Investigation on migrations and fates of arsenic, selenium and lead in ultra-low emission coal-fired power plants based on field measurement
-
摘要:
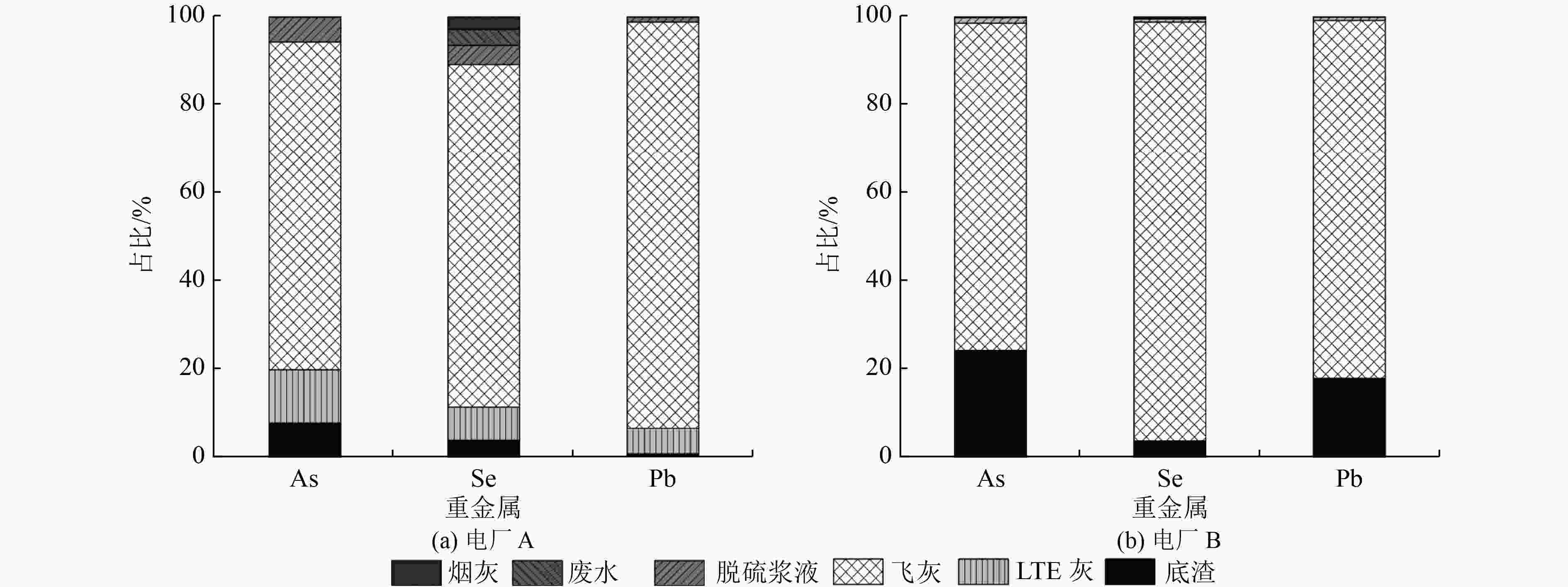
选择煤粉炉(PC)和循环流化床(CFB)超低排放燃煤电厂开展实测研究,同步采集烟气净化装置(APCDs)前后烟气样品进行分析;并同时采集分析入炉煤、飞灰、底渣、省煤器(LTE)灰、脱硫浆液和湿式电除尘器(WESP)废水等样品,以揭示砷(As)、硒(Se)和铅(Pb)迁移与排放特性。结果表明:两家电厂APCDs对烟气中As、Se和Pb的总协同脱除率达到96%,净烟气中污染物浓度低,分别为0.13~0.49、1.05~2.15和0.86~3.19 μg/m3;不同APCDs的协同脱除率存在较大差异,其中布袋除尘器(FF)最高(99.56%~99.74%),静电除尘器(ESP)次之(85.61%~98.44%),湿法烟气脱硫(WFGD)的脱除率波动较大,WESP脱除率为11.61%~55.08%。燃煤中As、Se和Pb大部分迁移到飞灰中,占比为74.38%~95.24%;CFB底渣占比为3.51%~24.08%;LTE灰占比为5.85%~12.11%;脱硫浆液中均低于6%;WESP废水和出口烟气中占比最低,分别为0.68%和0.62%。相对于煤粉炉,循环流化床电厂底渣中As和Pb富集性更高;而对于Se,则燃烧方式无明显影响,但其在净烟气中占比高于As和Pb。
Abstract:Extensive field tests were performed in ultra-low emission coal-fired power plants (ULE CFPPs), respectively installed with pulverized coal (PC) and circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers to investigate the migrations and fates of heavy metals such as arsenic (As), selenium (Se), and lead (Pb). Flue gas was simultaneously sampled at the inlet and outlet of each air pollution control devices (APCDs) and subsequently analyzed. Meanwhile, the samples of feed coal, fly ash, bottom ash, low-temperature economizer (LTE) ash, wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) slurry, and wet electrostatic precipitator (WESP) wastewater were collected for analyses. The results showed that the total synergistic removal efficiencies for As, Se, and Pb by APCDs in the two selected ULE CFPPs were all higher than 96%. The concentrations of pollutants in the clean flue gas were low, with As, Se, and Pb being 0.13-0.49, 1.05-2.15 and 0.86-3.19 μg/m3, respectively. Significant discrepancies were found in APCDs performance for heavy metal removal. The removal efficiency of fabric filter (FF) for As, Se, and Pb was the highest (99.56%-99.74%), followed by electrostatic precipitator (ESP) (85.61%-98.44%), while WFGD had a large fluctuation in the removal efficiency. WESP efficiency varied in the range of 11.61%-55.08%. The majority of As, Se, and Pb (74.38%-95.24%) were found in fly ash for the tested power plants. 3.51%-24.08% of these heavy metals remained in the bottom ash for CFB boiler. For PC boiler, 5.85%-12.11% of the metals were in LTE ash. They were below 6% in WFGD slurry. Around 0.68% and 0.62% of the metals were found in WESP drainage and outlet flue gas. More As and Pb were enriched in the bottom ash for CFB boiler in comparison with PC boiler. In terms of Se, no obvious effect of combustion modes was observed since it had relatively higher volatility. Its proportion in the clean flue gas was much higher than As and Pb for the two tested power plants.
-
Key words:
- ultra-low emission /
- coal-fired power plant /
- heavy metal /
- emission characteristics /
- migration
-
表 1 燃煤电厂基本情况
Table 1. Basic situation of the studied power plants
电厂 炉型 机组容量/MW 负荷/% 烟气脱硝 烟气除尘 烟气脱硫 超低排放烟气净化工艺流程 A 煤粉炉 300 75±5 SCR ESP、WESP WFGD SCR+ESP+WFGD+WESP B 循环流化床 350 75±5 SNCR FF、WESP WFGD、LIFAC LIFAC+SNCR+FF+WFGD+WESP 注:SCR为选择性催化还原脱硝;SNCR为选择性非催化还原脱硝;EPS为静电除尘;FF为布袋除尘;WESP为湿式电除尘;WFGD为湿法脱硫;LIFAC为炉内喷钙脱硫。 表 2 煤样的工业分析及重金属浓度
Table 2. Industrial analysis and heavy metals contents of coal samples
电厂 Mt/% Mad/% Aar/% Vdaf/% Qnet.ar/(MJ/kg) As浓度/(mg/kg) Se浓度/(mg/kg) Pb浓度/(mg/kg) A 16.20 10.29 12.80 37.05 21.37 1.39 1.06 10.94 B 6.60 0.77 46.35 16.83 3.01 6.83 4.98 16.79 注:Mt为全水分;Mad为空气干燥基水分;Aar为收到基灰分;Vdaf为干燥无灰基挥发分;Qnet.ar为收到基低位发热量。 表 3 烟气中As、Se和Pb浓度
Table 3. Mass concentration of heavy metals (i.e. As, Se, and Pb) in flue gas
μg/m3 电厂 重金属 SCR前 除尘前 除尘后 WFGD后 WESP后 US EPA排
放限值[51]A As 103.60 97.83 6.48 0.16 0.13 2.7 Se 58.04 50.57 7.28 4.80 2.15 8.2 Pb 816.27 702.61 10.95 1.12 0.86 2.7 B As — 491.48 1.41 0.96 0.49 2.7 Se — 290.74 1.28 1.19 1.05 8.2 Pb — 2 081.57 5.32 3.72 3.19 2.7 注:—表示无数据。 -
[1] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2020[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. [2] 史燕红, 吴华成.燃煤电厂重金属铅排放特性研究进展[J]. 热力发电,2016,45(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2016.01.001SHI Y H, WU H C. Emission characteristics of Pb in coal-fired plants: research development[J]. Thermal Power Generation,2016,45(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2016.01.001 [3] GINGERICH D B, ZHAO Y F, MAUTER M S. Environmentally significant shifts in trace element emissions from coal plants complying with the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments[J]. Energy Policy,2019,132:1206-1215. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.07.003 [4] SUN X D, GINGERICH D B, AZEVEDO I L, et al. Trace element mass flow rates from U. S. coal fired power plants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(10):5585-5595. [5] da SILVA E B, LI S W, de OLIVEIRA L M, et al. Metal leachability from coal combustion residuals under different pHs and liquid/solid ratios[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,341:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.010 [6] 熊传芳, 张征宇, 万梅, 等.嘉兴市大气PM2.5中金属元素污染特征、生态风险评价及来源分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):96-104.XIONG C F, ZHANG Z Y, WAN M, et al. Pollution characteristics, ecological risk assessment and source analysis of metal elements in atmospheric PM2.5 in Jiaxing City[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):96-104. [7] 邹天森, 康文婷, 张金良, 等.我国主要城市大气重金属的污染水平及分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2015,28(7):1053-1061.ZOU T S, KANG W T, ZHANG J L, et al. Concentrations and distribution characteristics of atmospheric heavy metals in urban areas of China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2015,28(7):1053-1061. [8] GEORGE A, SHEN B X, KANG D R. Emission control strategies of hazardous trace elements from coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2020,93:66-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.02.025 [9] TIAN K, WU Q M, LIU P, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Environment International,2020,136:105512. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105512 [10] 吕占禄, 张金良, 邹天森, 等.燃煤电厂周边土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):720-731.LÜ Z L, ZHANG J L, ZOU T S, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soil around coal-fired power plants[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):720-731. [11] 郑灿利, 范雪璐, 董娴, 等.贵阳市秋冬季PM2.5中重金属污染特征、来源解析及健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1376-1383.ZHENG C L, FAN X L, DONG X, et al. Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 collected between autumn and winter in Guiyang City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(6):1376-1383. [12] 朱法华, 许月阳, 孙尊强, 等.中国燃煤电厂超低排放和节能改造的实践与启示[J]. 中国电力,2021,54(4):1-8.ZHU F H, XU Y Y, SUN Z Q, et al. Practice and enlightenment of ultra-low emission and energy-saving retrofit of coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Electric Power,2021,54(4):1-8. [13] 向家涛, 黎俊廷, 周晓鸣, 等.燃煤烟气污控设备对挥发性有机物和常规污染物的协同控制特性[J]. 动力工程学报,2022,42(7):671-676.XIANG J T, LI J T, ZHOU X M, et al. Synergistic control characteristics of volatile organic compounds and conventional pollutants by air pollution control devices[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering,2022,42(7):671-676. [14] WANG C B, LIU H M, ZHANG Y, et al. Review of arsenic behavior during coal combustion: volatilization, transformation, emission and removal technologies[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2018,68:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2018.04.001 [15] ZHAO S L, DUAN Y F, TAN H Z, et al. Migration and emission characteristics of trace elements in a 660 MW coal-fired power plant of China[J]. Energy & Fuels,2016,30(7):5937-5944. [16] CHENG C M, HACK P, CHU P, et al. Partitioning of mercury, arsenic, selenium, boron, and chloride in a full-scale coal combustion process equipped with selective catalytic reduction, electrostatic precipitation, and flue gas desulfurization systems[J]. Energy & Fuels,2009,23(10):4805-4816. [17] WEN M N, WU Q R, LI G L, et al. Impact of ultra-low emission technology retrofit on the mercury emissions and cross-media transfer in coal-fired power plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,396:122729. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122729 [18] SENIOR C L, TYREE C A, MEEKS N D, et al. Selenium partitioning and removal across a wet FGD scrubber at a coal-fired power plant[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(24):14376-14382. [19] ZHAO Y C, YANG J P, MA S M, et al. Emission controls of mercury and other trace elements during coal combustion in China: a review[J]. International Geology Review,2018,60(5/6):638-670. [20] HAN L P, ZHAO Y, HAO R L. Arsenic emission and distribution characteristics in the ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(24):36814-36823. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16745-7 [21] HAN D M, WU Q R, WANG S X, et al. Distribution and emissions of trace elements in coal-fired power plants after ultra-low emission retrofitting[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,754:142285. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142285 [22] 环境保护部, 国家发展和改革委员会, 国家能源局. 关于印发《全面实施燃煤电厂超低排放和节能改造工作方案》的通知[EB/OL]. (2015-12-11)[2022-11-15]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bwj/201512/t20151215_319170.htm. [23] 国家发展和改革委员会, 环境保护部, 国家能源局. 关于印发《煤电节能减排升级与改造行动计划(2014—2020年)》的通知[EB/OL]. (2014-09-12)[2022-11-15]. https://mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/gwy/201409/t20140925_289556.htm. [24] 史文峥, 杨萌萌, 张绪辉, 等.燃煤电厂超低排放技术路线与协同脱除[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(16):4308-4318.SHI W Z, YANG M M, ZHANG X H, et al. Ultra-low emission technical route of coal-fired power plants and the cooperative removal[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2016,36(16):4308-4318. [25] 宋畅, 张翼, 郝剑, 等.燃煤电厂超低排放改造前后汞污染排放特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(5):672-677.SONG C, ZHANG Y, HAO J, et al. Mercury emission characteristics from coal-fired power plant before and after ultra-low emission retrofitting[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(5):672-677. [26] TANG Q, CHANG L R, HE F, et al. Impact of ultra-low emission retrofitting on partitioning and emission behavior of chromium in a Chinese coal-fired power plant[J]. Chemosphere,2022,302:134859. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134859 [27] 柴小康, 黄国和, 解玉磊, 等.某燃煤超低排放机组非常规污染物脱除[J]. 环境工程学报,2020,14(12):3480-3494. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202002032CHAI X K, HUANG G H, XIE Y L, et al. Unconventional pollutant removal from a coal-fired ultra-low emission unit[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2020,14(12):3480-3494. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202002032 [28] 石志鹏, 段伦博, 黄治军.1 000 MW超低排放机组Hg迁移特性[J]. 热力发电,2021,50(7):176-182.SHI Z P, DUAN L B, HUANG Z J. Migration characteristics of Hg from a 1 000 MW ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Thermal Power Generation,2021,50(7):176-182. [29] 张辰, 邓双, 张凡, 等.燃用高灰高硫煤电厂的汞排放研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2013,3(1):53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.01.010ZHANG C, DENG S, ZHANG F, et al. Study on mercury emissions from a power plant burning high ash and high sulfur coal[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2013,3(1):53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.01.010 [30] ZHAO S L, DUAN Y F, LI Y N, et al. Emission characteristic and transformation mechanism of hazardous trace elements in a coal-fired power plant[J]. Fuel,2018,214:597-606. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.093 [31] US EPA. Method 29 determination of metals emissions from stationary sources[EB/OL]. (2017-08-02)[2022-11-20]. https://www.epa.gov/emc/method-29-metals-emissions-stationary-sources. [32] 中国煤炭工业协会. 煤的工业分析方法: GB/T 212—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [33] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 煤的工业分析方法 仪器法: GB/T 30732—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. [34] WANG S X, ZHANG L, LI G H, et al. Mercury emission and speciation of coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2010,10(3):1183-1192. doi: 10.5194/acp-10-1183-2010 [35] QUICK W J, IRONS R M A. Trace element partitioning during the firing of washed and untreated power station coals[J]. Fuel,2002,81(5):665-672. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(01)00197-1 [36] 华伟, 孙和泰, 祁建民, 等.燃煤电厂超低排放机组重金属铅、砷排放特性[J]. 热力发电,2019,48(10):65-70.HUA W, SUN H T, QI J M, et al. Emission characteristics of Pb and As from an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Thermal Power Generation,2019,48(10):65-70. [37] 黄永达, 胡红云, 龚泓宇, 等.燃煤电厂砷、硒、铅的排放与控制技术研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(11):1281-1297.HUANG Y D, HU H Y, GONG H Y, et al. Research progress on emission and control technologies of arsenic, selenium and lead in coal-fired power plants[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2020,48(11):1281-1297. [38] WANG C, LIU X W, LI D, et al. Measurement of particulate matter and trace elements from a coal-fired power plant with electrostatic precipitators equipped the low temperature economizer[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,2015,35(3):2793-2800. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.07.004 [39] HU B, ZHANG L, YI Y, et al. PM2.5 and SO3 collaborative removal in electrostatic precipitator[J]. Powder Technology,2017,318:484-490. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.008 [40] 易红宏, 郝吉明, 段雷, 等.电厂除尘设施对PM10排放特征影响研究[J]. 环境科学,2006,27(10):1921-1927.YI H H, HAO J M, DUAN L, et al. Influence of dust catchers on PM10 emission characteristics of power plants[J]. Environmental Science,2006,27(10):1921-1927. [41] LUO Y, GIAMMAR D E, HUHMANN B L, et al. Speciation of selenium, arsenic, and zinc in class C fly ash[J]. Energy & Fuels,2011,25(7):2980-2987. [42] CONTRERAS M L, AROSTEGUI J M, ARMESTO L. Arsenic interactions during co-combustion processes based on thermodynamic equilibrium calculations[J]. Fuel,2009,88(3):539-546. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.09.028 [43] HUANG Y D, GONG H Y, HU H Y, et al. Migration and emission behavior of arsenic and selenium in a circulating fluidized bed power plant burning arsenic/selenium-enriched coal[J]. Chemosphere,2021,263:127920. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127920 [44] GULLETT B K, RAGHUNATHAN K. Reduction of coal-based metal emissions by furnace sorbent injection[J]. Energy Fuels,2002,8(5):1068-1076. [45] FLETCHER N H. Size effect in heterogeneous nucleation[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics,1958,29(3):572-576. doi: 10.1063/1.1744540 [46] FAN Y, QIN F H, LUO X S, et al. Heterogeneous condensation on insoluble spherical particles: modeling and parametric study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science,2013,102:387-396. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2013.08.040 [47] NOURI H, ZOUZOU N, MOREAU E, et al. Effect of relative humidity on current–voltage characteristics of an electrostatic precipitator[J]. Journal of Electrostatics,2012,70(1):20-24. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2011.08.011 [48] 左朋莱, 王晨龙, 佟莉, 等.小型燃煤机组烟气重金属排放特征研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(11):2599-2604.ZUO P L, WANG C L, TONG L, et al. Emission characteristics of heavy metal in flue gas of small coal-fired units[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(11):2599-2604. [49] 舒英钢. 燃煤电厂电除尘技术综述[C]//第十五届中国电除尘学术会议论文集. 蚌埠, 2013: 12-19. [50] 张序, 李建军.燃煤电厂烟气超低排放技术路线的研究[J]. 四川化工,2015,18(5):55-58.ZHANG X, LI J J. The study of ultra-low emission technology in coal-fired power plant[J]. Sichuan Chemical Industry,2015,18(5):55-58. [51] US EPA. National emission standards for hazardous air pollutants from coal- and oil-fired electric utility steam generating units and standards of performance for fossil-fuel-fired electric utility, industrial-commercial-institutional, and small industrial-commercial-institutional steam generating units[S/OL]. (2012-03-03)[2022-10-11]. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-12-489r. [52] 邓双, 张凡, 刘宇, 等.燃煤电厂铅的迁移转化研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2013,33(7):1199-1206.DENG S, ZHANG F, LIU Y, et al. Lead emission and speciation of coal-fired power plants in China[J]. China Environmental Science,2013,33(7):1199-1206. [53] CHANG L, YANG J P, ZHAO Y C, et al. Behavior and fate of As, Se, and Cd in an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,209:722-730. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.270 [54] 邹仁杰. 湿法烟气脱硫系统中硒迁移行为与强化脱除方法研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. [55] 赵士林, 段钰锋, 丁艳军, 等.320 MW燃煤电厂痕量元素的分布、脱除及排放特性[J]. 化工学报,2017,68(7):2910-2917.ZHAO S L, DUAN Y F, DING Y J, et al. Distribution, co-removal and emission characteristic of trace elements in 320 MW coal-fired power plant[J]. CIESC Journal,2017,68(7):2910-2917. [56] WANG H S, ZOU C, HU H Y, et al. Migration and emission characteristics of trace elements in coal-fired power plant under deep peak load regulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2023,868:161626. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161626 [57] XU L W, WU Q R, CHANG H Z, et al. Chemical deactivation of selective catalytic reduction catalyst: investigating the influence and mechanism of SeO2 poisoning[J]. Fuel,2020,269:117435. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117435 [58] KONG M, LIU Q C, WANG X Q, et al. Performance impact and poisoning mechanism of arsenic over commercial V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst[J]. Catalysis Communications,2015,72:121-126. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2015.09.029 [59] LINAK W P, WENDT J O L. Toxic metal emissions from incineration: mechanisms and control[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,1993,19(2):145-185. doi: 10.1016/0360-1285(93)90014-6 [60] WANG N N, SUN X Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Leachability and adverse effects of coal fly ash: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,396:122725. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122725 [61] JAMBHULKAR H P, SHAIKH S M S, KUMAR M S. Fly ash toxicity, emerging issues and possible implications for its exploitation in agriculture;Indian scenario: a review[J]. Chemosphere,2018,213:333-344. □ doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.045 -





 下载:
下载: