Study on decoupling relationship between industrial growth and carbon dioxide emission in the urban agglomeration in the Yellow River Basin
-
摘要:
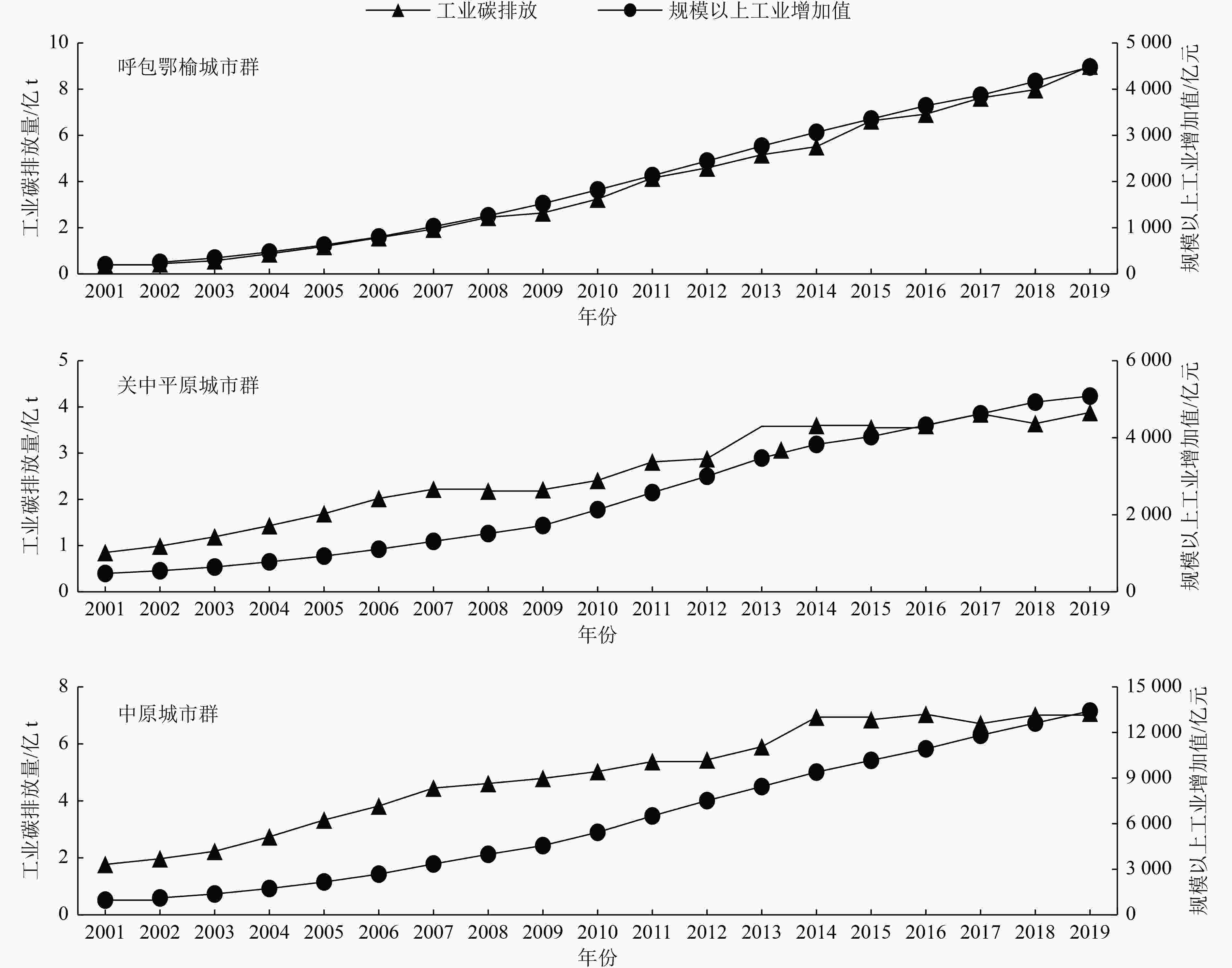
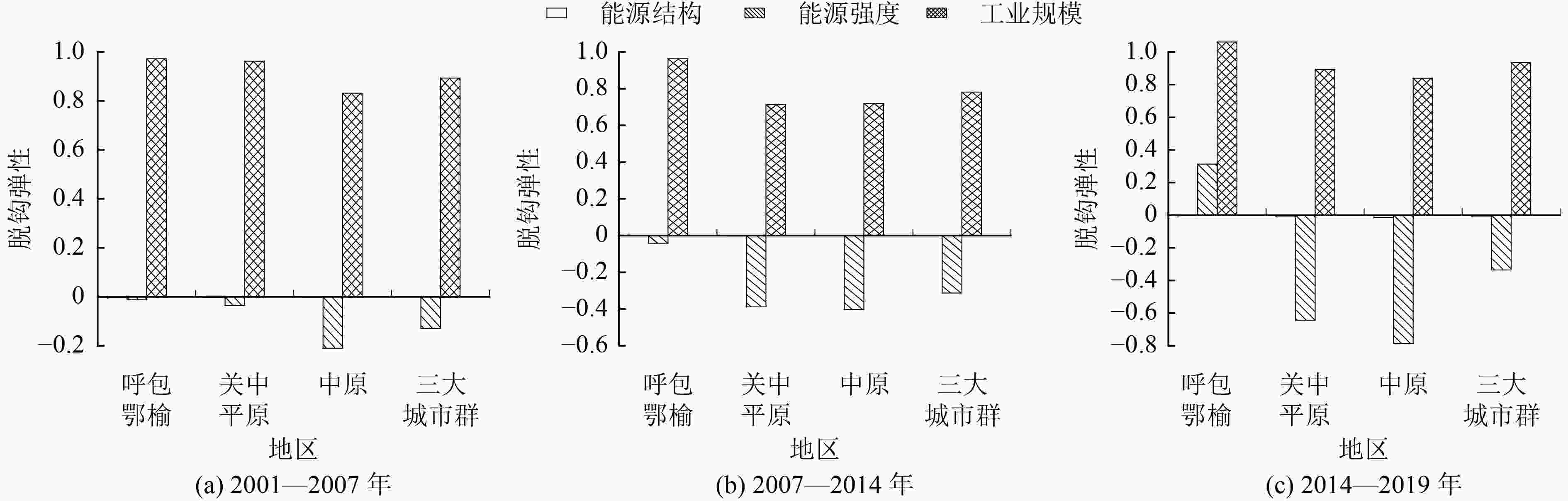
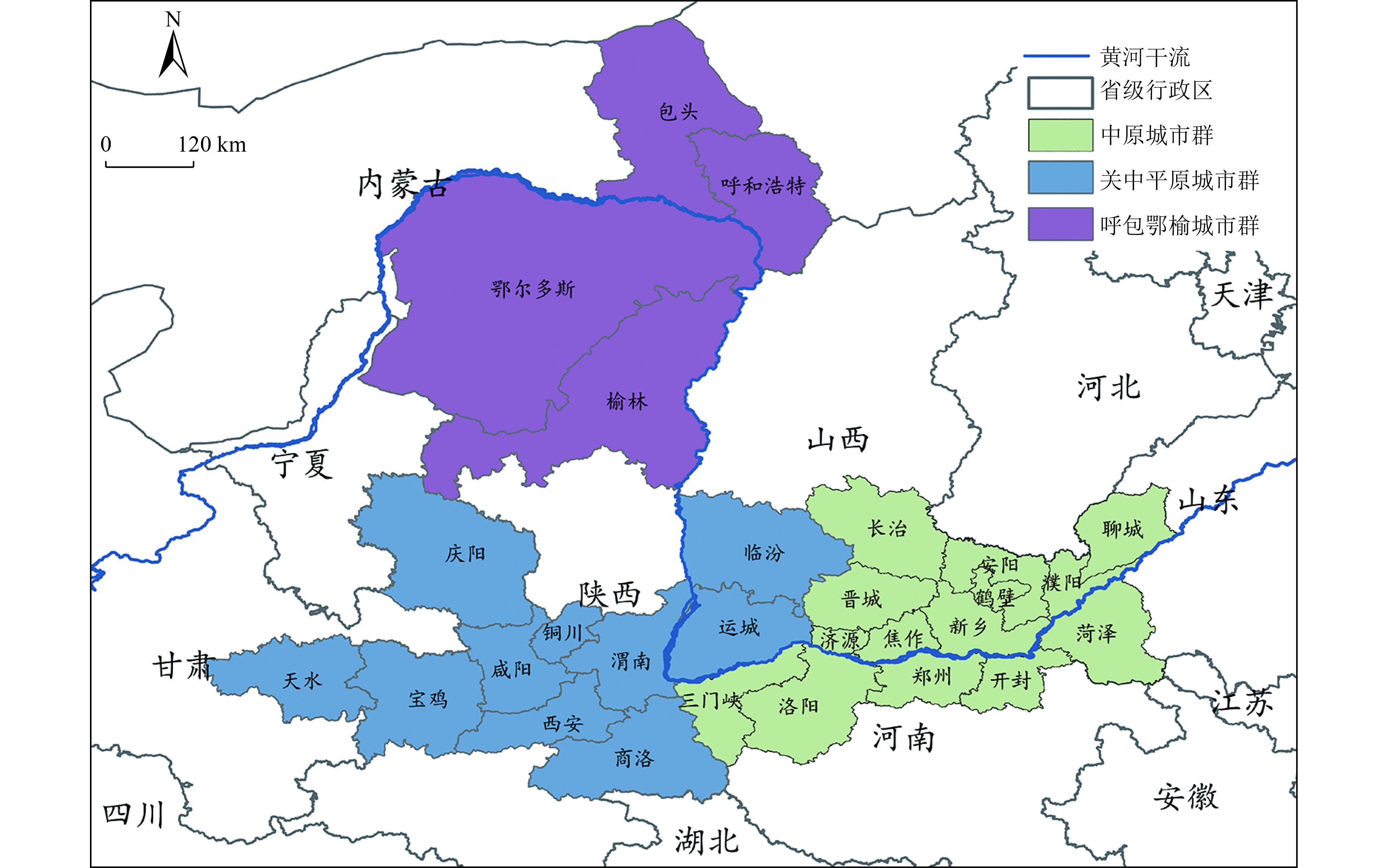
采用Tapio脱钩模型和LMDI分解法,在城市群尺度开展黄河流域工业增长、能源消费和碳排放耦合关系研究,以探索城市群与工业低碳转型和高质量协同发展。结果表明:呼包鄂榆城市群的工业经济与碳排放近似同步增长约23倍,关中平原和中原城市群则表现出明显的不同步现象;呼包鄂榆城市群的脱钩状态自2014年后由增长连结转为扩张型负脱钩,关中平原城市群脱钩状态自2007年后由增长连结转为弱脱钩,中原城市群始终处于弱脱钩状态;工业规模始终是3个城市群碳脱钩的主要抑制因素,能源强度对关中平原、中原城市群碳脱钩始终起到促进作用,但对呼包鄂榆城市群的影响自2014年后从促进转为抑制作用。建议结合国家2030年前碳达峰行动方案,制定差异化的城市群工业绿色转型与碳减排政策措施,进一步遏制呼包鄂榆城市群“两高项目”盲目发展,加快工业结构升级和节能改造,提高关中平原和中原城市群工业能效和减碳能力。
Abstract:The research on the coupling relationship between industrial growth, energy consumption and carbon emission in the Yellow River basin on the scale of urban agglomeration is of great significance for exploring the low-carbon transformation and high-quality coordinated development of urban agglomeration and industry. Hohhot-Baotou-Ordos-Yulin (HBOY), Guanzhong Plain (GZP) and Central Plains (CP) urban agglomerations were selected as the study areas. The Tapio decoupling model and LMDI factor decomposition method were used to study the decoupling relationship between industrial growth and carbon emission as well as the influencing factors. The results showed that: 1) The industrial economy and carbon emission of HBOY increased almost synchronously by 23 times, while GZP and CP showed obvious non-synchronization. 2) The HBOY moved from the "expansion connection" to the "expansive negative decoupling" since 2014, the GZP moved from the "expansion connection" to the "weak decoupling" since 2007,and the CP had been in a state of weak decoupling. 3) Industrial scale had always been the main restraining factor of carbon decoupling in the three urban agglomerations. Energy intensity had always played a role in promoting carbon decoupling in GZP and CP, but the impact in HBOY had changed from a promoting role to a restraining role since 2014. It was suggested that combined with the national action plan for peak carbon emissions by 2030, differentiated industrial green transformation and carbon emission reduction policies of urban agglomerations should be formulated, to further reduce the scale of high emission and high energy consumption industries in HBOY, to upgrade the industrial structure and energy saving transformation, and to improve the industrial energy efficiency and carbon reduction capacity of GZP and CP.
-
表 1 碳排放计算参数
Table 1. Carbon emission calculation parameters
能源种类 能源低位
发热值/
(kJ/kg)1)单位热值
含碳量/
(t/TJ)2)碳氧化率 二氧化碳
排放因子/
(kg/kg)3)原煤 20 908 26.37 0.94 1.900 3 焦炭 28 435 29.5 0.93 2.860 4 汽油 43 070 18.9 0.98 2.925 1 柴油 42 652 20.2 0.98 3.095 9 天然气 38 931 15.3 0.99 2.162 14) 1) 来自《中国能源统计年鉴 》(2018年);2) 来自《省级温室气体清单编制指南(试行)》(2011年);3) 二氧化碳排放因子=碳排放系数×能源低位发热值×(44/12)×碳氧化率×10−6;4)单位为kg/m3。 表 2 脱钩状态判定标准
Table 2. Criterion for decoupling state
状态 $ \Delta C $ $ \Delta I $ $D $ 脱钩 弱脱钩 >0 >0 0~<0.8 强脱钩 <0 >0 <0 衰退型脱钩 <0 <0 >1.2 连结 增长连结 >0 >0 0.8~1.2 衰退连结 <0 <0 0.8~1.2 负脱钩 弱负脱钩 <0 <0 0~<0.8 强负脱钩 >0 <0 <0 扩张型负脱钩 >0 >0 >1.2 表 3 2019年研究区主要工业经济指标与全国平均水平
Table 3. Main industrial economic indicators in the study area and national average level in 2019
研究区 工业增加值占GDP比
例/%工业能源消费量/亿t 清洁能源占一次能源消费比例/% 万元工业增加值能耗/t 万元工业增加值碳排放量/t 呼包鄂榆
城市群44.53 3.41 3.46 5.78 15.25 关中平原
城市群29.29 1.47 3.77 2.37 6.27 中原城市群 40.21 2.69 4.01 1.66 4.37 三大城市群 37.89 7.56 3.71 2.67 7.06 全国平均
水平32.00 32.25 8.58 1.02 2.90 注:研究区数据来源于2020年《中国城市统计年鉴》及各地市统计年鉴,全国平均水平相关数据来源于2020年《中国统计年鉴》。 表 4 三大城市群工业增长与碳排放脱钩相关指标结果
Table 4. Results of related indicators for the decoupling of industrial growth and carbon emission in the three major urban agglomerations
城市群 2001—2007年 2007—2014年 2014—2019年 $ {D}_{\mathrm{Ⅰ}} $ 脱钩状态 $ {D}_{\mathrm{Ⅱ}} $ 脱钩状态 $ {D}_{\mathrm{Ⅲ}} $ 脱钩状态 呼包鄂榆 0.956 增长连结 0.922 增长连结 1.372 扩张型负脱钩 关中平原 0.930 增长连结 0.322 弱脱钩 0.239 弱脱钩 中原 0.623 弱脱钩 0.315 弱脱钩 0.039 弱脱钩 研究区 0.764 弱脱钩 0.465 弱脱钩 0.589 弱脱钩 -
[1] 马丽, 田华征, 康蕾.黄河流域矿产资源开发的生态环境影响与空间管控路径[J]. 资源科学,2020,42(1):137-149. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.01.14MA L, TIAN H Z, KANG L. Eco-environmental impact and spatial control of mineral resources exploitation in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Resources Science,2020,42(1):137-149. doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.01.14 [2] 莫惠斌, 王少剑.黄河流域县域碳排放的时空格局演变及空间效应机制[J]. 地理科学,2021,41(8):1324-1335.MO H B, WANG S J. Spatio-temporal evolution and spatial effect mechanism of carbon emission at County level in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2021,41(8):1324-1335. [3] 吴晗, 滕柯延, 路超君. 部分国家和地区碳达峰情况比较研究及对中国的启示[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(6): 2032-2038.WU H, TENG K Y, LU C J. Comparative study on carbon dioxide peaking in some countries and regions and its enlightenment to China[J].Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2022,12(6): 2032-2038 [4] 国务院. 关于印发2030年前碳达峰行动方案的通知: 国发〔2021〕23号[A/OL]. (2021-10-24)[2021-12-30]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm [5] 马明娟, 李强, 周文瑞.碳中和视域下黄河流域碳生态补偿研究[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(12):5-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.12.002MA M J, LI Q, ZHOU W R. Study of carbon ecological compensation in Yellow River Basin based on carbon neutrality[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(12):5-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.12.002 [6] 国家统计局普查中心. 中国基本单位统计年鉴: 2020[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. [7] 国家统计局能源统计司. 中国能源统计年鉴: 2019[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. [8] OECD. Indicators to measure decoupling of environmental pressure from economic growth[J/OL].(2002-01-22). http://www.olis.oecd.org/olis/2002doc.nsf/LinkTo/sg-sd. [9] GAO C C, GE H Q, LU Y Y, et al. Decoupling of provincial energy-related CO2 emissions from economic growth in China and its convergence from 1995 to 2017[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,297:126627. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126627 [10] TAPIO P. Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001[J]. Transport Policy,2005,12(2):137-151. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001 [11] JIANG R, ZHOU Y L, LI R R. Moving to a low-carbon economy in China: decoupling and decomposition analysis of emission and economy from a sector perspective[J]. Sustainability,2018,10(4):978. doi: 10.3390/su10040978 [12] 罗芳, 郭艺, 魏文栋.长江经济带碳排放与经济增长的脱钩关系: 基于生产侧和消费侧视角[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(3):1364-1373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.03.047LUO F, GUO Y, WEI W D. Decoupling analysis between economic growth and carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: production and consumption perspectives[J]. China Environmental Science,2020,40(3):1364-1373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.03.047 [13] 张型芳, 罗宏, 吕连宏.碳排放与经济增长的协调性分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2017,7(4):517-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.04.071ZHANG X F, LUO H, LÜ L H. Coordination analysis on carbon emission and economic growth[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2017,7(4):517-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.04.071 [14] LUO Y S, LONG X L, WU C, et al. Decoupling CO2 emissions from economic growth in agricultural sector across 30 Chinese Provinces from 1997 to 2014[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2017,159:220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.076 [15] ZHAO X R, ZHANG X, LI N, et al. Decoupling economic growth from carbon dioxide emissions in China: a sectoral factor decomposition analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2017,142:3500-3516. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.117 [16] ZHAO X R, ZHANG X, SHAO S. Decoupling CO2 emissions and industrial growth in China over 1993-2013: the role of investment[J]. Energy Economics,2016,60:275-292. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2016.10.008 [17] 宋旭, 贾俊松, 陈春谛, 等.江西省能耗碳排放时空特征、脱钩关系及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(20):7451-7463.SONG X, JIA J S, CHEN C D, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics, decoupling relation and its driving factors of the carbon emission from energy consumption in underdeveloped Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(20):7451-7463. [18] 周彦楠, 杨宇, 程博, 等.基于脱钩指数和LMDI的中国经济增长与碳排放耦合关系的区域差异[J]. 中国科学院大学学报,2020,37(3):295-307. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2020.03.002ZHOU Y N, YANG Y, CHENG B, et al. Regional differences in the coupling relationship between Chinese economic growth and carbon emissions based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2020,37(3):295-307. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2020.03.002 [19] 张剑, 刘景洋, 董莉, 等. 中国能源消费CO2排放的影响因素及情景分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023,13(1):71-78.ZHANG J, LIU J Y, DONG L, et al. Influencing factors and scenario analysis of China's CO2 emission of energy consumption[J/OL]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023,13(1):71-78. [20] WANG Q, JIANG R. Is China's economic growth decoupled from carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,225:1194-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.301 [21] 郑思远.基于土地利用的江西省碳排放时空特征及脱钩关系研究[J]. 农业与技术,2021,41(13):133-136. [22] 黄国庆, 汪子路, 时朋飞, 等.黄河流域旅游业碳排放脱钩效应测度与空间分异研究[J]. 中国软科学,2021(4):82-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9753.2021.04.009HUANG G Q, WANG Z L, SHI P F, et al. Measurement and spatial heterogeneity of tourism carbon emission and its decoupling effects: a case study of the Yellow River Basin in China[J]. China Soft Science,2021(4):82-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9753.2021.04.009 [23] 公维凤, 范振月, 王传会, 等.黄河流域碳排放区域差异、成因及脱钩分析[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(12):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.12.003GONG W F, FAN Z Y, WANG C H, et al. Regional difference and driving factors of carbon emissions and the decoupling between carbon emissions and economic growth of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(12):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.12.003 [24] 徐泽, 李储, 牛陆.呼包鄂榆城市群土地混合利用与碳排放的脱钩关系[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(1):299-308.XU Z, LI C, NIU L. Decoupling relationship between land mixed use and carbon emissions in Hohhot-Baotou-Ordos-Yulin urban agglomeration[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(1):299-308. [25] 张昱. 山西省资源型产业发展与碳排放脱钩分析[D]. 太原: 山西财经大学, 2016. [26] 武娜, 沈镭, 钟帅, 等.晋陕蒙地区经济增长与碳排放时空耦合关系[J]. 经济地理,2019,39(9):17-23.WU N, SHEN L, ZHONG S, et al. Spatio-temporal coupling relationship between economic growth and carbon emission in Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia[J]. Economic Geography,2019,39(9):17-23. [27] 齐素素. 山东省工业行业经济增长与碳排放的脱钩关系研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019. [28] WANG Q, JIANG R. Is carbon emission growth decoupled from economic growth in emerging countries: new insights from labor and investment effects[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,248:119188. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119188 [29] WANG Z H, LI Y M, CAI H L, et al. Regional difference and drivers in China's carbon emissions embodied in internal trade[J]. Energy Economics,2019,83:217-228. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2019.06.023 [30] 江洪.金砖国家对外贸易隐含碳的测算与比较: 基于投入产出模型和结构分解的实证分析[J]. 资源科学,2016,38(12):2326-2337.JIANG H. Implied carbon in trade between BRIC countries based on input-output modeling and structural decomposition[J]. Resources Science,2016,38(12):2326-2337. [31] LIN S J, BEIDARI M, LEWIS C. Energy consumption trends and decoupling effects between carbon dioxide and gross domestic product in South Africa[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research,2015,15(7):2676-2687. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2015.04.0258 [32] ANG B W. LMDI decomposition approach: a guide for implementation[J]. Energy Policy,2015,86:233-238. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2015.07.007 [33] SALAMAH S, ZAKARIA W A, GUNARTO T, et al. Analysis of energy intensity decomposition in the textile industrial sub sector of Indonesia[J]. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy,2019,9(3):1-10. doi: 10.32479/ijeep.7457 [34] 刘茂辉, 翟华欣, 刘胜楠, 等.基于LMDI方法和STIRPAT模型的天津市碳排放量对比分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2023,13(1):63-70.LIU M H, ZHAI H X, LIU S N, et al. Comparative analysis of carbon emissions in Tianjin based on LMDI method and STIRPAT model[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology,2023,13(1):63-70. [35] 杨龙, 米鹏举.城市群何以成为国家治理单元[J]. 行政论坛,2020,27(1):120-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-460X.2020.01.018YANG L, MI P J. Why urban agglomerations become national governance units[J]. Administrative Tribune,2020,27(1):120-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-460X.2020.01.018 [36] 葛好晴. 省级碳排放驱动力及脱钩状态研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. [37] 刘博文, 张贤, 杨琳.基于LMDI的区域产业碳排放脱钩努力研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,2018,28(4):78-86.LIU B W, ZHANG X, YANG L. Decoupling efforts of regional industrial development on CO2 emissions in China based on LMDI analysis[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment,2018,28(4):78-86. [38] 刘玉珂, 金声甜.中部六省能源消费碳排放时空演变特征及影响因素[J]. 经济地理,2019,39(1):182-191. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.01.022LIU Y K, JIN S T. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and influencing factors of energy consumption carbon emissions in six provinces of central China[J]. Economic Geography,2019,39(1):182-191. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.01.022 [39] WANG Z H, YANG L. Delinking indicators on regional industry development and carbon emissions: Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei economic band case[J]. Ecological Indicators,2015,48:41-48. ⊕ doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.07.035 -




 下载:
下载: