Research trend and hot spot analysis of antibiotic pollution in water environment in recent 20 years based on bibliometrics
-
摘要:
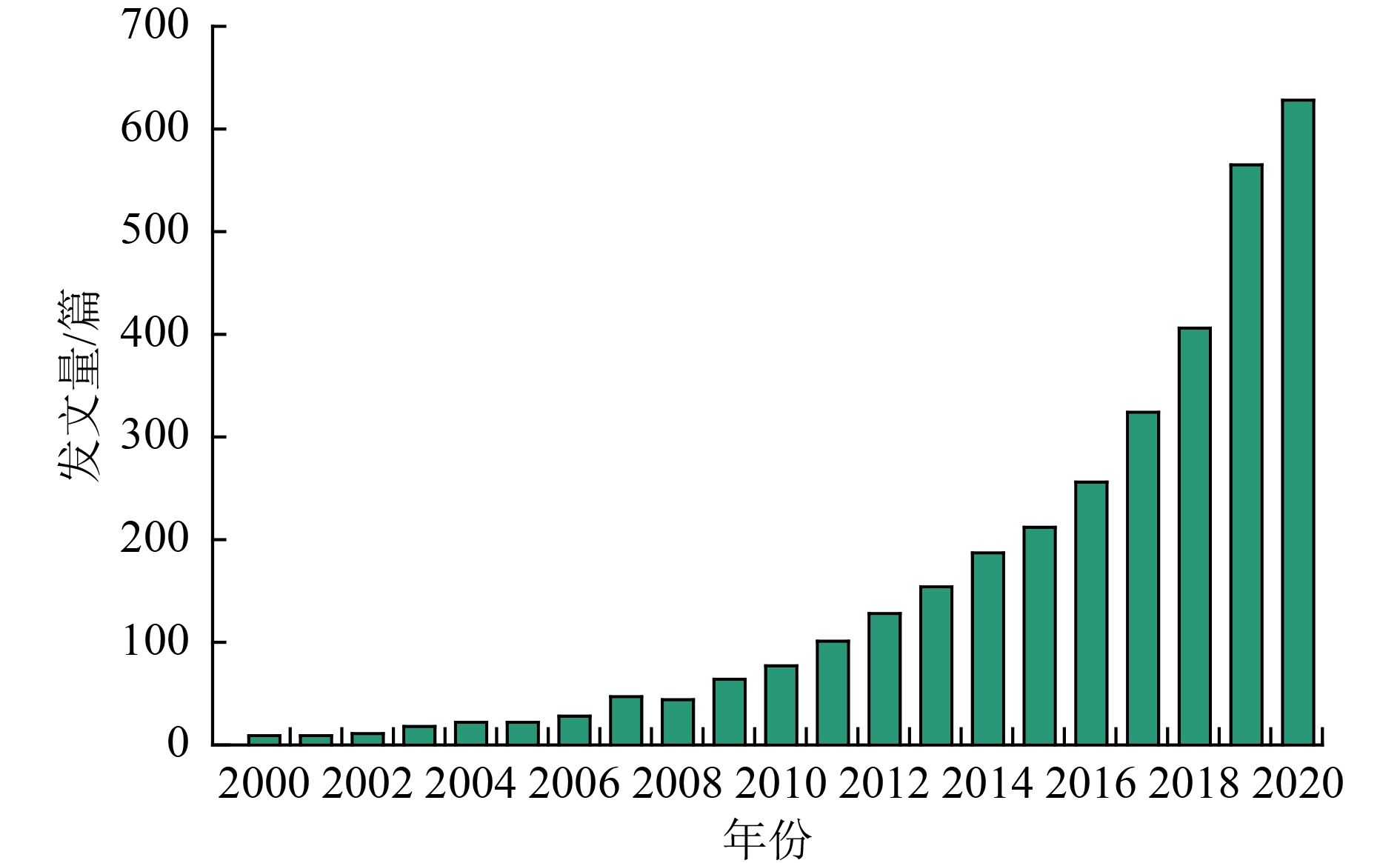
为探明水环境中抗生素污染特征及发展趋势,基于Web of Science(WoS)数据库2000—2020年发表的水环境中抗生素污染研究的相关文献信息,运用文献计量学方法对发文量、引用频次、作者、发文国家、研究机构、发文期刊、关键词等进行分析,解析近20年该领域的研究进展并对未来发展提出建议。结果表明:2000—2020年共发表水环境中抗生素污染研究相关文献3 312篇,年发文量呈上升趋势;文献涉及全球108个国家,其中中国发文量为1 208篇,占总发文量的36.46%;antibiotic resistance(抗生素抗性)、diversity(多样性)、drinking water(饮用水)是中介中心性较高的关键词,也是抗生素污染研究的核心内容;Science of the Total Environment和Environmental Science and Pollution Research是该领域文献的主要期刊载体;抗性基因对水生态系统造成的影响、抗性基因在食物链中的富集迁移特征等为近年来该领域的研究热点。
Abstract:To find out the present situation and development trend of antibiotic pollution characteristics in the water environment, based on the related literature information on the distribution characteristics of antibiotic pollution in the water environment published in Web of Science (WoS) database from 2000 to 2020, the annually published papers, citation frequency, authors, countries, institutions, journals, and keywords were analyzed by bibliometrics, the research progress in this field in the past 20 years was analyzed, and some suggestions for future development were put forward. The results showed that there were 3 312 papers published in the field of antibiotic pollution characteristics in the water environment from 2000 to 2020. The number of papers published annually showed an increasing trend. The literature covered 108 countries worldwide, and the number of published articles in China was 1 208, accounting for 36.46% of the total. Antibiotic resistanc, diversity and drinking water were keywords with high intermediary centrality and were also the core contents of antibiotic pollution research. Science of the Total Environment and Environmental Science and Pollution Research were the main periodical carriers of literature in this field. In recent years, the research on resistance genes' influence on aquatic ecosystem and their migration characteristics in the food chain were hot issues.
-
Key words:
- antibiotics /
- water environment /
- bibliometrics /
- visualization /
- research trend
-
表 1 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域发文量排名前10的国家
Table 1. Top 10 countries in the number of papers published of antibiotics pollution in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 国家 发文量/篇 发文量占比/% 1 中国 1 208 36.47 2 美国 539 16.27 3 印度 202 6.10 4 西班牙 167 5.04 5 德国 152 4.59 6 英国 120 3.62 7 加拿大 116 3.50 8 意大利 103 3.11 9 法国 93 2.81 10 巴西 91 2.75 表 2 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域发文量排名前10的作者
Table 2. Top 10 authors in the number of papers published of antibiotics pollution in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 作者 发文量/篇 发文量占比/% 1 Ying G G 29 0.88 2 Barcelo D 26 0.79 3 Chen J W 19 0.57 4 Zhang G 16 0.48 5 Chen H 16 0.48 6 Luo Y 13 0.39 7 Lu SY 13 0.39 8 Zhang S 13 0.39 9 Song H L 13 0.39 10 Li P 12 0.36 10 He Y L 12 0.36 10 Zeng G M 12 0.36 表 3 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域发文量排名前10的研究机构
Table 3. Top 10 most active institutions of publications of antibiotics pollution in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 研究机构 发文量/篇 发文量占比/% 1 中国科学院 274 8.27 2 中国科学院大学 85 2.57 3 清华大学 62 1.87 4 同济大学 41 1.24 5 中国环境科学研究院 40 1.21 6 赫罗纳大学(西班牙) 40 1.21 7 波尔图大学(葡萄牙) 39 1.18 8 北京大学 37 1.12 9 大连理工大学 35 1.06 10 浙江大学 34 1.03 表 4 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域发文量排名前10的期刊信息
Table 4. Top 10 journals with the number of antibiotics pollution in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 期刊 发文
量/篇发文量占比/% 学科类别 影响因子(2021年) 1 Science of the Total Environment 333 10.05 environmental sciences 7.963 2 Environmental Science and Pollution Research 139 4.20 environmental sciences 4.223 3 Chemosphere 129 3.90 environmental sciences 7.086 4 Environmental Pollution 118 3.56 environmental sciences 8.071 5 Water Research 105 3.17 environmental sciences 11.236 6 Environmental Science & Technology 80 2.42 environmental sciences 9.028 7 Journal of Hazardous Materials 64 1.93 environmental sciences 10.588 8 Frontiers in Microbiology 59 1.78 microbiology 5.640 9 Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 56 1.69 environmental sciences 6.291 10 Chemical Engineering Journal 54 1.63 engineering chemical 13.273 表 5 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域出现频次排名前10的关键词
Table 5. Top 10 keywords according to the frequency in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 关键词 出现频次 1 wastewater 696 2 pharmaceutical 647 3 antibiotic resistance 525 4 surface water 508 5 river 444 6 Escherichia coli 405 7 bacteria 398 8 personal care product 346 9 water 342 10 aquatic environment 339 表 6 2000—2020年水环境中抗生素污染研究领域中介中心性排名前10的关键词
Table 6. Top 10 keywords according to the mediating centrality in aquatic environment from 2000 to 2020
排序 关键词 中介中心性 1 antibiotic resistance 0.18 2 diversity 0.15 3 drinking water 0.13 4 sediment 0.12 5 identification 0.10 6 soil 0.08 7 fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent 0.08 8 wastewater 0.07 9 aquatic environment 0.07 10 bacterial community 0.07 -
[1] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(11):6772-6782. [2] KLEIN E Y, van BOECKEL T P, MARTINEZ E M, et al. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2018,115(15):3463-3470. [3] YAN Y, DENG Y, JI M, et al. Antibiotic pollution and risk assessment under different cultivation modes in aquaculture ponds of the Taihu Lake Basin, China[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research,2020,71(10):1234. doi: 10.1071/MF19224 [4] DU J, ZHAO H X, LIU S S, et al. Antibiotics in the coastal water of the South Yellow Sea in China: occurrence, distribution and ecological risks[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,595:521-527. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.281 [5] XU J, ZHANG Y, ZHOU C B, et al. Distribution, sources and composition of antibiotics in sediment, overlying water and pore water from Taihu Lake, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,497/498:267-273. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.114 [6] YAN Y, DENG Y, LI W J, et al. Phytoremediation of antibiotic-contaminated wastewater: insight into the comparison of ciprofloxacin absorption, migration, and transformation process at different growth stages of E. crassipes[J]. Chemosphere,2021,283:131192. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131192 [7] WANG Z Y, CHEN Q W, HU L M, et al. Combined effects of binary antibiotic mixture on growth, microcystin production, and extracellular release of Microcystis aeruginosa: application of response surface methodology[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018,25(1):736-748. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0475-3 [8] YAN Y, PENGMAO Y Z, XU X G, et al. Migration of antibiotic ciprofloxacin during phytoremediation of contaminated water and identification of transformation products[J]. Aquatic Toxicology,2020,219:105374. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105374 [9] SU H C, LIU S, HU X J, et al. Occurrence and temporal variation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in shrimp aquaculture: ARGs dissemination from farming source to reared organisms[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,607/608:357-366. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.040 [10] 李中浤, 张列宇, 许秋瑾, 等.基于文献计量学的环境领域病毒研究现状分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(6):1232-1240.LI Z H, ZHANG L Y, XU Q J, et al. Analysis of virus research status in the environmental filed based on bibliometrics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(6):1232-1240. [11] 张媛, 张艳杰, 朱静, 等.基于文献计量的湿地构建前沿进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(1):107-113. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200050ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y J, ZHU J, et al. A bibliometric analysis of the frontier progress in wetland construction[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(1):107-113. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200050 [12] 李海生, 李小敏, 赵玉婷, 等.基于文献计量分析的近40年国内外环境影响评价研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(5):1091-1101.LI H S, LI X M, ZHAO Y T, et al. Environmental impact assessment research in domestic and foreign literature in past four decades based on scientometric reviews[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(5):1091-1101. [13] 乔宇, 闫振飞, 冯承莲, 等.基于文献计量学的环境内分泌干扰物研究热点分析[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(2):424-434.QIAO Y, YAN Z F, FENG C L, et al. Research focus analysis of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) based on bibliometrics[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(2):424-434. [14] LI F F, CHEN L J, CHEN W D, et al. Antibiotics in coastal water and sediments of the East China Sea: distribution, ecological risk assessment and indicators screening[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,151:110810. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110810 [15] ZAINAB S M, JUNAID M, XU N, et al. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: a global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks[J]. Water Research,2020,187:116455. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116455 [16] ZHANG J N, YING G G, YANG Y Y, et al. Occurrence, fate and risk assessment of androgens in ten wastewater treatment plants and receiving rivers of South China[J]. Chemosphere,2018,201:644-654. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.144 [17] PETROVIC M, GROS M, BARCELO D. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2006,1124(1/2):68-81. [18] LIU S S, BEKELE T G, ZHAO H X, et al. Bioaccumulation and tissue distribution of antibiotics in wild marine fish from Laizhou Bay, North China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,631/632:1398-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.139 [19] HIRSCH R, TERNES T, HABERER K, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment[J]. Science of the Total Environment,1999,225(1/2):109-118. [20] ZHANG M, LIU Y S, ZHAO J L, et al. Occurrence, fate and mass loadings of antibiotics in two swine wastewater treatment systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,639:1421-1431. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.230 [21] CHEN H, LIU S, XU X R, et al. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,343:140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.017 [22] DENG W J, LI N, YING G G. Antibiotic distribution, risk assessment, and microbial diversity in river water and sediment in Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2018,40(5):2191-2203. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0092-1 [23] JELIC A, GROS M, GINEBREDA A, et al. Occurrence, partition and removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage water and sludge during wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research,2011,45(3):1165-1176. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.010 [24] RODRÍGUEZ-RODRÍGUEZ C E, JESÚS GARCÍA-GALÁN M, BLÁNQUEZ P, et al. Continuous degradation of a mixture of sulfonamides by Trametes versicolor and identification of metabolites from sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2012,213/214:347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.008 [25] KEMPER N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment[J]. Ecological Indicators,2008,8(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.06.002 [26] YAN C X, YANG Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: occurrence, distribution and risk assessment[J]. Environmental Pollution,2013,175:22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.12.008 [27] ZHANG Y Z, XU M Q, LIANG S X, et al. Mechanism of persulfate activation by biochar for the catalytic degradation of antibiotics: synergistic effects of environmentally persistent free radicals and the defective structure of biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,794:148707. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148707 [28] CHENG S A, MAO Z Z, SUN Y, et al. A novel electrochemical oxidation-methanogenesis system for simultaneously degrading antibiotics and reducing CO2 to CH4 with low energy costs[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,750:141732. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141732 [29] 敖蒙蒙, 魏健, 陈忠林, 等.四环素类抗生素环境行为及其生态毒性研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(2):314-324. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200096AO M M, WEI J, CHEN Z L, et al. Research progress on environmental behaviors and ecotoxicity of tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(2):314-324. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200096 [30] WEI L X, LI H X, LU J F. Algae-induced photodegradation of antibiotics: a review[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,272:115589. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115589 [31] HILLIS D G, FLETCHER J, SOLOMON K R, et al. Effects of ten antibiotics on seed germination and root elongation in three plant species[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2011,60(2):220-232. ◇ doi: 10.1007/s00244-010-9624-0 -





 下载:
下载: