveground biomass
g/m2 11方式 12方式 21方式 22方式 常规喷播 346.3±16.3b 421.7±41.8a 250.8±17.3c 318.2±9.7b 247.5±25.3c 注:不同字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同植被恢复方式下土壤物理性质
Table 3. Soil physical properties under different vegetation restoration methods
植被恢复方式 深度/cm 容重/(g/cm3) 含水率/% 总孔隙度/% 11方式 0~10 1.40±0.53b 19.72±8.35a 43.32±12.24b 10~20 1.57±0.62B 17.35±7.32B 34.39±7.83B 12方式 0~10 1.34±0.42c 21.08±10.03a 56.21±12.28a 10~20 1.51±0.63C 19.41±8.46A 38.61±10.29A 21方式 0~10 1.42±0.12b 20.12±9.65a 48.57±13.53b 10~20 1.68±0.47A 19.32±7.16A 37.38±11.47A 22方式 0~10 1.41±0.26b 19.61±9.05a 44.34±10.34a 10~20 1.59±0.26B 17.82±8.68B 36.25±9.69A 常规喷播 0~10 1.51±0.68a 17.94±8.35b 36.53±7.87c 10~20 1.58±0.51B 17.12±7.32B 37.41±9.26A 注:不同小写字母代表不同处理在0~10 cm深度的土壤物理性质有显著差异(P<0.05);不同大写字母代表不同处理在10~20 cm深度的土壤物理性质有显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 4 植被高度与土壤理化性质的相关性
Table 4. Correlation between vegetation height and soil physical and chemical properties
项目 高度 覆盖率 地上生物量 容重 孔隙度 含水率 有机质浓度 全氮浓度 碱解氮浓度 速效磷浓度 全钾浓度 速效钾浓度 高度 1.00 覆盖率 0.21* 1.00 地上生物量 0.62* 0.45* 1.00 容重 −0.308 −0.24* −0.37 1.00 孔隙度 0.65** 0.43** 0.55* −0.74** 1.00 含水率 0.21 0.42 0.45 −0.52* 0.32 1.00 有机质浓度 0.53* 0.176 0.50 −0.62* 0.55* −0.43* 1.00 全氮浓度 0.297 0.247* 0.324 −0.34 0.67** 0.52 0.72** 1.00 碱解氮浓度 0.41 0.32* 0.16 0.22 0.32 0.22 0.40* 0.213 1.00 速效磷浓度 0.35 0.34 0.51* −0.42 0.729** 0.174** 0.638* 0.76** 0.39 1.00 全钾浓度 0.35 0.20 −0.24* 0.17 0.54 0.323 0.23 0.42 0.11 0.27 1.00 速效钾浓度 −0.21 0.42* −0.37 0.28 0.13 0.42** 0.38 0.25 0.33* 0.25 0.22 1.00 注:*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。 表 5 经济效益对比
Table 5. Comparison of economic benefits
元/m2 项目 种子 施肥 保水剂 黏合剂 喷播费用 土地整理 总计 常规喷播 2.0 0.18 0.3~0.4 0.3~0.4 0.7 0 3.48~3.68 12方式 0.8~1.0 0.36 0 0 0 0.5~0.7 1.66~2.06 节省资金 1.0~1.2 −0.18 0.3~0.4 0.3~0.4 0.7 −0.7~ −0.5 1.62~2.02 -
[1] 张展, 高照良, 宋晓强, 等.我国高速公路建设对生态环境的影响初探[J]. 水土保持通报,2008,28(5):33-38.ZHANG Z, GAO Z L, SONG X Q, et al. Preliminary study of the effects of expressway construction on eco-environment in China[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2008,28(5):33-38. [2] 寇龙. 山区高速公路建设对水土流失环境影响与防治研究: 以西商高速公路为例[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019. [3] 徐斌, 高霞, 高照良.不同施肥下植物对交通运输弃土场土壤改良的分析[J]. 生态经济,2015,31(3):173-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2015.03.037XU B, GAO X, GAO Z L. Analysis on soil improvement of plants with different fertilization in spoil ground of transportation[J]. Ecological Economy,2015,31(3):173-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2015.03.037 [4] 王旭, 陈思, 邓瑞峰.张承高速公路边坡防护优化及取弃土场生态恢复研究[J]. 公路交通科技(应用技术版),2016,12(1):55-58. [5] CAO W, OMRAN B A, LEI Y K, et al. Studying early stage slope protection effects of vegetation communities for Xinnan Highway in China[J]. Ecological Engineering,2018,110:87-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.08.033 [6] 黄进勇, 严力蛟, 王兆骞.红壤小流域不同土地利用方式下的水土流失特征[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2002,28(1):78-82.HUANG J Y, YAN L J, WANG Z Q. The characteristics of soil and water loss of different land utilization models in small watersheds of red soil region[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University (Agriculture & Life Sciences),2002,28(1):78-82. [7] 肖胜生, 王聪, 郭利平, 等.南方红壤丘陵区水土保持生态服务功能提升研究进展: 以江西省兴国县塘背河小流域为例[J]. 水土保持通报,2019,39(6):289-294.XIAO S S, WANG C, GUO L P, et al. Progress of researches on enhancing soil erosion control and ecological services in red soil hilly region of South China: a case study at Tangbei River watershed of Xingguo County, Jiangxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,39(6):289-294. [8] 李栋, 孙午阳, 谷庆宝, 等.植物修复及重金属在植物体内形态分析综述[J]. 环境污染与防治,2017,39(11):1256-1263.LI D, SUN W Y, GU Q B, et al. Review on the research progress in phytoremediation and speciation analysis of heavy metals in plants[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2017,39(11):1256-1263. [9] 张家明, 陈积普, 杨继清, 等.中国岩质边坡植被护坡技术研究进展[J]. 水土保持学报,2019,33(5):1-7.ZHANG J M, CHEN J P, YANG J Q, et al. Advances in biological protection of rock slopes in China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,33(5):1-7. [10] 张璐瑶. 北京市房山区煤矿弃渣边坡生态恢复初期植物群落特征研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. [11] 李昂, 曹素珍, 李雪, 等.甘肃省沿黄灌区春小麦与披碱草/苜蓿混播对土壤盐渍化的影响[J]. 水土保持通报,2020,40(6):51-56,63.LI A, CAO S Z, LI X, et al. Effects of spring wheat and mixture sowed Elymus nutans and Medicago sativa on soil salinity in irrigated areas along Yellow River in Gansu Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,40(6):51-56,63. [12] QIN X. Research on fast ecological restoration technology of high and steep rocky slope of highway[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. Chongqing: AIP Conference, 2017. [13] 郭爽, 牛小云, 吴桐, 等.不同植被恢复类型对高速公路边坡土壤质量的影响[J]. 土壤通报,2018,49(1):84-92.GUO S, NIU X Y, WU T, et al. Effect of restoration of vegetation types on soil quality of highway slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2018,49(1):84-92. [14] 胡妍玢, 许秋瑾, 胡小贞, 等.新疆巴音布鲁克草原不同退化程度对土壤特性影响[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(5):579-586. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.04.180HU Y B, XU Q J, HU X Z, et al. Effects of different degradation degrees on soil characteristics in Bayanbulak Grassland, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(5):579-586. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.04.180 [15] 张英. 鄱阳湖沙山植被恢复对沙地土壤物理性质的影响研究: 以江西省都昌县多宝沙山为例[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2019. [16] JAŠA S, BADALÍKOVÁ B, ČERVINKA J. Influence of digestate on physical properties of soil in ZD Budišov[J]. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis,2019,67(1):75-83. doi: 10.11118/actaun201967010075 [17] 张杰, 刘魏卫.盐城市街头绿地土壤特征与植物长势衰弱的关系研究[J]. 现代园艺,2019(9):34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2019.09.014 [18] 李孟霞, 文国松, 李永忠.作物对土壤压实胁迫响应研究进展[J]. 山东农业科学,2019,51(1):154-160,167.LI M X, WEN G S, LI Y Z. Research progress of response of crops to soil compaction stress[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2019,51(1):154-160,167. [19] 何群, 席欢, 万婷.不同植被恢复模式对红原沙化草地土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 四川环境,2017,36(1):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2017.01.007HE Q, XI H, WAN T. Impact of different artificial vegetation restoration pattern on the physical and chemical properties of desertification grassland in Hongyuan County[J]. Sichuan Environment,2017,36(1):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2017.01.007 [20] LIN Y X, YE G P, KUZYAKOV Y, et al. Long-term manure application increases soil organic matter and aggregation, and alters microbial community structure and keystone taxa[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2019,134:187-196. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.03.030 [21] ZHU S S, VIVANCO J M, MANTER D K. Nitrogen fertilizer rate affects root exudation, the rhizosphere microbiome and nitrogen-use-efficiency of maize[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,2016,107:324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.07.009 [22] CHEN S M, WAGHMODE T R, SUN R B, et al. Root-associated microbiomes of wheat under the combined effect of plant development and nitrogen fertilization[J]. Microbiome,2019,7(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0750-2 [23] 任立军,赵文琪,安婷婷,等.不同施肥方式对设施土壤氨挥发特征的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(11):2731-2739.REN L J,ZHAO W Q,AN T T,et al. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil ammonia emission in greenhouse[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(11):2731-2739. [24] 诸海焘, 田吉林, 吕卫光, 等.不同有机物料对次生盐渍化设施土壤的修复效果研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2015,37(10):37-41,47.ZHU H T, TIAN J L, LYU W G, et al. The remediation of secondary salinization of greenhouse soil using different organic materials[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2015,37(10):37-41,47. □ -





 下载:
下载: