Research progress of artificial intelligence technology in the field of water pollution control
-
摘要:
人工智能技术具有自学习、自适应和自组织的独特性能,目前已被广泛地应用于水环境污染、大气污染、固废处理、气候变化等环境领域,是环境监控和治理的良好助力手段。在水资源严重短缺的今天,水污染防治至关重要。传统的水污染治理与监管技术存在水污染监测滞后、污水优化控制成本较高、污染物去除效率预测精度较低等问题,人工智能的引入能够有效克服上述问题。因此,开发人工智能在水污染治理领域的应用具有重大意义。论述了人工智能技术的特点和分类,综述了其在水污染治理领域的研究现状和应用进展,以期为全面加强水污染治理提供科学参考。
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have great potential in the field of environmental engineering because of the unique performance of self-learning, self-adaptation and self-organization. At present, they have been widely used in the environmental fields such as water pollution, air pollution, solid waste treatment, climate change, which indicate that AI technologies are good assistants for environmental monitoring and governance. In the current situation of serious water resources shoutage, water pollution prevention and control is of great importance. Traditional water pollution control and supervision technologies have problems such as serious lag effect of water pollution monitoring, high cost of sewage optimization control, and low prediction accuracy of pollutant removal efficiency. The introduction of artificial intelligence technology can effectively overcome the above problems. It is of great significance to develop the application of AI in water pollution control. The characteristics and classification of various AI technologies were discussed, the research status and application progress of AI technologies in the field of water pollution control were summarized, in order to provide scientific reference for comprehensively strengthening water pollution control.
-
Key words:
- artificial intelligence /
- environmental engineering /
- water pollution /
- water management /
- review
-
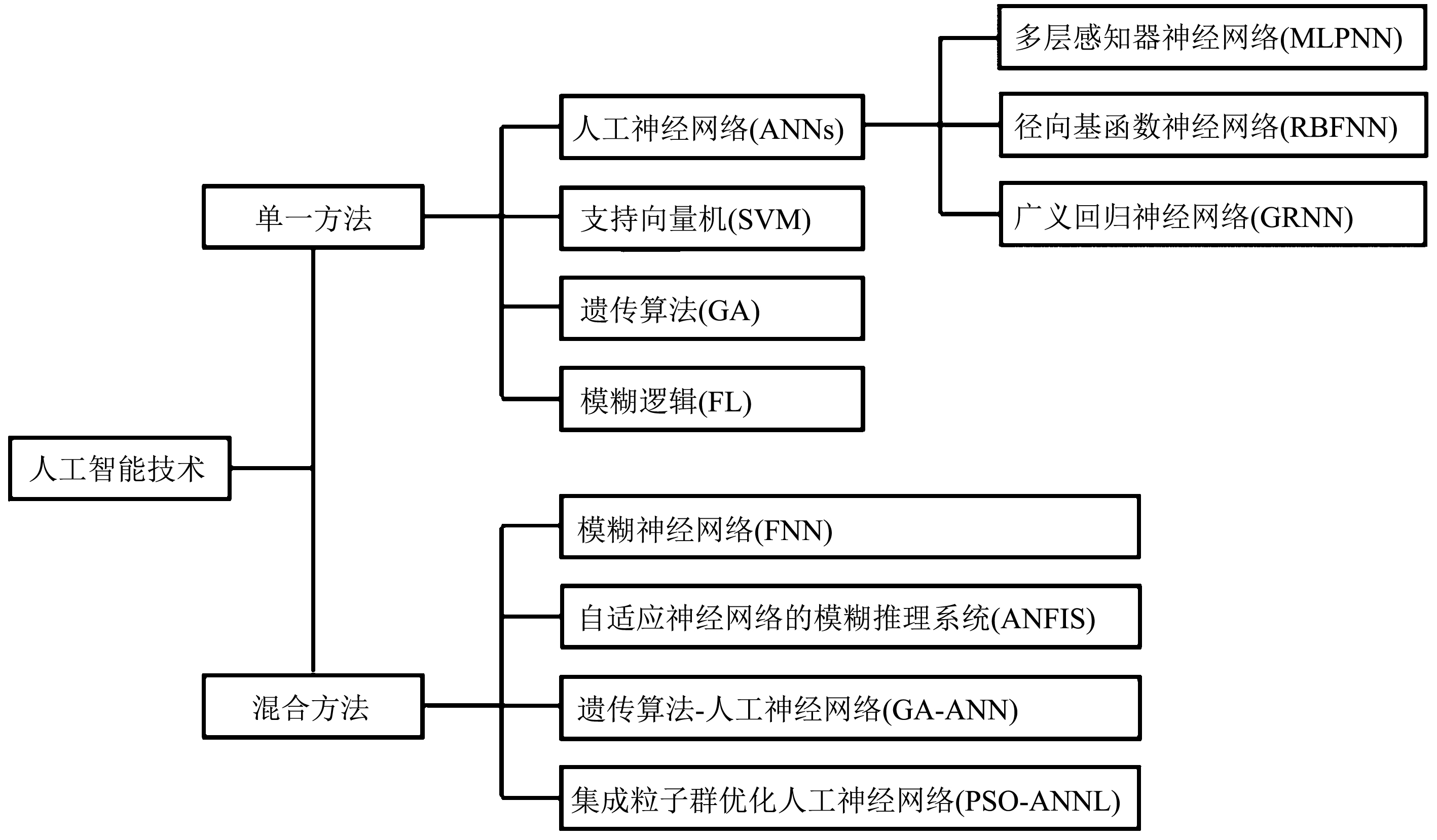
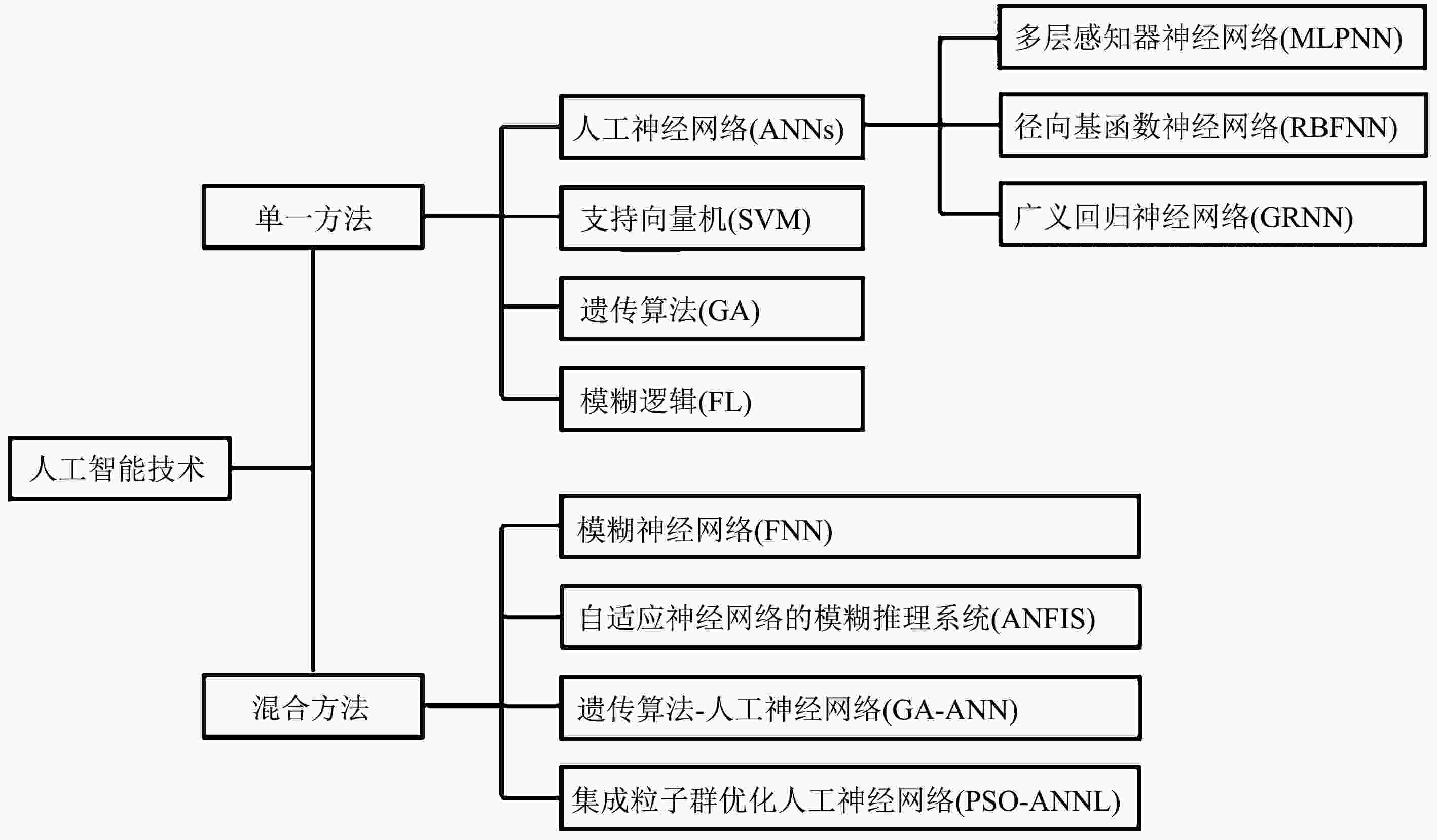
图 1 人工智能技术在水污染控制方面的应用模型分类[2]
Figure 1. Application model classification tree of AI technologies for water pollution control
表 1 不同人工智能技术在水污染治理领域的特点与比较
Table 1. Characteristics and comparison of AI technologies in the field of water pollution control
人工智能技术 优点 缺点 适用性 人工神经网络(ANNs) 由大量神经元组成,具有大规模并行,分布式存储和处理,自组织、自适应和学习能力,速度快,计算成本低,具有很强的容错性和鲁棒性 需要大量有代表性的数据,学习时间过长,可移植性较差 在模式识别、智能控制、组合优化、预测等领域得到成功应用,可应用于大气质量评价和预警系统、水处理软测量领域、水质预测预警、地表水污染特征识别、城市生活垃圾处理建模等[2] 多层感知器神经网络(MLPNN) 具有并行处理和自学习能力,能以任意精度逼近非线性函数 收敛速度慢,存在过度拟合和局部最小值的风险 在模式识别、函数逼近、风险预测和控制等领域中有广泛的应用,目前已经成为污水中污染物去除建模和优化的高效工具[12] BP神经网络 是一种按误差逆传播算法训练的多层前馈网络,具有较强的非线性映射能力、自学习和自适应能力,以及较强的泛化能力和容错能力 由于算法会陷入局部极值,使网络不能以高精度逼近实际系统,可能需要多次学习和调整才能成功;算法学习过程收敛速度慢,需要较长的训练时间;对学习样本依赖性较强;网络结构选择不一 是目前应用最广泛的神经网络模型之一,主要用在函数逼近、模式识别、分类、数据压缩等方面,如水处理过程中的优化与控制等[52] 径向基函数神经网络(RBFNN) 基函数可以是高斯函数,也可以是小波函数,支持在线和离线训练,逼近精度高,几乎能实现完全逼近;结构简单,训练速度快,可进行大范围的数据融合,可并行、高速地处理数据 需要大量的训练数据,需要大量隐层神经元[2] 被广泛用于函数逼近、时间序列分析、数据分类、模式识别、图像处理、系统建模、自动控制和故障诊断等领域,水环境治理方面主要应用于水质预测和污水中污染物去除等[53] 支持向量机(SVM) 在解决小样本、非线性及高维模式识别中具有优势;算法简单,具有较好的鲁棒性 在批量处理模式下训练时,需要大量内存和CPU时间;解决多分类问题存在困难;对缺失数据敏感,对参数和核函数的选择较敏感 具有更为严密的理论和数学基础,可以分析数据、识别模式,广泛应用于统计分类和回归分析,已成功应用于水处理控制、水环境预警与评估领域[28] (续表1) 人工智能技术 优点 缺点 适用性 遗传算法(GA) 搜索能力强,具有良好的全局优化能力;个体选择具有随机性;鲁棒性强;易与其他方法或模型相结合 编程较为复杂;很难处理和优化维数较高的问题;迭代次数多导致计算量大,模型效率较低;对初始种群的选择有一定的依赖性;容易出现过早收敛问题,局部搜索能力差 是一种强大的优化工具,目前可用于优化污水处理工艺条件和污染物去除参数,以降低控制成本[51] 模糊逻辑(FL) 可对任意复杂度的非线性函数进行建模;可容忍不精确的数据;具有灵活性,使用任何给定的系统,都可轻松实现更多功能,无需从头开始;鲁棒性强,尤其适用于非线性、时变、滞后系统的控制;有较强的容错能力 信息简单的模糊处理将导致系统的控制精度降低和动态品质变差;模糊控制的设计尚缺乏系统性,无法定义控制目标 应用于污水处理工艺参数的优化,另外,在环境质量指标设计方面具有巨大应用潜力[39,54] 模糊神经网络(FNN) 利用神经网络结构来实现模糊逻辑推理,包含模糊逻辑理论和神经网络,具有较强的自学习能力和自整定功能;人工干预少,精度较高,对专家知识的利用较好;对样本的要求较低 计算时间长;在多变量、复杂控制系统中,很难确定网络的结构和规则点的组合“爆炸”问题 可用于模糊回归、模糊控制器、模糊专家系统、模糊谱系分析、模糊矩阵方程、通用逼近器,适用于先进的控制系统,在污水处理领域得到广泛应用[11] 自适应神经网络模糊推理系统(ANFIS) 基于数据建模,不需实际辨识模式;可对非线性系统进行辨识;收敛快,误差小,泛化能力强 需要样本多,对训练数据质量依赖性高 在预测、控制、数据挖掘和噪声消除等诸多领域具有强大应用价值[48] 遗传算法-人工神经网络(GA-ANN) 搜索能力强;可防止局部最小值;快速收敛;精度高;有较好的鲁棒性 计算量大;无法确定隐藏神经元的数量 可用于环境预测预警系统、优化控制器参数、污染物去除建模与优化等领域[55] -
[1] BARR A, FEIGENBAUM E A. The handbook of artificial intelligence[M]. Los Altos, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1981. [2] YE Z P, YANG J Q, ZHONG N, et al. Tackling environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,699:134279. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134279 [3] HUNTINGFORD C, JEFFERS E S, BONSALL M B, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence to aid climate change research and preparedness[J]. Environmental Research Letters,2019,14(12):124007. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab4e55 [4] 陈能汪, 余镒琦, 陈纪新, 等.人工神经网络模型在水质预警中的应用研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(12):4771-4782.CHEN N W, YU Y Q, CHEN J X, et al. Artificial neural network models for water quality early warning: a review[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(12):4771-4782. [5] PARK Y, KIM M, PACHEPSKY Y, et al. Development of a nowcasting system using machine learning approaches to predict fecal contamination levels at recreational beaches in Korea[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality,2018,47(5):1094-1102. doi: 10.2134/jeq2017.11.0425 [6] WANG P, LIU Y, QIN Z D, et al. A novel hybrid forecasting model for PM10 and SO2 daily concentrations[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,505:1202-1212. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.078 [7] PALANISWAMY D, RAMESH G, SIVASANKARAN S, et al. Optimising biogas from food waste using a neural network model[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Municipal Engineer,2017,170(4):221-229. doi: 10.1680/jmuen.16.00008 [8] KATIP A. Meteorological drought analysis using artificial neural networks for Bursa City, Turkey[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research,2018,16(3):3315-3332. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1603_33153332 [9] SHOOSHTARI S J, SILVA T, NAMIN B R, et al. Land use and cover change assessment and dynamic spatial modeling in the Ghara-su Basin, Northeastern Iran[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,2020,48(1):81-95. doi: 10.1007/s12524-019-01054-x [10] GOVINDARAJU R S. Artificial neural networks in hydrology: Ⅰ. preliminary concepts[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering,2000,5(2):115-123. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2000)5:2(115) [11] OJHA V K, ABRAHAM A, SNÁŠEL V. Metaheuristic design of feedforward neural networks: a review of two decades of research[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2017,60:97-116. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2017.01.013 [12] YIN Z Y, JIA B Y, WU S Q, et al. Comprehensive forecast of urban water-energy demand based on a neural network model[J]. Water,2018,10(4):385. doi: 10.3390/w10040385 [13] JAMI M S, MUJELI M, KABBASHI N A. Simulation of ammoniacal nitrogen effluent using feedforward multilayer neural networks[J]. African Journal of Biotechnology,2011,81(10):18755-18762. [14] EBRAHIMPOOR S, KIAROSTAMI V, KHOSRAVI M, et al. Bees metaheuristic algorithm with the aid of artificial neural networks for optimization of acid red 27 dye adsorption onto novel polypyrrole/SrFe12O19/graphene oxide nanocomposite[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2019,76(12):6529-6553. doi: 10.1007/s00289-019-02700-7 [15] YU R F, CHI F H, CHENG W P, et al. Application of pH, ORP, and DO monitoring to evaluate chromium(Ⅵ) removal from wastewater by the nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2014,255:568-576. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.002 [16] BENSIDHOUM T, BOUAKRIF F, ZASADZINSKI M. Iterative learning radial basis function neural networks control for unknown multi input multi output nonlinear systems with unknown control direction[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control,2019,41(12):3452-3467. doi: 10.1177/0142331219826659 [17] WANG J Y, SONG P Z, WANG Z, et al. A combined model for regional eco-environmental quality evaluation based on particle swarm optimization-radial basis function network[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2016,41(4):1483-1493. doi: 10.1007/s13369-015-1958-5 [18] OZEL H U, GEMICI B T, OZEL H B, et al. Determination of water quality and estimation of monthly biological oxygen demand (BOD) using by different artificial neural networks models in the Bartin River[J]. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin,2017,26(8):5465-5476. [19] BOLANCA T, UKIC S, PETERNEL I, et al. Artificial neural network models for advanced oxidation of organics in water matrix-comparison of applied methodologies[J]. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology,2014,21(1):21-29. [20] ASFARAM A, GHAEDI M, AHMADI AZQHANDI M H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted binary adsorption of dyes onto Mn@CuS/ZnS-NC-AC as a novel adsorbent: application of chemometrics for optimization and modeling[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2017,54:377-388. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.06.018 [21] SINGH K P, GUPTA S, OJHA P, et al. Predicting adsorptive removal of chlorophenol from aqueous solution using artificial intelligence based modeling approaches[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2013,20(4):2271-2287. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1102-y [22] TURAN N G, MESCI B, OZGONENEL O. The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) from industrial leachate by pumice[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,171(3):1091-1097. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.005 [23] PAI P F, LIN K P, LIN C S, et al. Time series forecasting by a seasonal support vector regression model[J]. Expert Systems with Applications,2010,37(6):4261-4265. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2009.11.076 [24] VAPNIK V N. The nature of statistical learning theory[M]. New York: Springer, 1995. [25] JARAMILLO F, ORCHARD M, MUÑOZ C, et al. On-line estimation of the aerobic phase length for partial nitrification processes in SBR based on features extraction and SVM classification[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,331:114-123. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.185 [26] HUANG J, ZHANG X, SUN Q Y, et al. Simultaneous rapid analysis of multiple nitrogen compounds in polluted river treatment using near-infrared spectroscopy and a support vector machine[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2017,26(5):2013-2019. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/70002 [27] GAO K, XI X J, WANG Z, et al. Use of support vector machine model to predict membrane permeate flux[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2016,57(36):16810-16821. [28] ZHANG J, ZHOU J T, LI Y M, et al. Computer simulating effluent quality of vertical tube biological reactor using support vector machine[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,219/220:322-326. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.219-220.322 [29] KALOGIROU S A. Artificial intelligence for the modeling and control of combustion processes: a review[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2003,29(6):515-566. doi: 10.1016/S0360-1285(03)00058-3 [30] AL-OBAIDI M A, LI J P, ALSADAIE S, et al. Modelling and optimisation of a multistage reverse osmosis processes with permeate reprocessing and recycling for the removal of N-nitrosodimethylamine from wastewater using Species Conserving Genetic Algorithms[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,350:824-834. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.022 [31] LOUZADAVALORY J P, REIS J A T D, MENDONÇA A S F. Combining genetic algorithms with a water quality model to determine efficiencies of sewage treatment systems in watersheds[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering,2016,142(3):04015080. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001048 [32] BRAND N, OSTFELD A. Optimal design of regional wastewater pipelines and treatment plant systems[J]. Water Environment Research,2011,83(1):53-64. doi: 10.2175/106143010X12780288628219 [33] YETILMEZSOY K, OZKAYA B, CAKMAKCI M. Artificial Intelligence-based prediction models for environmental engineering[J]. Neural Network World,2011,21(3):193-218. doi: 10.14311/NNW.2011.21.012 [34] de OLIVEIRA M D D, de REZENDE O L T d, OLIVEIRA S M A C, et al. Nova abordagem doíndice de qualidade deágua bruta utilizando a lógica fuzzy[J]. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental,2014,19(4):361-372. doi: 10.1590/S1413-41522014019000000803 [35] AL-ZAHRANI M, MOIED K. Identifying water quality monitoring stations in a water supply system[J]. Water Science and Technology:Water Supply,2014,14(6):1076-1086. doi: 10.2166/ws.2014.069 [36] SARI H, YETILMEZSOY K, ILHAN F, et al. Fuzzy-logic modeling of Fenton's strong chemical oxidation process treating three types of landfill leachates[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2013,20(6):4235-4253. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1370-6 [37] LIU B, HUANG J J, MCBEAN E, et al. Risk assessment of hybrid rain harvesting system and other small drinking water supply systems by game theory and fuzzy logic modeling[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,708:134436. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134436 [38] de OLIVEIRA M D, de REZENDE O L T, de FONSECA J F R, et al. Evaluating the surface water quality index fuzzy and its influence on water treatment[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2019,32:100890. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100890 [39] FLORES-ASIS R, MÉNDEZ-CONTRERAS J M, ALVARADO-LASSMAN A, et al. Analysis of the behavior for operation parameters in the anaerobic digestion process with thermal pretreatment, using fuzzy logic[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering,2019,54(6):592-602. [40] DOGDU G, YALCUK A, POSTALCIOGLU S. Application of the removal of pollutants from textile industry wastewater in constructed wetlands using fuzzy logic[J]. Environmental Technology,2017,38(4):443-455. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2016.1196741 [41] SUTHAR S, VERMA R, DEEP S, et al. Optimization of conditions (pH and temperature) for Lemna gibba production using fuzzy model coupled with Mamdani ′s method[J]. Ecological Engineering,2015,83:452-455. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.07.006 [42] RAHIMZADEH A, ASHTIANI F Z, OKHOVAT A. Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system as a reliable approach for prediction of oily wastewater microfiltration permeate volume[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2016,4(1):576-584. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.011 [43] KIM C M, PARNICHKUN M. Prediction of settled water turbidity and optimal coagulant dosage in drinking water treatment plant using a hybrid model of k-means clustering and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[J]. Applied Water Science,2017,7(7):3885-3902. doi: 10.1007/s13201-017-0541-5 [44] TAN H M, POH P E, GOUWANDA D. Resolving stability issue of thermophilic high-rate anaerobic palm oil mill effluent treatment via adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system predictive model[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,198:797-805. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.027 [45] NAJAFZADEH M, ZEINOLABEDINI M. Prognostication of waste water treatment plant performance using efficient soft computing models: an environmental evaluation[J]. Measurement,2019,138:690-701. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.02.014 [46] SADI M, FAKHARIAN H, GANJI H, et al. Evolving artificial intelligence techniques to model the hydrate-based desalination process of produced water[J]. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination,2019,9(4):372-384. doi: 10.2166/wrd.2019.024 [47] HUANG M Z, MA Y W, WAN J Q, et al. Improving nitrogen removal using a fuzzy neural network-based control system in the anoxic/oxic process[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2014,21(20):12074-12084. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3092-4 [48] AZQHANDI M H A, FOROUGHI M, YAZDANKISH E. A highly effective, recyclable, and novel host-guest nanocomposite for Triclosan removal: a comprehensive modeling and optimization-based adsorption study[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,551:195-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.007 [49] GHAEDI M, ANSARI A, BAHARI F, et al. A hybrid artificial neural network and particle swarm optimization for prediction of removal of hazardous dye brilliant green from aqueous solution using zinc sulfide nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,137:1004-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.08.011 [50] GHAEDI M, DASHTIAN K, GHAEDI A M, et al. A hybrid model of support vector regression with genetic algorithm for forecasting adsorption of malachite green onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes: central composite design optimization[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2016,18(19):13310-13321. doi: 10.1039/C6CP01531J [51] GHAEDI A M, GHAEDI M, POURANFARD A R, et al. Adsorption of Triamterene on multi-walled and single-walled carbon nanotubes: artificial neural network modeling and genetic algorithm optimization[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2016,216:654-665. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.01.068 [52] 陈威, 陈会娟, 戴凡翔, 等.基于人工神经网络的污水处理出水水质预测模型[J]. 给水排水,2020,46(增刊1):990-994.CHEN W, CHEN H J, DAI F X, et al. Effluent water quality prediction model based on artificial neural network for wastewater treatment[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering,2020,46(Suppl1):990-994. [53] GHAEDI A M, VAFAEI A. Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: a review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2017,245:20-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.015 [54] PECHE R, RODRÍGUEZ E. Development of environmental quality indexes based on fuzzy logic: a case study[J]. Ecological Indicators,2012,23:555-565. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.04.029 [55] FAN M Y, HU J W, CAO R S, et al. A review on experimental design for pollutants removal in water treatment with the aid of artificial intelligence[J]. Chemosphere,2018,200:330-343. ⊗ doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.111 -




 下载:
下载: