Effects of thermal desorption on the complex contaminated soils of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals
-
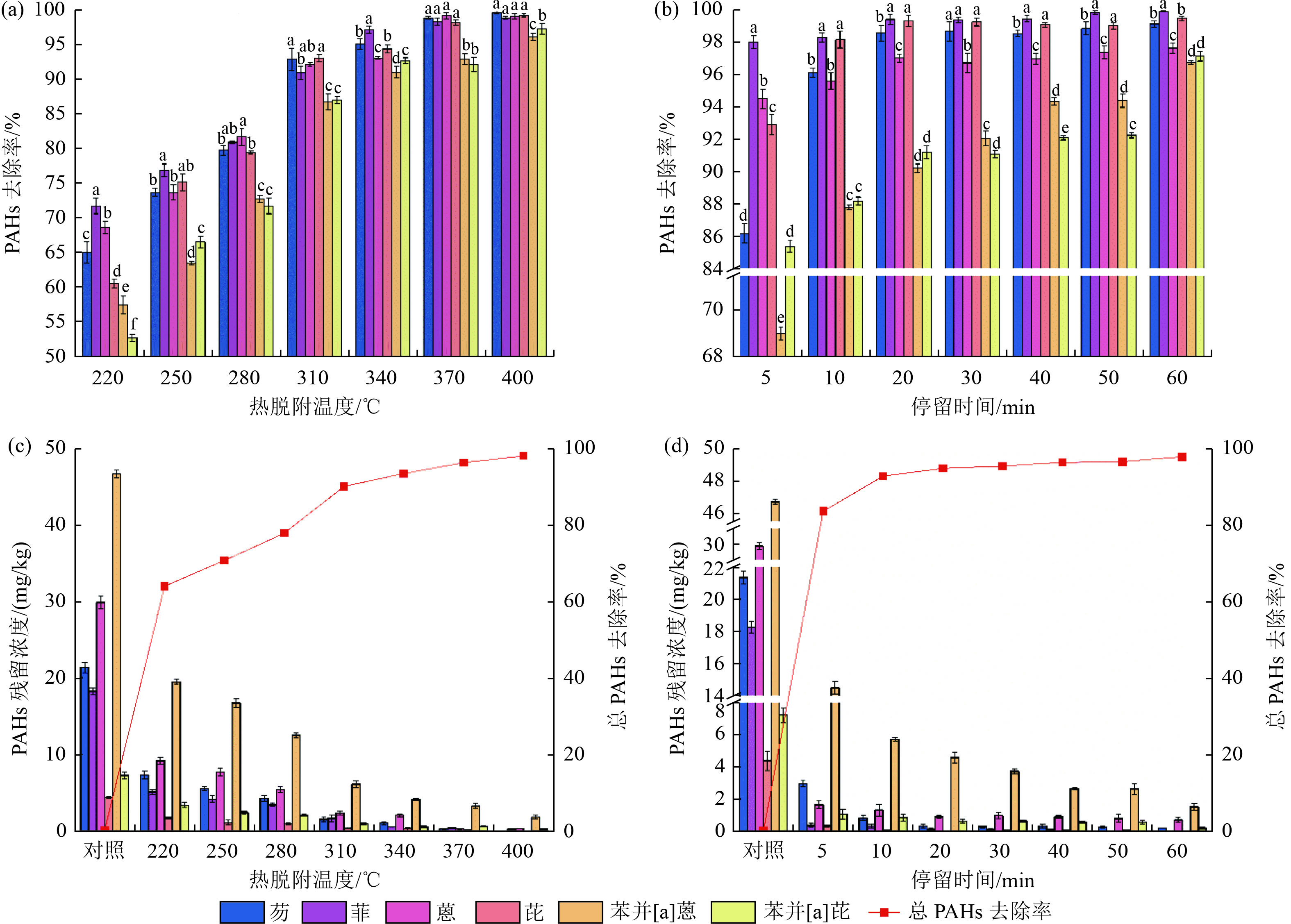
摘要:
热脱附技术被广泛用于污染场地修复,但其对多环芳烃(PAHs)与重金属复合污染土壤的综合影响仍不清楚。选用PAHs和重金属复合污染模拟土壤,探究热脱附温度(220~400 ℃)和停留时间(5~60 min)对土壤中PAHs的影响,分析空气与氮气气氛下热脱附温度(310、340和370 ℃)对土壤中重金属Cu、Pb、As和Cd形态分布的影响。结果表明:随热脱附温度和停留时间的增加,土壤中PAHs去除率显著增加;低环PAHs占比逐渐减少,而高环PAHs占比逐渐增加。在2种气氛热脱附后,Cu、Pb和As弱酸提取态占比略有增加,而Cd弱酸提取态占比显著降低;可还原态和可氧化态的转化趋势具有差异性。随着热脱附温度的升高,Cu、Pb、As和Cd 4种重金属的残渣态占比均逐渐增加,说明热脱附有利于4种重金属的固定。相较于空气,氮气条件下4种重金属可氧化态和残渣态占比均增加;Cu和Pb可还原态占比显著降低,而As可还原态占比有所降低,Cd可还原态占比变化不大。氮气更有利于Cu、Pb和Cd的稳定;相反,空气更有利于As的稳定。
-
关键词:
- 热脱附 /
- 多环芳烃(PAHs) /
- 重金属 /
- 形态转化
Abstract:Thermal desorption technology is widely used for the remediation of contaminated sites. However, the combined effects of thermal desorption on the complex contaminated soils of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and heavy metals were still unclear. The complex contaminated simulated soils of PAHs and heavy metals were selected to investigate the effects of thermal desorption temperature (220-400 ℃) and residence time (5-60 min) on PAHs in the soil and to analyze the effects of thermal desorption temperature (310, 340, and 370 ℃) on the morphological distribution of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, As, and Cd) in soil under air and nitrogen atmosphere. The results showed that the removal of PAHs from contaminated soil increased significantly with the increase in thermal desorption temperature and residence time. The proportion of low-ring PAHs gradually decreased while that of high-ring PAHs gradually increased. After thermal desorption treatment in both atmospheres, the proportion of Cu, Pb, and As weakly acid-extracted states increased slightly, while the proportion of Cd weakly acid-extracted states decreased significantly. The conversion trends of the reducible and oxidizable states were different. The proportion of residue states of four heavy metals, Cu, Pb, As, and Cd, increased gradually with the increase of thermal desorption temperature, which indicated that thermal desorption was beneficial to the immobilization of the four heavy metals. Compared with air, the proportions of oxidizable and residual states of four heavy metals increased under nitrogen conditions. The proportions of Cu and Pb reducible states decreased significantly, while the proportions of As reducible states decreased and the proportions of Cd reducible states did not change significantly. These results showed that nitrogen was more favorable for the stabilization of Cu, Pb, and Cd. On the contrary, the air was more beneficial to the stabilization of As.
-
Key words:
- thermal desorption /
- polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) /
- heavy metals /
- speciation
-
表 1 试验土壤重金属各形态占比
Table 1. Proportion of heavy metals in experimental soil
% 重金属 重金属形态 酸可提取态 可还原态 可氧化态 残渣态 Cu 17.243 32.358 33.487 16.912 Pb 20.013 42.169 28.558 9.260 As 22.016 30.124 34.968 12.892 Cd 19.683 25.687 37.485 17.145 表 2 试验土壤PAHs浓度
Table 2. PAHs contents in experimental soil
mg/kg Fle Phe Ant Pyr Baa Bap 总PAHs 21.34 18.26 29.87 4.38 46.72 7.21 127.78 -
[1] 白璐, 乔琦, 钟琴道, 等. 铅冶炼行业重金属污染防控监管现状分析及对策[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(2):232-241.BAI L, QIAO Q, ZHONG Q D, et al. Analysis and countermeasures for supervision and management of heavy metal pollution prevention and control of lead smelting industry[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(2):232-241. [2] 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[EB/OL]. [2023-02-10]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201404/W020140417558995804588.pdf. [3] 朱岗辉, 孙璐, 廖晓勇, 等. 郴州工业场地重金属和PAHs复合污染特征及风险评价[J]. 地理研究,2012,31(5):831-839.ZHU G H, SUN L, LIAO X Y, et al. Combined pollution of heavy metals and PAHs and its risk assessment in industrial sites of Chenzhou City[J]. Geographical Research,2012,31(5):831-839. [4] SU C, JIANG L Q, ZHANG W J. A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: situation, impact and remediation techniques[J]. Environmental Skeptics and Critics,2014,3(2):24-38. [5] SANSOM GARETT T, FAWKES LEANNE S, THOMPSON COURTNEY M, et al. Cancer risk associated with soil distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons within three environmental justice neighborhoods in Houston, Texas[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2022,45(2):1-10. [6] 苑舒琪, 吴玉锋, 赵智博, 等. 电子废弃物拆解污染区土壤生态健康风险研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报,2022,17(3):167-179.YUAN S Q, WU Y F, ZHAO Z B, et al. Research progress on soil ecological and health risks of E-waste disman-tling polluted area[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2022,17(3):167-179. [7] ZWOLAK A, SARZYŃSKA M, SZPYRKA E, et al. Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: a review[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2019, 230(7): 164. [8] 徐飞, 沈婷婷. 热脱附技术在化工厂污染土壤修复中的工程应用[J]. 当代化工,2020,49(5):997-1000.XU F, SHEN T T. Engineering application of thermal desorption technology in the remediation of contaminated soil in chemical plant[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry,2020,49(5):997-1000. [9] 舒心, 胡培良, 李东阳, 等. 某炼铁厂汞和多环芳烃复合污染土壤热脱附试验研究[J]. 广东化工,2022,49(14):90-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.14.032SHU X, HU P L, LI D Y, et al. Experimental study on thermal desorption of mercury and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons composite contaminated soil in an ironmaking plant[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2022,49(14):90-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.14.032 [10] 柴丽娜, 张文文, 许端平, 等. 调理剂对多环芳烃污染黏性土壤热脱附的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2023,36(1):72-80.CHAI L N, ZHANG W W, XU D P, et al. Effects of conditioners on thermal desorption of clay soil contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2023,36(1):72-80. [11] 夏天翔, 姜林, 魏萌, 等. 焦化厂土壤中PAHs的热脱附行为及其对土壤性质的影响[J]. 化工学报,2014,65(4):1470-1480.XIA T X, JIANG L, WEI M, et al. PAHs thermal desorption behavior of coking plant soil and its effect on soil characteristics[J]. CIESC Journal,2014,65(4):1470-1480. [12] 魏萌. 焦化污染场地土壤中PAHs的赋存特征及热脱附处置研究[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2013. [13] 张学良, 廖朋辉, 李群, 等. 复杂有机物污染地块原位热脱附修复技术的研究[J]. 土壤通报,2018,49(4):993-1000.ZHANG X L, LIAO P H, LI Q, et al. Remediation of complex organic compounds in contaminated plot with in-situ thermal desorption[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2018,49(4):993-1000. [14] BONNARD M, DEVIN S, LEYVAL C, et al. The influence of thermal desorption on genotoxicity of multipolluted soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2010,73(5):955-960. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.02.023 [15] 万梦雪, 焦文涛, 胡文友, 等. 城市工业区土壤重金属累积特征与来源解析: 以上海市闵行区典型工业区为例[J]. 环境化学,2023,42(6):1886-1898.WAN M X, JIAO W T, HU W Y, et al. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metals in urbanindustrial soils: a case study in Minhang District of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2023,42(6):1886-1898. [16] DUSENGEMUNGU L, MUBEMBA B, GWANAMA C. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in copper mine tailing soils of Kitwe and Mufulira, Zambia, for reclamation prospects[J]. Scientific Reports,2022,12(1):1-16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99269-x [17] HUO A D, WANG X, ZHAO Z X, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils at the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(22):14962. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214962 [18] 陈驰. 多环芳烃-重金属复合污染土壤热脱附-稳定化联合修复工艺研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2022. [19] 勾立争, 刘长波, 刘诗诚, 等. 热脱附法修复多环芳烃和汞复合污染土壤实验研究[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(2):184-187.GOU L Z, LIU C B, LIU S C, et al. Experimental research on thermal desorption to repair soil with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-mercury compund contamination[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(2):184-187. [20] 马迅,杨超,翁群强, 等. 退役油制气场地原位燃气热脱附应用效果[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):280-286. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210656MA X,YANG C, WENG Q Q, et al. Study on application effect of in-situ gas thermal remediation in decommissioned oil-to-gas production site[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):280-286. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210656 [21] GAO Y, DIAS Da SILVA P, ALVAREZ P J J, et al. Integrating thermal analysis and reaction modeling for rational design of pyrolytic processes to remediate soils contaminated with heavy crude oil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2021,55(17):11987-11996. [22] CHENG Y, SUN H, YANG E T, et al. Distribution and bioaccessibility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in industrially contaminated site soils as affected by thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,411:125129. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125129 [23] 李进平, 胡云娇, 陈思奇. 污泥热干化过程中重金属Pb、Cu、Zn的形态转化及稳定特性[J]. 环境工程学报,2015,9(12):6041-6044.LI J P, HU Y J, CHEN S Q. Stability characteristic and species transformation of Pb, Cu, Zn by thermal drying of sewage sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2015,9(12):6041-6044. [24] 张慷, 邓浩旺, 田科. 污泥热解与燃烧促进重金属固定化[J]. 湘潭大学学报(自然科学版),2022(5):102-110.ZHANG K, DENG H W, TIAN K. Sludge pyrolysis and combustion promote the immobilization of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Xiangtan University (Natural Science Edition),2022(5):102-110. [25] RUAN M, ZHANG Y, WU X, et al. Effects of initial particle sizes of Triarrhena lutarioriparia on processing performance, material properties, and heavy metal speciation in sewage sludge composting[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2022,30(8):19980-19993. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-23501-y [26] 李佳. 有机污染土壤修复决策模型与化学氧化—热脱附耦合技术研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. [27] 张怡斐. 市政污泥热处理过程中主要污染物的迁移转化[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2011. [28] 郭子逸. 污泥微波热解过程重金属迁移转化特性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2016. [29] BANDARA T, CHATHURIKA J B A J, FRANKS A, et al. Interactive effects of biochar type and pH on the bioavailability of As and Cd and microbial activities in co-contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2021,23:101767. [30] 朱雨锋, 孙柳, 李立青, 等. 黑臭水体治理: Ⅰ. 水体氧状态对沉积物中重金属形态及生物有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2023,43(2):1-10.ZHU Y F, SUN L, LI L Q, et al. Treatment of black and odorous water: Ⅰ. effects of water oxygen state on speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2023,43(2):1-10. [31] 黄永炳, 王丽丽, 李晓娟, 等. 砷形态转化及其环境效应研究[J]. 环境污染与防治,2013,35(1):16-19.HUANG Y B, WANG L L, LI X J, et al. Transformation of arsenic species and its environmental effect[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control,2013,35(1):16-19. [32] 刘殊嘉. 餐厨垃圾高温好氧快速发酵过程中重金属形态转化特征及影响机制[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021. [33] WU B, GUO S H, ZHANG M, et al. Coupling effects of combined thermal desorption and stabilisation on stability of cadmium in the soil[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022,310:119905. ⊗ doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119905 -





 下载:
下载: