Bibliometric analysis of lake sediments based on Web of Science and CNKI
-
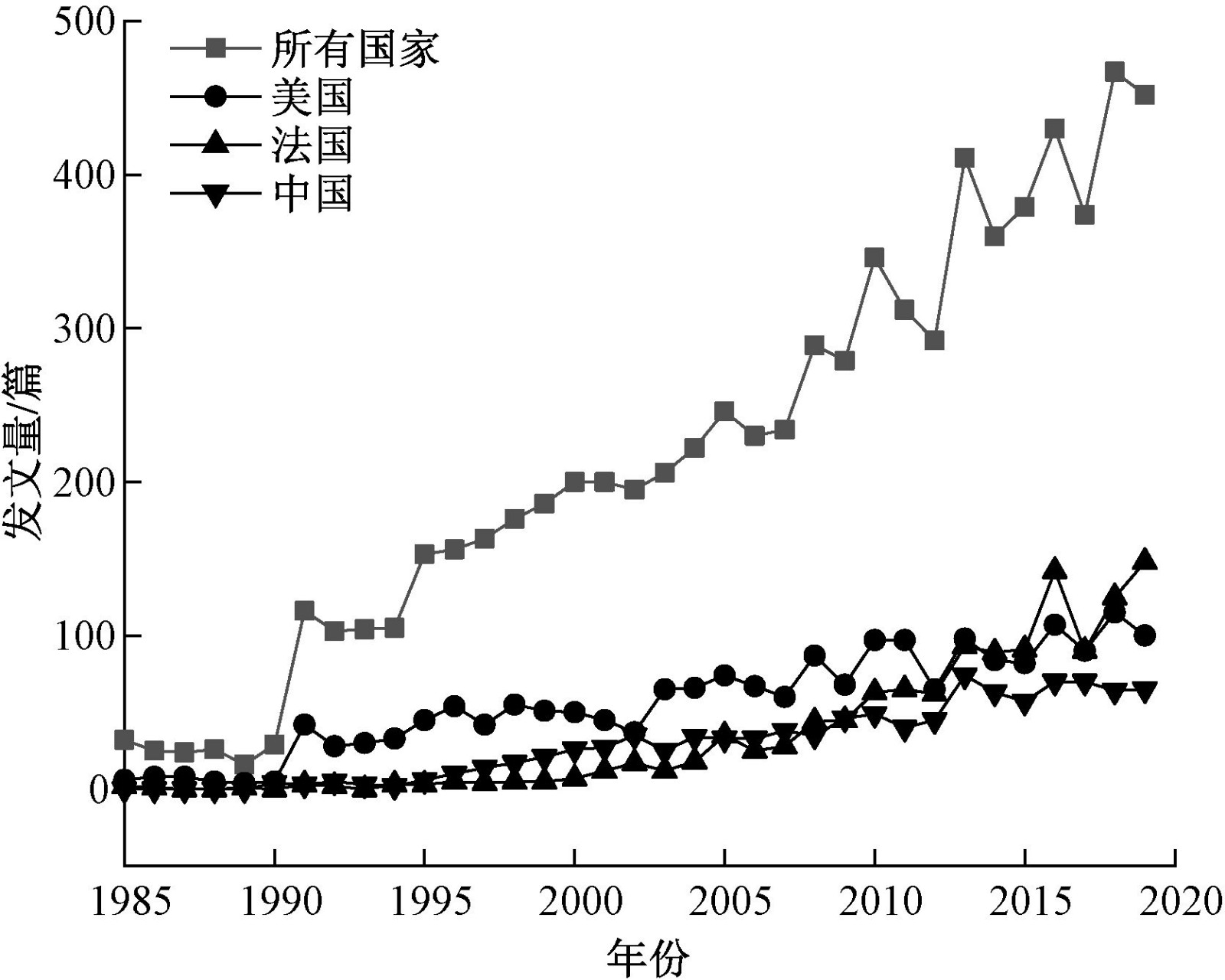
摘要: 为了解湖泊沉积物研究领域现状和未来发展趋势,采用信息可视化、网络分析的研究方法,以Web of Science(WoS)和中国知网(CNKI)数据库中近35年(1985—2019年)湖泊沉积物研究领域的论文作为数据来源绘制社会网络图谱,剖析湖泊沉积物研究领域的发展动态、研究热点及前沿趋势。结果表明:WoS数据库近35年来湖泊沉积物研究领域的发文量呈显著上升趋势,发文量位居前3的国家依次为美国、中国和德国;近5年中国发文量较高,但发文总被引频次相对较低;Bindler R、Birks H J B和Bakke J为该领域以第一作者发文量排名前3的作者,Journal of Paleolimnology、Hydrobiologia和Limnology and Oceanography为发文量排名前3的期刊。CNKI数据库的发文量滞后于WoS数据库,国内研究者有偏向于投稿国外期刊的趋势;CNKI数据库中湖泊沉积物研究领域发文量最高的期刊为《湖泊科学》,张恩楼、金章东和薛斌为发文量排名前3的作者。国内外湖泊沉积物研究领域的研究热点大致相同,主要包括沉积物重金属和有机物的污染与风险评估、湖泊沉积物与气候变化研究等方面,未来该领域在正定矩阵因子分析模型和多元统计方法包括相关性分析、聚类分析、因子分析等方向的研究有待进一步加强。
-
关键词:
- 湖泊沉积物 /
- 网络分析 /
- 文献计量学 /
- CiteSpace软件 /
- Web of Science(WoS) /
- 知网(CNKI)
Abstract: To understand the related research situation and future development trend of lake sediment research, the research methods of information visualization and network analysis were adopted, and the social network was drawn based on the papers in the field of lake sediment research for nearly 35 years (1985-2019) from Web of Science (WoS) and CNKI. The development trends, research hotspots and cutting-edge trends in the field of lake sediment research were analyzed. WoS database showed that the number of papers published in the field of lake sediment research at home and abroad showed a significant upward trend in recent 35 years. The top three countries in terms of document volume were the United States, China and Germany. In recent five years, the number of papers published in China was the highest, but the total citation frequency was relatively low. Bindler R, Birks H J B and Bakke J were the top 3 authors in the field.Journal of Paleolimnology, Hydrobiologia,and Limnology and Oceanography were the top 3 journals in this field in WoS database. The results showed that the number of papers published in CNKI database lagged behind that in WoS database, and domestic researchers tended to contribute to foreign journals. Journal of Lake Sciences was the largest source of literatures in CNKI database, among which Zhang Enlou, Jin Zhangdong and Xue Bin were the top three authors. Based on the results of the two databases, the research hotspots in the field of lake sediment research at home and abroad were roughly the same, mainly including the pollution and risk assessment of heavy metals and organic pollutants in sediments, and lake sediments and climate change research, etc. In the future, the research on PMF model and multivariate statistical methods, including correlation analysis, cluster analysis and factor analysis, need to be further strengthened.-
Key words:
- lake sediments /
- network analysis /
- bibliometrics /
- CiteSpace software /
- Web of Science(WoS) /
- CNKI
-
图 2 WoS中湖泊沉积物研究领域国家之间研究合作网络图谱
注:节点的大小和颜色分别表示发文量和节点所属的集群,其中绿色圆圈代表美国集群,蓝色圆圈代表中国-加拿大集群,红色圆圈代表德国集群;节点之间线条的粗细代表国家之间合作的强度[33],线条越粗,表示国家之间的合作越强。
Figure 2. Research collaboration network between countries in the field of lake sediments in WoS
表 1 WoS中1985—2019年湖泊沉积物研究领域以第一作者发文量排名前10的作者的发文情况
Table 1. Top 10 authors ranked by the number of first authors in the field of lake sediments from 1985 to 2019 in WoS
排序 第一作者 所属国家 所属机构 发文量/篇 1 Smol J P 加拿大 皇后大学 73 2 Brauer A 德国 波茨坦大学 59 3 Rose N L 英国 伦敦大学学院 58 4 Renberg I 瑞典 于默奥大学 57 5 Zolitschka B 德国 布莱梅大学 49 6 Wolfe A P 加拿大 阿尔伯塔大学 46 7 Appleby P G 英格兰 利物浦大学 45 8 Grosjean M 瑞士 伯尔尼大学 44 9 Bjorck S 瑞典 隆德大学 44 10 Wang Y 中国 西安建筑科技大学 42 表 2 WoS中1985—2019年湖泊沉积物研究领域被引次数排名前10的论文
Table 2. Top 10 cited papers in the field of lake sediments from 1985 to 2019 in WoS
排名 篇名 发表年份 总被引
次数/次年平均被引
次数/次1 Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments:reproducibility and comparability of results 2001 2 534 126.70 2 PAHs in the Fraser River Basin:a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition 2002 2 446 128.74 3 Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle 1996 1 272 50.88 4 Dissimilatory Fe(Ⅲ) and Mn(Ⅳ) reduction 1991 1 259 41.97 5 Search for past life on Mars:possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001 1996 1 191 47.64 6 Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation 1997 1 112 46.33 7 Lacustrine organic geochemistry:an overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments 1993 1 084 38.71 8 Biomass burning:a review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion 2002 906 47.68 9 Correlation between climate events in the north-atlantic and China during last glaciation 1995 902 34.69 10 Applications of organic geochemistry to paleolimnological reconstructions: a summary of examples from the Laurentian Great Lakes 2003 861 47.83 -
[1] 金相灿, 王圣瑞, 席海燕.湖泊生态安全及其评估方法框架[J]. 环境科学研究,2012,25(4):357-362.JIN X C, WANG S R, XI H Y. Lake ecological security and assessment methodology framework[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2012,25(4):357-362. [2] 车霏霏, 陈俊伊, 王书航, 等.南湖水系水-沉积物磷时空分布、影响因素及控制对策[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2020,10(6):928-935. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068CHE F F, CHEN J Y, WANG S H, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution, influencing factors and control strategies of phosphorus in water-sediment of Nanhu Lake water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2020,10(6):928-935. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068 [3] 杨文焕, 张元, 王志超, 等.寒旱区湖泊沉积物中固氮微生物群落特征: 以包头南海湖为例[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(6):2674-2682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.06.038YANG W H, ZHANG Y, WANG Z C, et al. Community characteristics of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in lake sediment: taking Nanhaihu Lake as example[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(6):2674-2682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.06.038 [4] 沈颜奕, 陈星.城市湖泊生态系统健康评价与修复研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2017,28(2):82-85. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2017.02.14SHEN Y Y, CHEN X. Study on health assessment and restoration of urban lake ecosystem[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2017,28(2):82-85. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2017.02.14 [5] 刘广容. 湖泊底泥污染化学钝化与电动生物修复研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2010. [6] Jr MOORE A, REDDY K R. Role of eh and pH on phosphorus geochemistry in sediments of Lake Okeechobee, Florida[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,1994,23(5):955-964. [7] 王坤, 张岚, 姜霞, 等.高原深水湖泊沉积物重金属背景值研究及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(12):2124-2132.WANG K, ZHANG L, JIANG X, et al. Determination of background value and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of a deep plateau lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(12):2124-2132. [8] 沈吉.湖泊沉积研究的历史进展与展望[J]. 湖泊科学,2009,21(3):307-313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.03.001SHEN J. Progress and prospect of palaeolimnology research in China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2009,21(3):307-313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.03.001 [9] NIPKOW T, WENZEL M, PAULSON L C. Isabelle/HOL[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2002. [10] RITTENBERG S C, EMERY K O, ORR W L. Regeneration of nutrients in sediments of marine basins[J]. Deep Sea Research (1953),1955,3(1):23-45. doi: 10.1016/0146-6313(55)90034-4 [11] 馬溶之.四川威遠附近地質對土壤之影響[J]. 地质论评,1940(6):521-532. [12] 熊毅.江西更新统粘土之性质及其生成[J]. 地质论评,1944(增刊1):109-120. [13] 王苏民, 薛滨.中更新世以来若尔盖盆地环境演化与黄土高原比较研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),1996,26(4):323-328. [14] 沈吉, 吕厚远, 王苏民, 等.错鄂孔深钻揭示的青藏高原中部2.8 MaBP以来环境演化及其对构造事件响应[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2004,34(4):359-366. [15] 王崇德.论文献计量学的测量[J]. 情报科学,1988,6(1):7-15.WANG C D. On the measurement of bibliometrics[J]. Information Science,1988,6(1):7-15. [16] HSIEH W H, CHIU W T, LEE Y S, et al. Bibliometric analysis of patent ductus arteriosus treatments[J]. Scientometrics,2004,60(2):105-215. doi: 10.1023/B:SCIE.0000027793.12866.58 [17] HO Y S. Bibliometric analysis of adsorption technology in environmental science[J]. Journal of Environmental Protection Science,2007,1(1):1-11. [18] CHEN S R, CHIU W T, HO Y S. Asthma in children: mapping the literature by bibliometric analysis[J]. Revue Française d'Allergologie et d'Immunologie Clinique,2005,45(6):442-446. [19] GLÄNZEL W, SCHUBERT A, CZERWON H J. A bibliometric analysis of international scientific cooperation of the European Union (1985-1995)[J]. Scientometrics,1999,45(2):185-202. doi: 10.1007/BF02458432 [20] RAAN A. Advanced bibliometric methods for the evaluation of universities[J]. Scientometrics,1999,45(3):417-423. doi: 10.1007/BF02457601 [21] WANG M H, YU T C, HO Y S. A bibliometric analysis of the performance of Water Research[J]. Scientometrics,2010,84(3):813-820. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0112-0 [22] ABRAMO G, D’ANGELO C A, VIEL F. The field-standardized average impact of national research systems compared to world average: the case of Italy[J]. Scientometrics,2011,88(2):599-615. doi: 10.1007/s11192-011-0406-x [23] WANG Y R, WANG Q J, WEI X Z, et al. Global scientific trends on exosome research during 2007-2016: a bibliometric analysis[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(29):48460-48470. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17223 [24] 张媛, 张艳杰, 朱静, 等.基于文献计量的湿地构建前沿进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2021,11(1):107-113. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200050ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y J, ZHU J, et al. A bibliometric analysis of the frontier progress in wetland construction[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2021,11(1):107-113. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200050 [25] 蔡深文, 高智席, 颜雄, 等.基于Web of Science的河流重金属污染文献计量分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2018,35(10):53-57. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170334CAI S W, GAO Z X, YAN X, et al. Bibliometric analysis of heavy metal pollution in river indexed by Web of Science[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2018,35(10):53-57. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20170334 [26] 封勇丽. 转基因食品安全研究的文献计量学分析[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016. [27] 王瑞杰, 李刚, 徐耀阳.湖泊沉积物文献信息的网络分析: 研究现状和热点[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2019,28(1):192-201.WANG R J, LI G, XU Y Y. Network analysis of literature in formation of lake sediment: research status and hotspot[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2019,28(1):192-201. [28] 姜春林, 陈玉光.CSSCI数据导入Bibexcel实现共现矩阵的方法及实证研究[J]. 图书馆杂志,2010,29(4):58-63.JIANG C L, CHEN Y G. Transform CSSCI data to bibexcel data to actualize co-occurrence matrix and a case study[J]. Library Journal,2010,29(4):58-63. [29] BATAGELJ V, MRVAR A. Pajek[M]. New York: Springer New York, 2014. [30] ECK N J, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping[J]. Scientometrics,2010,84(2):523-538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 [31] HAN D, CHEN X M. Environmental cost research hotspots and frontier analysis: visual analysis based on CiteSpaceⅤ[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2019,332(2):022057. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/332/2/022057 [32] ZHENG T L, WANG J, WANG Q H, et al. A bibliometric analysis of micro/nano-bubble related research: current trends, present application, and future prospects[J]. Scientometrics,2016,109(1):53-71. doi: 10.1007/s11192-016-2004-4 [33] LI J, RENIERS G, COZZANI V, et al. A bibliometric analysis of peer-reviewed publications on domino effects in the process industry[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries,2017,49:103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2016.06.003 [34] ZHANG L, WANG M H, HU J, et al. A review of published wetland research, 1991-2008: ecological engineering and ecosystem restoration[J]. Ecological Engineering,2010,36(8):973-980. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.04.029 [35] YU J J, WANG M H, XU M, et al. A bibliometric analysis of research papers published on photosynthesis: 1992-2009[J]. Photosynthetica,2012,50(1):5-14. doi: 10.1007/s11099-012-0010-1 [36] 言宗骋, 高红杰, 郭旭晶, 等.蘑菇湖沉积物间隙水溶解性有机质紫外可见光谱研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(6):685-691. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.160YAN Z C, GAO H J, GUO X J, et al. Study on UV-vis spectra of dissolved organic matter from sediment interstitial water in Moguhu Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2019,9(6):685-691. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.05.160 [37] HEIRI O, LOTTER A F, LEMCKE G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology,2001,25(1):101-110. doi: 10.1023/A:1008119611481 [38] ZHOU W J, AN Z S, PORTER S C, et al. Correlation of climatic events between East Asia and Norwegian Sea during last deglaciation[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,1997,40(5):496-501. ◇ doi: 10.1007/BF02877615 -





 下载:
下载: