Effect of inoculation of functional bacteria on the remediation of petroleum polluted soil and the microbial community
-
摘要:
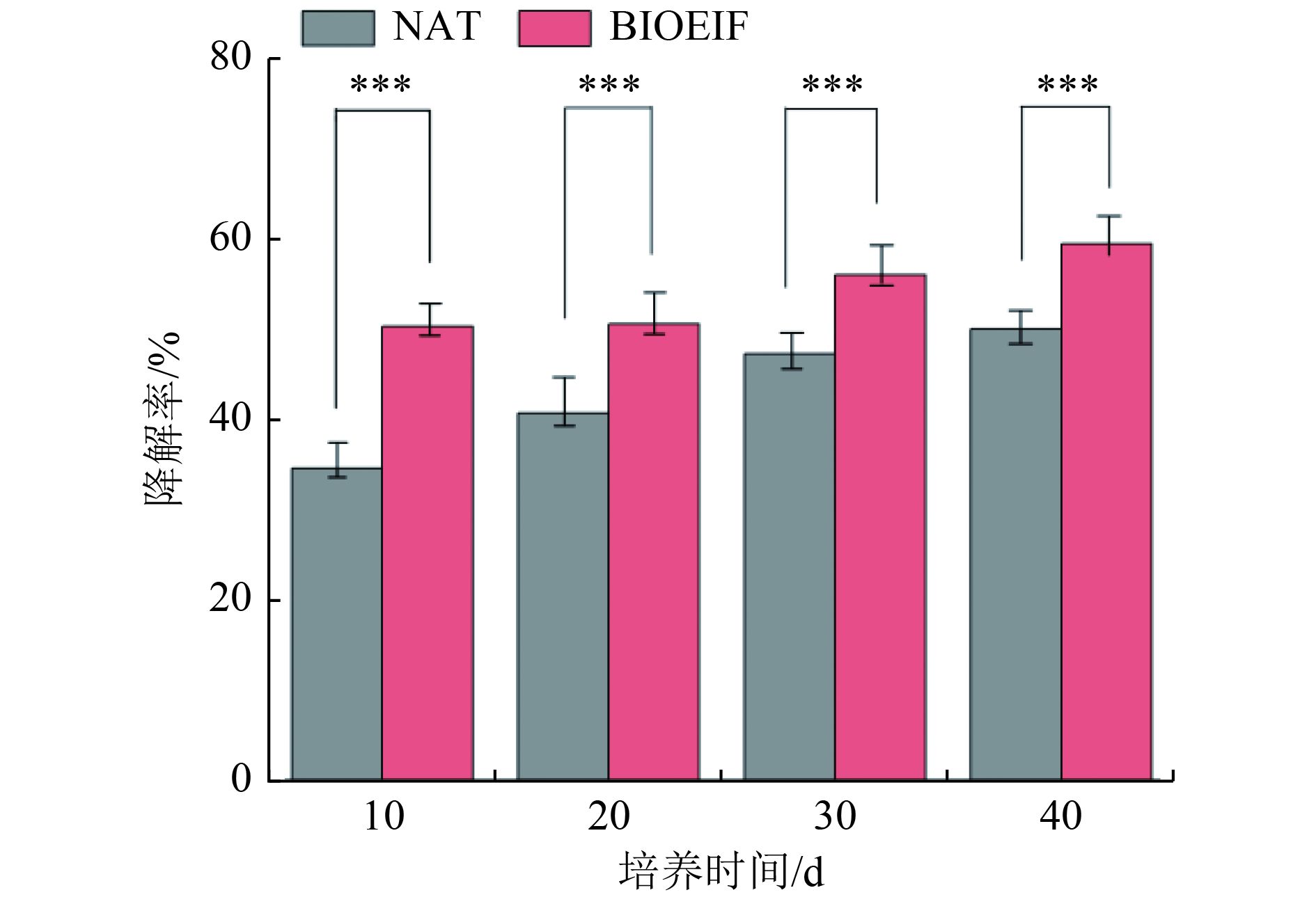
利用定向筛选驯化的二苯并噻吩(DBT)降解菌对石油污染土壤进行为期40 d的土壤模拟培养试验,研究了功能菌(红球菌,Rhodococcus sp. ZYL-1)接种对石油污染土壤中DBT的降解效果,结合16S rDNA高通量测序及生物信息学分析,解析了功能菌接种对土壤细菌群落演替的影响。结果表明:在25 ℃的暗箱培养过程中,红球菌添加显著提高了DBT污染土壤的降解率(P<0.001),生物接种处理组(BIOEIF)的DBT降解主要发生在培养前10 d,培养结束后DBT降解率接近60%,比依赖土壤土著微生物的自然衰减组(NAT)降解率提升10%以上;对比BIOEIF组和NAT组土壤培养过程中细菌群落组成,BIOEIF组香农多样性指数和系统发育指数显著低于NAT组,但接种红球菌未对DBT污染土壤的细菌群落组成造成显著影响,Micromonospora、Bacillus、unclassified_f_Planococcaceae为污染土壤培养过程中的优势菌属,而接种的红球菌并未成为优势菌属;网络分析表明,功能菌接种显著提升污染土壤微生物的DBT关键降解菌属类群,通过强化土壤土著微生物Shimazuella协同降解DBT,进而提升了石油烃污染土壤的修复效果,Shimazuella可能是参与DBT的代谢的关键微生物。所接种的功能菌(红球菌)可协同提高土著微生物对于石油污染土壤DBT的生物降解,具有较高的土壤修复应用潜力。
-
关键词:
- 二苯并噻吩(DBT) /
- 生物修复 /
- 红球菌 /
- 细菌群落演替
Abstract:The dibenzothiophene (DBT) degrading bacteria screened and domesticated based on previous culture experiment was inoculated into the petroleum contaminated soil for a 40 day simulated soil remediation experiment. The degradation effect of functional bacteria (Rhodococcus sp. ZYL-1) and the succession of bacterial community in the petroleum contaminated soil was analyzed. The results showed the addition of Rhodococcus sp. ZYL-1 increased significantly the degradation efficiency of DBT compared to control during the incubation at 25 ℃ in the dark chamber (P<0.001). The DBT degradation in the bioaugmentation treatment (BIOEIF) mainly occurred in the first 10 days after soil incubation, in which DBT degradation rate was close to 60% at the end of incubation, higher than that in the control, i.e., natural attenuation treatment (NAT) relying on soil indigenous microorganisms. Compared with the bacterial community composition between BIOEIF treatment and NAT treatment in the soil incubating process, the Shannon diversity index and phylogenetic diversity index of BIOEIF were significantly lower than that in NAT, but the inoculation of Rhodococcus sp. ZYL-1 did not affect significantly the composition of the soil bacterial community. Micromonospora, Bacillus, and unclassified_f_Planococcaceaeis were detected as the dominated taxa in the petroleum contaminated soil, but Rhodococcus which was inoculated did not have an obviously high abundance in soils. Network analysis showed that key functional bacteria for DBT degradation had significantly improved in the contaminated soil in BIOEIF, which might be due to the symbiosis of Shimazuella with indigenous microorganism. In conclusion, the inoculated functional bacteria (Rhodococcus sp. ZYL-1) could obviously improve the biodegradation of DBT in petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil based on enhancing the degradation function of indigenous microorganisms.
-
Key words:
- dibenzothiophene (DBT) /
- bioremediation /
- Rhodococcus /
- bacterial community succession
-
-
[1] DU W D, WAN Y Y, ZHONG N N, et al. Status quo of soil petroleum contamination and evolution of bioremediation[J]. Petroleum Science,2011,8(4):502-514. doi: 10.1007/s12182-011-0168-3 [2] PATEL A B, SHAIKH S, JAIN K R, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: sources, toxicity, and remediation approaches[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:562813. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.562813 [3] 贺光秀, 张枝焕, 彭旭阳, 等.北京地区表层土壤中含氧、含硫杂环芳烃化合物的分布特征及污染源分析[J]. 环境科学,2011,32(11):3284-3293. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.11.033HE G X, ZHANG Z H, PENG X Y, et al. Distribution and sources of oxygen and sulfur heterocyclic aromatic compounds in surface soil of Beijing, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science,2011,32(11):3284-3293. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.11.033 [4] RAEZ-VILLANUEVA S, PERONO G A, JAMSHED L, et al. Effects of dibenzothiophene, a sulfur-containing heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and its alkylated congener, 2,4,7-trimethyldibenzothiophene, on placental trophoblast cell function[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2021,41(9):1367-1379. doi: 10.1002/jat.4128 [5] RISER-ROBERTS E. Remediation of petroleum contaminated soils: biological, physical, and chemical processes[M]. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers, 1998. [6] 冒学宇, 李勇, 吴丛杨慧, 等.石油烃降解菌的筛选及其降解特性研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2022,12(3):886-892. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210203MAO X Y, LI Y, WU C Y H, et al. Research on the screening of petroleum hydrocarbon degrading bacteria and their degradation characteristics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(3):886-892. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210203 [7] 王欣, 范超, 刘伟, 等.基于Thiobacillus thioparus菌株的生物脱硫工艺参数优化研究[J]. 中国沼气,2019,37(5):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2019.05.006WANG X, FAN C, LIU W, et al. Process parameter optimization of bio-desulfurization based on Thiobacillus thioparus strain[J]. China Biogas,2019,37(5):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2019.05.006 [8] 余玲, 王雪梅, 刘梦娟, 等.高效石油降解菌的筛选及降解特性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,2023,46(1):7-14. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.0912.22.338YU L, WANG X M, LIU M J, et al. Screening of high-efficient petroleum degradation bacteria and study on their degradation characteristics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2023,46(1):7-14. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.0912.22.338 [9] ZHANG T, ZHANG H J. Microbial consortia are needed to degrade soil pollutants[J]. Microorganisms,2022,10(2):261. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020261 [10] 代小丽, 王硕, 李佳斌, 等.石油污染土壤原位生物修复强化技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(3):456-466. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190141DAI X L, WANG S, LI J B, et al. Research progress on in situ bioremediation enhancement technology of oil contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(3):456-466. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190141 [11] 陈婧, 聂红云, 聂麦茜, 等.嗜油菌NY3与土著菌FF生物强化降解石油烃的协同机理研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2023,30(2):173-179. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20220176CHEN J, NIE H Y, NIE M Q, et al. Synergistic degradation mechanism of petroleum hydrocarbons bioaugmented by oleophilic strain NY3 and indigenous strain FF[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2023,30(2):173-179. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20220176 [12] ZHOU H H, LIU Q, JIANG L J, et al. Enhanced remediation of oil-contaminated intertidal sediment by bacterial consortium of petroleum degraders and biosurfactant producers[J]. Chemosphere,2023,330:138763. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138763 [13] 吴蔓莉, 陈凯丽, 叶茜琼, 等.堆肥-生物强化对重度石油污染土壤的修复作用[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(10):4412-4419. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201702056WU M L, CHEN K L, YE X Q, et al. Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil using a bioaugmented compost technique[J]. Environmental Science,2017,38(10):4412-4419. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201702056 [14] CHEN S F, ZHOU Y Q, CHEN Y R, et al. Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor[J]. Bioinformatics,2018,34(17):i884-i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560 [15] MAGOČ T, SALZBERG S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies[J]. Bioinformatics,2011,27(21):2957-2963. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507 [16] EDGAR R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads[J]. Nature Methods,2013,10(10):996-998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604 [17] STACKEBRANDT E, GOEBEL B M. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,1994,44(4):846-849. doi: 10.1099/00207713-44-4-846 [18] WANG Q, GARRITY G M, TIEDJE J M, et al. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2007,73(16):5261-5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 [19] OKSANEN J, KINDT R, PLEGENDR E, et al. The vegan package[J]. Community Ecology Package,2007,10:719. [20] KEMBEL S W, COWAN P D, HELMUS M R, et al. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology[J]. Bioinformatics,2010,26(11):1463-1464. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq166 [21] DENG Y, JIANG Y H, YANG Y F, et al. Molecular ecological network analyses[J]. BMC Bioinformatics,2012,13:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-113 [22] 郭志国, 鲁建江, 戴大章, 等.基于响应面法的二苯并噻吩生物降解条件的优化[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2012,32(1):106-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2012.01.022GUO Z G, LU J J, DAI D Z, et al. Optimization of biodegradation of dibenzothiophene using response surface methodology[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology,2012,32(1):106-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2012.01.022 [23] 祁燕云, 吴蔓莉, 祝长成, 等.基于高通量测序分析的生物修复石油污染土壤菌群结构变化[J]. 环境科学,2019,40(2):869-875. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201805174QI Y Y, WU M L, ZHU C C, et al. Microbial community structure shift during bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil using high throughput sequencing[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(2):869-875. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201805174 [24] 余天飞, 柳晓东, 艾加敏, 等.石油污染土壤富集前后细菌群落组成和共现网络分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(8):3858-3866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.08.044YU T F, LIU X D, AI J M, et al. Bacterial community composition and co-occurrence network before and after enrichment of oil-contaminated soil[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(8):3858-3866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.08.044 [25] 潘云飞, 唐正, 彭欣怡, 等.石油烃污染土壤微生物修复技术研究现状及进展[J]. 化工进展,2021,40(8):4562-4572. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-2013PAN Y F, TANG Z, PENG X Y, et al. Microbial remediation techniques for petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil: a review[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(8):4562-4572. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-2013 [26] BUZANELLO E, REZENDE R, SOUSA F, et al. A novel Bacillus pumilus-related strain from tropical landfarm soil is capable of rapid dibenzothiophene degradation and biodesulfurization[J]. BMC Microbiology,2014,14(1):257. [27] 彭子淇, 罗宇同, 陆阳阳, 等.我国主要河口沉积物中多环芳烃细菌降解及生物修复强化方式的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报,2022,62(6):2311-2327. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20220272PENG Z Q, LUO Y T, LU Y Y, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of main estuaries in China by bacteria and the methods to enhance the degradation[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2022,62(6):2311-2327. □ doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20220272 -





 下载:
下载: