Spatio-temporal distribution of phosphorus pollution in the upper reaches of Beijing-Hangzhou Canal and its source analysis
-
摘要:
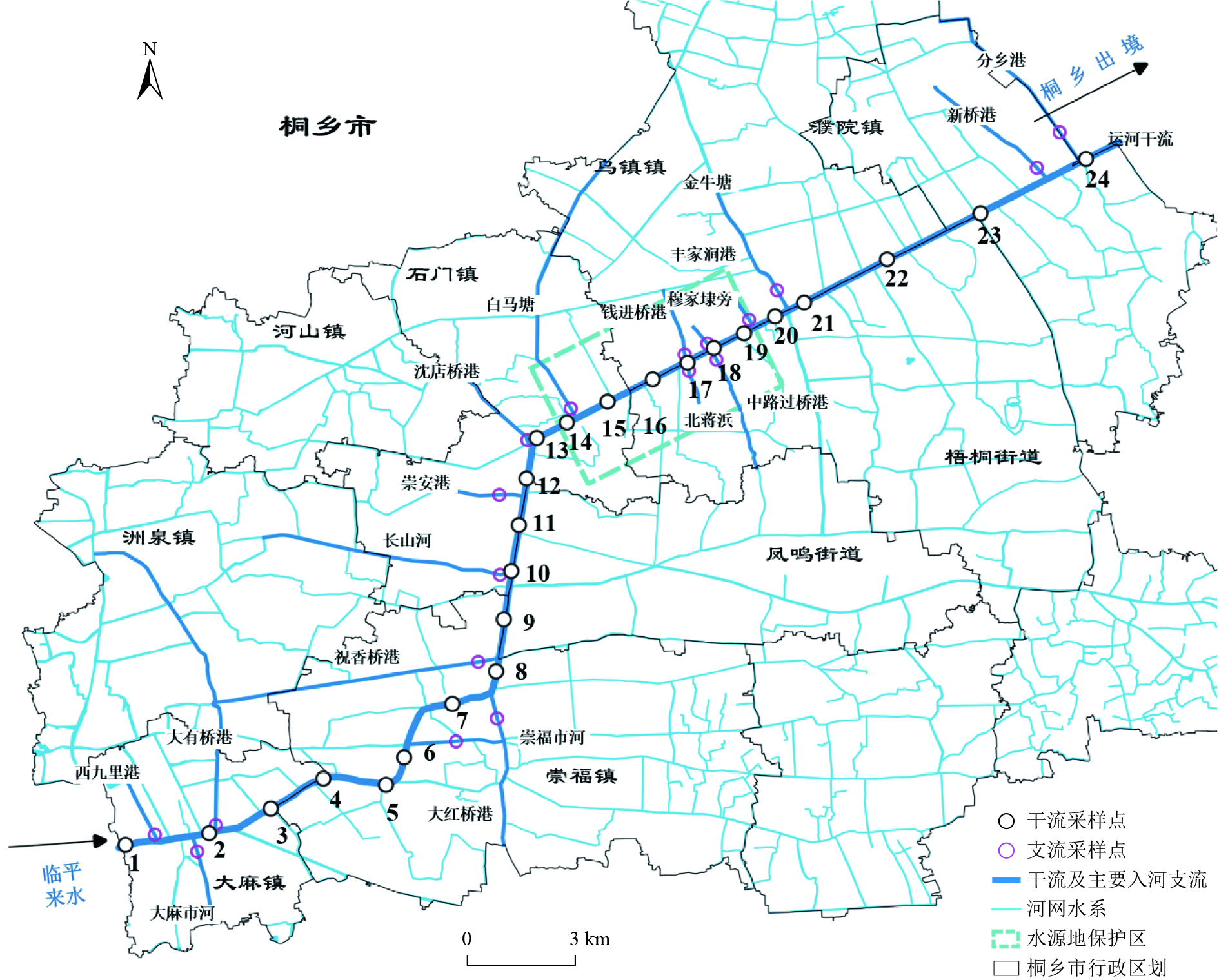
为揭示京杭运河上游桐乡段总磷浓度不能稳定达到GB 3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准》Ⅲ类标准的原因,在桐乡段干流布设24个采样点,入河支流布设18个采样点,开展水质加密监测,研究磷污染发生的时空变化规律;基于水质常规指标的主成分分析,以及各主成分因子中强载荷指标与三维荧光组分的相关性分析,对重点河段磷的主要污染源进行解析;并基于绝对主成分—多元线性回归模型,定量评价主要磷污染源的贡献率。结果表明:1)京杭运河上游桐乡段干流入境水总磷浓度为0.14~0.20 mg/L,沿程监测点5~7、9和21~24有明显变差趋势,最高浓度达0.40 mg/L;部分入河支流水质较差,总磷浓度达到0.44 mg/L。2)主成分分析得到3个主因子,因子1以氨氮、溶解态磷为主要载荷,与类蛋白质组分显著相关,代表生产生活污染;因子2以高锰酸盐指数、溶解态磷、颗粒态氮为主要载荷,与类腐殖质组分显著相关,代表农业源;因子3以颗粒态磷、颗粒态氮为主要载荷,与浊度显著相关,代表码头污染与底泥源。3)运河上游河段的磷污染主要发生在干流监测点5~7和9,主要为码头污染与底泥源,其在丰水期和平水期的贡献率分别为65.9%和31.8%;监测点21~24主要为农业源,其在丰水期和平水期的贡献率分别为34.0%和32.1%;此外,生产生活污染在丰水期也有较大影响,其对监测点5~7和9、21~24的贡献率分别为42.6%、31.8%。
-
关键词:
- 磷污染 /
- 主成分分析(PCA) /
- 绝对主成分—多元线性回归(APCS-MLR) /
- 污染源解析 /
- 平原河网
Abstract:To reveal the reason why total phosphorus failed to consistently meet the Class Ⅲ standard of Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002) in Tongxiang segment of Beijing-Hangzhou Canal, 24 sampling sites were set up in Tongxiang section of the mainstream and 18 sampling sites were set up in the tributaries to carry out water quality monitoring and study the spatio-temporal changes of phosphorus pollution. The main sources of phosphorus pollution in key river segments were analyzed by the principal component analysis based on routine water quality indexes, and the correlation analysis of strong load index in each principal component factor and three-dimensional fluorescence component. The quantitative evaluation of the contribution of major pollution sources was conducted using the absolute principal component-multiple linear regression model. The research results revealed that the total phosphorus concentration originating from Tongxiang segment of Beijing-Hangzhou Canal's upper reaches was 0.14-0.20 mg/L, while the water quality along the monitoring sites 5-7, 9 and 21-24 tended to deteriorate significantly, with the highest concentration reaching 0.40 mg/L. Certain tributaries into the mainstream exhibited poor water quality, and the total phosphorus concentration reached 0.44 mg/L. Three main factors were obtained by the principal component analysis. Factor 1 was mainly loaded with ammonia nitrogen and dissolved phosphorus, and was significantly correlated with protein-like component, representing production and domestic pollution. Factor 2, with permanganate index, dissolved phosphorus and particulate nitrogen as the main loads, was significantly correlated with humic-like component, representing agricultural sources. Factor 3, with particulate phosphorus and nitrogen as the main loads, was significantly correlated with turbidity, representing the dock and sediment source. The phosphorus pollution in the upper reaches of the canal mainly occurred at the monitoring sites 5-7 and 9, mainly from the dock and sediment sources, with contribution rates of 65.9% and 31.8% during the high and flat water periods, respectively. At monitoring sites 21-24, agriculture was the primary source of phosphorus pollution, contributing at rates of 34.0% and 32.1% during the high and flat water periods, respectively. Furthermore, the production and domestic pollution exhibited a significant influence during the high water periods. The contribution rates of the prodution and domestic to the monitoring sites 5-7, 9 and 21-24 were 42.6% and 31.8%.
-
表 1 运河干流水体其他水质指标浓度和荧光组分强度
Table 1. Concentration of other water quality indexes and intensity of fluorescence components in the mainstream water of the canal
月份 水质指标/(mg/L) 荧光组分强度/R.U. 浊度1) 溶解氧
浓度高锰酸盐
指数总氮浓度 溶解态氮
浓度颗粒态氮
浓度氨氮浓度 硝态氮
浓度C1荧光
强度C2荧光
强度C3荧光
强度5月(平水期) 230±77 5.1±0.9 6.0±0.6 3.52 ± 0.32 2.74±0.30 0.77±0.30 0.30±0.17 2.08 ±0.35 2.38±0.90 0.68±0.19 0.33±0.03 6月(丰水期) 221±70 2.9±0.5 5.2±0.7 4.29±0.37 3.80±0.25 0.49±0.29 1.40±0.34 1.56±0.54 1.52±0.51 0.53±0.09 0.60±0.04 12月(枯水期) 553±310 9.9±0.4 3.9±0.6 4.03±0.55 3.44±0.32 0.59±0.38 0.79±0.14 2.62±0.25 1.58±0.40 0.58±0.15 0.15±0.02 1)单位为NTU。 表 2 运河干流重点河段旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 2. Rotation factor loading matrix in key river segments of canal mainstream
指标 因子1 因子2 因子3 溶解态磷 0.596 0.518 −0.476 颗粒态磷 0.049 −0.023 0.872 高锰酸盐指数 −0.252 0.892 0.087 氨氮 0.910 −0.078 −0.351 颗粒态氮 −0.097 0.618 0.565 溶解态氮 0.492 0.205 −0.699 硝态氮 −0.881 −0.091 −0.138 溶解氧 −0.503 −0.810 0.122 浊度 −0.224 −0.646 0.190 注:数字加粗表示强、中载荷。 -
[1] WEATHERS K C, STRAYER D L, LIKENS G E. Fundamentals of ecosystem science[M]. 2nd Ed. Utah: Academic Press, 2021: 189-213.WEATHERS K C, STRAYER D L, LIKENS G E. Fundamentals of ecosystem science[M]. 2nd Ed. Utah: Academic Press, 2021: 189-213. [2] BOWES M J, SMITH J T, NEAL C, et al. Changes in water quality of the River Frome (UK) from 1965 to 2009: is phosphorus mitigation finally working[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2011,409(18):3418-3430. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.049 [3] CHENG X, CHEN L D, SUN R H, et al. An improved export coefficient model to estimate non-point source phosphorus pollution risks under complex precipitation and terrain conditions[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(21):20946-20955. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2191-z [4] WANG M H, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Natural and anthropogenic determinants of riverine phosphorus concentration and loading variability in subtropical agricultural catchments[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 287: 106713. [5] 夏峰. 京杭运河稳定断面形态及其应用研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. [6] LI A, JANG J K, SCHEFF P A. Application of EPA CMB8.2 model for source apportionment of sediment PAHs in Lake Calumet, Chicago[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2003,37(13):2958-2965. [7] 陈锋, 孟凡生, 王业耀, 等. 地表水环境污染物受体模型源解析研究与应用进展[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2016,14(2):32-37.CHEN F, MENG F S, WANG Y Y, et al. Research and application progress of source apportionment in receptor model for surface water pollutant[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2016,14(2):32-37. [8] 程思茜. 基于PMF和PCA-APCS-MLR受体模型的地下水污染源定性识别和定量解析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021. [9] SHEN D L, HUANG S H, ZHANG Y P, et al. The source apportionment of N and P pollution in the surface waters of lowland urban area based on EEM-PARAFAC and PCA-APCS-MLR[J]. Environmental Research,2021,197:111022. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111022 [10] LIU L L, DONG Y C, KONG M, et al. Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models[J]. Chemosphere,2020,242:125272. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125272 [11] 后希康, 张凯, 段平洲, 等. 基于APCS-MLR模型的沱河流域污染来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究,2021,34(10):2350-2357. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.05.30HOU X K, ZHANG K, DUAN P Z, et al. Pollution source apportionment of Tuohe River based on absolute principal component score-multiple linear regression[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(10):2350-2357. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.05.30 [12] YANG L Y, HAN D H, LEE B M, et al. Characterizing treated wastewaters of different industries using clustered fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC and FT-IR spectroscopy: implications for downstream impact and source identification[J]. Chemosphere,2015,127:222-228. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.028 [13] 李昊璋. 平原河网区域的水环境容量研究: 以嘉兴北部地区为例[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020. [14] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2002. [15] SANCHEZ N P, SKERIOTIS A T, MILLER C M. Assessment of dissolved organic matter fluorescence PARAFAC components before and after coagulation-filtration in a full scale water treatment plant[J]. Water Research,2013,47(4):1679-1690. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.12.032 [16] 李昀, 魏鸿杰, 王侃, 等. 溶解性有机物(DOM)与区域土地利用的关系: 基于三维荧光-平行因子分析(EEM-PARAFAC)[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(4):1751-1759.LI Y, WEI H J, WANG K, et al. Analysis of the relationship between dissolved organic matter (DOM) and watershed land-use based on three-dimensional fluorescence-parallel factor (EEM-PARAFAC) analysis[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(4):1751-1759. [17] GUPTA S, ROY M. Land use/land cover classification of an urban area: a case study of Burdwan Municipality, India[J]. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences,2011,2(4):1014-1026. [18] 胡海珍. 典型平原河网区污染负荷与水质响应关系模拟研究: 以常州市为例[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2023. [19] 熊传芳, 张征宇, 万梅, 等. 嘉兴市大气PM2.5中金属元素污染特征、生态风险评价及来源分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):96-104.XIONG C F, ZHANG Z Y, WAN M, et al. Pollution characteristics, ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of mental elements in PM2.5 in Jiaxing City[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):96-104. [20] PEKEY H, KARAKAŞ D, BAKOGˇLU M. Source apportionment of trace metals in surface waters of a polluted stream using multivariate statistical analyses[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2004,49(9/10):809-818. [21] 柳强, 张鹏, 史箴, 等. 三峡库区上游沱江流域总磷浓度时空变化特性及影响因素分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(2):459-467.LIU Q, ZHANG P, SHI Z, et al. Characterization of the spatio-temporal variations of total phosphorus concentrations and influencing factors analysis in Tuojiang River Basin, an upstream tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(2):459-467. [22] 丁淼, 金梦, 兰亚琼, 等. 基于3DEMMs-PARAFAC技术的运河桐乡水源地夏季低溶解氧成因研究[J]. 环境化学,2023,42(6):1933-1944. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012006DING M, JIN M, LAN Y Q, et al. Study on the cause of low dissolved oxygen in summer in Tongxiang water source of Canal based on 3DEMMs-PARAFAC technology[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2023,42(6):1933-1944. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012006 [23] 郑倩玉, 刘硕, 万鲁河, 等. 松花江哈尔滨段水环境质量评价及污染源解析[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(3):507-513.ZHENG Q Y, LIU S, WAN L H, et al. Water environmental quality assessment and source apportionment in Harbin section of Songhua River[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(3):507-513. [24] SU S L, LI D, ZHANG Q, et al. Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in different functional zones of Qiantang River, China[J]. Water Research,2011,45(4):1781-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.030 [25] SIMEONOV V, STRATIS J A, SAMARA C, et al. Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece[J]. Water Research,2003,37(17):4119-4124. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00398-1 [26] 胡国仲, 谭印月, 林欢, 等. 京杭运河常州段水质提升策略研究[J]. 清洗世界,2023,39(2):125-127.HU G Z, TAN Y Y, LIN H, et al. Study on water quality improvement strategy of Changzhou section of Beijing-Hangzhou Canal[J]. Cleaning World,2023,39(2):125-127. [27] 刘琳. 环渤海河流卤代阻燃剂的入海通量及其在典型河口的环境行为研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2022. [28] 刘丽贞, 黄琪, 吴永明, 等. 鄱阳湖CDOM三维荧光光谱的平行因子分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2018,38(1):293-302.LIU L Z, HUANG Q, WU Y M, et al. Fluorescent characteristics of CDOM in Poyang Lake analyzed by three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis[J]. China Environmental Science,2018,38(1):293-302. [29] TAO P R, JIN M, YU X B, et al. Spatiotemporal variations in chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in a mixed land-use river: implications for surface water restoration[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,277:111498. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111498 [30] HUANG F, WANG X Q, LOU L P, et al. Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques[J]. Water Research,2010,44(5):1562-1572. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.003 [31] BAKER A, INVERARITY R. Protein-like fluorescence intensity as a possible tool for determining river water quality[J]. Hydrological Processes,2004,18(15):2927-2945. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5597 [32] 徐爱喆, 韩晓昆, 刘铭轩, 等. 渤海湾两条河流及其近岸海域水体中DOM的光谱特征及影响因素[J]. 地球与环境,2022,50(4):526-536. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.006XU A Z, HAN X K, LIU M X, et al. Spectral characteristics and influencing factors of dissolved organic matter in two rivers and their coastal waters in the Bohai Bay[J]. Earth and Environment,2022,50(4):526-536. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.006 [33] 孙婵. 水生植物群落建植对城市湖泊水环境影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2008. [34] 李凯. 旅游活动对西湖水质的影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2012. [35] SYVITSKI J P M, VÖRÖSMARTY C J, KETTNER A J, et al. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean[J]. Science,2005,308(5720):376-380. doi: 10.1126/science.1109454 [36] RUSPITA R, AULIA A. Analysis of water quality and pollution index at Karangantu fishing port area, Banten[J]. Journal Akademika Kimia,2022,11(2):96-104. doi: 10.22487/j24775185.2022.v11.i2.pp96-104 [37] 杨卫, 李瑞清. 长江和汉江总磷污染特征及成因分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2021(1):42-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.01.009YANG W, LI R Q. Characteristics and causes of the total phosphorus pollution in the Yangtze River and Han River[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2021(1):42-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.01.009 [38] 毕业亮, 王华彩, 夏兵, 等. 雨源型城市河流水污染特征及水质联合评价: 以深圳龙岗河为例[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(2):782-794.BI Y L, WANG H C, XIA B, et al. Pollution characterization and comprehensive water quality assessment of rain-source river: a case study of the Longgang River in Shenzhen[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(2):782-794. [39] 黄健, 王萌, 宋箭, 等. 高碳氮废水处理中有机物的荧光光谱特征分析[J]. 中国给水排水,2015,31(3):28-31.HUANG J, WANG M, SONG J, et al. Analysis of fluorescent properties of organic matter in high carbon-nitrogen wastewater[J]. China Water & Wastewater,2015,31(3):28-31. [40] LEORA N, WILLIAMS M W, CAMPBELL D H, et al. Evaluating regional patterns in nitrate sources to watersheds in National Parks of the Rocky Mountains using nitrate isotopes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2008,42(17):6487-6493. [41] 刘瑞霞, 王立阳, 孙菲, 等. 以农业面源污染阻控为目标的河流生态缓冲带研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报,2022,16(1):25-39.LIU R X, WANG L Y, SUN F, et al. Research progress in riverine ecological buffer zone for control of agricultural non-point source pollution[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2022,16(1):25-39. [42] YANG X L, YU X B, CHENG J R, et al. Impacts of land-use on surface waters at the watershed scale in southeastern China: insight from fluorescence excitation-emission matrix and PARAFAC[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:647-657. ◇ doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.279 -





 下载:
下载: