Research progress in advanced oxidation technologies for remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soils
-
摘要:
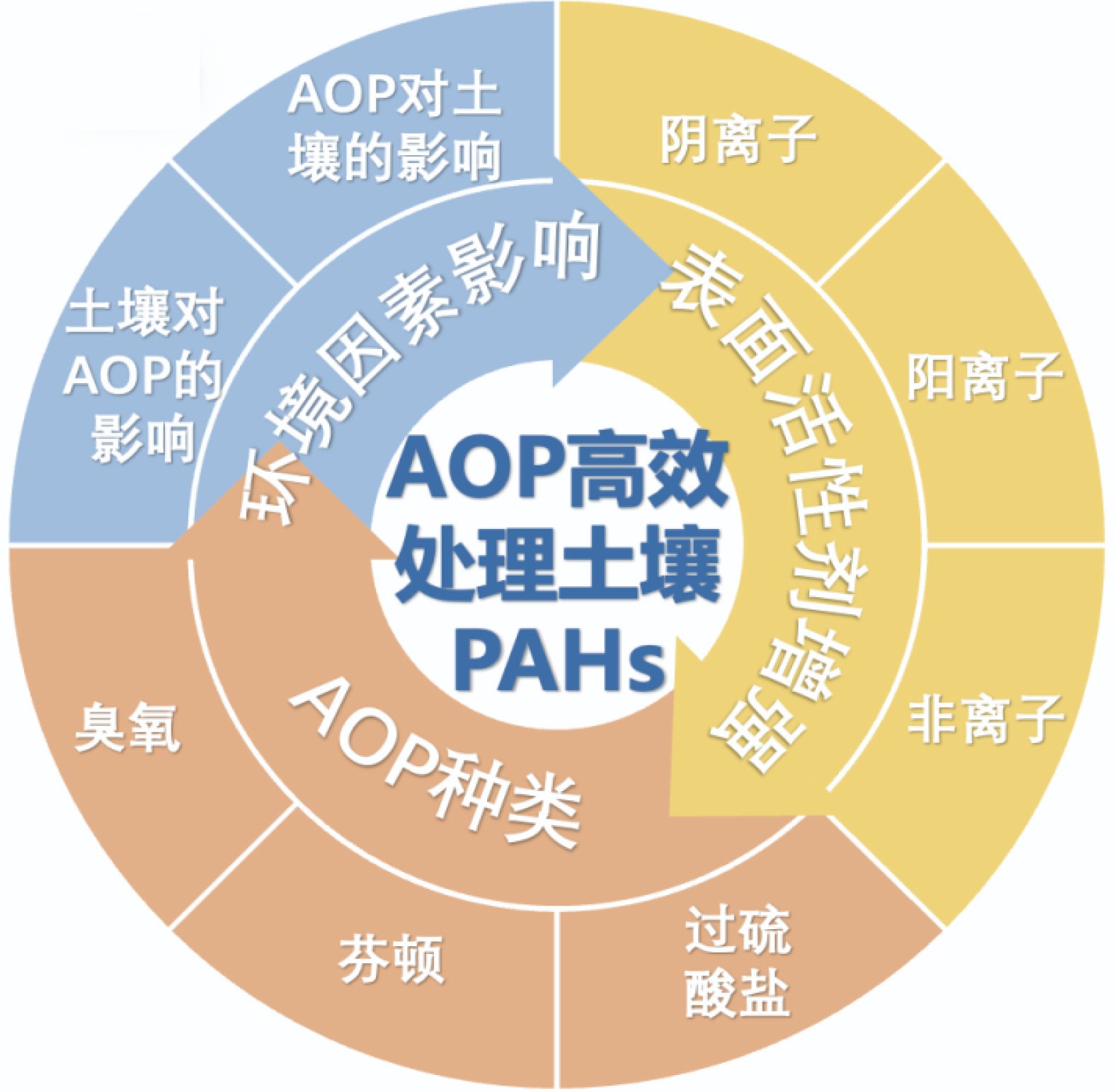
多环芳烃(PAHs)是由2个或2个以上苯环组成的碳氢化合物,其致癌、致突变、致畸等特性对人类健康和生态环境产生不利的影响。由于PAHs具有低水溶性、高疏水性和难降解性等特点,导致PAHs污染土壤修复具有巨大挑战。高级氧化技术是处理PAHs污染土壤的有效手段。对高级氧化技术在PAHs污染土壤修复领域的研究进展进行了总结,对臭氧氧化、芬顿氧化和过硫酸盐氧化等高级氧化技术的优劣进行了分析;此外,探讨了表面活性剂在提升高级氧化效果方面的作用以及土壤理化环境条件对氧化过程的影响,分析了氧化过程对土壤微环境的潜在影响;最后,指出了高级氧化修复PAHs污染土壤的研究难点和未来方向。
-
关键词:
- 多环芳烃(PAHs) /
- 焦化土壤 /
- 高级氧化 /
- 土壤污染治理
Abstract:Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are hydrocarbon compounds composed of two or more benzene rings. Their carcinogenic, mutagenic and teratogenic properties have adverse effects on human health and ecological environment. Due to the characteristics of low water solubility, high hydrophobicity and difficult degradation of PAHs, the remediation of PAHs-contaminated soil poses significant challenges. Advanced oxidation technologies have emerged as effective approaches for addressing PAHs contamination in soil. The research progress in the field of advanced oxidation technologies for the remediation of PAHs-contaminated soil was summarized, with a focus on the advantages and disadvantages analysis of ozone oxidation, Fenton oxidation, and persulfate oxidation. Furthermore, the role of surfactants in enhancing the effectiveness of advanced oxidation was explored and the influence of soil physicochemical conditions on the oxidation process was discussed. Potential impacts of the oxidation process on the soil microenvironment were also analyzed. Finally, the research difficulties and future directions of remediation of PAHS-contaminated soil by advanced oxidation were pointed out.
-
图 2 表面活性剂促进高级氧化降解机理(以过硫酸盐为例)[83]
Figure 2. Mechanism of surfactant promoting AOP degradation (taking persulfate as an example)
表 1 臭氧氧化对PAHs污染土壤修复研究进展
Table 1. Research progress in remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by ozone oxidation
表 2 芬顿氧化修复PAHs污染土壤实例
Table 2. Research progress in remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by Fenton oxidation
污染物(浓度)反应条件 降解
率/%数据
来源氧化剂浓度 催化剂/辅助材料 pH 温度/℃ 水土比/(mL/g) 反应时间 Phe(25 mg/kg) 5 mol/L H2O2 25 mg/kg针铁矿 7 25 3/1 7 h 89 文献[35] BaP(0.1 mmol/kg) 14 mol/L H2O2,
23.4 mmol/L FeSO4天然土壤矿物 2~8 25 8/1 24 h 85 文献[23] 16种PAHs(222 g/kg) 2.8 mol/L H2O2,
0.1 mol/L FeSO4Tween 80 等 4种表面活性剂 7 25 17/20 49 d 60 文献[36] 23种PAHs 15% H2O2,5 mmol/L FeSO4 乙醇 2-3 25 1/1 1 h 68 文献[30] 表 3 过硫酸盐高级氧化对PAHs污染土壤修复研究进展
Table 3. Research progress in remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by advanced oxidation of persulfate
污染物(浓度)反应条件 降解率/% 数据来源 氧化剂浓度 催化剂/辅助材料 pH 温度/℃ 水土比/(mL/g) 反应时间/d 16种PAHs (0.81 g/kg) 7.2 mmol/L PDS 7 60 15/1 7 45.5 文献[72] 16种PAHs (1.36 g/kg) 10% PDS 10%磁铁矿 7 25 10/1 7 66 文献[73] PAHs (16.98 mg/kg) 0.13 mol/L PDS 3.5 g mZVI 7 25 1/1 105 69.1 文献[48] 3.5 g nZVI 82.2 3.5 g C-nZVI 62.8 PAHs (340 mg/kg) 0.5 mol/L PDS 碱 10 25 3/1 3 55 文献[56] 11 62 12 65 PAHs (420 mg/kg) 0.2 mmol/L PMS 4.7 V/m电流 7 25 31/100 56 35 文献[74] PAHs (1.1 g/kg) 0.04 mol/L PDS 1.2 mol/L H2O2 7.8 25 1/0.63 0.2 上层土壤6,
下层土壤26文献[54] 16种PAHs (335 mg/kg) 0.3 mol/L PDS 0.3 mol/L CA, 0.075 mol/L HPCD,
0.15 mol/L Fe2+6 25 3/1 0.25 94 文献[68] -
[1] PENG X, XU P F, DU H, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research,2018,16(5):6419-6440. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1605_64196440 [2] SAKSHI, SINGH S K, HARITASH A K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: soil pollution and remediation[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2019,16(10):6489-6512. doi: 10.1007/s13762-019-02414-3 [3] RUGE Z, MUIR D, HELM P, et al. Concentrations, trends, and air-water exchange of PAHs and PBDEs derived from passive samplers in lake superior in 2011[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(23):13777-13786. [4] LLOBET J M, FALCÓ G, BOCIO A, et al. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through consumption of edible marine species in Catalonia, Spain[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2006,69(10):2493-2499. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-69.10.2493 [5] GHOSAL D, GHOSH S, DUTTA T K, et al. Current state of knowledge in microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2016,7:1369. [6] KALMYKOVA Y, MOONA N, STRÖMVALL A M, et al. Sorption and degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, alkylphenols, bisphenol A and phthalates in landfill leachate using sand, activated carbon and peat filters[J]. Water Research,2014,56:246-257. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.011 [7] LIU H Z, BRUTON T A, DOYLE F M, et al. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated groundwater by persulfate: decomposition by Fe(Ⅲ)- and Mn(Ⅳ)-containing oxides and aquifer materials[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(17):10330-10336. [8] ZHOU Z, LIU X T, SUN K, et al. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,372:836-851. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.213 [9] JI H D, GONG Y Y, DUAN J, et al. Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in seawater by simulated surface-level atmospheric ozone: reaction kinetics and effect of oil dispersant[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,135:427-440. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.047 [10] ZHANG X X, CHENG S P, ZHU C J, et al. Microbial PAH-degradation in soil: degradation pathways and contributing Factors[J]. Pedosphere,2006,16(5):555-565. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(06)60088-X [11] BERNAL-MARTINEZ A, CARRÈRE H, PATUREAU D, et al. Ozone pre-treatment as improver of PAH removal during anaerobic digestion of urban sludge[J]. Chemosphere,2007,68(6):1013-1019. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.019 [12] BOUZID I, MAIRE J, BRUNOL E, et al. Compatibility of surfactants with activated-persulfate for the selective oxidation of PAH in groundwater remediation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5(6):6098-6106. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.11.038 [13] BROWN G S, BARTON L L, THOMSON B M. Permanganate oxidation of sorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Waste Management,2003,23(8):737-740. doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00119-8 [14] BELTRÁN F J, OVEJERO G, RIVAS J. Oxidation of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in water: 3. UV radiation combined with hydrogen peroxide[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,1996,35(3):883-890. [15] LEDAKOWICZ S, MILLER J S, OLEJNIK D. Oxidation of PAHs in water solution by ozone combined with ultraviolet radiation[J]. International Journal of Photoenergy,2001,3(2):95-101. doi: 10.1155/S1110662X01000113 [16] GOI A, TRAPIDO M. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil: the Fenton reagent versus ozonation[J]. Environmental Technology,2004,25(2):155-164. doi: 10.1080/09593330409355448 [17] RUSSO L, RIZZO L, BELGIORNO V. Ozone oxidation and aerobic biodegradation with spent mushroom compost for detoxification and benzo(a)pyrene removal from contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere,2012,87(6):595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.012 [18] NAM K, KUKOR J J. Combined ozonation and biodegradation for remediationof mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil[J]. Biodegradation,2000,11(1):1-9. doi: 10.1023/A:1026592324693 [19] EBERIUS M, BERNS A, SCHUPHAN I. Ozonation of pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene in silica and soil-14C-mass balances and chemical analysis of oxidation products as a first step to ecotoxicological evaluation[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry,1997,359(3):274-279. doi: 10.1007/s002160050572 [20] LI X, LUO T, WANG Y X, et al. Removal of benzo[a]pyrene in contaminated soil by ozonation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,43:171-177. [21] PÉREZ M, TORRADES F, DOMÈNECH X, et al. Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation of textile effluents[J]. Water Research,2002,36(11):2703-2710. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00506-1 [22] 潘玉兰. Fenton试剂氧化降解水和土壤中多环芳烃[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. [23] WATTS R J, STANTON P C, HOWSAWKENG J, et al. Mineralization of a sorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in two soils using catalyzed hydrogen peroxide[J]. Water Research,2002,36(17):4283-4292. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00142-2 [24] BOGAN B W, TRBOVIC V, PATEREK J R. Inclusion of vegetable oils in Fenton’s chemistry for remediation of PAH-contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere,2003,50(1):15-21. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00490-3 [25] HOMEM V, DIAS Z, SANTOS L, et al. Preliminary feasibility study of benzo(a)pyrene oxidative degradation by Fenton treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental and Public Health,2009,2009:149034. [26] FLOTRON V, DELTEIL C, PADELLEC Y, et al. Removal of sorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil, sludge and sediment samples using the Fenton's reagent process[J]. Chemosphere,2005,59(10):1427-1437. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.065 [27] BALDRIAN P, CAJTHAML T, MERHAUTOVÁ V, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by heterogeneous polymeric metal chelates[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2005,59:267-274. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.02.010 [28] MAZARJI M, MINKINA T, SUSHKOVA S, et al. Impact of humic acid on degradation of benzo(a)pyrene polluted Haplic Chernozem triggered by modified Fenton-like process[J]. Environmental Research,2020,190:109948. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109948 [29] MAZARJI M, MINKINA T, SUSHKOVA S, et al. Biochar-assisted Fenton-like oxidation of benzo[a]pyrene-contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2022,44(1):195-206. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00801-1 [30] LUNDSTEDT S, PERSSON Y, ÖBERG L. Transformation of PAHs during ethanol-Fenton treatment of an aged gasworks' soil[J]. Chemosphere,2006,65(8):1288-1294. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.031 [31] JONSSON S, PERSSON Y, FRANKKI S, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in contaminated soils by Fenton's reagent: a multivariate evaluation of the importance of soil characteristics and PAH properties[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007,149(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.057 [32] YAP C L, GAN S Y, NG H K. Ethyl lactate-Fenton treatment of soil highly contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,200/201/202:247-256. [33] DU Y C, DOU J F, DING A Z, et al. Study on characteristics and influencing factors of PAHs degradation in soil by Fenton-like reagent[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2011,5:1882-1886. [34] QI H M. Application of ex-situ Fenton-like chemical oxidation in remedying PAHs polluted site[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2018,12:3260-3268. [35] KANEL S R, NEPPOLIAN B, CHOI H, et al. Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation of phenanthrene by hydrogen peroxide in soil slurry: kinetics, mechanism, and implication[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal,2003,12(1):101-117. doi: 10.1080/713610963 [36] PISKONEN R, ITÄVAARA M. Evaluation of chemical pretreatment of contaminated soil for improved PAH bioremediation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2004,65(5):627-634. [37] LU M, ZHANG Z Z, QIAO W, et al. Removal of residual contaminants in petroleum-contaminated soil by Fenton-like oxidation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,179(1/2/3):604-611. [38] BOKARE A D, CHOI W. Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,275:121-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054 [39] SIRGUEY C, TEREZA de SOUZA E SILVA P, SCHWARTZ C, et al. Impact of chemical oxidation on soil quality[J]. Chemosphere,2008,72(2):282-289. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.027 [40] WACŁAWEK S, LUTZE H V, GRÜBEL K, et al. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,330:44-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.132 [41] WANG J L, WANG S Z. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,334:1502-1517. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.059 [42] RYBNIKOVA V, SINGHAL N, HANNA K. Remediation of an aged PCP-contaminated soil by chemical oxidation under flow-through conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,314:202-211. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.120 [43] TSITONAKI A, PETRI B, CRIMI M, et al. in situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology,2010,40(1):55-91. doi: 10.1080/10643380802039303 [44] 周金倩, 马建立, 商晓甫, 等.过硫酸盐氧化修复多环芳烃污染土壤的研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(3):482-486.ZHOU J Q, MA J L, SHANG X F, et al. Persulfate oxidation for remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(3):482-486. [45] DENG D Y, LIN X T, OU J M, et al. Efficient chemical oxidation of high levels of soil-sorbed phenanthrene by ultrasound induced, thermally activated persulfate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,265:176-183. [46] PENG H J, ZHANG W, XU L Y, et al. Oxidation and mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) by thermally activated persulfate (TAP) in a soil system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,306:226-232. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.066 [47] LIU Y K, WANG S Y, WU Y L, et al. Degradation of ibuprofen by thermally activated persulfate in soil systems[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,356:799-810. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.002 [48] SONG Y, FANG G D, ZHU C Y, et al. Zero-valent iron activated persulfate remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soils: an in situ pilot-scale study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,355:65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.126 [49] PARDO F, ROSAS J M, SANTOS A, et al. Remediation of a biodiesel blend-contaminated soil with activated persulfate by different sources of iron[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution,2015,226(2):17. [50] DESALEGN B, MEGHARAJ M, CHEN Z L, et al. Green mango peel-nanozerovalent iron activated persulfate oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbons in oil sludge contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2018,11:142-152. [51] PELUFFO M, ROSSO J A, MORELLI I S, et al. Strategies for oxidation of PAHs in aged contaminated soil by batch reactors[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,151:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.067 [52] LOMINCHAR M A, SANTOS A, de MIGUEL E, et al. Remediation of aged diesel contaminated soil by alkaline activated persulfate[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,622/623:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.263 [53] EBERLE D E H. Combined desorption and oxidation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated waters and sediments: a laboratory-scale study[D]. Rhode Island: University of Rhode Island, 2012. [54] LEMAIRE J, LAURENT F, LEYVAL C, et al. PAH oxidation in aged and spiked soils investigated by column experiments[J]. Chemosphere,2013,91(3):406-414. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.003 [55] ANTONIOU M G, deLa CRUZ A A, DIONYSIOU D D. Degradation of microcystin-LR using sulfate radicals generated through photolysis, thermolysis and e− transfer mechanisms[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2010,96(3/4):290-298. [56] ZHAO D, LIAO X Y, YAN X L, et al. Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,254/255:228-235. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.056 [57] COSTANZA J, OTAÑO G, CALLAGHAN J, et al. PCE oxidation by sodium persulfate in the presence of solids[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(24):9445-9450. [58] WANG Z, DENG D Y, YANG L L. Degradation of dimethyl phthalate in solutions and soil slurries by persulfate at ambient temperature[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,271:202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02.027 [59] PENG L B, DENG D Y, GUAN M Y, et al. Remediation HCHs POPs-contaminated soil by activated persulfate technologies: feasibility, impact of activation methods and mechanistic implications[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2015,150:215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.002 [60] DO S H, JO J H, JO Y H, et al. Application of a peroxymonosulfate/cobalt (PMS/Co(Ⅱ)) system to treat diesel-contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere,2009,77(8):1127-1131. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.061 [61] PELUFFO M, PARDO F, SANTOS A, et al. Use of different kinds of persulfate activation with iron for the remediation of a PAH-contaminated soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,563/564:649-656. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.034 [62] OH S Y, KANG S G, CHIU P C. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2010,408(16):3464-3468. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.04.032 [63] KIM C, AHN J Y, KIM T Y, et al. Activation of persulfate by nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI): mechanisms and transformation products of nZVI[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(6):3625-3633. [64] FERRARESE E, ANDREOTTOLA G, OPREA I A. Remediation of PAH-contaminated sediments by chemical oxidation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,152(1):128-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.080 [65] DOMBROWSKI P M, KAKARLA P, CALDICOTT W, et al. Technology review and evaluation of different chemical oxidation conditions on treatability of PFAS[J]. Remediation Journal,2018,28(2):135-150. doi: 10.1002/rem.21555 [66] FURMAN O S, TEEL A L, AHMAD M, et al. Effect of basicity on persulfate reactivity[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering,2011,137(4):241-247. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000323 [67] AHMAD M, TEEL A L, WATTS R J. Mechanism of persulfate activation by phenols[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(11):5864-5871. [68] CHEN F, LUO Z B, LIU G J, et al. Remediation of electronic waste polluted soil using a combination of persulfate oxidation and chemical washing[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2017,204:170-178. [69] PELUFFO M, MORA V C, MORELLI I S, et al. Persulfate treatments of phenanthrene-contaminated soil: effect of the application parameters[J]. Geoderma,2018,317:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.12.016 [70] PARDO F, SANTOS A, ROMERO A. Fate of iron and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during the remediation of a contaminated soil using iron-activated persulfate: a column study[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,566/567:480-488. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.197 [71] MORA V C, MADUEÑO L, PELUFFO M, et al. Remediation of phenanthrene-contaminated soil by simultaneous persulfate chemical oxidation and biodegradation processes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2014,21:7548-7556. [72] RANC B, FAURE P, CROZE V, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness of soil heating prior or during in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) of aged PAH-contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(12):11265-11278. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8731-0 [73] USMAN M, FAURE P, RUBY C, et al. Application of magnetite-activated persulfate oxidation for the degradation of PAHs in contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere,2012,87(3):234-240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.001 [74] ISOSAARI P, PISKONEN R, OJALA P, et al. Integration of electrokinetics and chemical oxidation for the remediation of creosote-contaminated clay[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007,144(1/2):538-548. [75] BI E P, SCHMIDT T C, HADERLEIN S B. Environmental factors influencing sorption of heterocyclic aromatic compounds to soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(9):3172-3178. [76] HAAPEA P, TUHKANEN T. Integrated treatment of PAH contaminated soil by soil washing, ozonation and biological treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2006,136(2):244-250. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.033 [77] ZHOU W J, ZHU L Z. Solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by anionic–nonionic mixed surfactant[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2005,255(1/2/3):145-152. [78] HARITASH A K, KAUSHIK C P. Biodegradation aspects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,169(1/2/3):1-15. [79] BOULANGÉ M, LORGEOUX C, BIACHE C, et al. Fenton-like and potassium permanganate oxidations of PAH-contaminated soils: impact of oxidant doses on PAH and polar PAC (polycyclic aromatic compound) behavior[J]. Chemosphere,2019,224:437-444. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.108 [80] YOSHIMURA T, OHNO A, ESUMI K. Mixed micellar properties of cationic trimeric-type quaternary ammonium salts and anionic sodium n-octyl sulfate surfactants[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2004,272(1):191-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2003.12.021 [81] BESHA A T, BEKELE D N, NAIDU R, et al. Recent advances in surfactant-enhanced In-Situ Chemical Oxidation for the remediation of non-aqueous phase liquid contaminated soils and aquifers[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2018,9:303-322. [82] LI Y, LIAO X Y, HULING S G, et al. The combined effects of surfactant solubilization and chemical oxidation on the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,647:1106-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.420 [83] NADARAJAH N, van HAMME J, PANNU J, et al. Enhanced transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using a combined Fenton's reagent, microbial treatment and surfactants[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2002,59(4):540-544. [84] ALCÁNTARA M T, GÓMEZ J, PAZOS M, et al. PAHs soil decontamination in two steps: desorption and electrochemical treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,166(1):462-468. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.050 [85] KIEM R, KÖGEL-KNABNER I. Refractory organic carbon in particle-size fractions of arable soils: Ⅱ. organic carbon in relation to mineral surface area and iron oxides in fractions <6 μm[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2002,33(12):1699-1713. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00112-2 [86] AHMAD M, TEEL A L, WATTS R J. Persulfate activation by subsurface minerals[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2010,115(1/2/3/4):34-45. [87] QI C D, LIU X T, LIN C Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by microwave irradiation for degradation of organic contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,315:201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.012 [88] YANG Y, ZHANG J, CHEN K, et al. Chemical oxidation of coking plant soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2016,10(1):427-431. [89] ZHUO C Y, HU S J, YANG Y, et al. Effects of the structures and micropores of sedimentary organic matter on the oxidative degradation of benzo(a)pyrene by Na2S2O8[J]. Water Research,2020,174:115635. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115635 [90] XU Q H, SHI F, YOU H, et al. Integrated remediation for organic-contaminated site by forcing running-water to modify alkali-heat/persulfate via oxidation process transfer[J]. Chemosphere,2021,262:128352. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128352 [91] SUTTON N B, LANGENHOFF A A M, et al. Efforts to improve coupled in situ chemical oxidation with bioremediation: a review of optimization strategies[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2011,11(1):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s11368-010-0272-9 [92] TSITONAKI A, SMETS B F, BJERG P L. Effects of heat-activated persulfate oxidation on soil microorganisms[J]. Water Research,2008,42(4/5):1013-1022. [93] LIANG C J, LEE I L, HSU I Y, et al. Persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene with and without iron activation in porous media[J]. Chemosphere,2008,70(3):426-435. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.077 [94] CUYPERS C, GROTENHUIS T, JOZIASSE J, et al. Rapid persulfate oxidation predicts PAH bioavailability in soils and sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2000,34(10):2057-2063. [95] SUTTON N B, KALISZ M, KRUPANEK J, et al. Geochemical and microbiological characteristics during in situ chemical oxidation and in situ bioremediation at a diesel contaminated site[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(4):2352-2360. [96] CUYPERS C, GROTENHUIS T, NIEROP K G J, et al. Amorphous and condensed organic matter domains: the effect of persulfate oxidation on the composition of soil/sediment organic matter[J]. Chemosphere,2002,48(9):919-931. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00123-6 [97] MARTÍNEZ-PASCUAL E, GROTENHUIS T, SOLANAS A M, et al. Coupling chemical oxidation and biostimulation: effects on the natural attenuation capacity and resilience of the native microbial community in alkylbenzene-polluted soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,300:135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.061 [98] SILVA-CASTRO G A, RODELAS B, PERUCHA C, et al. Bioremediation of diesel-polluted soil using biostimulation as post-treatment after oxidation with Fenton-like reagents: assays in a pilot plant[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2013,445/446:347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.081 [99] DI S R, ZHANG C, YAN Z, et al. Oxidative degradation effect of sodium persulfate on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in typical Chinese soils[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(1):95-101. [100] 麻俊胜, 苟雅玲, 王兴润, 等.化学氧化后深层土壤中多环芳烃的缺氧微生物降解[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(1):97-104.MA J S, GOU Y L, WANG X R, et al. Anoxic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)in aged deep soil pretreated with chemical oxidation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(1):97-104. [101] GARA P M D, BOSIO G N, GONZALEZ M C, et al. Kinetics of the sulfate radical-mediated photo-oxidation of humic substances[J]. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics,2008,40(1):19-24. doi: 10.1002/kin.20287 [102] RICHARDSON S D, LEBRON B L, MILLER C T, et al. Recovery of phenanthrene-degrading bacteria after simulated in situ persulfate oxidation in contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2011,45(2):719-725. □ -





 下载:
下载: