Research on the preparation and application of collaborative turbidity and fluorine removal agents for typical coal mine water in the Yellow River basin
-
摘要:
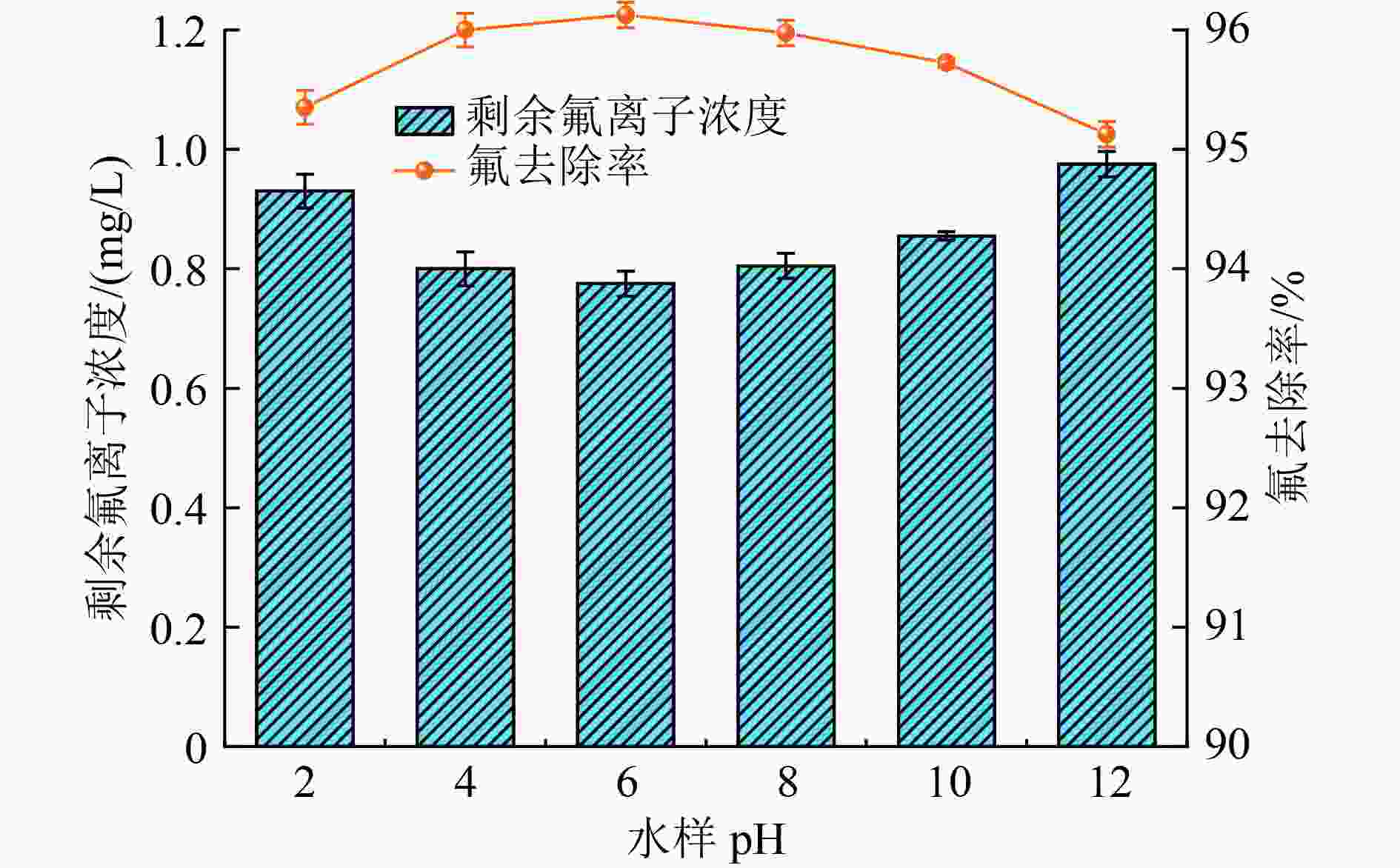
黄河流域是我国煤炭潜力最大的区域,矿井水涌水量大但资源利用率不高,尤其在干旱和半干旱的高氟地区,矿井水中氟离子超标已成为制约提高矿井水资源利用率的主要因素之一。采用正交试验筛选出高效除氟药剂的5种组分〔聚合氯化铝(PAC)、聚合硅酸铝、硝酸镁、聚合氯化铁、羧甲基淀粉钠〕,采用单因素试验探讨了不同制备条件和反应条件对除氟效果的影响,并通过X射线能谱分析(EDS)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)表征探讨了除氟机理。结果表明:在金属总量M/Si、Al/Mg、Al/Fe的摩尔比分别为43、40、40条件下研制的除氟药剂,均可将含氟废水中氟离子浓度由20 mg/L降至1.0 mg/L以下,达到GB 3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准》Ⅲ类中氟化物浓度限值要求(1.0 mg/L);当除氟药剂投加量为1.25 g/L,初始pH为2~12,悬浮物浓度为100~2 000 mg/L,聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)投加量为0.4 mg/L时,处理后上清液剩余氟离子浓度均可控制在1.0 mg/L以下,氟离子去除率达95%以上;除氟药剂中Al、Si元素起到重要的除氟作用,主要通过形成Al—F—Al等金属络合物沉淀被去除;将除氟药剂应用于黄河流域某煤矿含氟矿井水的处理,在除氟药剂投加量为400 mg/L、PAM投加量为0.2 mg/L时,氟离子浓度从5.6 mg/L降至0.85 mg/L,并协同将矿井水浊度从500 NTU降至4.59 NTU,吨水处理药剂成本为1.602元。该除氟药剂在黄河流域含氟矿井水处理中具有较好的应用潜力。
Abstract:The Yellow River basin is the region with the greatest coal potential in China. Although the amount of coal mine water inflow is large, the resource utilization rate is not high and, especially in arid and semi-arid areas with high fluorine content, the excessive fluoride ions in coal mine water have become one of the main factors restricting the improvement of mine water resource utilization rate. Orthogonal experiments were used to screen out five components of efficient defluorination agents, including polyaluminium chloride (PAC), poly-aluminum silicate, magnesium nitrate, poly-ferric chloride (PFC), and carboxyl methyl starch sodium. The single factor experimental method was used to explore the effects of different preparation and reaction conditions on the defluorination effect, and the defluorination mechanism was preliminarily explored through X-ray energy spectrum analysis (EDS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) characterization. The experimental results showed that the fluoride removal agent developed under the conditions of the total amount of metal to Si molar ratio of 43, Al/Mg molar ratio of 40, and Al/Fe molar ratio of 40 could reduce the concentration of fluoride ions in wastewater from 20 mg/L to below 1.0 mg/L, meeting the Class Ⅲ water fluoride limit requirements (1.0 mg/L) of Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002). When the dosage of the fluoride removal agent was 1.25 g/L, the initial pH was 2-12, the suspended solids concentration was 100-2 000 mg/L, and the polyacrylamide (PAM) dosage was 0.4 mg/L, the residual fluoride ion concentration in the supernatant after treatment could be controlled below 1.0 mg/L, and the fluoride removal rate could reach over 95%. Al and Si elements of the defluorination agent played an important role in defluorination, and their mechanism was mainly through the formation of metal complexes such as Al-F-Al for precipitation and removal. Applying defluorination agents to the treatment of fluorinated mine water in a certain coal mine in the Yellow River Basin, the concentration of fluoride ions decreased from 5.6 mg/L to 0.85 mg/L when the dosage of defluorination agents was 400 mg/L and PAM was 0.2 mg/L. Simultaneously, the turbidity of mine water could be reduced from 500 NTU to 4.59 NTU. The cost of water treatment agents per ton was 1.602 yuan. The defluorination agent has good application potential in the treatment of mine water containing fluorine in the Yellow River basin.
-
表 1 正交试验结果
Table 1. Orthogonal experiment results
项目 因素 指标 铝盐类(A) 铁盐类(B) 镁盐类(C) 高分子化合物类(D) 剩余氟浓度/(mg/L) 氟离子去除率/% 1 A3〔Al2(SO4)3〕 B2(FeCl3) C1(MgCl2) D1(羧甲基壳聚糖) 3.15 84.25 2 A3〔Al2(SO4)3〕 B3〔Fe2(SO4)3〕 C1(MgCl2) D2(羧甲基纤维素钠) 3.23 83.85 3 A2〔AlCl3〕 B1(聚合氯化铁) C1(MgCl2) D2(羧甲基纤维素钠) 1.04 94.80 4 A2〔AlCl3〕 B3〔Fe2(SO4)3〕 C2〔Mg(NO3)2〕 D1(羧甲基壳聚糖) 1.41 92.95 5 A2〔AlCl3〕 B2(FeCl3) C1(MgCl2) D3(羧甲基淀粉钠) 1.28 93.60 6 A1〔PAC〕 B3〔Fe2(SO4)3〕 C1(MgCl2) D3(羧甲基淀粉钠) 1.26 93.70 7 A1〔PAC〕 B1(聚合氯化铁) C1(MgCl2) D1(羧甲基壳聚糖) 1.00 95.00 8 A3〔Al2(SO4)3〕 B1(聚合氯化铁) C2〔Mg(NO3)2〕 D3(羧甲基淀粉钠) 2.75 86.25 9 A1(PAC) B2(FeCl3) C2〔Mg(NO3)2〕 D2(羧甲基纤维素钠) 1.20 94.00 k1 94.267 92.050 90.867 90.767 k2 93.817 90.650 91.067 90.917 k3 84.817 90.200 91.217 极差(R) 9.45 1.85 0.2 0.3 因素主次 A>B>D>C 最优组合 A1B1C2D3 注:k1、k2、k3指每个因素各水平所对应的试验指标的数值之和。 表 2 实际矿井水除氟试验结果
Table 2. Results of fluoride removal from actual mine water
除氟药剂投加
量/(mg/L)PAM投加
量/(mg/L)剩余氟离子
浓度/(mg/L)剩余浊度/
NTU250 0.2 1.57 10.92 380 0.2 1.10 9.16 400 0.2 0.85 4.59 700 0.2 0.74 4.56 900 0.2 0.68 4.17 -
[1] 张春晖, 吴盟盟, 张益臻. 碳中和目标下黄河流域产业结构对生态环境的影响及展望[J]. 环境与可持续发展,2021,46(2):50-55.ZHANG C H, WU M M, ZHANG Y Z. Impact and prospect of industrial structure on ecology and environment in the Yellow River Basin under carbon neutrality target[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development,2021,46(2):50-55. [2] 田美荣, 冯朝阳, 王世曦, 等. 近70年来黄河流域生态修复历程及系统性修复思考[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(5):1787-1797.TIAN M R, FENG C Y, WANG S X, et al. The course of ecological restoration and systematic restoration in the Yellow River Basin in recent 70 years[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(5):1787-1797. [3] 乔柄霖, 彭海兵, 刘兆祥, 等. 补连塔煤矿矿井水综合利用研究及其具体成效[J]. 中国煤炭,2023,49(增刊1):93-98.QIAO B L, PENG H B, LIU Z X, et al. Research on comprehensive utilization of mine water in Bulianta Coal Mine and its specific results[J]. China Coal,2023,49(Suppl 1):93-98. [4] 郝春明, 张伟, 何瑞敏, 等. 神东矿区高氟矿井水分布特征及形成机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1966-1977.HAO C M, ZHANG W, HE R M, et al. Formation mechanisms for elevated fluoride in the mine water in Shendong coal-mining district[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(6):1966-1977. [5] 王甜甜, 薛建坤, 尚宏波, 等. 蒙陕接壤区矿井水中氟的污染特征及形成机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(11):4127-4138.WANG T T, XUE J K, SHANG H B, et al. Fluorine pollution characteristics and formation mechanism of mine water in Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia contiguous area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(11):4127-4138. [6] WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first and second addenda[S]. Geneva: WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee, 2022. [7] 国家卫生健康委员会. 生活饮用水卫生标准: GB 5749—2022[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. [8] 国家环境保护总局. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [9] CHOI A L, SUN G F, ZHANG Y, et al. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives,2012,120(10):1362-1368. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104912 [10] REN T, GAO X R, ZHENG T, et al. Study on Treatment of acidic and highly concentrated fluoride waste water using calcium oxide-calcium chloride[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2016,39:012003. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/39/1/012003 [11] 肖雪峰, 孙永军, 梅凯, 等. 钙沉淀混凝处理太阳能电池生产高氟废水研究[J]. 水处理技术,2017,43(5):30-32.XIAO X F, SUN Y J, MEI K, et al. Study on the treatment of solar cell produced wastewater containing high fluoride by calcium coagulation-sedimentation[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2017,43(5):30-32. [12] HE Z, LAN H C, GONG W X, et al. Coagulation behaviors of aluminum salts towards fluoride: significance of aluminum speciation and transformation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2016,165:137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.01.017 [13] SINGH S, KHARE A, CHAUDHARI S. Enhanced fluoride removal from drinking water using non-calcined synthetic hydroxyapatite[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8(2):103704. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.103704 [14] SHEN J J, RICHARDS B S, SCHÄFER A I. Renewable energy powered membrane technology: case study of St. Dorcas borehole in Tanzania demonstrating fluoride removal via nanofiltration/reverse osmosis[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2016,170:445-452. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.042 [15] SHEN J J, SCHÄFER A I. Factors affecting fluoride and natural organic matter (NOM) removal from natural waters in Tanzania by nanofiltration/reverse osmosis[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,527/528:520-529. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.037 [16] 尚勇, 史贞峰, 戚翠红, 等. 一种新型深度除氟药剂及其应用: CN110054275A[P]. 2019-07-26. [17] 王恒, 杨友鑫, 康勇锋, 等. 一种高效除氟复配药剂: CN109574177A[P]. 2019-04-05. [18] 刘芳池, 戚凯, 李向东. 粉煤灰加载絮凝处理煤矿矿井水的试验研究[J]. 能源环境保护,2022,36(1):44-50.LIU F C, QI K, LI X D. Experimental study on optimization of fly ash loading flocculation treatment of coal mine water[J]. Energy Environmental Protection,2022,36(1):44-50. [19] 章丽萍, 吴二勇, 姚瑞涵, 等. 高效除氟药剂对神东矿区含氟矿井水的处理研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(2):84-90.ZHANG L P, WU E Y, YAO R H, et al. Treatment of fluoride-containing mine water from Shendong coalmine with high efficiency defluoridation agent[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2022,36(2):84-90. [20] 章丽萍, 安逸云, 吴二勇, 等. 响应曲面法优化含氟矿井水处理及除氟机理研究[J]. 矿业科学学报,2022,7(6):782-792.ZHANG L P, AN Y Y, WU E Y, et al. Optimization of fluorine mine water treatment and fluorine removal mechanism using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2022,7(6):782-792. [21] 许德超, 衷从强, 朱婷婷, 等. 铁铝硅摩尔比对新型混凝剂除氟效果的影响[J]. 广州化工,2018,46(18):70-73.XU D C, ZHONG C Q, ZHU T T, et al. Effects of Fe/Al/Si molar ratio on fluoride removal by a new coagulant[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2018,46(18):70-73. [22] FENG C H, BI Z, ZHAO S, et al. Quantification analysis of polymeric Al species in solutions with electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-TOF-MS)[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry,2012,309:22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2011.08.020 [23] FENG C H, BI Z, TANG H X. Electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrum analysis method of polyaluminum chloride flocculants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(1):474-480. [24] ZHAO H, LIU H J, QU J H. Aluminum speciation of coagulants with low concentration: analysis by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2011,379(1/2/3):43-50. [25] TIAN C H, WU Y H, WEI M Z, et al. A novel understanding of residual nano-Al13 formation and degradation during coagulation and flocculation: a proof based on ESI-TOF-MS[J]. Environmental Science:Nano,2018,5(11):2712-2721. doi: 10.1039/C8EN00921J [26] 王俊杰, 赵娇娇, 孟旭超, 等. 光伏光电行业含氟废水及污泥利用处置研究现状及展望[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2018,8(3):333-342.WANG J J, ZHAO J J, MENG X C, et al. Research status and prospect of fluorinated wastewater and sludge utilization in photovoltaic industry[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2018,8(3):333-342. [27] TSUCHIYA K, FUCHIDA S, TOKORO C. Experimental study and surface complexation modeling of fluoride removal by magnesium hydroxide in adsorption and coprecipitation processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8(6):104514. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104514 [28] LI L X, XU D, LI X Q, et al. Excellent fluoride removal properties of porous hollow MgO microspheres[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2014,38(11):5445-5452. doi: 10.1039/C4NJ01361A [29] 郭中权, 郑利祥, 徐旭峰, 等. 络合诱导除氟剂去除矿井水中氟离子实验研究[J]. 能源环境保护,2023,37(1):42-49.GUO Z Q, ZHENG L X, XU X F, et al. Experimental study on fluoride removal from mine water by complexing-induction fluoride removal agent[J]. Energy Environmental Protection,2023,37(1):42-49. [30] CHAI L Y, WANG Y Y, ZHAO N, et al. Sulfate-doped Fe3O4/Al2O3 nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water[J]. Water Research,2013,47(12):4040-4049. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.057 [31] WANG X, XU H, WANG D S. Mechanism of fluoride removal by AlCl3 and Al13: the role of aluminum speciation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,398:122987. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122987 [32] WANG X, ZHANG G, LAN H C, et al. Preparation of hollow Fe-Al binary metal oxyhydroxide for efficient aqueous fluoride removal[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2017,520:580-589. [33] CHO D W, HAN Y S, LEE J, et al. Water defluorination using granular composite synthesized via hydrothermal treatment of polyaluminum chloride (PAC) sludge[J]. Chemosphere,2020,247:125899. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125899 [34] GONG W X, QU J H, LIU R P, et al. Effect of aluminum fluoride complexation on fluoride removal by coagulation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2012,395:88-93. [35] LI R, HE C, HE Y L. Preparation and characterization of poly-silicic-cation coagulants by synchronous-polymerization and co-polymerization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,223:869-874. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.010 [36] XU M, ZHOU W B, ZHU Z Q, et al. Study on the preparation of polysilicate ferric flocculant and its treatment of high turbidity tailings water[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2021,44:102457. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102457 [37] LIAN X J, ZHANG K S, LUO Q F, et al. A possible structure of retrograded maize starch speculated by UV and IR spectra of it and its components[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2012,50(1):119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.10.009 [38] LIU X W, GUO Q, WEI C B, et al. Preparation and kinetics of thermal analysis of inorganic-organic composite modified carboxymethyl starch and its applicability as flocculant for oily wastewater treatment[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2022,31:1839-1852. [39] HAROON M, WANG L, YU H J, et al. Synthesis of carboxymethyl starch- g-polyvinylpyrolidones and their properties for the adsorption of Rhodamine 6G and ammonia[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,186:150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.052 [40] PUSHPAMALAR V, LANGFORD S J, AHMAD M, et al. Optimization of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from sago waste[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2006,64(2):312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.12.003 [41] LI Y Y, ZHANG H, WANG X Y, et al. Preparation and flocculation performance of polysilicate aluminum-cationic starch composite flocculant[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2020, 231: 1-7. [42] 冯帆, 姜永海, 廉新颖, 等. 地下水回补引发含水层氟释放次生风险的模拟研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1440-1450. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.04.10FENG F, JIANG Y H, LIAN X Y, et al. Simulation study on secondary risk of aquifer fluoride release induced by groundwater recharge[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(6):1440-1450. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.04.10 [43] LI S, YANG S A, YI P, et al. Preparation of aluminum–ferric–magnesium polysilicate and its application on oily sludge[J]. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society,2015,80:1553-1565. doi: 10.2298/JSC141229057L [44] LI R, HE C, HE Y L. Preparation and characterization of poly-silicic-cation coagulant from industrial wastes[J]. Desalination,2013,319:85-91. ◇ doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2013.03.024 -





 下载:
下载: