Characterization of heavy metals solidification during hydrothermal synthesis of tobermorite from incineration fly ash
-
摘要:
城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰的环境安全利用处置已成为当前环境管理部门和行业部门亟待解决的问题。为降低焚烧飞灰中重金属对环境的潜在风险,以水洗飞灰为原料水热合成托贝莫来石,探讨Ca与(Si+Al)的摩尔比〔以Ca/(Si+Al)表示〕对水热产物的晶相组成、微观形貌和表面官能团的影响,研究水热过程中重金属(Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn和Cr)的浸出浓度、浸出率、液相迁移率、形态分布和环境风险的变化。结果表明:Ca/(Si+Al)对水热产物的类型具有重要影响,Ca/(Si+Al)的增加有利于抑制沸石类结构的生成,促进托贝莫来石的形成。随着托贝莫来石的形成,水热产物中5种重金属的毒性浸出浓度和浸出率逐渐降低,相较于水洗飞灰,在最佳比例为1.10的条件下水热产物中重金属的浸出浓度分别下降99.5%、99.0%、99.4%、88.9%和63.7%,浸出率低至0.25%、0.08%、0.01%、0.01%和2.73%,同时重金属向液相的迁移率仅为1.41%、4.28%、0.29%、0.05%和0%,表明大部分重金属均稳定地存在于固相产物中,而不是迁移至水热液中。这归因于托贝莫来石的形成增加了5种重金属残渣态的占比,降低了重金属的迁移性。风险评价指数(risk assesssment code,RAC)结果显示,最佳比例条件下水热产物中5种重金属的RAC均低于10%,达到环境低风险水平。综上,水热合成托贝莫来石是一种稳定焚烧飞灰中重金属很有前景的方法,为富含重金属的危险废物的安全处置和回收利用提供了一种可行的替代方案。
Abstract:The environmentally safe utilization and disposal of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash is an urgent problem that needs to be addressed by environmental management and industry departments. To mitigate the potential risk of heavy metals in incineration fly ash to the environment, the effects of Ca/(Si+Al) (molar ratio) on the crystalline phase composition, microscopic morphology, and surface functional groups of hydrothermally synthesized tobermorite using washed fly ash were investigated. Additionally, the changes in leaching concentration, leaching rate, liquid-phase mobility, morphological distribution, and environmental risk of heavy metals (Hg, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Cr) during the hydrothermal process were examined. The results demonstrated that Ca/(Si+Al) had a significant impact on the type of hydrothermal products, higher Ca/(Si+Al) molar ratio was favorable for inhibiting the formation of zeolite-like structures and promoting the formation of tobermorite. As tobermorite formed, the toxic leaching concentrations and leaching rates of the five heavy metals in the hydrothermal products gradually decreased. Compared to washed fly ash, the leaching concentrations of heavy metals in the hydrothermal products under the optimal ratio (1.1) condition decreased by 99.5%, 99.0%, 99.4%, 88.9%, and 63.7%, respectively, while the leaching rates reached as low as 0.25%, 0.08%, 0.01%, 0.01%, and 2.73%. Moreover, the migration of heavy metals to the liquid phase was limited to 1.41%, 4.28%, 0.29%, 0.05%, and 0%, indicating that most heavy metals were stably present in solid-phase products rather than migrating to the hydrothermal liquid. This was attributed to the formation of tobermorite, which increased the proportion of the five heavy metal residue states and decreased heavy metal mobility. The risk assessment code (RAC) results revealed that RAC of the five heavy metals in the hydrothermal products under the optimal ratio conditions was less than 10%, reaching an environmentally low-risk level. In summary, hydrothermal synthesis of tobermorite was a promising method for stabilizing heavy metals in incineration fly ash, providing a viable alternative for the safe disposal and recycling of hazardous wastes rich in heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- waste incineration fly ash /
- tobermorite /
- harmless /
- hydrothermal treatment /
- leaching toxicity
-
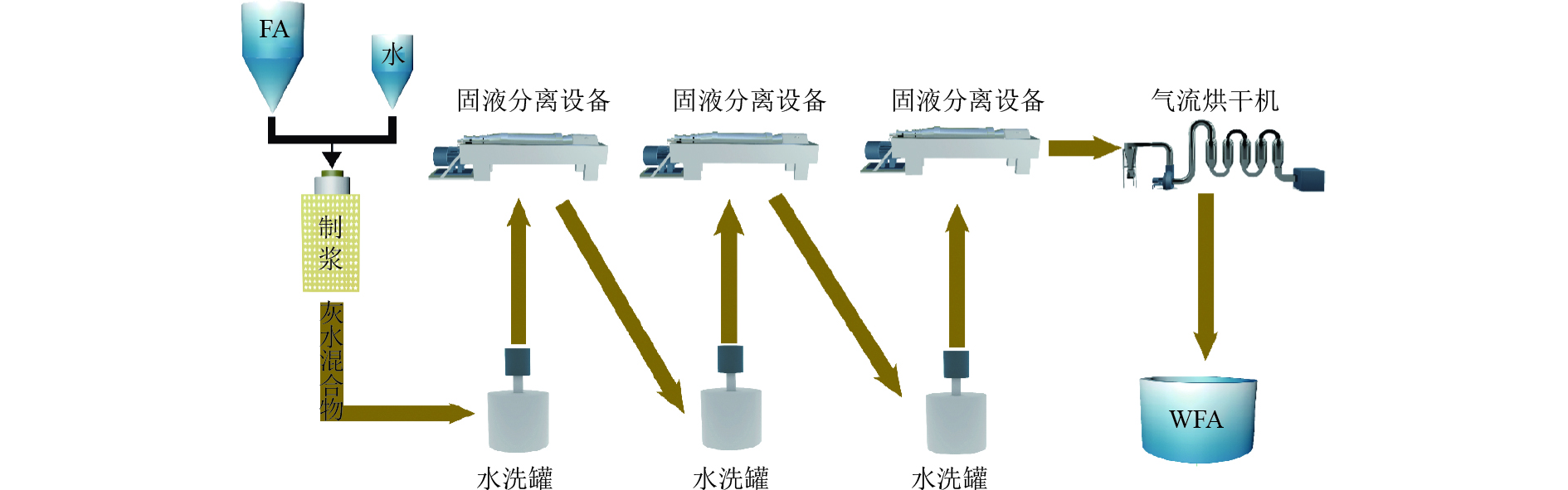
表 1 WFA的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of WFA
元素 占比/% 元素 占比/% Ca 78.9 K 0.90 Si 2.80 Ti 1.35 Al 1.29 Fe 2.40 Cl 1.50 Zn 1.78 S 4.19 Na 0.59 表 2 WFA和水热产物中的重金属浓度
Table 2. Heavy metal contents of WFA and hydrothermal products
mg/kg 样品 Hg Ni Pb Zn Cr WFA 17.7 27.8 857.7 4 818.2 76.9 WHT-1 5.9 13.3 308.0 2 420.4 55.7 WHT-2 7.9 15.1 455.0 2 890.5 58.8 WHT-3 10.9 15.9 521.9 3 099.0 69.3 表 3 WFA和水热产物中的重金属浸出浓度和浸出率
Table 3. Heavy metal leaching concentrations and leaching rates of WFA and hydrothermal products
样品 浸出浓度/(mg/L) 浸出率/% Hg Ni Pb Zn Cr Hg Ni Pb Zn Cr WFA 0.210 0.103 0.325 0.198 0.545 11.86 3.71 0.38 0.04 7.09 WHT-1 0.027 0.011 0.038 0.062 0.291 4.49 0.83 0.12 0.03 5.22 WHT-2 0.019 0.002 0.017 0.073 0.226 2.43 0.15 0.04 0.03 3.85 WHT-3 0.003 0.001 0.002 0.022 0.189 0.25 0.08 0.01 0.01 2.73 GB 5085.3—2007中浓度限值 0.10 5.00 5.00 100 15 表 4 WFA和水热产物的RAC评价结果
Table 4. Results of RAC evaluation of WFA and hydrothermal products
% 样品 Hg Ni Zn Pb Cr WFA 44.68 13.56 0.57 2.03 6.52 WHT-1 1.55 4.23 0.11 0.07 5.48 WHT-2 1.34 5.03 0.07 0.05 3.72 WHT-3 1.04 0.95 0.04 0.04 2.40 -
[1] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2022[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. [2] LU J W, ZHANG S K, HAI J, et al. Status and perspectives of municipal solid waste incineration in China: a comparison with developed regions[J]. Waste Management,2017,69:170-186. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.014 [3] TIAN X, RAO F, LI C X, et al. Solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and immobilization of heavy metals using waste glass in alkaline activation system[J]. Chemosphere,2021,283:131240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131240 [4] 吴昊, 刘宏博, 田书磊, 等.城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰利用处置现状及环境管理[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(5):1034-1040.WU H, LIU H B, TIAN S L, et al. Current situation for utilization and disposal and environmental management of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(5):1034-1040. [5] 黄楠楠, 吴昊, 田书磊, 等.膜浓缩液淋滤飞灰重金属迁移特性及化学形态变化特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(6):1490-1498.HUANG N N, WU H, TIAN S L, et al. Migration and morphological characteristics of heavy metals in fly ash from membrane concentrate leaching[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(6):1490-1498. [6] 王庆旭, 李松, 吴昊, 等.纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤焚烧飞灰过程中氯盐溶出及重金属的迁移特性[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(8):1958-1965.WANG Q X, LI S, WU H, et al. Characteristics of chloride salt dissolution and heavy metal migration during leaching of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with membrane concentrate[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(8):1958-1965. [7] WU K, SHI H S, de SCHUTTER G, et al. Preparation of alinite cement from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2012,34(3):322-327. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.11.016 [8] FAN W D, LIU B, LUO X, et al. Production of glass-ceramics using municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. Rare Metals,2019,38(3):245-251. doi: 10.1007/s12598-017-0976-8 [9] WONG G, GAN M, FAN X H, et al. Co-disposal of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and bottom slag: a novel method of low temperature melting treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,408:124438. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124438 [10] HAN S Y, SONG Y C, JU T Y, et al. Recycling municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in super-lightweight aggregates by sintering with clay and using SiC as bloating agent[J]. Chemosphere,2022,307:135895. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135895 [11] ZHANG R C, WEI X F, HAO Q, et al. Bioleaching of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: availability of recoverable sulfur prills and form transformation of heavy metals[J]. Metals,2020,10(6):815. doi: 10.3390/met10060815 [12] WANG H, ZHU F F, LIU X Y, et al. A mini-review of heavy metal recycling technologies for municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. Waste Management & Research:the Journal for a Sustainable Circular Economy,2021,39(9):1135-1148. [13] SHI H S, KAN L L. Characteristics of municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI) fly ash-cement matrices and effect of mineral admixtures on composite system[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2009,23(6):2160-2166. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.12.016 [14] 刘项, 李传强, 许林季.垃圾焚烧飞灰处理技术研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2021,50(9):2501-2508.LIU X, LI C Q, XU L J. Research progress on treatment technology of MSWI fly ash[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2021,50(9):2501-2508. [15] TANG H L, ERZAT A, LIU Y S. Recovery of soluble chloride salts from the wastewater generated during the washing process of municipal solid wastes incineration fly ash[J]. Environmental Technology,2014,35(22):2863-2869. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2014.924568 [16] XUE Y, LIU X M. Detoxification, solidification and recycling of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,420:130349. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130349 [17] SUN Y, ZHENG J C, ZOU L Q, et al. Reducing volatilization of heavy metals in phosphate-pretreated municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by forming pyromorphite-like minerals[J]. Waste Management,2011,31(2):325-330. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.10.011 [18] ZHANG Z K, WANG Y L, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Stabilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash via hydrothermal treatment with coal fly ash[J]. Waste Management,2022,144:285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2022.03.022 [19] BAYUSENO A P, SCHMAHL W W, MÜLLEJANS T. Hydrothermal processing of MSWI fly ash-towards new stable minerals and fixation of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,167(1/2/3):250-259. [20] 阮煜. 水热法协同处置不同炉型的垃圾焚烧炉飞灰及其机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学,2019. [21] SHI D Z, HU C Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Silicon-aluminum additives assisted hydrothermal process for stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash from MSW incineration[J]. Fuel Processing Technology,2017,165:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.05.007 [22] COLEMAN N J, BRASSINGTON D S, RAZA A, et al. Sorption of Co2+ and Sr2+ by waste-derived 11 Å tobermorite[J]. Waste Management,2006,26(3):260-267. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2005.01.019 [23] KOMARNENI S, ROY D M. New tobermorite cation exchangers[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1985,20(8):2930-2936. doi: 10.1007/BF00553057 [24] PARDAL X, POCHARD I, NONAT A. Experimental study of Si-Al substitution in calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) prepared under equilibrium conditions[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2009,39(8):637-643. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.05.001 [25] LI M Q, CHEN Y F, XIA S Q, et al. Microstructure and processing of ultra-light calcium silicate insulation material[J]. Journal Chinese Ceramic Society,2000,28(5):401-406. [26] DING J, TANG Z H, MA S H, et al. A novel process for synthesis of tobermorite fiber from high-alumina fly ash[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2016,65:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2015.10.017 [27] KLIMESCH D S, RAY A, GUERBOIS J P. Differential scanning calorimetry evaluation of autoclaved cement based building materials made with construction and demolition waste[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2002,389(1/2):195-198. [28] 郭梦茹, 张冰如, 席佳锐, 等.垃圾分类前后焚烧飞灰的理化性质及重金属污染特性[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):843-850.GUO M R, ZHANG B R, XI J R, et al. Physicochemical properties and heavy metal pollution characteristics of incineration fly ash before and after refuse classification[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):843-850. [29] LIU X M, ZHAO X B, YIN H F, et al. Intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials prepared by MSWI fly ash and other solid wastes: hydration characteristics and heavy metals solidification behavior[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,349:262-271. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.072 [30] YAO Z D, TAMURA C, MATSUDA M, et al. Resource recovery of waste incineration fly ash: synthesis of tobermorite as ion exchanger[J]. Journal of Materials Research,1999,14(11):4437-4442. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1999.0601 [31] SHI D Z, ZHANG C, ZHANG J L, et al. Seed-assisted hydrothermal treatment with composite silicon-aluminum additive for solidification of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. Energy & Fuels,2016,30(12):10661-10670. [32] GUO X L, SONG M. Micro-nanostructures of tobermorite hydrothermal-synthesized from fly ash and municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,191:431-439. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.030 [33] RAURET G, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F, SAHUQUILLO A, et al. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring,1999,1(1):57-61. doi: 10.1039/a807854h [34] ZHOU Y, NING X N, LIAO X K, et al. Characterization and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals found in fly ashes from waste filter bags obtained from a Chinese steel plant[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2013,95:130-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.026 [35] MOSTAFA N Y, SHALTOUT A A, OMAR H, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of aluminium and sulfate substituted 1.1nm tobermorites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2009,467(1/2):332-337. [36] QU X L, ZHAO Z G, ZHAO X G. Microstructure and characterization of aluminum-incorporated calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) under hydrothermal conditions[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(49):28198-28208. doi: 10.1039/C8RA04423F [37] LECOMTE I, HENRIST C, LIÉGEOIS M, et al. (Micro)-structural comparison between geopolymers, alkali-activated slag cement and Portland cement[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2006,26(16):3789-3797. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.12.021 [38] GARCÍA LODEIRO I, MACPHEE D E, PALOMO A, et al. Effect of alkalis on fresh C–S–H gels. FTIR analysis[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2009,39(3):147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.01.003 [39] CRIADO M, FERNÁNDEZ-JIMÉNEZ A, PALOMO A. Alkali activation of fly ash: effect of the SiO2/Na2O ratio[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2007,106(1/2/3):180-191. [40] YANG L Y, QIAN X M, YUAN P, et al. Green synthesis of zeolite 4A using fly ash fused with synergism of NaOH and Na2CO3[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,212:250-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.259 [41] YU P, KIRKPATRICK R J, POE B, et al. Structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H): near-, mid-, and far-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2004,82(3):742-748. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb01826.x [42] LOTHENBACH B, JANSEN D, YAN Y, et al. Solubility and characterization of synthesized 11Å Al-tobermorite[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2022,159:106871. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2022.106871 [43] MOSTAFA N Y, KISHAR E A, ABO-EL-ENEIN S A. FTIR study and cation exchange capacity of Fe3+- and Mg2+-substituted calcium silicate hydrates[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2009,473(1/2):538-542. [44] GRUTZECK M, BENESI A, FANNING B. Silicon-29 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance study of calcium silicate hydrates[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,1989,72(4):665-668. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb06192.x [45] WANG Z H, MA S H, ZHENG S L, et al. Incorporation of Al and Na in hydrothermally synthesized tobermorite[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2017,100(2):792-799. doi: 10.1111/jace.14599 [46] WANG S P, PENG X Q, TANG L P, et al. Influence of inorganic admixtures on the 11Å-tobermorite formation prepared from steel slags: XRD and FTIR analysis[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2014,60:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.03.002 [47] PAN Y, WU Z M, ZHOU J Z, et al. Chemical characteristics and risk assessment of typical municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash in China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,261:269-276. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.038 [48] HUANG H J, YUAN X Z, ZENG G M, et al. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals' pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology,2011,102(22):10346-10351. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.117 [49] CAPRAI V, SCHOLLBACH K, BROUWERS H J H. Influence of hydrothermal treatment on the mechanical and environmental performances of mortars including MSWI bottom ash[J]. Waste Management,2018,78:639-648. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.06.030 [50] 李建新. 垃圾焚烧过程重金属污染物迁移机理及稳定化处理技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2004. [51] IZQUIERDO M, QUEROL X. Leaching behaviour of elements from coal combustion fly ash: an overview[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2012,94:54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.10.006 [52] JING Z Z, FAN X W, ZHOU L, et al. Hydrothermal solidification behavior of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash without any additives[J]. Waste Management,2013,33(5):1182-1189. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.01.038 [53] LI X Y, CHEN Q Y, ZHOU Y S, et al. Stabilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash using silica fume[J]. Waste Management,2014,34(12):2494-2504. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.08.027 [54] HALIM C E, AMAL R, BEYDOUN D, et al. Implications of the structure of cementitious wastes containing Pb(Ⅱ), Cd(Ⅱ), As(Ⅴ), and Cr(Ⅵ) on the leaching of metals[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2004,34(7):1093-1102. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.11.025 [55] LIU H L, LI L Q, YIN C Q, et al. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Moshui Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2008,20(4):390-397. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62069-0 [56] HU Y Y, ZHANG P F, LI J P, et al. Stabilization and separation of heavy metals in incineration fly ash during the hydrothermal treatment process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,299:149-157. ⊗ doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.002 -





 下载:
下载: